A Byte of Python 笔记(7)数据结构:列表、元组、字典,序列
第9章 数据结构
数据结构,即可以处理一些数据的结构。或者说,它们是用来存储一组相关数据的。
python 有三种内建的数据结构--列表、元组和字典。
list = ['item1', 'item2', 'item3', 'item4']
len(list) 列表长度
list.append('item5') 为列表添加一个项目
sort(list) 对列表进行排序
del(list[0]) 删除列表中的第一个元素
tuple = ('item1', 'item2', 'item3', 'item4')
dict = {'key1':'value1', 'key2':'value2', 'key3':'value3'}
列表
list 是处理一组有序项目的数据结构,即你可以在一个列表中存储一个 序列 的项目,每个项目之间用逗号分割。
列表是 可变的 数据类型,项目包括在方括号中,用户可以添加、删除或搜索列表中的项目。
列表是使用对象和实例的一个例子。当你使用变量 i 并给它赋值时,比如 i=5,你可以认为你创建了一个类(类型) int 的对象(实例)i。
类也有方法,即仅仅为类而定义的函数。类的对象可以使用这些功能。如,python 为 list 类提供了 append 方法,该方法可以让用户在列表尾添加一个项目。
mylist.append('an item'),在列表 mylist 中增加字符串,此处使用点号来使用对象的方法。
类也有域,它是仅为类而定义的变量。只有类的对象可以使用这些变量/名称。类通过点号使用,如 mylist.field。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filename: using_list.py shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana'] print 'I have', len(shoplist), 'items to purchase.' print 'These items are:',
for item in shoplist:
print item, print '\nI also have to buy rice.'
shoplist.append('rice')
print 'My shopping list is now', shoplist
print 'I will sort my list now'
shoplist.sort()
print 'Sorted shopping list is', shoplist print 'The first item I will buy is', shoplist[0]
olditem = shoplist[0]
del shoplist[0]
print 'I bought the', olditem
print 'My shopping list is now', shoplist

shoplist 是一个列表,可以在列表中添加 任何种类的对象,包括数甚至其他列表。
列表(list)是一个序列
print 语句结尾使用逗号(,) 来消除每个 print 语句自动打印的换行符
列表是 可变的 而字符串是 不可变的。
元组
元组和列表类似,但元组和字符串一样是 不可变的,即你不能修改元组。元组通过圆括号中用逗号分割的项目定义。
元组通常用在使语句或用户定义的函数能够安全地采用一组值的时候,即被使用的元组的值不会改变。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filename: using_tuple.py zoo = ('wolf', 'elephant', 'penguin')
print 'Number of animals in the zoo is', len(zoo) new_zoo = ('monkey', 'dolphin', zoo)
print 'Number of animals in the new zoo is', len(new_zoo)
print 'All animals in new zoo are', new_zoo
print 'Animals brought from old zoo are', new_zoo[2]
print 'Last animal brought from old zoo is', new_zoo[2][2]
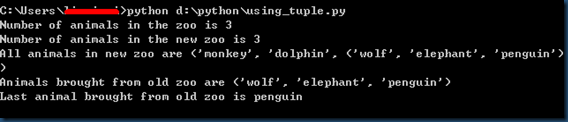
zoo 是一个元组,len 函数可以用来获取元组的长度。元组也是一个序列。
可以通过 索引 运算符指明某个项目的位置来访问元组中的项目。
含有 0个 或 1个 项目的元组:
一个空的元组,由一对空的圆括号组成,如 myempty = ()
含有单个元素的元组,必须在第一个(唯一一个)项目后跟一个逗号,如 singleton = (2, ),这样才能区分元组和表达式中一个带圆括号的对象。
元组与打印语句
元组最通常的用法是用在打印语句中。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filename: print_tuple.py age = 2
name = 'Tom' print '%s is %d years old' % (name, age)
