MCMC and Bayesian Data Analysis(PPT在文件模块)
How to generate a sample from $p(x)$?
Let's first see how Matlab samples from a $p(x)$. In Matlab, there are several common probability distributions.

Try univariate Gaussian distribution
p= normpdf(linspace(xmin , xmax , num_of_points) , mean, standard_deviation);%PDF
c= normcdf(linspace(xmin , xmax , num_of_points) , mean, standard_deviation);%CDF
y=normrnd(mean, standard_deviation,number_of_samples, 1);%Random Number Generating Method
Try PDF:
x=linespace(-1,1,1000);
p=normpdf(x ,0, 1);
plot(x,p);
Note: linespace returns a vector which is usually accessed like this
x(1)%the first elem, not x(0)
x(:)
x(1,:)
Try RSM:
y=normrnd(0, 1,100, 1);%试试采10000个样本
hist( y , 20 );%20 bars
Try univariate uniform distribution
p= unifpdf(linspace(xmin , xmax , num_of_points) , a,b);%PDF
c= unifcdf(linspace(xmin , xmax , num_of_points) , a,b);%CDF
y=unifrnd(a,b,number_of_samples, 1);%RNG
Try PDF:
x=linespace(-10,10,1000);
p= unifpdf(x ,-5,5);
plot(x,p);
Try RSM:
y=unifrnd(-5, 5,100, 1);%试试采10000个样本
hist( y , 20 );%20 bars
Matlab provides random number generating functions for some standard $p(x)$, it doesn't provide us sampling functions for a general $p(x)$. Here I show some common sampling methods.
Inverse Transform Sampling(ITS)
with descret variables
This method generates random numbers from any probability distribution given the inverse of its cumulative distribution function. The idea is to sample uniformly distributed random numbers (between 0 and 1) and then transform these values using the inverse cumulative distribution function(InvCDF)(which can be descret or continous). If the InvCDF is descrete, then the ITS method just requires a table lookup, like shown in Table 1.
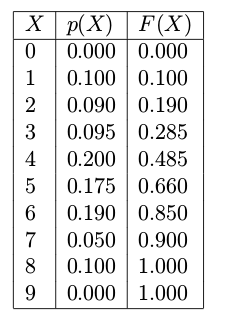
Table 1. Probability of digits observed in human random digit generation experiment
There is a method called randsample in Matlab that can implement the sampling process using the Table 1. See the code below.
%Note: The randsample doesn't defaultly exist in Octave-core package, install statistic package from http://octave.sourceforge.net/statistics/ before using randsample. % probabilities for each digit
theta=[0.000; ... % digit 0
0.100; ... % digit 1
0.090; ... % digit 2
0.095; ... % digit 3
0.200; ... % digit 4
0.175; ... % digit 5
0.190; ... % digit 6
0.050; ... % digit 7
0.100; ... % digit 8
0.000]; seed = 1; rand( 'state' , seed );% fix the random number generator
K = 10000;% let's say we draw K random values
digitset = 0:9;
Y = randsample(digitset,K,true,theta);
figure( 1 ); clf;
counts = hist( Y , digitset );
bar( digitset , counts , 'k' );
xlim([-0.5 9.5]);
xlabel( 'Digit' );
ylabel( 'Frequency' );
title( 'Distribution of simulated draws of human digit generator' );
pause;
Instead of using the built-in functions such as randsample or mnrnd, it is helpful to consider how to implement the underlying sampling algorithm using the inverse transform method which is:
(1) Calculate $F(X)$.
(2) Sample u from Uniform(0,1).
(3) Get a sample $x^{i}$ of $P(X)$, which is $F(u)^{-1}$.
(4) Repeat (2) and (3) until we get enough samples.
Note: For discrete distributions, $F(X)^{-1}$ is discrete, the way to get a sample $x^{i}$ is illustrated below where $u=0.8,~x^{i}=6$ .

with continuous variables
This can be done with the following procedure:
(1) Draw U ∼ Uniform(0, 1).
(2) Set $X=F(U)^{-1}$
(3) Repeat
For example, we want to sample random numbers from the exponential distribution where its CDF is F (x|λ) = 1 − exp(−x/λ) . Then $F(u|\gamma)^{-1}=-log(1-u)\gamma$. Therefore replace $F(U)^{-1}$ with $F(u|\gamma)^{-1}$.
p=-log(1-unifrnd(0,1,10000,1))*2;
hist(p,30);
Reject Sampling
Applied situation: impossible/difficult to compute CDF of $P(X)$.
Advantage: unlike MCMC, it doesn't require of any “burn-in” period, i.e., all samples obtained during sampling can immediately be used as samples from the target distribution $p(\theta)$.

Based on the Figure above, the method is:
(1) Choose a proposal distribution q(θ) that is easy to sample from.
(2) Find a constant c such that cq(θ) ≥ p(θ) for all θ.
(3) Draw a proposal θ from q(θ).
(4) Draw a u from Uniform[0, cq(θ)].
(5) Reject the proposal if u > p(θ), accept otherwise. Actually, since u is sampled from Uniform[0, cq(θ)], it is equal to state like this " Reject if $u\in[p(\theta),cq(\theta)]$, accept otherwise".
(6) Repeat steps 3, 4, and 5 until desired number of samples is reached; each accepted sample $\theta$ is a draw from p(θ).
For example

then the code is
k=100000;%draw k samples
c=2;
theta_vec=unifrnd(0,1,k,1)%gen a proposal vector from q($\theta$)
cq_vec=c*unifpdf(theta_vec);%cq(theta) vector
p_vec=2*theta_vec;%p(theta) vector
u_vec=[];
for cq=cq_vec
u_vec=[u_vec;unifrnd(0,cq)];
end
r=theta_vec.*(u_vec<p_vec);
r(r==0)=[];%remove the “0” elements
hist(r,20);

MCMC Sampling
Before getting to know MCMC sampling, we first get to know Monte Carlo Integration and Markov Chain.



