Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) E. Famil Door and Roads (树形dp,lca)
Famil Door’s City map looks like a tree (undirected connected acyclic graph) so other people call it Treeland. There are n intersections
in the city connected by n - 1 bidirectional roads.
There are m friends of Famil Door living in the city. The i-th
friend lives at the intersection ui and
works at the intersection vi.
Everyone in the city is unhappy because there is exactly one simple path between their home and work.
Famil Door plans to construct exactly one new road and he will randomly choose one among n·(n - 1) / 2 possibilities. Note,
that he may even build a new road between two cities that are already connected by one.
He knows, that each of his friends will become happy, if after Famil Door constructs a new road there is a path from this friend home to work and back that doesn't visit the same road twice. Formally, there is a simple cycle containing both ui and vi.
Moreover, if the friend becomes happy, his pleasure is equal to the length of such path (it's easy to see that it's unique). For each of his friends Famil Door wants to know his expected pleasure, that is the expected length of the cycle containing both ui and vi if
we consider only cases when such a cycle exists.
The first line of the input contains integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 100 000) —
the number of the intersections in the Treeland and the number of Famil Door's friends.
Then follow n - 1 lines describing bidirectional roads. Each of them contains two integers ai and bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n) —
the indices of intersections connected by the i-th road.
Last m lines of the input describe Famil Door's friends. The i-th
of these lines contain two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi) —
indices of intersections where the i-th friend lives and works.
For each friend you should print the expected value of pleasure if he will be happy. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b.
The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 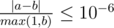 .
.
4 3
2 4
4 1
3 2
3 1
2 3
4 1
4.00000000
3.00000000
3.00000000
3 3
1 2
1 3
1 2
1 3
2 3
2.50000000
2.50000000
3.00000000
题意:给你一棵节点数为n的树,随机地在树上的任意两个点连一条边,给你m个询问,每次询问两个点,问连一条边后如果这两个点能在简单环中,简单环的期望是多少。
简单环即这两个点在一个环上,这个环是没有重边的。
思路:这里先设置几个变量dep[i]:i节点的深度,这里记dep[0]=0,dep[1]=1;sz[i]:i节点的子树的节点总数;f[i][j]:i节点的2^j倍父亲;sdown[i]:i节点子树中的所有点到i节点的距离和;sall[i]:所有点到i节点的距离和;t=lca(u,v).
先考虑lca(u,v)!=u && lca(u,v)!=v的情况,想要使得u,v都在简单环中,那么连边的两个端点一定是一个在u的子树中,另一个在v的子树中,且连边的方案数为sz[u]*sz[v],那么我们得到的期望值是sdown[u]/sz[u]+sdown[v]/sz[v]+1+dep[u]+dep[v]-2*dep[t].这里dep[u]+dep[v]-2*dep[t]+1是每一个形成的简单环都有的长度,所以可以先加上去.
然后考虑lca(u,v)==u || lca(u,v)==v的情况,不妨假设lca(u,v)=v,那么连边的两个端点一端一定在u的子树中,另一端在v的上面,即树上的所有点除去不包括u这个节点的子树,我们得到的期望值是sdown[u]/sz[u]+(sall[v]-sdown[v1]-sz[v1])/(n-sz[v1]) (v1是u,v路径上v的子节点).
第一次dfs先求出sdown[i],然后第二次dfs就能求出sall[i]了.
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ldb;
#define inf 99999999
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define maxn 100050
int sz[maxn],dep[maxn],f[maxn][23];
ll sdown[maxn],sall[maxn];
int n;
struct edge{
int to,next;
}e[2*maxn];
int first[maxn];
void dfs1(int u,int father,int deep)
{
int i,j,v;
dep[u]=dep[father]+1;
sz[u]=1;sdown[u]=0;
for(i=first[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next){
v=e[i].to;
if(v==father)continue;
f[v][0]=u;
dfs1(v,u,dep[u]);
sz[u]+=sz[v];
sdown[u]+=sdown[v]+sz[v];
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int father)
{
int i,j,v;
for(i=first[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next){
v=e[i].to;
if(v==father)continue;
sall[v]=sall[u]+n-2*sz[v]; //这里是主要的公式,可以这样理解:所有点到父亲节点u的距离和sall[u]已经算出来了,那么算v这个节点的时候,不在v子树范围内的点到v的距离都多了1,所以加上n-sz[v],v的子树的点到v的距离都减少了1,所以要减去sz[v].
