Newly Setting up a CentOS-7 system
yum install -y epel-release glibc.i686 libtools vim clang git autoconf automake w3m glibc screen
the most import sentence I learned in meeting compiling prerequisites:
yum whatprovides */libcap* | grep dev
in *nix systems, the concept of runlevel is always met, and some softwares needs to do some changes in the relative folders.. /etc/rc3.d/..
here are some quotes from askubuntu..:
<QUOTE>{
To see the current (and previous) runlevel:
runlevel
To switch runlevels:
sudo init $runlevel
For example, to reboot:
sudo init
The init you are reading about was replaced by upstart starting with Edgy Eft 6.10; and, one of the programs provided by upstart is its own implementation of init. Here are the docs for 10.04.
To change the default runlevel, use your favorite text editor on /etc/init/rc-sysinit.conf...
sudo vim /etc/init/rc-sysinit.conf
Change this line to whichever runlevel you want...
env DEFAULT_RUNLEVEL=
Then, at each boot, upstart will use that runlevel.
}</QUOTE>
and note that the default runlevel of systems is 3 usually..
some init files..
~/.profile /etc/profile ~/.xprofile : things to do when login in graphical mode, /etc/profile is for all users
~/.bash_profile :things to do when login as personal user in bash/sh/rxvt/urxvt.
~/.bashrc : things to do when opening new bash/sh/rxvt/urxvt, open ssh, scp, sudo
~/.xinitrc : things to do when starting x server
~/.i3/config : things to do when starting i3
----orignal file above-- here are contents updated Sept. 26, 2017----
to start something while startup have several ways, one is to add a service at path /usr/lib/systemd/system/
a service file usually seems like:
[Unit]
Description=...
Documentation=man:..(id) man:..(id)
After=
Wants= [Service]
Type=
PIDFile=
EnvironmentFile
ExecStart=
ExecReload=
KillMode=
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec= [Install]
WantedBy=
to know more about the [Service] part of a service file, see man systemd.service. Other parts contains: man systemd.unit, man systemd.exec, man systemd.kill, man systemd.resource-control
some interesting [Service] settings:
Type, here specifies type of the service. Choices can be one of: simple, forking, oneshot, notify, dbus, idle.
quote from here, types have the following meaning:
Type=simple(default): systemd considers the service to be started up immediately. The process must not fork. Do not use this type if other services need to be ordered on this service, unless it is socket activated.Type=forking: systemd considers the service started up once the process forks and the parent has exited. For classic daemons use this type unless you know that it is not necessary. You should specifyPIDFile=as well so systemd can keep track of the main process.Type=oneshot: this is useful for scripts that do a single job and then exit. You may want to setRemainAfterExit=yesas well so that systemd still considers the service as active after the process has exited.Type=notify: identical toType=simple, but with the stipulation that the daemon will send a signal to systemd when it is ready. The reference implementation for this notification is provided by libsystemd-daemon.so.Type=dbus: the service is considered ready when the specifiedBusNameappears on DBus's system bus.Type=idle: systemd will delay execution of the service binary until all jobs are dispatched. Other than that behavior is very similar toType=simple.
ExecStart, ExecStop (either one should be specified, or the service file is illegal) is executable is prefixed with '-', then an exit code of command usually is considered as failure is ignored and considered success. If prefixed with '+', then it is executed with full privilege. If file prefixed with '@', then second token be passed as argv[0] to process. All the three prefixes can be used together.
ExecStartPre, ExecStartPost (any of the above commands fails, the service is stopped heresince and considered a failure, and continues with commands specified in ExecStopPost. ExecStop commands will also be skipped. (It is not started)
ExecStop, this command should be one that synchronously stops the process running.
RuntimeMaxSec, WatchdogSec(this should be used together with Type=Notify, NotifyAccess=main/all/.., otherwise it is defaults to 0/forever)
Restart, on-success, on-failure, no, on-abnormal, on-watchdog, on-abort, always.
RestartSec, specifies the seconds that waits before restart the service.
