[Linux系统] (8)Nginx
一、高并发基础架构
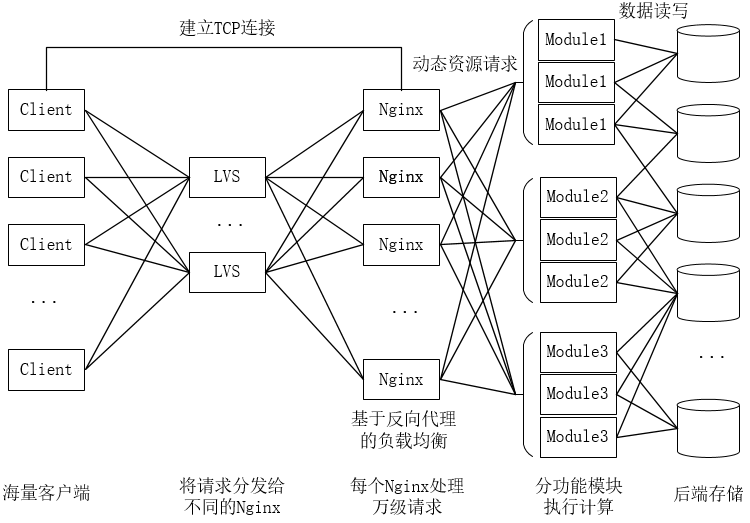
简要流程:
1.客户端发请求。
2.又LVS等四层负载均衡系统将请求转发给不同的Nginx服务器。
3.Nginx与客户端建立TCP连接,拿到请求后分析URI,然后将其转发给对应的功能模块服务(Tomcat容器)。
4.等待后端功能模块服务的响应。
5.功能模块进行计算,并从后端存储中获取数据,并返回。
6.Nginx收到响应后返回给客户端。
二、Nginx和Tengine
Nginx(engin x)是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,也是一个IMAP/POP3/SMTP代理服务器。
主要以稳定性、丰富的功能集、低系统资源消耗而闻名。
官方测试nginx能够支撑5万并发连接,并且CPU、内存等资源消耗非常低,运行稳定。
什么是反向代理(通俗理解)?
正向代理:是代用户访问远程资源。 例如我们要访问国外的网站,我们可以通过位于香港等地的代理服务器来帮我们从国外获取资源,但我们请求的目的还是真正的国外服务器地址。国外服务器看到的请求方是代理服务器。
反向代理:就是帮后端资源进行代理,也就是我们看到的目标服务器就是该反向代理服务器,而看不到真正提供资源的服务器。我们看到的资源地址是反向代理服务器。
Nginx相对apache的优点:
1.nginx是轻量级,同样web服务,比apache占用更少的内存及资源。
2.抗并发,nginx是异步非阻塞的,而apache是阻塞型的,在高并发下nginx保持低资源消耗,高性能
3.高度模块化的设计,编写模块相对简单
4.社区活跃,各种高性能模块出品迅速
5.配置简洁
apache的优点:
1.rewrite强大
2.模块超多
3.bug少
最核心的不同:
apache是同步多进程模型(select),一个链接对应一个进程;nginx是异步(epoll),多个链接(万级别)对应一个进程。
nginx不会浪费时间在进程的切换上,所以效率很高。
三、安装Nginx(Tengine)
1.安装依赖
yum install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel -y
2.下载tengine包,并解压
cd ~
wget http://tengine.taobao.org/download/tengine-2.3.0.tar.gz
tar zxf tengine-2.3..tar.gz
3.安装tengine
cd tengine-2.3.
