【转】在SpringMVC Controller中注入Request成员域
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/abcwt112/p/7777258.html
原文作者:abcwt112
主题
在工作中遇到1个问题....我们定义了一个Controller基类,所有Springmvc自定义的controller都继承它....在它内部定义一个@Autowired HttpServletRequest request;可不可以? 能不能从这个对象里取requestParamters和attributes? 多线程之间会不会影响?
思考
初次思考,我想这应该是不行的.为什么呢?
注入bean是在spring容器启动的时候...request的实现类是在tomcat里(我使用的servlet容器是tomcat)....我又没在spring的容器里配置这个bean.注入应该是失败的...
退一步说,就算是成功了....那注入的也就是1个对象而已.每次servlet接受到请求都会重新生成1个request...这明显和之前启动的那个对象不同吧....怎么想都不可能成功...
如果确实是这样的....那就没有这篇文章了....后来实践了一下..发现这个注入是可以的.使用起来取数据也没任何问题....
其实我那个时候debug看了一下,基本就知道为什么可以取到数据了..但是我并不知道原理和Spring(Springmvc)的处理流程...所以现在研究了一下并记录下来...
原理
首先给大家看一下在方法中注入request作为参数和在成员域中注入request的 注入的request对象之间的区别....
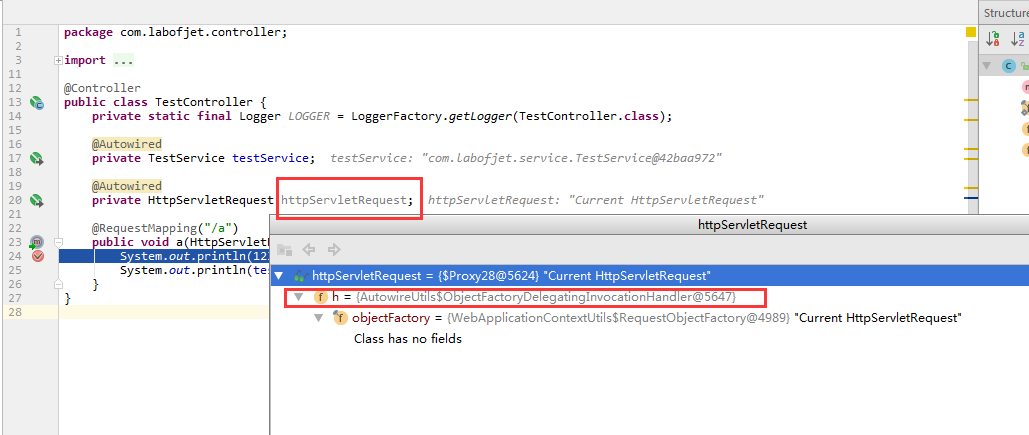
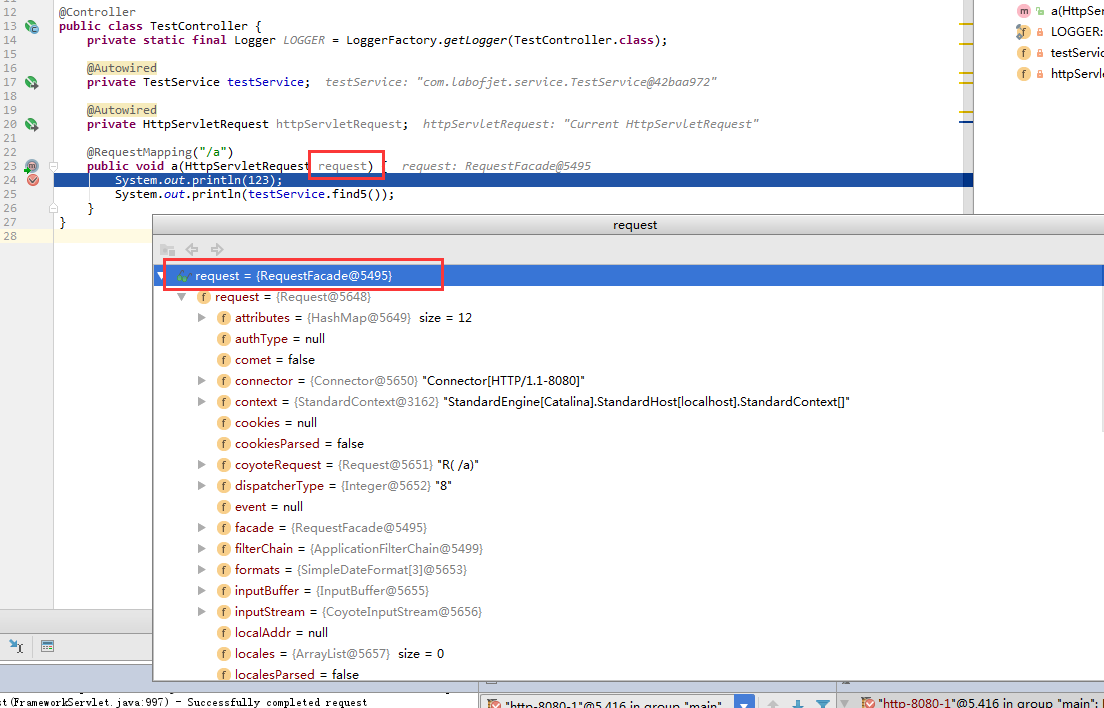
成员域注入的时候注入的是1个代理对象.是 AutowireUtils.ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler的实例.
方法注入的就是一般tomcat原生的requestFacade对象.
所以这是不同的...
/**
* Reflective InvocationHandler for lazy access to the current target object.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private final ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory; public ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
} @Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.equals("equals")) {
// Only consider equal when proxies are identical.
return (proxy == args[0]);
}
else if (methodName.equals("hashCode")) {
// Use hashCode of proxy.
return System.identityHashCode(proxy);
}
else if (methodName.equals("toString")) {
return this.objectFactory.toString();
}
try {
return method.invoke(this.objectFactory.getObject(), args);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
当代理对象(就是成员域request)的大部分方法被调用的时候,ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler会使用objectFactory获取对象(原生request),再调用对象上的方法.
然后我们来看下XmlWebApplicationContext初始化到请求到进入controller里几个对注入request成员域有影响的步骤.
refresh方法和postProcessBeanFactory方法
ApplicationContext的抽象实现类AbstractApplicationContext(基本是所有ac的父类)里定义了ac的refresh方法(包含了使用BeanFactory注入bean)的流程..