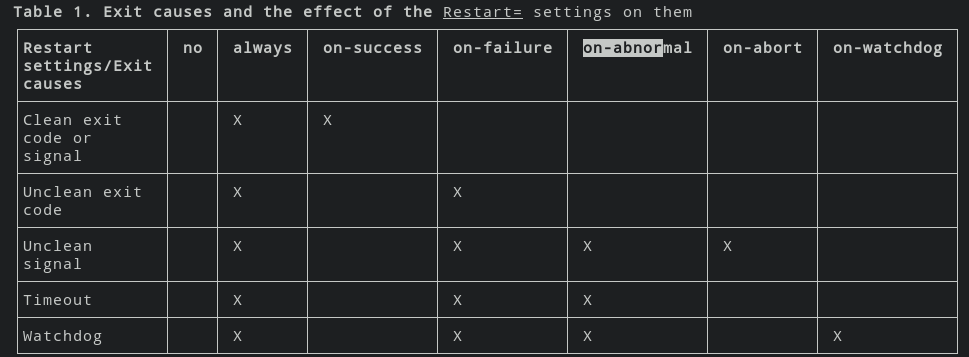
Some [Unit] settings:
Wants, Requires, Requisite, BindsTo: services Requires will be started as well when this service is started(list order is of-no-importance when being started), however, if services Requisite not running while starting this service, the start process will be failed. Wants services will also be started when this service starts, but this service will not be failed immediately when wanted services fails. When BindsTo services stopped, this service will be stopped also.
PartOf: when the specified services being started, this service will also be started, similar to Requires
Before, After, this service is before/after the mentioned services when being started, and also when stops, the inverse ordering is applied
OnFailure, services to be run when fails
ConditionArchitecture, ConditionVirtualization, ConditionHost, ConditionKernelCommandLine, ConditionPathExists, ConditionFileNotEmpty,
Some [Install] settings: the settings here be affecting systemctl enable commands
Alias,
WantedBy, RequiredBy, reverse form of Wants, Requires. But in order to take effect, this service should be enabled by systemctl enable and thus symlinks is created in the wants folder.
some services can be started as multiple instances, these are services end up like "name@.service", when start an instance of such service, use systemctl start name@helloworld1.service, where the helloworld1 part is the name of the instance.. and can be reached inside the service file by using %i. Here are all the escapers listed in man systemd.unit..
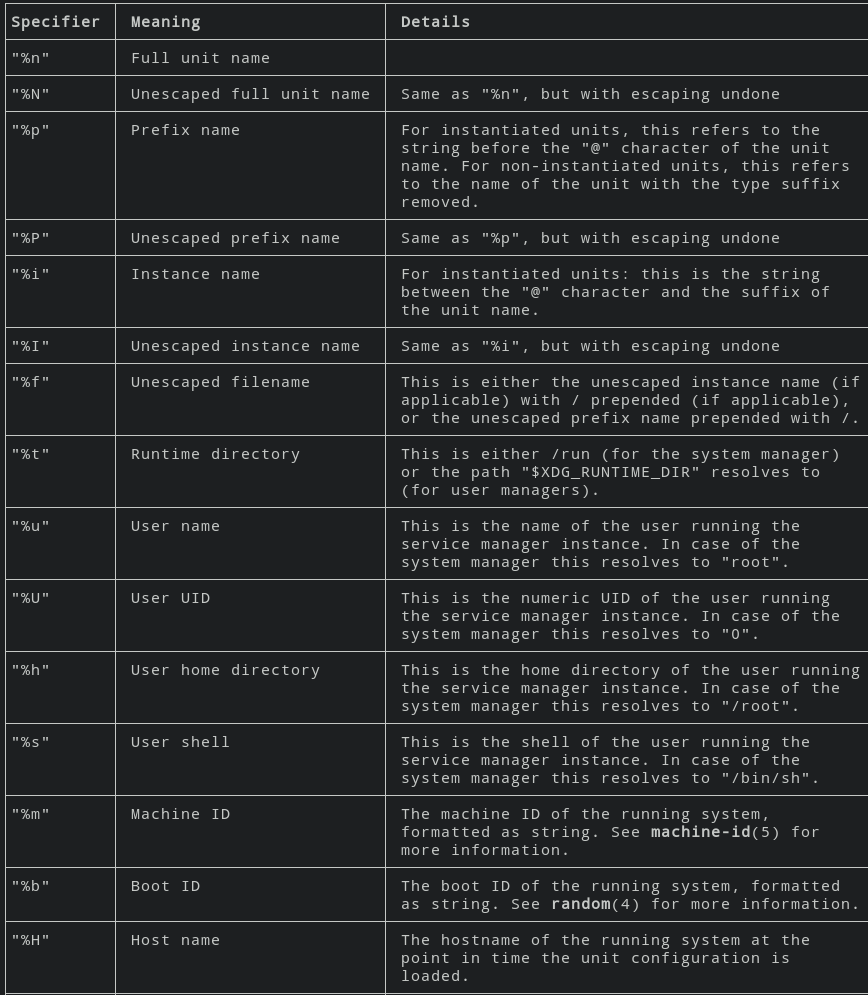
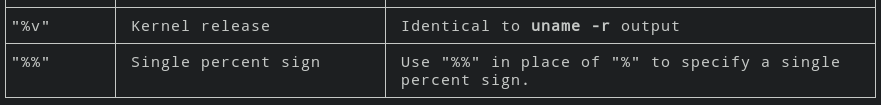
Service variables:
$MAINPID, $SERVICE_RESULT, $EXIT_CODE, $EXIT_STATUS
Newly Setting up a CentOS-7 system的更多相关文章
- 编写CentOS的System V init启动脚本
系统本身自带了说明,在/usr/share/doc/initscripts-(*)/sysvinitfiles,内容如下: 所有System V init脚本都命名为/etc/rc.d/init.d/ ...