dfs2(v,u);
}
}
void init()
{
dep[0]=0;
dfs1(1,0,0);
sall[1]=sdown[1];
dfs2(1,0);
}
int lca(int x,int y){
int i;
if(dep[x]<dep[y]){
swap(x,y);
}
for(i=20;i>=0;i--){
if(dep[f[x][i] ]>=dep[y]){
x=f[x][i];
}
}
if(x==y)return x;
for(i=20;i>=0;i--){
if(f[x][i]!=f[y][i]){
x=f[x][i];y=f[y][i];
}
}
return f[x][0];
}
int up(int u,int deep)
{
int i,j;
for(i=20;i>=0;i--){
if((1<<i)<=deep){
u=f[u][i];
deep-=(1<<i);
}
}
return u;
}
int main()
{
int m,i,j,tot,c,d,v,u,k;
double sum;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
tot=0;
memset(first,-1,sizeof(first));
for(i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&c,&d);
tot++;
e[tot].next=first[c];e[tot].to=d;
first[c]=tot;
tot++;
e[tot].next=first[d];e[tot].to=c;
first[d]=tot;
}
init();
for(k=1;k<=20;k++){
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
f[i][k]=f[f[i][k-1]][k-1];
}
}
for(i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
int t=lca(u,v);
sum=(double)(dep[u]+dep[v]-2*dep[t])+1;
if(t==u || t==v){
if(t==u)swap(u,v);
int v1=up(u,dep[u]-dep[v]-1);
ll num1=sall[v]-sdown[v1]-sz[v1];
sum+=(double)sdown[u]/(double)sz[u]+(double)(num1)/(double)(n-sz[v1]);
printf("%.10f\n",sum);
}
else{
sum+=(double)sdown[u]/(double)sz[u]+(double)sdown[v]/(double)sz[v];
printf("%.10f\n",sum);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) E. Famil Door and Roads (树形dp,lca)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) E. Famil Door and Roads lca 树形dp
E. Famil Door and Roads 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/629/problem/E Description Famil Door ...
- Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) E. Famil Door and Roads
题目链接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/629/problem/E 题解: 树形dp. siz[x]为x这颗子树的节点个数(包括x自己) dep[x]表示x这个 ...
- Codeforces Round #384 (Div. 2)D - Chloe and pleasant prizes 树形dp
D - Chloe and pleasant prizes 链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/743/problem/D 题面 Generous sponsors of ...
- Codeforces Round #551 (Div. 2) D. Serval and Rooted Tree (树形dp)
题目:http://codeforces.com/contest/1153/problem/D 题意:给你一棵树,每个节点有一个操作,0代表取子节点中最小的那个值,1代表取子节点中最大的值,叶子节点的 ...
- Codeforces Round #419 (Div. 2) E. Karen and Supermarket(树形dp)
http://codeforces.com/contest/816/problem/E 题意: 去超市买东西,共有m块钱,每件商品有优惠卷可用,前提是xi商品的优惠券被用.问最多能买多少件商品? 思路 ...
- Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) C. Famil Door and Brackets dp
C. Famil Door and Brackets 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/629/problem/C Description As Fami ...
- Codeforces Round #343 (Div. 2) C. Famil Door and Brackets
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/629/problem/C 题意: 长度为n的括号,已经知道的部分的长度为m,现在其前面和后面补充‘(',或')',使得其长度为 ...
- Codeforces Round #263 (Div. 2) D. Appleman and Tree(树形DP)
题目链接 D. Appleman and Tree time limit per test :2 seconds memory limit per test: 256 megabytes input ...
- Codeforces Round #564 (Div. 2) D. Nauuo and Circle(树形DP)
D. Nauuo and Circle •参考资料 [1]:https://www.cnblogs.com/wyxdrqc/p/10990378.html •题意 给出你一个包含 n 个点的树,这 n ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode498 对角线遍历
给定一个含有 M x N 个元素的矩阵(M 行,N 列),请以对角线遍历的顺序返回这个矩阵中的所有元素,对角线遍历如下图所示. 示例: 输入: [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 4, 5, 6 ], ...
- nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (10013:
问题出现 今天在win10安装nginx时候,启动nginx.exe时在dos窗口出现了这个错误,特此记录一下. 解决方法 上面报错信息的意思大概是:0.0.0:80地址访问不被允许.可能是80端口号 ...
- Docker haproxy应用构建 (五)
编写dockerfile from centos-base:v1 MAINTAINER 57674891@qq.com RUN mkdir -p /data/{soft,src,logs,script ...
- python函数2-函数参数
rgb法则:
- Assuming that agent dropped connection because of access permission
Assuming that agent dropped connection because of access permission
- Web安全之CSRF(跨站请求伪造)
CSRF(跨站请求伪造)概述 Cross-site request forgery 简称为"CSRF",在CSRF的攻击场景中攻击者会伪造一个请求(这个请求一般是一个链接),然后欺 ...
- online创建索引中途取消导致索引无法删除解决办法
问题:有一个表ID栏位没有索引,但是在一个update语句的where中被使用,因此打算online创建索引,但是长时间没有成功,此时决定取消,取消后发现索引无法删除 过程: 数据库监控报警有行锁,进 ...
- undefined和null区别
undefined类型只有一个值就是undefined,没有必要显式地声明一个变量为undefined. null类型其实就是一个对象的空指针,所以用typeof null 才会显示为object. ...
- 爬虫学习(三)Chrome浏览器使用
一.新建隐身窗口 在打开隐身窗口的时候,第一次请求某个网站是没有携带cookie的,和代码请求一个网站一样,不携带cookie.这样就能够尽可能的理解代码请求某个网站的结果:除非数据是通过js加载出来 ...
- Flask的“中间件”
特殊装饰器 from flask import Flask,render_template,request app = Flask(__name__) @app.before_request def ...