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 记录开始wac开始初始化的时间,设置激活标记,servlet的相关param设置到env(之前做过1次),校验env中必须的props
prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 将旧的BF里的bean删掉,新建1个BF,设置部分属性,加载XML配置文件
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 1.设置BF解析bean配置需要用到的一些对象比如env. 2.注册一些BeanPostProcessor比如ApplicationContextAwareProcessor去设置Aware需要的对象
// 3.忽略一些特定class注入的对象,设置一些特定class注入的对象为指定值
// 4.将一些env中的properties map当做bean注册到BF中
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 1.设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象
// 2.在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope
// 3.把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 初始化并调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册BeanPostProcessors并注册到BF中去
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex); // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}
其中有1个模板方法
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
这个方法允许AbstractApplicationContext的子类覆盖它并实现对BF的定制(这个时候bean的defination路径已经指定了,但是bean还没加载).
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext覆盖了这个方法
/**
* Register request/session scopes, a {@link ServletContextAwareProcessor}, etc.
* 1.设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象
* 2.在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope
* 3.把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中
*
*/
@Override
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 设置一个BeanPostProcess为ServletContextAware的实现类注入servlet相关对象
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ServletContextAwareProcessor(this.servletContext, this.servletConfig));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ServletConfigAware.class); // 在BF中增加requetsScope等Scope
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
// 把servletContext,Config,ServletInitParams,ServletAttribute当做Bean注册到BF中
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(beanFactory, this.servletContext, this.servletConfig);
}
其中有一步
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerWebApplicationScopes(beanFactory, this.servletContext);
这里设置了一些特殊的bean的scope,比如request,session,globalSession,application.(当然这个不是我这篇文章的主题.)
