Python并行编程(二):基于线程的并行
1、介绍
软件应用中使用最广泛的并行编程范例是多线程。通常一个应用有一个进程,分成多个独立的线程,并行运行、互相配合,执行不同类型的任务。
线程是独立的处理流程,可以和系统的其他线程并行或并发地执行。多线程可以利用共享内存空间共享数据和资源。线程和进程的具体实现取决于你要运行的操作系统,但是总体来讲,我们可以说线程是包含在进程中的,同一个进程的多个不同的线程可以共享相同的资源,而进程之间不会共享资源。
每一个线程基本上包含3个元素:程序计数器,寄存器和栈。与同一进程的其他线程共享的资源基本上包括数据和系统资源。每一个线程也有自己的运行状态,可以和其他线程同步,线程的状态大体上可以分为ready,running,blocked。线程的典型应用是应用软件的并行化,目的是为了充分利用现代的多核处理器,使每个核心可以运行单个线程。相比于进程,使用线程的优势主要是性能,相比之下,在进程之间切换上下文要比在统一进程的多线程之间切换上下文要重的多。
2、定义一个线程
使用线程最简单的方式是用一个目标函数实例化一个Thread然后调用start()方法启动它。Python的threading模块提供了Thread()方法在不同的线程中运行函数或处理过程等。
class threading.Thread(group=None, target=None, name=None, args=(), kwargs={})
- group:特性预留
- target:当线程启动的时候要执行的函数
- name:线程的名字,默认为Thread-N
- args:传递给target的参数,要试用tuple类型
- kwargs:同上,试用字段类型dict
线程代码用例:
import threading def function(i):
print("I am thread-%s" %i)
return threads = [] for i in range(5):
t = threading.Thread(target=function, args=(i,))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
t.join()
t.join:主线程会调用t线程,然后等待t线程完成再执行for循环开启下一个t线程。可理解为阻塞主线程。
3、确认一个线程
使用参数来确认或命名线程是没有必要的,每一个Thread实例创建的时候都有一个带默认值的名字,并且可以修改。在服务端通常一个服务进程都有多个线程服务,负责不同的操作,这时候命名线程是很实用的。
自定义线程名称用例:
import threading
import time def first_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) def second_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) def third_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) if __name__ == "__main__":
t1 = threading.Thread(name='first_function', target=first_function)
t2 = threading.Thread(name='second_function', target=second_function)
t3 = threading.Thread(name='third_function', target=third_function) t1.start()
t2.start()
t3.start() t1.join()
t2.join()
t3.join()
运行结果:

如果不自定义名称如下:
import threading
import time def first_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) def second_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) def third_function():
print("%s is starting" %threading.currentThread().getName())
time.sleep(2)
print("%s is exiting" %threading.currentThread().getName()) if __name__ == "__main__":
# t1 = threading.Thread(name='first_function', target=first_function)
# t2 = threading.Thread(name='second_function', target=second_function)
# t3 = threading.Thread(name='third_function', target=third_function) t1 = threading.Thread(target=first_function)
t2 = threading.Thread(target=second_function)
t3 = threading.Thread(name='third_function', target=third_function) t1.start()
t2.start()
t3.start() t1.join()
t2.join()
t3.join()
运行结果:

4、使用线程
在子类中实现线程:
import threading
import time exit_flag = 0 class myThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, threadID, name, counter):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.threadID = threadID
self.name = name
self.counter = counter def run(self):
print("Starting %s" %self.name)
print_time(self.name, self.counter, 5)
print("Exiting %s" %self.name)
def print_time(threadName, delay, counter):
while counter:
if exit_flag:
import _thread
_thread.exit()
time.sleep(delay)
print("%s:%s" %(threadName, time.ctime(time.time())))
counter -= 1
# 创建实例
thread1 = myThread(1, "Thread-1", 1)
thread2 = myThread(2, "Thread-2", 2) thread1.start()
thread2.start() thread1.join()
thread2.join()
print("Exiting Main Thread")
运行结果如下:
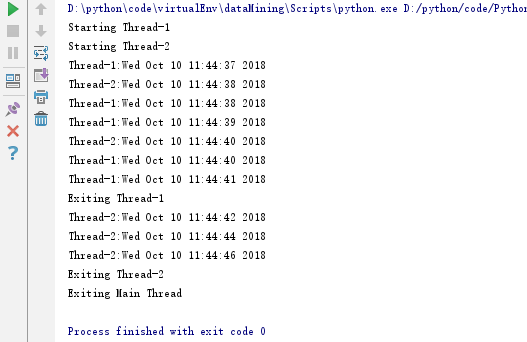
线程模块是创建和管理线程的首选形式。每一个线程都通过一个集成Thread的子类代表,覆盖run()方法来实现逻辑,这个方法是线程的入门,执行start()即调用此方法。
Python并行编程(二):基于线程的并行的更多相关文章
- C#并行编程-PLINQ:声明式数据并行
目录 C#并行编程-相关概念 C#并行编程-Parallel C#并行编程-Task C#并行编程-并发集合 C#并行编程-线程同步原语 C#并行编程-PLINQ:声明式数据并行 背景 通过LINQ可 ...