./configure --prefix=/opt/nginx
**企业标准安装:
./configure
--prefix=/usr
--sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx
--conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log
--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log
--pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid
--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock
--user=nginx
--group=nginx
--with-http_ssl_module
--with-http_flv_module
--with-http_stub_status_module
--with-http_gzip_static_module
--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/
--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/
--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/
--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi
--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi
--with-pcre
make && make install
4.设置nginx为系统服务
添加nginx.service文件:
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit]
Description=The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/opt/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/opt/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
ExecStart=/opt/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
注意,所有path的部分都要修改为实际安装nginx的目录。
使用systemctl启动nginx:
systemctl start nginx.service
使用浏览器访问(默认监听80端口,可以在nginx.conf中修改):
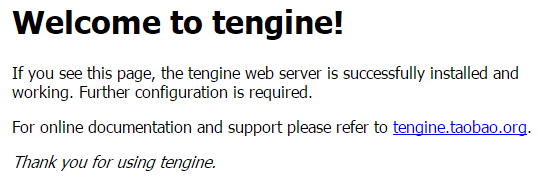
其他服务操作:
# 设置开机启动
systemctl enable nginx.service
# 停止服务
systemctl stop nginx.service
# 重启服务
systemctl restart nginx.service
# 取消开机启动
systemctl disable nginx.service
# 查看服务运行状态
systemctl status nginx.service
查看所有已启动服务:
systemctl list-units --type=service
查看开机启动服务列表:
[root@real-server- conf]# systemctl list-unit-files
UNIT FILE STATE
proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.automount static
dev-hugepages.mount static
dev-mqueue.mount static
proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount static
sys-fs-fuse-connections.mount static
sys-kernel-config.mount static
sys-kernel-debug.mount static
tmp.mount disabled
brandbot.path enabled
systemd-ask-password-console.path static
systemd-ask-password-plymouth.path static
systemd-ask-password-wall.path static
session-.scope static
arp-ethers.service disabled
auditd.service enabled
autovt@.service enabled
blk-availability.service disabled
brandbot.service static
chrony-dnssrv@.service static
chrony-wait.service disabled
chronyd.service enabled
console-getty.service disabled
console-shell.service disabled
container-getty@.service static
cpupower.service disabled
crond.service enabled
dbus-org.freedesktop.hostname1.service static
dbus-org.freedesktop.import1.service static