同时设置了一些特殊的autowired bean
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletRequest.class, new RequestObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ServletResponse.class, new ResponseObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(HttpSession.class, new SessionObjectFactory());
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(WebRequest.class, new WebRequestObjectFactory());
ServletRequest的实现类(比如HttpServletRequest)被指定使用RequestObjectFactory注入.
RequestObjectFactory
RequestObjectFactory就是1个ObjectFactory就是前面ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler里的ObjectFactory.所以在成员域request对象上调用方法其实就是通过RequestObjectFactory获取对象再调用方法.
/**
* Factory that exposes the current request object on demand.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
private static class RequestObjectFactory implements ObjectFactory<ServletRequest>, Serializable { @Override
public ServletRequest getObject() {
return currentRequestAttributes().getRequest();
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "Current HttpServletRequest";
}
}
/**
* Return the current RequestAttributes instance as ServletRequestAttributes.
* @see RequestContextHolder#currentRequestAttributes()
*/
private static ServletRequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes requestAttr = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
if (!(requestAttr instanceof ServletRequestAttributes)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Current request is not a servlet request");
}
return (ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttr;
}
RequestObjectFactory的getObject方法很简单,就是调用静态方法
RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes().getRequest()
RequestContextHolder
public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException {
RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes == null) {
if (jsfPresent) {
attributes = FacesRequestAttributesFactory.getFacesRequestAttributes();
}
if (attributes == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No thread-bound request found: " +
"Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, " +
"or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? " +
"If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, " +
"your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet/DispatcherPortlet: " +
"In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request.");
}
}
return attributes;
}
/**
* Return the RequestAttributes currently bound to the thread.
* @return the RequestAttributes currently bound to the thread,
* or {@code null} if none bound
*/
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder =
new NamedThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request attributes"); private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder =
new NamedInheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes>("Request context");
上面是一些关键方法
所以最终其实request是从threadlocal中取...
FrameworkServlet
那么request是什么时候设置到threadlocal中去的呢?
是在Springmvc的dispatcherServlet的父类FrameworkServlet里操作的.
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response);
} @Override
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response);
}
不管你是doGet还是doPost还是doXXX方法都是委托processRequest方法去做的.
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
} publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
其中调用了
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
private void initContextHolders(
HttpServletRequest request, LocaleContext localeContext, RequestAttributes requestAttributes) { if (localeContext != null) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Bound request context to thread: " + request);
}
}
就是在这里设置到RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去的...
小结
1.在controller中注入的request是jdk动态代理对象,ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler的实例.当我们调用成员域request的方法的时候其实是调用了objectFactory的getObject()对象的相关方法.这里的objectFactory是RequestObjectFactory.
2.RequestObjectFactory的getObject其实是从RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去取值的.
3.请求刚进入springmvc的dispatcherServlet的时候会把request相关对象设置到RequestContextHolder的threadlocal中去.
