Ant之build.xml配置详解【转】
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/mevicky/article/details/72828554
前言
国内关于build.xml的配置资料太零散了,实在是受不了,故而将自己的笔记整理成博文,方便大家查阅和理解。
build.xml配置参数
构建文件默认叫build.xml,其有很多配置参数。
project
每个构建文件都有一个project标签,有以下属性:
- default:表示默认的运行目标,这个属性是必须的。
- basedir:表示项目的基准目录。
- name:表示项目名。
- description:表示项目的描述。
如下:
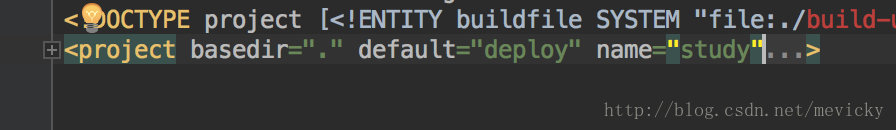
每个项目对应一个构建文件,但是如果项目比较复杂,业务线比较多,则有可能对应很多个构建文件,比如:
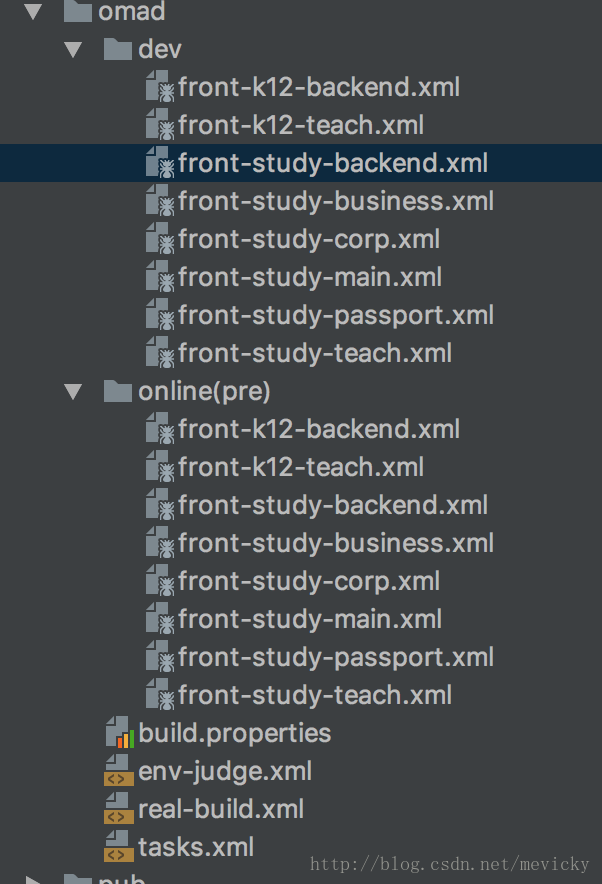
这时我们需要注意,每个构建文件都需要以project标签包含起来。
property
类似于常量,可以供给build.xml中的其他标签使用。有两个特点:
- 大小写敏感
- 不可改变,谁先设定,之后的都不能改变。
该标签可以与多个属性配合使用。
- name和value:
<property name="module_name" value="admin"/>
后面直接使用即可:
<echo message="begin nej-build ${module_name}..."/>
- name和refid:
<property name="srcpath" refid="dao.compile.classpath"/>
其中的dao.compile.classpath在别的地方进行了定义。当然,也可以通过直接引用的方式:
<property name="baseline.dir" value="${ob_baseline.dir}"/>
- name和location:
<property name="srcdir" location="src"/>
将srcdir的值设置为当前文件路径/src。
- file:
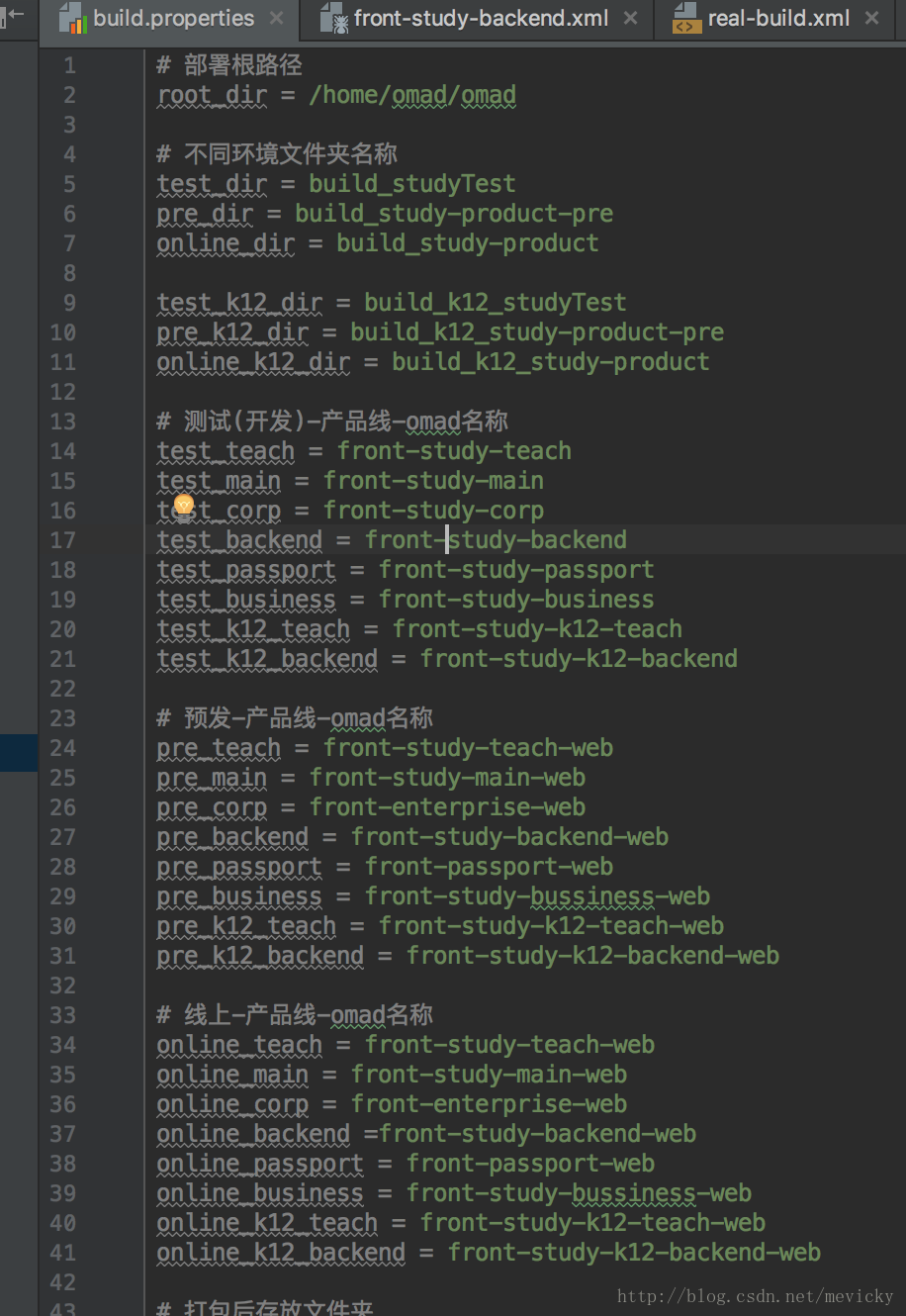
<property file="./omad/build.properties"/>
导入相对文件中的所有变量,这里的build.properties专门用来存放各种变量,示例如下:
url:
<property url="http://www.mysite.com/bla/props/foo.properties"/>
导入对应文件的属性
environment:
<property environment="env"/>
设置系统的环境变量前缀为env。比如
<property name="tomcat.home" value="${env.CATALINA_HOME}"/>
将系统的tomcat安装目录设置到tomcat.home属性中。
import
引入别的xml文件,提高复用性:
<import file="./env-judge.xml"/>
<import file="./tasks.xml"/>
甚至可以批量匹配:
<copy todir="${basedir}/src/html/${html.dir}" overwrite="true" includeEmptyDirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/lib">
<include name="module-*/**" />
</fileset>
</copy>
target
任务,一个project标签下有一个或多个target标签,代表任务,任务间可以存在依赖关系。有如下属性:
- name:用于标识,这个是必须的
- depends:用来指定所依赖的任务。
<!-- 初始化任务 -->
<target name="init">
<echo message=" init ${init} ..."/>
</target> <!-- 编译 -->
<target name="compile" depends="init">
<delete dir="${classes.dir}" />
<mkdir dir="${classes.dir}" />
<javac srcdir="${src.dir}" destdir="${classes.dir}">
<classpath refid="master-classpath" />
</javac>
</target>
1 if:当属性设置时才执行该任务。
<target name="sync_module_k12_teach" if="${is_k12_teach}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="org"/>
</antcall>
</target> <target name="sync_module_backend" if="${is_backend}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="admin"/>
</antcall>
</target> <target name="sync_module_k12_backend" if="${is_k12_backend}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="admin"/>