dbus-org.freedesktop.locale1.service static
dbus-org.freedesktop.login1.service static
dbus-org.freedesktop.machine1.service static
dbus-org.freedesktop.timedate1.service static
dbus.service static
debug-shell.service disabled
dm-event.service static
dnsmasq.service disabled
四、配置Nginx(Tengine)
1.修改nginx配置文件
[root@real-server- conf]# vi /opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# 虽然user nobody是注释掉的,但仍然在使用,当然也可以修改为任意用户。子进程worker是nobody用户所有。父进程是root用户的。
#user nobody;
# worker_processes 是真正做事的进程的数量,一般为物理核心的1-2倍
worker_processes ;
# 配置日志
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#error_log "pipe:rollback logs/error_log interval=1d baknum=7 maxsize=2G";
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
# worker_connection很重要,除了修改此处的数字,还需要修改操作系统内核允许进程所能操作文件描述符的数量。
# 使用ulimit -a可以查看当前内核允许的进程操作文件描述符的数量(open files)。
# 操作系统所能操作文件描述符的总数一般和内存成正比(例如1GB对应10W个文件描述符)。
# 我们在考虑worker_connnection时,除了考虑客户端连接数,还要考虑nginx从后端请求数据时的socket,所以需要配置得更大一些。
# 使用ulimit -SHn 65535可以修改内核限制,并且这里也修改为对应的数量。
events {
#worker_connections ;
worker_connections ;
}
# load modules compiled as Dynamic Shared Object (DSO)
#
#dso {
# load ngx_http_fastcgi_module.so;
# load ngx_http_rewrite_module.so;
#}
# http区域块,定义nginx的核心web功能
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# 日志记录的格式化,控制日志怎么记录,做日志分析的时候可以参照这里的规范(重要)
# 有些公司使用nginx做小数据的采集,就可以直接使用日志来记录,例如传感器数据,直接访问nginx,将小数据传递过来,写进日志。
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#access_log "pipe:rollback logs/access_log interval=1d baknum=7 maxsize=2G" main;
# (重要)零拷贝,例如nginx读取文件内容,然后返回给客户端的过程。首先调内核,让内核读取文件,读到的内容放在内核的缓冲区。
# 然后将内核缓冲区的内容拷贝到用户态buffer中。当要从socket发送给客户端时,又要从用户态buffer将内容拷贝到socket在内核的缓冲区。
# 这样就要进行两次内核态和用户态之间的数据拷贝。
# 零拷贝的意思就是,nginx调内核读取文件的时候,直接告诉内核文件和socker(也就是输入和输出),然后内核读取数据后,直接将数据用socket发送给客户端。
# 这就减少了2次拷贝的时间,效率大大提高。
sendfile on;
# 就是socket buffer是否写满才发送,类似于执行不执行flush。
#tcp_nopush on;
# http1.1扩充了一个字段叫keepalive,就是tcp链接保持长连接多久才断开。做实验我们为了看效果,设置为0。正式环境应该配一个合适的值。
keepalive_timeout ;
#keepalive_timeout ;
# 返回时是否压缩数据,减少IO和带宽消耗。可以提供更多的请求响应。
#gzip on;
# 其中一个虚拟服务器(nginx可以支持多个虚拟服务器,他可以用请求头中的Host域名来区分,通过浏览器F12查看)
# 也就是说如果DNS上有两个域名指向同一个IP地址,nginx可以通过两个域名来提供2个虚拟服务,都使用80端口
server {
# 监听的端口是80
listen ;
# 虚拟服务器名,就是域名。例如DNS中有两个域名,www.123.com,www.234.com,这里填写其中一个。
server_name localhost; # www..com
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#access_log "pipe:rollback logs/host.access_log interval=1d baknum=7 maxsize=2G" main;
# 访问的根,也就是http://www.123.com/
location / {
# root是相对路径,html就是我们安装nginx的地方/opt/nginx/html目录
root html;