For example:
%Implement the Markov Chain involving x under Beta(200(0.9x^((t-1))+0.05),200(1-0.9x^((t-1)-0.05))
fa=inline('','x')%parameter a for beta
fb=inline('200*(1-0.9*x-0.05)','x');%parameter b for beta
no4mc=4;%4 markove chains
states=unifrnd(0,1,1,no4mc);%initial states
N=1000;%200 samples drawn from 4 chains
X=states;
for i=1:N
states=betarnd(fa(states),fb(states));
X=[X;states];
end;
plot(X);
pause;

Metroplis Sampling
MCMC and Bayesian Data Analysis(PPT在文件模块)的更多相关文章
- 《利用Python进行数据分析: Python for Data Analysis 》学习随笔
NoteBook of <Data Analysis with Python> 3.IPython基础 Tab自动补齐 变量名 变量方法 路径 解释 ?解释, ??显示函数源码 ?搜索命名 ...
- 深入浅出数据分析 Head First Data Analysis Code 数据与代码
<深入浅出数据分析>英文名为Head First Data Analysis Code, 这本书中提供了学习使用的数据和程序,原书链接由于某些原因不 能打开,这里在提供一个下载的链接.去下 ...
- 数据分析---《Python for Data Analysis》学习笔记【04】
<Python for Data Analysis>一书由Wes Mckinney所著,中文译名是<利用Python进行数据分析>.这里记录一下学习过程,其中有些方法和书中不同 ...
- 数据分析---《Python for Data Analysis》学习笔记【03】
<Python for Data Analysis>一书由Wes Mckinney所著,中文译名是<利用Python进行数据分析>.这里记录一下学习过程,其中有些方法和书中不同 ...
- 数据分析---《Python for Data Analysis》学习笔记【02】
<Python for Data Analysis>一书由Wes Mckinney所著,中文译名是<利用Python进行数据分析>.这里记录一下学习过程,其中有些方法和书中不同 ...
- 数据分析---《Python for Data Analysis》学习笔记【01】
<Python for Data Analysis>一书由Wes Mckinney所著,中文译名是<利用Python进行数据分析>.这里记录一下学习过程,其中有些方法和书中不同 ...
- Aspose是一个很强大的控件,可以用来操作word,excel,ppt等文件
Aspose是一个很强大的控件,可以用来操作word,excel,ppt等文件,用这个控件来导入.导出数据非常方便.其中Aspose.Cells就是用来操作Excel的,功能有很多.我所用的是最基本的 ...
- 《python for data analysis》第五章,pandas的基本使用
<利用python进行数据分析>一书的第五章源码与读书笔记 直接上代码 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-# <python for data analysis>第五 ...
- 《python for data analysis》第四章,numpy的基本使用
<利用python进行数据分析>第四章的程序,介绍了numpy的基本使用方法.(第三章为Ipython的基本使用) 科学计算.常用函数.数组处理.线性代数运算.随机模块…… # -*- c ...
随机推荐
- 装饰模式(Decorator pattern)
装饰模式(Decorator pattern): 又名包装模式(Wrapper pattern), 它以对客户端透明的方式扩展对象的功能,是继承关系的一个替代方案. 装饰模式以对客户透明的方式动态的给 ...
- Python-os
os.listdir(path)返回一个list,其中包括该目录下所以文件和文件夹的名字,是str格式.ex.['file_1.ext','folder_name'] file_name, exten ...
- PHP开发网站之微信登录、绑定
)))刷新access_token()); ); ); curl_setopt($curlobj, CURLOPT_SSL_VERIFYPEER, FALSE); curl_setopt($curlo ...
- json与对象转化
/// <summary> /// 把JSON字符串还原为对象 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">对 ...
- hg常用命令
关于hg命令选项 如果你是在windows系统下,使用的是图像界面,你很可能不常用它.但是一旦你了解这些命令之后,会觉得很方便.hg有很多命令,这些命令都有一定的选项,在开始的时候,只知道用它,有时候 ...
- iOS开发app启动原理及视图和控制器的函数调用顺序
main()函数是整个程序的入口,在程序启动之前,系统会调用exec()函数.在Unix中exec和system的不同在于,system是用shell来调用程序,相当于fork+exec+waitpi ...
- 删除表空间的时候遇到的问题:ORA-02429: 无法删除用于强制唯一/主键的索引
今天打算删除orcale数据库中无用的表空间,发现报错,查资料删除,写个过程留着备用.1.drop tablespace dldata INCLUDING CONTENTS CASCADE CONST ...
- angularjs(一)基础概念
一.前言 前端技术的发展是如此之快,各种优秀技术.优秀框架的出现简直让人目不暇接,作为一名业界新秀,紧跟时代潮流,学习掌握新知识自然是不敢怠慢.当听到AngularJs这个名字并知道是google在维 ...
- 介绍开源的.net通信框架NetworkComms框架 源码分析(二十三 )TCPConnection
原文网址: http://www.cnblogs.com/csdev Networkcomms 是一款C# 语言编写的TCP/UDP通信框架 作者是英国人 以前是收费的 目前作者已经开源 许可是 ...
- Mybatis之关联查询
一.一对一关联 1.1.提出需求 根据班级id查询班级信息(带老师的信息) 1.2.创建表和数据 创建一张教师表和班级表,这里我们假设一个老师只负责教一个班,那么老师和班级之间的关系就是一种一对一的关 ...