</antcall>
</target>
通过判断变量是否存在,执行不同的任务。
- unless:当属性未设置时才执行。
- description:任务描述。
echo
控制台显示
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>
delete
删除文件或文件目录,有如下属性
- file:删除文件
- dir:删除目录
- includeEmptyDirs:值得是否删除空目录,默认是true
- failonerror:报错是否停止,默认是true
- verbose:是否列出删除的文件,默认是false
示例如下:
<!--clean other dir-->
<target name="clean_other_dir">
<echo message="begin clean_other_dir..."/>
<delete dir="${basedir}/${compress.dir}"/>
<delete dir="${basedir}/pub"/>
<echo message="begin clean html module-xx..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/src/html" >
<include name="**/module-*/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/res" >
<include name="module-*/**"/>
<include name="component-*/**"/>
<include name="res-base/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
</target>
mkdir
创建一个目录
<mkdir dir=”${class.root}”/>
copy
拷贝文件或文件目录,属性如下:
- file:表示源文件。
- tofile:表示目标文件。
- todir:表示目标目录。
- overwrite:是否覆盖目标文件,默认为false。
- includeEmptyDirs:是否拷贝空目录,默认为true。
- failonerror:如目标没有发现是否自动停止,默认值true。
- verbose:是否显示详细信息,默认值false。
示例:
<target name="cp">
<copy todir="${compress.dir}" overwrite="true">
<fileset dir="${ob_baseline.dir}">
<include name="pub/" />
<include name="res/" />
<include name="mail_template/" />
</fileset>
</copy>
</target>
fileset
文件集标签,通常与任务结合来使用,例如上面的copy的demo中,通过将fileset定义的文件路径下的文件,拷贝到todir指定的路径中。
也可以用于批量删除:
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/src/html" >
<include name="**/module-*/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
<echo message="begin clean res/module-xx、component-xx、res-base..."/>
<delete includeemptydirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/res" >
<include name="module-*/**"/>
<include name="component-*/**"/>
<include name="res-base/**"/>
</fileset>
</delete>
也就是说,但凡遇到文件集操作,都需要用到fileset标签。
exec
用来执行系统命令,或者指定环境的命令。
比如:
<target name="test">
<exec executable="cmd.exe">
<arg line="/c dir"/>
</exec>
</target>
打开命名行,并转到c盘执行dir命令。
能够执行系统命令,就相当于可以执行各种环境比如node、gulp、bower等等:
<!--build style-->
<target name="build_style">
<echo message="begin build_style..."/>
<exec dir="." executable="gulp" failonerror="true">
<arg line="scss"/>
</exec>
</target> <!--bower cache clean if必须是${]才是判断true,false, 否则只要有设定值即可执行-->
<target name="bower_cache_clean" if="${is_bower_cache_clean}">
<echo message="begin bower_cache_clean ..."/>
<exec dir="." executable="bower" failonerror="true">
<arg line="cache clean" />
