(原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 1) Linear Regression
Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml
在Linear Regression部分出现了一些新的名词,这些名词在后续课程中会频繁出现:
| Cost Function | Linear Regression | Gradient Descent | Normal Equation | Feature Scaling | Mean normalization |
| 损失函数 | 线性回归 | 梯度下降 | 正规方程 | 特征归一化 | 均值标准化 |
Model Representation
- m: number of training examples
- x(i): input (features) of ith training example
- xj(i): value of feature j in ith training example
- y(i): “output” variable / “target” variable of ith training example
- n: number of features
- θ: parameters
- Hypothesis: hθ(x) = θ0 + θ1x1 + θ2x2 + … +θnxn
Cost Function
IDEA: Choose θso that hθ(x) is close to y for our training examples (x, y).
A.Linear Regression with One Variable Cost Function
Cost Function: 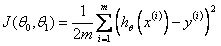
Goal: 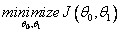
Contour Plot:
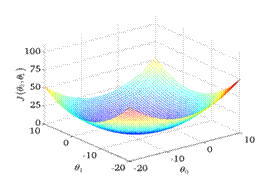
B.Linear Regression with Multiple Variable Cost Function
Cost Function: 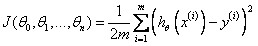
Goal: 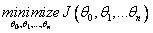
Gradient Descent
Outline

Gradient Descent Algorithm
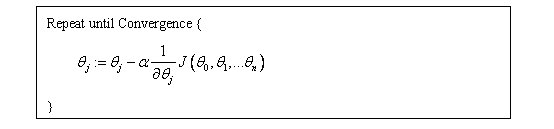
迭代过程收敛图可能如下:
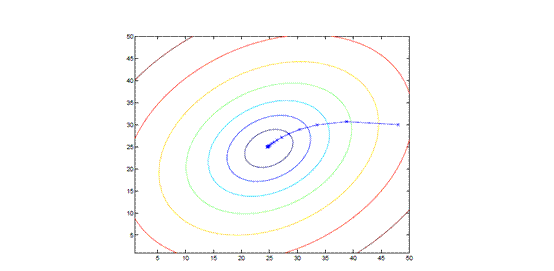
(此为等高线图,中间为最小值点,图中蓝色弧线为可能的收敛路径。)
Learning Rate α:
1) If α is too small, gradient descent can be slow to converge;
2) If α is too large, gradient descent may not decrease on every iteration or may not converge;
3) For sufficiently small α , J(θ) should decrease on every iteration;
Choose Learning Rate α: Debug, 0.001, 0.003, 0.006, 0.01, 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 1.0;
“Batch” Gradient Descent: Each step of gradient descent uses all the training examples;
“Stochastic” gradient descent: Each step of gradient descent uses only one training examples.
Normal Equation
IDEA: Method to solve for θ analytically.
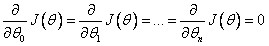 for every j, then
for every j, then 
Restriction: Normal Equation does not work when (XTX) is non-invertible.
PS: 当矩阵为满秩矩阵时,该矩阵可逆。列向量(feature)线性无关且行向量(样本)线性无关的个数大于列向量的个数(特征个数n).
Gradient Descent Algorithm VS. Normal Equation
Gradient Descent:
- Need to choose α;
- Needs many iterations;
- Works well even when n is large; (n > 1000 is appropriate)
Normal Equation:
- No need to choose α;
- Don’t need to iterate;
- Need to compute (XTX)-1 ;
- Slow if n is very large. (n < 1000 is OK)
Feature Scaling
IDEA: Make sure features are on a similar scale.
好处: 减少迭代次数,有利于快速收敛
Example: If we need to get every feature into approximately a -1 ≤ xi ≤ 1 range, feature values located in [-3, 3] or [-1/3, 1/3] fields are acceptable.