print 'Why is %s playing with that python?' % name

print 语句可以使用跟着 % 符号的项目元组的字符串。这些字符串具备定制的功能。定制让输出满足某种特定的格式。
定制可以是 %s 表示字符串 或 %d 表示整数,元组必须按照相同的顺序来对应这些定制。
python 在这里所做的是把元组中的每个项目转换成字符串并且用字符串的值替换定制的位置。
字典
字典类似于你通过联系人名字查找地址和联系人详细情况的地址簿,即把键(名字)和值(详细情况)联系在一起。注意,键必须是唯一的。
注意:字典的键必须是不可变的对象(如,字符串),字典的值可以是 不可变或可变的对象。
键值对在字典中以 d = {key1:value1, key2:value2} 的方式标记。
字典中的 键/值对 是没有顺序的,如果想要制定顺序,应该在使用前进行排序。
字典是 dict 类的实例/对象。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filename: using_dict.py # 'ab' is short of 'address book'
ab = {
'Swaroop':'swaroopch@byteofpython.info',
'Larry':'larry@wall.org',
'Matsumoto':'matz@ruby-lang.org',
'Spammer':'spammer@hotmail.com'
}
print "Swaroop's address is %s", ab['Swaroop'] # Adding a key/value pair
ab['Guido'] = 'guid@python.org' # Deleting a key/value pair
del ab['Spammer'] print '\nThere are %d contacts in the address-book\n' % len(ab) for name, address in ab.items():
print 'Contact %s at %s' % (name, address) if 'Guido' in ab:
print "\nGuido's address is %s" % ab['Guido'] print '\nab.items():', ab.items()

ab['new_key'] = 'new_value' 增加新的键值对
del['key1'] 删除键/值对,无需知道键所对应的值。
使用 items() 方法来使用字典中的每个键值对,返回一个元组的列表,其中每个元组都包含一对项目--键与对应的值
可以使用 in 操作符来检验一个键值对是否存在,或者使用 dict 类的 has_key 方法。
关键字参数与字典
如果换一个角度看待你在函数中使用的关键字参数的话,你已经使用字典了!只需想一下——你在函数定义的参数列表中使用的键/值对。当你在函数中使用变量的时候,它只不过是使用一个字典的键(这在编译器设计的术语中被称作 符号表 )。
序列
序列的两个主要特点是 索引操作符 和 切片操作符,列表、元组和字符串都是序列。
索引操作符:可以从序列中抓取一个特定的项目;
切片操作符:能够获取序列的一个切片,即一部分序列。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Filename: seq.py shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana']
print 'shoplist is', shoplist # Indexing or 'Subscription' operation
print 'Item 0 is', shoplist[0]
print 'Item 1 is', shoplist[1]
print 'Item 2 is', shoplist[2]
print 'Item 3 is', shoplist[3]
print 'Item -1 is', shoplist[-1]
print 'Item -2 is', shoplist[-2] # Slicing on a list
print 'Item 1 to 3 is', shoplist[1:3]
print 'Item 2 to end is', shoplist[1:]
print 'Item 1 to -1 is', shoplist[1:-1]
print 'Item start to end is', shoplist[:] # Slicing on a string
name = 'swaroop'
print 'name is', name
print 'characters 1 to 3 is', name[1:3]
print 'characters 2 to end is', name[2:]
print 'characters 1 to -1 is', name[1:-1]
print 'characters start to end is', name[:]
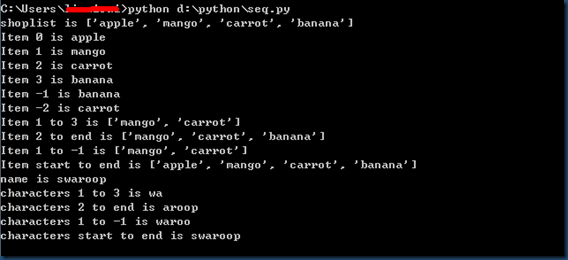
下标操作:使用索引来取得序列中的单个项目。每当用方括号中的一个数来指定一个序列的时候,python 会为你抓取序列中对应位置的项目。
注意:python 从 0 开始计数,因此 shoplist[0] 抓取第1个元素,shoolist[3] 抓取第4个元素。