</exec>
</target>
antcall
执行某个定义的任务。
<target name="sync_module_teach" if="${is_teach}">
<antcall target="sync_module_item">
<param name="html.dir" value="org"/>
</antcall>
</target>
执行sync_module_item任务,并设置参数html.dir的值为org。
该任务定义如下:
<target name="sync_module_item">
<echo message="begin sync_module ${html.dir}..."/>
<copy todir="${basedir}/src/html/${html.dir}" overwrite="true" includeEmptyDirs="true">
<fileset dir="${basedir}/lib">
<include name="module-*/**" />
</fileset>
</copy>
</target>
或者更为简单的表达:
<target name="deploy">
<echo message="begin auto deploy......"/>
<antcall target="clean"/>
<antcall target="bower_install"/>
<antcall target="cnpm_install"/>
<antcall target="sync_module"/>
<antcall target="build_style"/>
<antcall target="nej_build" />
<antcall target="cp"/>
</target>
parallel
并行执行多个子任务。
<parallel failonany="true">
<antcall target="sync_module_corp"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_main"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_teach"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_backend"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_passport"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_business"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_k12_teach"/>
<antcall target="sync_module_k12_backend"/> <antcall target="build_style"/>
</parallel>
通过failonany控制如果一个失败,则不执行。通过并行执行,来提升性能,降低构建花费的时间。
regexp
用于正则的定义的使用,可以与matches结合使用。
比如,定义正则:
<regexp id="regexp_env_test" pattern="^${root_dir}/(${test_dir}|${test_k12_dir})/.+"/>
<regexp id="regexp_env_pre" pattern="^${root_dir}/(${pre_dir}|${pre_k12_dir})/.+"/>
通过pattern指定正则内容,通过id标识。
在需要匹配的时候,使用之:
<condition property="is_test">
<matches string="${basedir}">
<regexp refid="regexp_env_test"/>
</matches>
</condition>
condition
用来判断,如果包含的内容符合条件,则将property指定的属性设置为true,否则为false。
比如上面的例子中,就是将basedir变量的值和regexp_env_test对应的正则匹配,如果正确,就将is_test设置为true,然后后面的流程再去判断。
与之配合的标签有很多,下面一一介绍:
- istrue,isfalse:断言
<condition property="is_test_backend">
<and>
<istrue value="${is_test}"/>
<istrue value="${is_backend}"/>
</and>
</condition>
只有is_test和is_backend变量的值均为true,is_test_backend的值才为true。
- and:逻辑与,需要都满足条件才行,如上例所述。
- not:逻辑非,反过来的结果。
- or,xor:逻辑或和逻辑异或。
- isset:指定属性是否存在:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果属性name不存在则返回false-->
<isset property="name"/>
</condition>
equils:指定属性是否相等:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果arg1的值与arg2的值相等返回true,否则为false-->