# index用来定义默认根页面
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page /.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
} # server的end
} # http的end
其中Location是非常重要的,我们可以参看官方文档中Location的语法:
http://tengine.taobao.org/nginx_docs/cn/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#location
可以看到以下内容:
让我们用一个例子解释上面的说法:
location = / {
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
[ configuration B ]
}
location /documents/ {
[ configuration C ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
[ configuration D ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
[ configuration E ]
}
请求“/”匹配配置A, 请求“/index.html”匹配配置B, 请求“/documents/document.html”匹配配置C, 请求“/images/.gif”匹配配置D, 请求“/documents/.jpg”匹配配置E。
符号解释:
"=":精确匹配
"/dir/":当前路径及子路径都匹配,最大前缀匹配,但注意,是用这个字段去和用户请求的URI匹配,而不是反过来。
"~":后面用正则表达式。区分大小写
"~*":后面用正则表达式。不区分大小写
"^~":阻断,匹配到这里就不再进行正则匹配,例如上面的/images/1.gif,匹配到/images/,就不再匹配后面的".gif结尾"。
匹配规则:
他们有优先级关系: "=" > "^~" > "~ | ~*" > "/ | /dir/"
普通location之间是无匹配顺序的。而正则location之间是有顺序的,只要匹配到第一个就不匹配后面的。
如果匹配到^~项,后面的正则也不进行匹配。
普通location和正则location之间,先匹配普通的,再考虑是否匹配正则:
这里的考虑就是指“可能”,当普通location前使用了^~,则不匹配后面的正则。或者当普通location刚好匹配好(非最大前缀匹配),则也不匹配后面的正则。
如下图所示:

2.添加一个虚拟服务器(yum本地源)
# 这里添加一个虚拟服务器www.repo.com,将/mnt作为repo源,通过nginx发布
server {
listen ;
server_name www.repo.com;
location / {
root /mnt;
# autoindex就是将/mnt的文件列表展示出去
autoindex on;
}
}
这里的域名为www.repo.com,而访问index.html的域名为www.123.com,所以可以区分我们要访问哪个服务器。
配置完nginx.conf后,我们要重置nginx:
systemctl reload nginx.service
将光盘挂载在/mnt:
mount /dev/cdrom /mnt
在浏览器操作系统的hosts中添加响应的DNS映射:
#在windows的hosts中添加以下内容
192.168.1.201 real-server- www..com www.repo.com
此时我们访问http://www.repo.com:80:
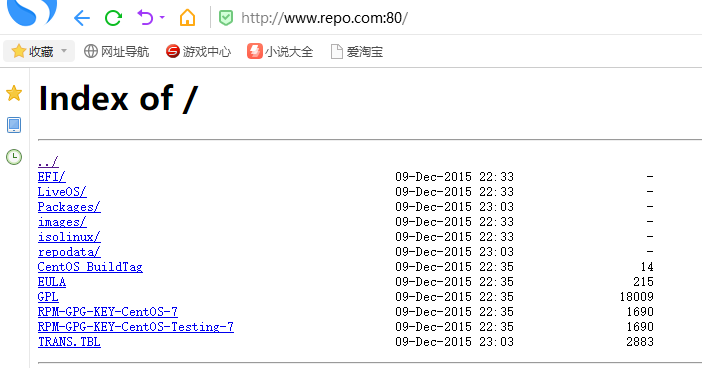
在访问http://www.123.com:80:
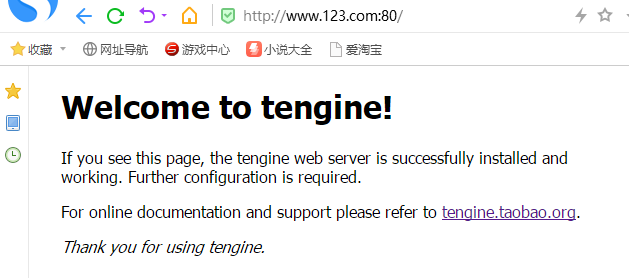
我们在浏览器的F12中查看一下两个域名访问时的host字段:
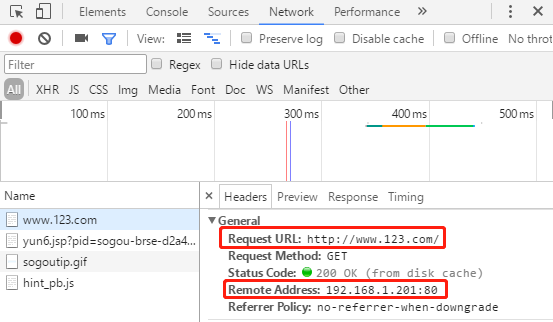
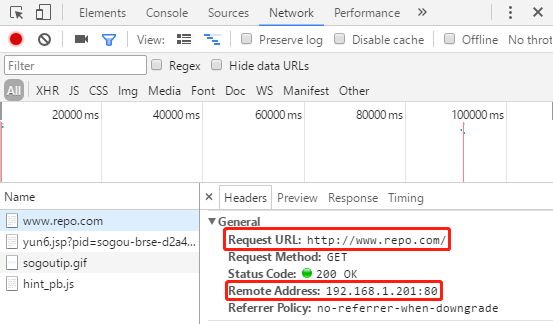
我们可以看到,两次请求的请求头中的Request URL分别是两个域名,Nginx就可以通过域名与配置文件的server_name匹配来区分我们要访问的服务,匹配到某个服务名后,再将域名后的URI(也就是"/"、"/search/"等)用location字段去匹配。
3.反向代理
在location中配置反向代理,将上面第一个server配置加上一个location做反向代理:
server {
listen ;
server_name www..com;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 反向代理,访问192.168.1.202:80
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.202:80/;
}
}
此时,我们访问www.123.com:80,就不是返回tengine的默认页面,而是会帮我们请求192.168.1.202:80的页面;
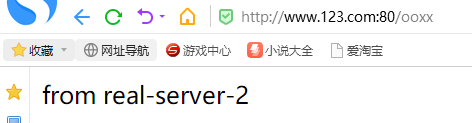
从结果可以看出,我们通过www.123.com:80/ooxx(也就是real-server-1 192.168.1.201)访问了real-server-2(192.168.1.202的服务),并返回给客户端。
示例:反向代理www.baidu.com:
server {
listen ;
server_name www..com;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 反向代理,访问192.168.1.:
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.202:80/;
}
# 代理baidu首页
location /baidu {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com/;
}
}
使用浏览器访问http://www.123.com/baidu:

注意,这里的proxy_pass配置的是https://www.baidu.com。如果配置成http://www.baidu.com,则百度可能先返回页面跳转给浏览器,浏览器会直接用https://www.baidu.com去访问百度。所以这里一定要写成https协议。
我们使用代理后的百度进行搜索:
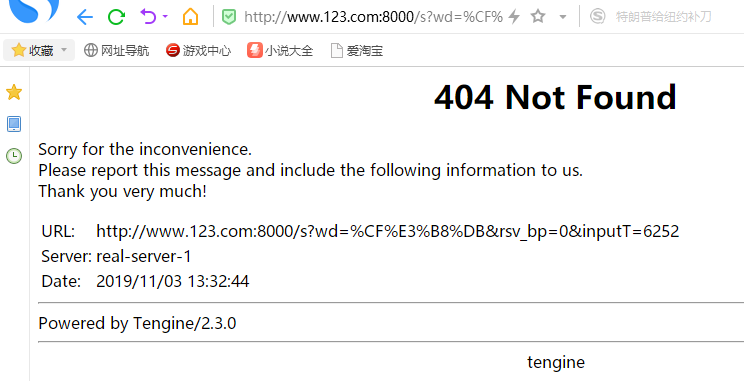
报错信息:找不到URL,主要关注后面的URI(s?wd=*****):
我们再添加一跳location:
server {
listen ;
server_name www..com;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
# 反向代理,访问192.168.1.:
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.202:80/;
}
# 代理baidu首页
location /baidu {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com/;
}
# 匹配以/s开头的URI
location ~* ^/s {
proxy_pass https://www.baidu.com;
}
}
注意:location /baidu和location ~* ^/s的proxy_pass最后一个带"/",一个不带"/",区别很大。
如果带"/"或"/xxx",则会直接使用其进行访问,例如www.baidu.com/xxx。
如果什么都不带,则会使用location的匹配到的URI来串接在后面进行访问,例如www.baidu.com/s?xxxxxxx(location ~* ^/s)。
此时使用代理baidu搜索"香港":
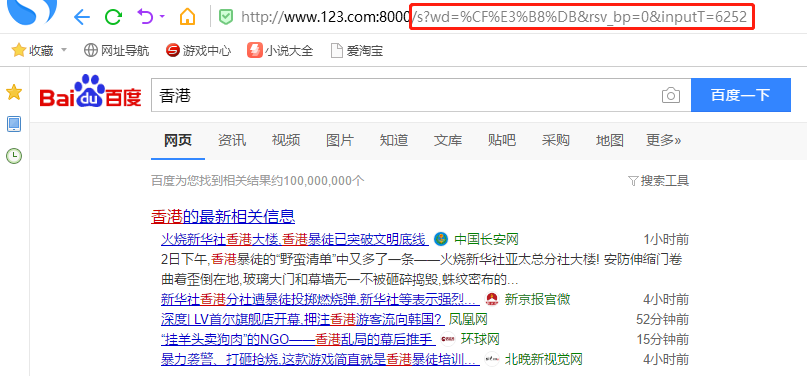
4.负载均衡
在nginx配置文件中配置负载均衡:
# 在server前面定义一个upstream池
upstream leeoo {
server 192.168.1.121:;
server 192.168.1.202;
} # 然后在对应的location中,将目标服务器的域名或IP替换为leeoo
location /ooxx {
proxy_pass http://leeoo/;
}
此时,当我们访问http://www.123.com:80/ooxx时,nginx会自动进行负载均衡,将轮询访问leeoo中的两台real server。
5.Session一致性问题
如果我们的后端服务器使用的是tomcat等容器,需要为用户保存Session。当Nginx将一个用户链接负载到不同的后端服务器时,我们需要保证他们能够使用同一个Session对用户进行验证,否则会出现让用户重复登录的问题;
1)首先,要保证集群中的服务器时间一致性。
2)使用专门管理Session的软件,或者使用memcache、Redis等内存数据库等来帮助Tomcat共享Session。
在192.168.1.199上安装memcached:
yum install memcached -y
使用以下命令启动:
memcached -d -m 128m -p -l 192.168.1.199 -u root -P /tmp/
-m是使用128M内存空间
-p是使用11211端口进行通信
-l是服务器地址
-u用户名
使用netstat查看memcached监听情况:
[root@lvs-server- etc]# netstat -natp | grep
tcp 192.168.1.199: 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN /memcached
在192.168.1.202和192.168.1.121上安装JDK和Tomcat:
下载JDK和Tomcat:
apache-tomcat-7.0..tar.gz
jdk-7u80-linux-x64.rpm
安装JDK:
rpm -i jdk-7u80-linux-x64.rpm
配置环境变量:
vi /etc/profile # 在最后添加
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1..0_80
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin # 使其生效
source /etc/profile
运行jps命令,检查是否安装成功:
[root@real-server- etc]# jps
Jps
解压Tomcat:
tar xf apache-tomcat-7.0..tar.gz
创建一个页面,让其打印Session:
cd ~/apache-tomcat-7.0./webapps/ROOT
cp index.jsp index.jsp.bak
vi index.jsp from 192.168.1.202<br>Session: <%= session.getId()%>
启动Tomcat:
cd ~/apache-tomcat-7.0./bin
./startup.sh
[root@real-server- bin]# ./startup.sh
Using CATALINA_BASE: /root/apache-tomcat-7.0.