索引同样可以是负数,位置从序列尾开始计算。shoplist[-1] 表示序列的最后一个元素,shoplist[-2] 抓取序列的倒数第二个项目。
切片操作符 [m : n],m n是可选的,冒号是必须的。m 表示切片的开始位置,n 表示切片的结束位置,如果不指定 m,从序列首开始;如果不指定 n,到序列尾停止。
注意:返回序列从开始位置 开始,在结束 位置之前结束。即开始位置是包含在序列切片中的,结束位置被排斥在切片外。
参考
当用户创建一个对象并给它赋一个变量的时候,这个变量仅仅 参考 那个对象,而不是表示这个对象本身。即,变量名指向你计算机中存储那个对象的内存。这被称作名称到对象的绑定。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filename: reference.py print 'Simple Assignment'
shoplist = ['apple', 'mango', 'carrot', 'banana']
mylist = shoplist # mylist is just another name pointing to the same object! del shoplist[0] print 'shoplist is', shoplist
print 'mylist is', mylist
# notice that both shoplist and mylist both print the same list without
# the 'apple' confirming that they point to the same object print 'Copy by making a full slice'
mylist = shoplist[:] # make a copy by doing a full slice
del mylist[0] print 'shoplist is', shoplist
print 'mylist is', mylist
# notice that now the two lists are different
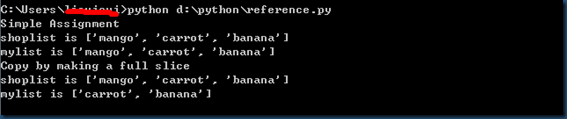
如果你想复制一个列表或者类似的序列或者其他复杂的对象(不是如整数那样的简单对象),那么你必须使用切片操作符来取得拷贝。如果你只是想要使用另一个变量名,两个名称都参考同一个对象,使用赋值语句即可。
| 记住列表的赋值语句不创建拷贝。你得使用切片操作符来建立序列的拷贝。 |
更多字符串的内容
字符串也是对象,同样具有方法,这些方法包括检验一部分字符串和去除空格在内的各种工作。
程序中使用的字符串都是 str 类的对象。可以通过 help(str) 了解 str 方法的完整列表。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Filaneme: str_methods.py name = 'swaroop' if name.startswith('swa'):
print 'Yes, the string starts with "swa"' if 'a' in name:
print 'Yes, it contains the string "a"' if name.find('war') != -1:
print 'Yes, it contains the string "war"' delimiter = '_*_'
mylist = ['Brazil', 'Russia', 'India', 'China']
print delimiter.join(mylist)

startswith 方法 用来测试字符串是否以给定字符串开始
in 操作符 用来检验一个给定字符串是否为另一个字符串的一部分
find 方法 用来找出给定字符串在另一个字符串中的位置,返回 –1 表示找不到子字符串
str 类 有一个作为分隔符的字符串 join 序列的项目的整洁方法,返回一个生成的大字符串。
A Byte of Python 笔记(7)数据结构:列表、元组、字典,序列的更多相关文章
- Python笔记——基本数据结构:列表、元组及字典
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/wklken/archive/2011/04/10/6312888.aspx Python基本数据结构:列表,元组及字典 一.列表 一组有序项 ...
- Python入门基础学习(列表/元组/字典/集合)
Python基础学习笔记(二) 列表list---[ ](打了激素的数组,可以放入混合类型) list1 = [1,2,'请多指教',0.5] 公共的功能: len(list1) #/获取元素 lis ...
- Python列表,元组,字典,序列,引用
1.列表 # Filename: using_list.py # This is my shopping list shoplist=["apple", "mango&q ...
- Python自动化开发 - 字符串, 列表, 元组, 字典和和文件操作
一.字符串 特性:字符串本身不可修改,除非字符串变量重新赋值.Python3中所有字符串都是Unicode字符串,支持中文. >>> name = "Jonathan&q ...