<equals arg1="${name}" arg2="this is name"/>
</condition>
filesmatch:指定文件是否相等:
<condition property="scondition">
<!--如果file1所代表的文件与file2所代表的文件相等返回true,否则为false-->
<filesmatch file1="testfile1.txt" file2="testfile2.txt"/>
</condition>
Ant之build.xml配置详解【转】的更多相关文章
- ant+jmeter中build.xml配置详解
- java web.xml配置详解(转)
源出处:java web.xml配置详解 1.常规配置:每一个站的WEB-INF下都有一个web.xml的设定文件,它提供了我们站台的配置设定. web.xml定义: .站台的名称和说明 .针对环境参 ...
- web.xml配置详解之listener
web.xml配置详解之listener 定义 <listener> <listener-class>nc.xyzq.listener.WebServicePublishLis ...
- Spring 入门 web.xml配置详解
Spring 入门 web.xml配置详解 https://www.cnblogs.com/cczz_11/p/4363314.html https://blog.csdn.net/hellolove ...
- tomcat中server.xml配置详解(转载)(一)
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/starhu/p/5599773.html tomcat中server.xml配置详解 Tomcat Server的结构图如下:(该文件描述了如 ...
- Web.xml配置详解(转)
Web.xml配置详解 Posted on 2010-09-02 14:09 chinaifne 阅读(295105) 评论(16) 编辑 收藏 1 定义头和根元素 部署描述符文件就像所有XML文件一 ...
- SpringBoot—整合log4j2入门和log4j2.xml配置详解
关注微信公众号:CodingTechWork,一起学习进步. 引言 对于一个线上程序或者服务而言,重要的是要有日志输出,这样才能方便运维.而日志的输出需要有一定的规划,如日志命名.日志大小,日志分 ...
- Tomcat中的Server.xml配置详解
Tomcat中的Server.xml配置详解 Tomcat Server的结构图如下: 该文件描述了如何启动Tomcat Server <Server> <Listener /> ...
- Log4j2详解——XML配置详解
Log4j2详解--XML配置详解 找到了个很详细的文章链接 https://www.jianshu.com/p/bfc182ee33db
随机推荐
- 20165235 祁瑛 Java第四周考试总结
20165235 祁瑛 Java第四周考试总结 课后习题p29 p45 代码编写 import java.util.*; class Example2_5{ public static void ma ...
- 归并排序(Java实现)
package sort; public class MergeSort { static void msort(int []a,int start,int end){ int mid=(start+ ...
- 爬虫之xpath用法
导包用: from lxml import etree
- Tallest Cow POJ - 3263 (区间点修改)
FJ's N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10,000) cows conveniently indexed 1..N are standing in a line. Each cow has a positi ...
- pyspider 启动错误
[root@localhost python]# pyspider all [W 180629 07:08:26 run:413] phantomjs not found, continue runn ...
- java多线程之守护线程(Daemon)
https://blog.csdn.net/u010739551/article/details/51065923/
- 快速上手Git
本文主要摘录于廖雪峰的Git教程,个别地方做了可能不恰当的修改或补充,主要方便自己回顾.查看更详细内容请移步廖老师博客.同时,感谢廖老师写出这么好的入门指导. (有彩蛋!!!) 一.热身 1.初始化一 ...
- c++ stod很慢
C++ Convert String to Double Speed (There is also a string-to-int performance test.) A performance b ...
- VC6.0学习C语言入门SDK
度网盘链接 VC6.0 密码:t6bd VS2010 密码:3of2 C语言入门教程 在线视频地址(PS此链接摘抄至博主lellansin) Acfun.tv:http://www.acfun. ...
- 《动物世界》的剪刀石头布 HDU --- 6418
题目连接: https://vjudge.net/problem/1812686/origin emmm 这一题的资料来自<动物世界>这一个李易峰演的电影.. 主要的思路就是概率,但是会牵 ...