Using CATALINA_HOME: /root/apache-tomcat-7.0.
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /root/apache-tomcat-7.0./temp
Using JRE_HOME: /usr/java/jdk1..0_80
Using CLASSPATH: /root/apache-tomcat-7.0./bin/bootstrap.jar:/root/apache-tomcat-7.0./bin/tomcat-juli.jar
Tomcat started.
访问192.168.1.202:8080:

重复刷新,Session是不会变化的,因为我们访问的是同一个Tomcat服务器。
在192.168.1.202和192.168.1.121上都安装好Tomcat之后,我们使用nginx来做负载均衡(192.168.1.201上):
在/opt/nginx/conf/nginx.conf中做如下配置:
upstream tom {
server 192.168.1.121:;
server 192.168.1.202:;
}
server {
listen ;
server_name www..com;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /cat/ {
proxy_pass http://tom/;
}
}
重新载入:
systemctl reload nginx
然后此时访问www.123.com:80:
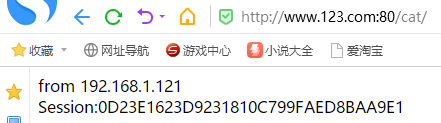
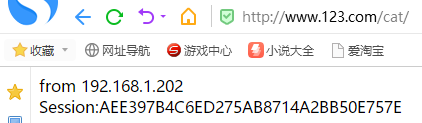
我们可以看到,重复访问的时候,负载均衡是起效的,但是他们的Session不一致的。
停掉两台机器的Tomcat:
cd ~/apache-tomcat-7.0./bin
./shutdown.sh
配置Tomcat使用memcached:
cd /root/apache-tomcat-7.0./conf
vi context.xml
在最后添加如下内容:
<Manager className="de.javakaffee.web.msm.MencachedBackupSessionManager"
memcachedNodes="n1:192.168.1.199:11211"
sticky="false"
lockingMode="auto"
sessionBackupAsync="false"
requestUriIgnorePattern=".*\.(ico|png|gif|jpg|css|js)$"
sessionBackupTimeout="" transcoderFactoryClass="de.javakaffee.web.msm.serializer.kryo.KryoTranscoderFactory"
/>
再为Tomcat的lib中补充需要的一些jar包:
[root@real-server- tomcat_jar]# ll
total
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb asm-3.2.jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb kryo-1.04.jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb kryo-serializers-0.11.jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb memcached-session-manager-1.7..jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb memcached-session-manager-tc7-1.8..jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb minlog-1.2.jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb msm-kryo-serializer-1.7..jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb reflectasm-1.01.jar
-rw-r--r-- root root Feb spymemcached-2.7..jar
将这些jar包拷贝到Tomcat的lib目录中:
cp ~/tomcat_jar/* ~/apache-tomcat-7.0.96/lib
重新启动tomcat,后再次尝试访问http://www.123.com/cat,发现负载均衡正常,Session也不会发生变化。
[Linux系统] (8)Nginx的更多相关文章
- linux系统下nginx安装目录和nginx.conf配置文件目录
linux系统下nginx安装目录和nginx.conf配置文件目录 1.查看nginx安装目录 输入命令 # ps -ef | grep nginx 返回结果包含安装目录 root 26 ...