对于原文的补充
原文没有详细描述成员域request注入的具体过程,补充如下:
ApplicationContext的初始化调用过程如下:
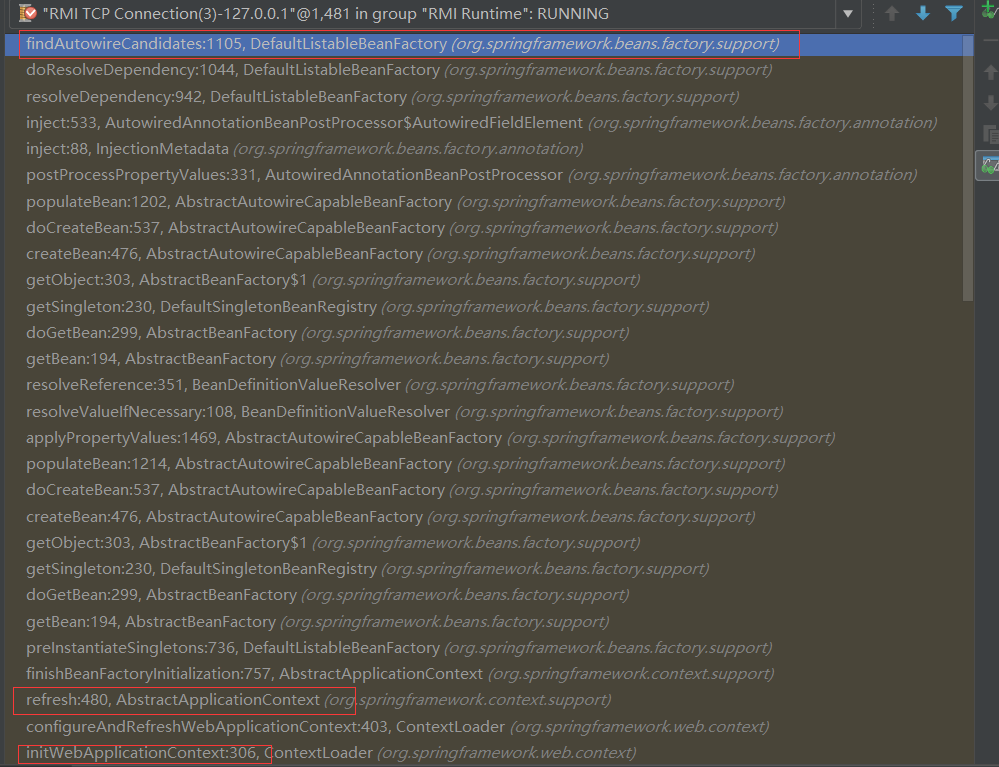
在refresh方法被调用后,会调用org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#findAutowireCandidates
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates(
String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) { String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(
this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager());
Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<String, Object>(candidateNames.length);
for (Class<?> autowiringType : this.resolvableDependencies.keySet()) {
if (autowiringType.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
Object autowiringValue = this.resolvableDependencies.get(autowiringType);
autowiringValue = AutowireUtils.resolveAutowiringValue(autowiringValue, requiredType);
if (requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
result.put(ObjectUtils.identityToString(autowiringValue), autowiringValue);
break;
}
}
}
for (String candidateName : candidateNames) {
if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidateName) && isAutowireCandidate(candidateName, descriptor)) {
result.put(candidateName, getBean(candidateName));
}
}
if (result.isEmpty()) {
DependencyDescriptor fallbackDescriptor = descriptor.forFallbackMatch();
for (String candidateName : candidateNames) {
if (!candidateName.equals(beanName) && isAutowireCandidate(candidateName, fallbackDescriptor)) {
result.put(candidateName, getBean(candidateName));
}
}
}
return result;
}
该方法内部会调用:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AutowireUtils#resolveAutowiringValue
public static Object resolveAutowiringValue(Object autowiringValue, Class<?> requiredType) {
if (autowiringValue instanceof ObjectFactory && !requiredType.isInstance(autowiringValue)) {
ObjectFactory<?> factory = (ObjectFactory<?>) autowiringValue;
if (autowiringValue instanceof Serializable && requiredType.isInterface()) {
autowiringValue = Proxy.newProxyInstance(requiredType.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[] {requiredType}, new ObjectFactoryDelegatingInvocationHandler(factory));
}
else {
return factory.getObject();
}
}
return autowiringValue;
}
可以看到,如果需要注入的对象是接口类型的话,则为其创建代理对象。
【转】在SpringMVC Controller中注入Request成员域的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC Controller中注入Request成员域和在方法中定义中HttpServletRequest有啥区别
先说结论,在Controller中注入Request是线程安全的. 以下是解释: 我们先来看看这两者有什么不同 在controller注入成员变量request 可以看到注入的是一个代理对象 写在方法 ...