- linux mysql无故无法启动了,centos 7
转自: http://support.moonpoint.com/software/database/mysql/not-running-centos7.php 下面简单翻译一下. 详细内容可以阅读英 ...
- centos 7 上安装 testlink 1.9.15/1.9.16/1.9.17/1.9.18 (mysql/php/httpd)
1.9.18 的System Requirements - server.注意,适用于 1.9.15 及以后. Server environment should consist of: web-se ...
- CentOS 7上更改MySQL数据库存储目录浅析
个人之前总结过两篇文章"MySQL更改数据库数据存储目录"和"Ubuntu上更改MySQL数据库数据存储目录",都是在工作中遇到相关案例后的一个简单总结.当 ...
- 转:CentOS/Debian/Ubuntu一键安装LAMP(Apache/MySQL/PHP)环境
CentOS/Debian/Ubuntu一键安装LAMP(Apache/MySQL/PHP) 今天遇到一个网友提到需要在Linux VPS服务器中安装LAMP(Apache/MySQL/PHP)网站环 ...
- 使用dnsmasq来提升CentOS上网速度
1. 安装dnsmasq dnsmasq的官方网址是:http://www.thekelleys.org.uk/dnsmasq/doc.html.利用里面的下载链接下载dnsmasq-2.72.tar ...
- Install FFMPEG and FFMPEG-PHP in CentOS 6 with Virtualmin
Install FFMPEG and FFMPEG-PHP in CentOS 6 with Virtualmin 1 year ago - by Daniel - howto centos v ...
- CentOS 7 install slurm cluster
//slurm install //CentOS 7 system //192.168.159.141 node01 //192.168.159.142 node02 systemctl stop f ...
- CentOS 7 单用户模式+救援模式
CentOS 7 单用户模式+救援模式 CentOS 7 单用户模式+救援模式.有时候大家可能会忘记自己的root密码,或者错误(命令输入错误,命令位置输入有误等)编辑了一个/etc目录下的核心文件导 ...
随机推荐
- sublime eslint setup
[Setting Up ESLint] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QUK4hMoYv_c
- git三个区域详解
一.可以将git简单的分为三个区域 1.工作区(working directory) 2.暂缓区(stage index) 3.历史记录区(history) 二.三个区域关系:工作区 ...
- 信息处理,分而治之-- ESFramework 使用技巧
ESFramework开发手册系列文章已经详细介绍了如何使用ESPlus提供的ESPlus.Application.CustomizeInfo空间来发送和处理自定义信息,而且,在我们在前面介绍的de ...
- js 日期格式化 函数
function formatDate(date,format){ var paddNum = function(num){ num += ""; return num.repla ...
- java邮件发送(以163邮箱为例)
1.首先应该开通163邮箱的smtp和pop3,得到授权码 2.其次建立一个web项目,否则需要倒jar包mail.jar 3.创建一个类 4.注意:邮件内容必须为正式话语,否则系统会认为是垃圾邮件而 ...
- 第二次冲刺spring会议(第三次会议)
[例会时间]2014/5/6 21:15 [例会地点]9#446 [例会形式]轮流发言 [例会主持]马翔 [例会记录]兰梦 小组成员:兰梦 ,马翔,李金吉,赵天,胡佳奇
- Android JNI的使用浅析
介绍JNI的好文章: http://blog.csdn.net/yuanzeyao/article/details/42418977 JNI技术对于多java开发的朋友相信并不陌生,即(java na ...
- java集合概念
Collection(单列集合) List(有序,可重复) ArrayList 底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢 线程不安全,效率高 Vector 底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢 线程安全,效率 ...
- 十七、oracle 权限
一.介绍这一部分我们主要看看oracle中如何管理权限和角色,权限和角色的区别在哪里.当刚刚建立用户时,用户没有任何权限,也不能执行任何操作.如果要执行某种特定的数据库操作,则必须为其授予系统的权限: ...
- jquery 1.9版本后不在支持browser 方法的解决方案
今天对jquery 进行升级,导致项目出错,原来在1.9版本之后 jquery 不支持browser 方法了. 官方建议的又不好用,所以我所jquery 原来的代码摘除来,又扩展回去. //解决jq ...
