android Fragment 笔记
Fragment多用于平板中,Fragment当成Activity的一个界面的一个组成部分,Fragment有自己的生命周期,但是必须依托在Activity中。
参考链接
https://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html?hl=zh-cn
Fragment 生命周期如下

AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.example.fragmenttest.MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fragment 1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fragment 2" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fragment_place"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"></FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
效果图如下:

创建Fragment1
Fragment1.java
package com.example.fragmenttest;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.content.Context;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment1 extends Fragment {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_fragment1, container, false);
}
}
Fragment1布局
fragment_fragment1.xml
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.fragmenttest.Fragment1">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="fragment 1" />
</FrameLayout>
创建Fragment
Fragment2.java
package com.example.fragmenttest;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class Fragment2 extends Fragment {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_fragment2, container, false);
}
}
fragment_fragment2.xml
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.fragmenttest.Fragment2">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:text="fragment 2" />
</FrameLayout>
MainActivity.java
package com.example.fragmenttest;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button btn1, btn2;
Fragment fr;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
btn2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
btn1.setOnClickListener(listener);
btn2.setOnClickListener(listener);
}
View.OnClickListener listener = new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.button1:
fr = new Fragment1();
break;
case R.id.button2:
fr = new Fragment2();
break;
}
FragmentManager fm = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fm.beginTransaction();
// 将activity_main中的fragment转换成fragment1或者fragment2
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.fragment_place, fr);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
};
}
管理fragment需要使用FragmentManager.使用getFragmentManager()获得。
操作fragemnt需要使用FragmentTransaction的api。使用beginTransaction()获得。
在用replace函数替换fragment.
应用到 Activity,您必须调用 commit()
运行情况,点击button1

点击button2
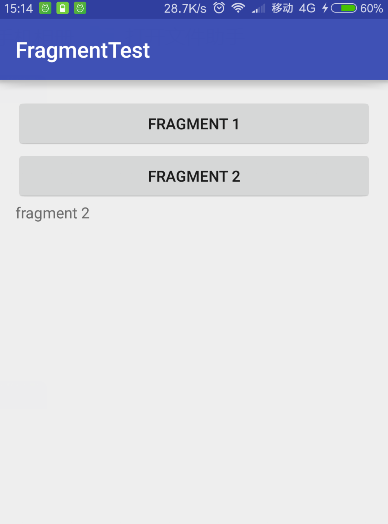
Activity通信
片段可以通过 getActivity() 访问 Activity 实例,并轻松地执行在 Activity 布局中查找视图等任务。
View listView = getActivity().findViewById(R.id.list);
Activity 也可以使用 findFragmentById() 或 findFragmentByTag(),通过从 FragmentManager 获取对 Fragment 的引用来调用片段中的方法。例如:
ExampleFragment fragment = (ExampleFragment) getFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.example_fragment);
Tony Liu
2017-3-14, Shenzhen
android Fragment 笔记的更多相关文章
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四二):Fragment(7):切换效果
目录(?)[-] 利用setTransition 利用setCustomAnimations 通过ObjectAnimator自定义动态效果 程序代码的编写 利用fragment transactio ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四十):Fragment(5):适应不同屏幕或排版
目录(?)[-] 设置横排和竖排的不同排版风格 改写代码 对于fragment,经常涉及不同屏幕尺寸和不同的排版风格.我们在基础小例子上做一下改动,在横排的时候,仍是现实左右两个fragment,在竖 ...
- Android编程权威指南笔记3:Android Fragment讲解与Android Studio中的依赖关系,如何添加依赖关系
Android Fragment 当我在学习时,了解了Fragment词汇 Fragment是一种控制器对象,我就把所了解的简单说一下.activity可以派fragment完成一些任务,就是管理用户 ...
- Android Fragment使用(三) Activity, Fragment, WebView的状态保存和恢复
Android中的状态保存和恢复 Android中的状态保存和恢复, 包括Activity和Fragment以及其中View的状态处理. Activity的状态除了其中的View和Fragment的状 ...
- Fragment笔记整理
前言 一直在用Fragment,但是没有系统的整理过,Google了一下相关文章,看到了几篇,将几篇还不错的文章重点整理了下,很多是直接Copy的,只为做个笔记,以后翻来看比较方便,建议大家看一下下面 ...
- 【转】Android开发笔记(序)写在前面的目录
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/aqi00/article/details/50012511 知识点分类 一方面写写自己走过的弯路掉进去的坑,避免以后再犯:另一方面希望通过分享自己的经 ...
- [置顶] Android开发笔记(成长轨迹)
分类: 开发学习笔记2013-06-21 09:44 26043人阅读 评论(5) 收藏 Android开发笔记 1.控制台输出:called unimplemented OpenGL ES API ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(五六):配置变化
目录(?)[-] Activity的destorycreate过程 Fragment的destorycreate过程 onSaveInstanceState saveFragmentInstanceS ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(五一):ActionBar(4):标准和Tab模式
之前,我们学习的Action Bar是标准模式,Tab模式的如下图所示. 对于Tab,我们在Android学习笔记(二二): 多页显示-Tag的使用中学习过,但Action Bar的tab更适合fra ...
随机推荐
- Linux内核(14) - 二分法与printk
人生就是一个茶几,上面摆满了杯具.内核也是一个大茶几,不过它上面的杯具是一个个的bug.确定bug什么时候被引入是一个很关键的步骤,在这个定位bug的过程中,不论有意或无意,都会很自然地用到二分查找的 ...
- mysql 返回多列的方式
SELECT * FROM (SELECT 'success' as _result) a,(SELECT @gid as gid) b;
- 深入浅出Node.js--数据通讯,NET模块运行机制
互联网的运作,最根本的驱动就是信息的交互,NodeJS 在数据交互这一块做的很带感,异步编程让人很惬意,关于 NodeJS 的数据通信,最基础的两个模块是 NET 和 HTTP,前者是基于 TCP 的 ...
- 微服务架构的进程间通信(IPC)
先抛出几个问题: 微服务架构的交互模式有哪些? 微服务常用的进程间通信技术有哪些? 如何处理部分请求失败? API的定义需要注意的事项有哪些 微服务的通信机制与SOA的通信机制之间的关系与区别 微服务 ...
- quartusii 使用ModelSim do文件实现仿真(Verilog)
QuartusII从9.1之后的版本都已经取消了内部自带的仿真器,都需要借助第三方仿真软件比如Modelsim才能实现仿真.一般在进行代码编写的时候,如果结合功能仿真,可以很快的验证代码实现的逻辑是否 ...
- Amoeba软件实现mysql读写分离
一般不用,大公司都是自己程序实现的. 安装amoeba
- [na]wireshark抓包排错-tcp.flags.reset
这是以前处理无线portal问题时候的一个梗. 一 抓包思路-用抓包来解决问题 ,了解协议交互大概过程 ,抓包 抓包法则: .最小化原则,过滤到想要的最小数据,别忽略上下文数据包 .对比法, 正常的包 ...
- hdu 1532 最大流
#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> ...
- C++ HOJ 猴子分桃
[题目描写叙述] 老猴子辛苦了一辈子,给那群小猴子们留下了一笔巨大的財富--一大堆桃子.老猴子决定把这些桃子分给小猴子. 第一个猴子来了,它把桃子分成五堆,五堆一样多,但还多出一个.它把剩下的一个留给 ...
- CCEaseElasticOut调整速度和振幅
pSprite->setAnchorPoint(CCPoint(,)); pSprite->setPosition(CCPoint(,)); CCFiniteTimeAction* pAc ...