- C#并行编程-PLINQ:声明式数据并行-转载
C#并行编程-PLINQ:声明式数据并行 目录 C#并行编程-相关概念 C#并行编程-Parallel C#并行编程-Task C#并行编程-并发集合 C#并行编程-线程同步原语 C#并行编程-P ...
- Python网络编程02 /基于TCP、UDP协议的socket简单的通信、字符串转bytes类型
Python网络编程02 /基于TCP.UDP协议的socket简单的通信.字符串转bytes类型 目录 Python网络编程02 /基于TCP.UDP协议的socket简单的通信.字符串转bytes ...
- Python并行编程(五):线程同步之信号量
1.基本概念 信号量是由操作系统管理的一种抽象数据类型,用于在多线程中同步对共享资源的使用.本质上说,信号量是一个内部数据,用于标明当前的共享资源可以有多少并发读取. 同样在threading中,信号 ...
- Python并发编程二(多线程、协程、IO模型)
1.python并发编程之多线程(理论) 1.1线程概念 在传统操作系统中,每个进程有一个地址空间,而且默认就有一个控制线程 线程顾名思义,就是一条流水线工作的过程(流水线的工作需要电源,电源就相当于 ...
- Python并发编程之谈谈线程中的“锁机制”(三)
大家好,并发编程 进入第三篇. 今天我们来讲讲,线程里的锁机制. 本文目录 何为Lock( 锁 )?如何使用Lock( 锁 )?为何要使用锁?可重入锁(RLock)防止死锁的加锁机制饱受争议的GIL( ...
- C#并行编程(3):并行循环
初识并行循环 并行循环主要用来处理数据并行的,如,同时对数组或列表中的多个数据执行相同的操作. 在C#编程中,我们使用并行类System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel提供的静态方法 ...
- python 并发编程 多线程 开启线程的两种方式
一 threading模块介绍 multiprocess模块的完全模仿了threading模块的接口,二者在使用层面,有很大的相似性 二 开启线程的两种方式 第一种 每造一个进程,默认有一个线程,就是 ...
- Python并行编程(九):线程通讯queue
1.基本概念 当线程之间要共享资源或数据的时候,可能变的非常复杂.Python的threading模块提供了很多同步原语,包括信号量,条件变量,事件和锁.如果可以使用这些原语的话,应该优先考虑使用这些 ...
随机推荐
- linux服务器 IE中ico 不能正常显示
问题: mime_type: image/vnd.microsoft.icon 的,但发现在 IE 下面,直接打开 icon 的地址,图标不能正常显示 1.将ico放在windows服务器上,直接访问 ...
- Unix系统编程()改变信号处置:signal
Unix系统提供了两种方法来改变信号处置:signal和sigaction.这篇描述的是signal系统调用,是设置信号处理的原始API,所提供的接口比sigaction简单.另一方面,sigacti ...
- myeclipse 上安装 Maven3<转>
环境准备: JDK 1.6 Maven 3.0.4 myeclipse 8.6.1 安装 Maven 之前要求先确定你的 JDK 已经安装配置完成.Maven是 Apache 下的一个项目,目前最新版 ...
- php 的rabbitmq 扩展模块amqp安装
php 的rabbitmq 扩展模块amqp安装 2017年10月08日 10:34:22 阅读数:240 使用PHP开发,要使用中间队列rabbitmq, 必须要安装PHP的扩展模块amqp, 服务 ...
- Linux - Windows10连接linux服务器
当我们通过windows连接服务器时,大多数用的是ssh客户端软件,推荐使用ssh,安全系数比较高.下面介绍用telnet连接服务器. 客户端:C:\Users\dell>systeminfo主 ...
- EasyUI 表单 tree
第一步:创建HTML标记 <divid="dlg"style="padding:20px;"> <h2>Account Info ...
- Could not contact Selenium Server; have you started it on 'localhost:4444'
今天学习selenium RC例子的时候遇到一个问题:java.lang.RuntimeException: Could not contact Selenium Server; have you s ...
- 【剑指offer】翻转单词顺序
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ns_code/article/details/27372033 题目描写叙述: JOBDU近期来了一个新员工Fish,每天早晨总是会拿着一本 ...
- media wiki run on nginx
1. 环境安装: nginx安装 nginx-1.5.7 php安装 PHP 5.4.10 (cli) (built: Jul 30 2014 16:45:08) mysql安装 Ver 14.14 ...
- 插件之下拉框Select2
select2为代替常规的select而出现,可自定义select的样式,最明显的功能就是集合中可以搜索 关于浏览器要求,ie8+,Chrome 8+,Firefox 10+,Safari 3+,Op ...