- python基础之02列表/元组/字典/set集合
python中内置的数据类型有列表(list)元组(tuple)字典(directory). 1 list list是一种可变的有序的集合.来看一个list实例: #第一种方法: >>&g ...
- python的对象类型-----列表&元组&字典
列表: #定义列表 l=[1,'a',[3,4]] #l=list([1,'a',[3,4]]) #取值 print(l[0]) print(l[2][0]) l=[1,2,[['a','b'],'c ...
- Python第三天 序列 数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典
Python第三天 序列 数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 数据类型数值字符串列表元组字典 序列序列:字符串.列表.元组序列的两个主要特点是索引操作符和切片操作符- 索引操作符让我 ...
- python3笔记十八:python列表元组字典集合文件操作
一:学习内容 列表元组字典集合文件操作 二:列表元组字典集合文件操作 代码: import pickle #数据持久性模块 #封装的方法def OptionData(data,path): # ...
- Python第三天 序列 5种数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 各种数据类型的的xx重写xx表达式
Python第三天 序列 5种数据类型 数值 字符串 列表 元组 字典 各种数据类型的的xx重写xx表达式 目录 Pycharm使用技巧(转载) Python第一天 安装 shell ...
- python中列表 元组 字典 集合的区别
列表 元组 字典 集合的区别是python面试中最常见的一个问题.这个问题虽然很基础,但确实能反映出面试者的基础水平. (1)列表 什么是列表呢?我觉得列表就是我们日常生活中经常见到的清单.比如,统计 ...
随机推荐
- 安装python模块
要想在python中使用import的一些模块,前提是要安装这些模块. 可以使用pip来导入模块. 打开终端,输入命令: sudo easy_install pip 安装好pip后,就可以使用pip来 ...
- cf-A. Wet Shark and Odd and Even(水)
A. Wet Shark and Odd and Even time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inpu ...
- Android快速开发框架汇总
知乎贴:Android 开发有什么好的架构么? 里面这篇不错:Architecting Android…The clean way? 知乎贴: 一.如果对App的性能.包size有要求,对代码有洁癖不 ...
- MyEclipse 2013 导入MyEclipse 9.0的EJB项目时,需要注意
点击“next”按钮,出现下面的对话框: 再点击“next”按钮,出现下面的对话框:
- 张孝祥Java高新技术汇总
一.自动装箱和拆箱: 在Java中有8种基本数据类型:byte,short,int,long,float,double,char,boolean.而基本数据类型不是对象,这时人们给他们定义了包装类,使 ...
- js点击事件代理时切换图片如何防抖动
由于图片的加载速度比较慢,我们可以直接用64base对图片进行编码,把编码加在图片的url中~~~这样加载会快一些,也不会有切换图片时出现的抖动效果
- JQuery 在$(window).load() 事件中 不运行 $(window).resize()
本文转载至: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2597152/jquery-window-resize-doesnt-work-on-load 原文标题 :J ...
- zoj 2071 Technology Trader 最大权闭合子图
传送门 和上一题一样, 也是一个最大权闭合子图.不过建图好麻烦的感觉 写了好久. 源点和原材料连边, 权值为val. 汇点和产品连边, 权值为val. 产品与和它有关系的材料连边, 权值inf. 最 ...
- 有关extern的用法
1.引言 C++语言的创建初衷是“a better C”,但是这并不意味着C++中类似C语言的全局变量和函数所采用的编译和连接方式与C语言完全相同.作为一种欲与C兼容的语言, C++保留了一部分过程式 ...
- 闪存主控IC的作用
闪存主要是由闪存芯片.主控芯片.晶振.PCB板等部件组成的.其中主控芯片相当于闪存的“灵魂”,它控制着闪存的工作.主控芯片也是处理单元,在里面写入的程序对整个电路做控制.主控IC是把flash跟hos ...