Mean normalization: 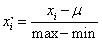
HOMEWORK
好了,既然看完了视频课程,就来做一下作业吧,下面是Linear Regression部分作业的核心代码:
1.computeCost.m/computeCostMulti.m
J=/(*m)*sum((theta'*X'-y').^2);
2.gradientDescent.m/gradientDescentMulti.m
h=X*theta-y;
v=X'*h;
v=v*alpha/m;
theta1=theta;
theta=theta-v;
(原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 1) Linear Regression的更多相关文章
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 3) Logistic Regression & Regularization
coursera上面Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml 我曾经使用Logistic Regressio ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 10) Large Scale Machine Learning & Application Example
本栏目来源于Andrew NG老师讲解的Machine Learning课程,主要介绍大规模机器学习以及其应用.包括随机梯度下降法.维批量梯度下降法.梯度下降法的收敛.在线学习.map reduce以 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 8) Clustering & Dimensionality Reduction
本周主要介绍了聚类算法和特征降维方法,聚类算法包括K-means的相关概念.优化目标.聚类中心等内容:特征降维包括降维的缘由.算法描述.压缩重建等内容.coursera上面Andrew NG的Mach ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 7) Support Vector Machines
本栏目内容来源于Andrew NG老师讲解的SVM部分,包括SVM的优化目标.最大判定边界.核函数.SVM使用方法.多分类问题等,Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.c ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 9) Anomaly Detection&Recommender Systems
这部分内容来源于Andrew NG老师讲解的 machine learning课程,包括异常检测算法以及推荐系统设计.异常检测是一个非监督学习算法,用于发现系统中的异常数据.推荐系统在生活中也是随处可 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 4) Neural Networks Representation
Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml 神经网络一直被认为是比较难懂的问题,NG将神经网络部分的课程分为了 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 1) Introduction
最近学习了coursera上面Andrew NG的Machine learning课程,课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml 在Introduction部分 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 5) Neural Networks Learning
本栏目内容来自Andrew NG老师的公开课:https://class.coursera.org/ml/class/index 一般而言, 人工神经网络与经典计算方法相比并非优越, 只有当常规方法解 ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 6) Advice for Applying Machine Learning & Machine Learning System Design
(1) Advice for applying machine learning Deciding what to try next 现在我们已学习了线性回归.逻辑回归.神经网络等机器学习算法,接下来 ...
随机推荐
- js刷新页面方法 -- (转)
1,reload 方法,该方法强迫浏览器刷新当前页面. 语法:location.reload([bForceGet]) 参数: bForceGet, 可选参数, 默认为 false,从客户端缓存里 ...
- hadoop2.4.1伪分布式环境搭建
注意:所有的安装用普通哟用户安装,所以首先使普通用户可以以sudo执行一些命令: 0.虚拟机中前期的网络配置参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/qlqwjy/p/7783253.ht ...
- centos7.2进入单用户模式修改密码
1 - 在启动grub菜单,选择编辑选项启动 2 - 按键盘e键,来进入编辑界面 3 - 找到Linux 16的那一行,将ro改为rw init=/sysroot/bin/sh 4 - 现在按下 Co ...
- mysql where/having区别
mysql> select 2-1 as a,password from mysql.user where user='root' having a>0; +---+----------- ...
- 一种面向云服务的UCON多义务访问控制方法及系统
)设置每一云服务的义务项:建立每一云服务所包含的义务图:2)根据用户所请求的云服务查找该云服务的所有强制义务图和可选义务图,并提取该用户对该云服务的历史完成情况:3)对每一强制义务图,监控其每一义务项 ...
- 天气api接口
python调用天气api接口: http://www.sojson.com/open/api/weather/json.shtml?city=北京 http://www.sojson.com/blo ...
- 64_l4
libnormaliz-devel-3.1.4-2.fc26.i686.rpm 23-May-2017 00:24 31214 libnormaliz-devel-3.1.4-2.fc26.x86_6 ...
- Android 开发之避免被第三方使用代理抓包
现象:charles抓不到包,但wireshark,HttpAnalyzor可以抓到包. 关键代码: URL url = new URL(urlStr); urlConnection = (HttpU ...
- leetcode 343. Integer Break(dp或数学推导)
Given a positive integer n, break it into the sum of at least two positive integers and maximize the ...
- 基数排序c++实现
基数排序:是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较.由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数.但在 ...