- linux系统中Nginx+FFmPeg+vlc实现网页视频播放配置过程
linux系统中Nginx+FFmPeg实现网页监控视频播放配置过程 1.安装好的nginx上添加模块nginx-http-fiv-module-master 此模块是rtmp模块的升级版,有它所有的 ...
- Linux系统下Nginx安装详解
该随笔为个人原创,后期会根据项目实践实时更新,如若转载,请注明出处,方便大家获得最新博文! 注:安装Nginx需要Linux系统已经安装 openssl-fips-2.0.2.tar.gz zli ...
- Linux系统下Nginx+PHP 环境安装配置
一.编译安装Nginx 官网:http://wiki.nginx.org/Install 下载:http://nginx.org/en/download.html # tar -zvxf nginx- ...
- linux系统下nginx/mysql/php启动、停止、重启命令
/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /etc/init.d/mysql start /usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm start #nginx命令 ...
- Linux系统上Nginx服务器的安装与配置
前言: 详细步骤移步菜鸟教程 一. 安装Nginx,注意虚拟机与宿主机的网络连通性 l 安装编译工具及库文件(zlib库. ssl) yum -y install make zlib zlib-de ...
- 嵌入式之Linux系统裁剪和定制---(kernel+busyboxy+dropbear+nginx)
本文将介绍通过完全手动定制内核,在此基础上添加 busybox ,并实现远程登陆,使裁剪的 linux 能够运行 nginx . 在此之前介绍一下 linux 系统的启动流程. linux系统启动流程 ...
- Nginx在Windows系统和Linux系统下的重启
一.Windows系统下重启nginx 1.杀掉nginx进程 tskill nginx echo 已终止所有ginx进程 2.启动nginx cd f:\nginx- nginx.exe ...
- CentOS 6.5结合busybox完成自制Linux系统及远程登录和nginx安装测试
前言 系统定制在前面的博文中我们就有谈到过了,不过那个裁减制作有简单了点,只是能让系统跑起来而,没有太多的功能,也没的用户登录入口,而这里我们将详细和深入的来谈谈Linux系统的详细定制过程和实 ...
随机推荐
- sqlalchemy链接数据库
from sqlalchemy import create_engine HOSTNAME = '127.0.0.1' PORT = 3306 DATABASE = 'first_sqlalchemy ...
- mybatis批量更新update-设置多个字段值allowMultiQueries=true
mybatis由于简单易用性得到大家的认可和使用 但是在批量更新操作中,网上介绍的貌似不全,正好今天做个记录,大家一起进步 在实际项目开发过程中,常有这样的需求:根据ids更新表的某一个字段值,这时的 ...
- Palindromic Substrings
Given a string, your task is to count how many palindromic substrings in this string. The substrings ...
- PHP中的接口
对象接口 使用接口(interface),可以指定某个类必须实现哪些方法,但不需要定义这些方法的具体内容. 接口是通过 interface 关键字来定义的,就像定义一个标准的类一样,但其中定义所有的方 ...
- [Bzoj1001][BeiJing2006]狼抓兔子(网络流/对偶图)
题目链接:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1001 看到大佬们都是对偶图过的,写了个最大流水过去了QAQ,网络流的无向图直接建双向边( ...
- JavaScript更改css样式
来源:https://www.w3school.com.cn/js/js_htmldom_css.asp 1, document.getElementById(id).style.property = ...
- AppCan调试问题
来源:http://edu.appcan.cn/theVideoMain1.html?chapterId=248_1 第1步, 生成AppCan调试中心 第2步, 启动AppCan调试中心 第3步, ...
- Git上传相关资料
############ssh key及 配置信息############# 设置Git的user name和email: $ git config --global user.name " ...
- pc端和移动端的“窗口”(viewport)故事(part1)
A tale of two viewports - part one 在以下的系列文章中,我将为大家解释浏览器中的视窗和一些重要的元素的尺寸是如何起作用的,如:大家最熟悉的html元素以及window ...
- 05 Python网络爬虫的数据解析方式
一.爬虫数据解析的流程 1.指定url 2.基于requests模块发起请求 3.获取响应中的数据 4.数据解析 5.进行持久化存储 二.解析方法 (1)正则解析 (2)bs4解析 (3)xpath解 ...