- 在SpringMVC Controller中注入Request成员域
主题 在工作中遇到1个问题....我们定义了一个Controller基类,所有Springmvc自定义的controller都继承它....在它内部定义一个@Autowired HttpServlet ...
- spring mvc controller中获取request head内容
spring mvc controller中获取request head内容: @RequestMapping("/{mlid}/{ptn}/{name}") public Str ...
- SpringMVC在Controller层中注入request的坑
记一次为了节省代码没有在方法体中声明HttpServletRequest,而用autowire直接注入所钻的坑 结论 给心急的人. 直接在Controller的成员变量上使用@Autowire声明Ht ...
- Spring @Autowired注解在非Controller中注入为null
问题描述 今天在写一个工具类,里面用了@Autowired注入了StringRedisTemplate以及RedisTemplate时,在template.opsForValue().set(key, ...
- 在springMVC的controller中获取request,response对象的一个方法
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttr ...
- 在Spring MVC Controller中注入HttpServletRequest对象会不会造成线程安全的问题
做法: 1.比如我们在Controller的方法中,通常是直接将HttpServletRequest做为参数,而为了方便节省代码,通常会定义为全局变量,然后使用@Autowire注入. 说明: 1.观 ...
- SpringMVC controller中业务方法的参数、返回值
业务方法的参数 业务方法的参数类型.参数个数是任意的,根据需要使用. 常见的参数类型: HttpServletRequest.HttpServletResponse.HttpSession 获取 ...
- Spring boot @Autowired注解在非Controller中注入为null
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35056292/article/details/78430777
随机推荐
- ssh推送.py程序到服务器端运行
C:\Users\jiangshan>ssh jiangshan@192.168.1.191jiangshan@192.168.1.191's password:Last login: Sun ...
- selenium自动化环境搭建(Windows)
参考内容:虫师<selenium2自动化测试实战-基于python语言> 一.selenium介绍 selenium主要用于web应用程序的自动化测试,还支持所有基于web的管理任务自动化 ...
- Android String.xml中的符号总结
<b></b>加粗字体 <i></i> 斜体字体 <u></u> 给字体加下划线 \n 换行 \u0020表示空格 \u2026 ...
- 微信小程序开发 [00] 写在前面的话,疯狂唠唠
我总是喜欢在写东西之前唠唠嗑,按照惯例会在博文的开篇写这么一段"写在前面的话",这次却为了这个唠嗑单独开了一篇文,大概预想着要胡说八道的话有点多. 前段时间突然对小程序来了兴趣,说 ...
- STM32 CAN总线标识符过滤器难点解析
STM32 CAN总线标识符过滤器难点解析 原创 2016年05月31日 15:12:24 标签: stm32 / CAN 4910 CAN总线是目前应用非常多的一种总线,在汽车电子,航空航天中应用广 ...
- [笔记] Redis的安装与配置超级详细
目录 Windows下安装与配置 下载 安装 验证安装 配置服务 测试 Linux下安装与配置 准备工作 安装 验证与测试 Macox下安装与配置 准备工作 安装 验证与测试 Redis 在 Wind ...
- mfc CImageList和CListCtrl
知识点: CImageList类的运用 CListCtrl添加图标 一.CImageList CImageList*SetImageList(CImageList*pImageList,int nIm ...
- HTML基础语法
目录 HTML基础语法 1.全局架构标签 2.标题 3.段落 4.文本 5.属性 6.链接 7.图片 8.列表 9.表格 10.区块 11.布局 12.表单 13.框架 14.头部 HTML基础语法 ...
- IP 解析器(IpParser) test 和 生产环境 实现
注意:之前我maven居然没有引入 StringUtils 的包,然后引入了一个路径类似,但其实包路径不一样的 StringUtils ,居然是划掉的状态,像这样 StringUtils ,这个其实不 ...
- python的多继承关系
python和C++一样,支持多继承.概念虽然容易,但是困难的工作是如果子类调用一个自身没有定义的属性,它是按照何种顺序去到父类寻找呢,尤其是众多父类中有多个都包含该同名属性. class P1 #( ...
