RouterOS 设定NAT loopback (Hairpin NAT)回流
In the below network topology a web server behind a router is on private IP address space, and the router performs NAT to forward traffic to its public IP address to the web server behind it.
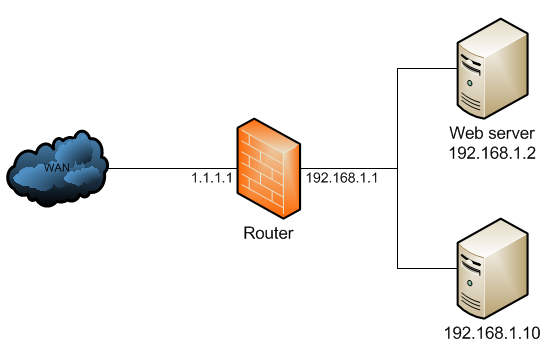
The NAT configuration would look like below:
/ip firewall natadd chain=dstnat dst-address=1.1.1.1 protocol=tcp dst-port=80 \ action=dst-nat to-address=192.168.1.2add chain=srcnat out-interface=WAN action=masquerade
When a client out on the Internet with IP address 2.2.2.2 establishes a connection to the web server, the router performs NAT as configured.
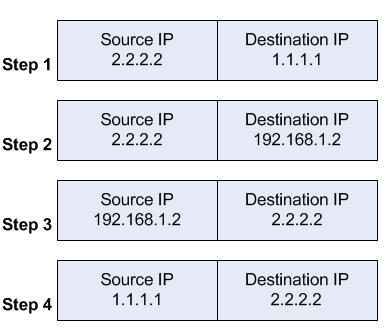
- the client sends a packet with a source IP address of 2.2.2.2 to a destination IP address of 1.1.1.1 on port tcp/80 to request some web resource.
- the router destination NATs the packet to 192.168.1.2 and replaces the destination IP address in the packet accordingly. The source IP address stays the same: 2.2.2.2.
- the server replies to the client's request and the reply packet has a source IP address of 192.168.1.2 and a destination IP address of 2.2.2.2.
- the router determines that the packet is part of a previous connection and undoes the destination NAT, and puts the original destination IP address into the source IP address field. The destination IP address is 2.2.2.2, and the source IP address is 1.1.1.1.
The client receives the reply packet it expects, and the connection is established.
When a client on the same internal network as the web server requests a connection to the web server's public IP address, the connection breaks.
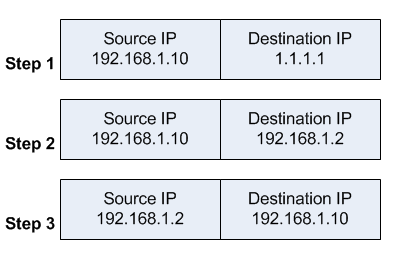
- the client sends a packet with a source IP address of 192.168.1.10 to a destination IP address of 1.1.1.1 on port tcp/80 to request some web resource.
- the router destination NATs the packet to 192.168.1.2 and replaces the destination IP address in the packet accordingly. The source IP address stays the same: 192.168.1.10.
- the server replies to the client's request. However, the source IP address of the request is on the same subnet as the web server. The web server does not send the reply back to the router, but sends it back directly to 192.168.1.10 with a source IP address in the reply of 192.168.1.2.
The client receives the reply packet, but it discards it because it expects a packet back from 1.1.1.1, and not from 192.168.1.2. As far as the client is concerned the packet is invalid and not related to any connection the client previously attempted to establish.
To fix the issue, an additional NAT rule needs to be introduced on the router to enforce that all reply traffic flows through the router, despite the client and server being on the same subnet. The rule below is very specific to only apply to the traffic that the issue could occur with - if there are many servers the issue occurs with, the rule could be made broader to save having one such exception per forwarded service.
/ip firewall natadd chain=srcnat src-address=192.168.1.0/24 \ dst-address=192.168.1.2 protocol=tcp dst-port=80 \ out-interface=LAN action=masquerade
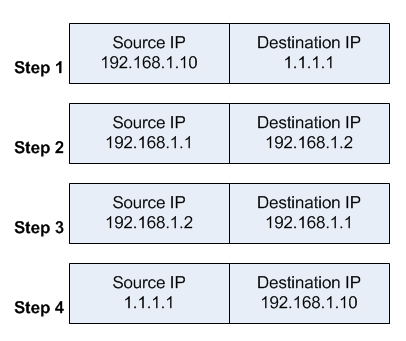
With that additional rule, the flow now changes:
- the client sends a packet with a source IP address of 192.168.1.10 to a destination IP address of 1.1.1.1 on port tcp/80 to request some web resource.
- the router destination NATs the packet to 192.168.1.2 and replaces the destination IP address in the packet accordingly. It also source NATs the packet and replaces the source IP address in the packet with the IP address on its LAN interface. The destination IP address is 192.168.1.2, and the source IP address is 192.168.1.1.
- the web server replies to the request and sends the reply with a source IP address of 192.168.1.2 back to the router's LAN interface IP address of 192.168.1.1.
- the router determines that the packet is part of a previous connection and undoes both the source and destination NAT, and puts the original destination IP address of 1.1.1.1 into the source IP address field, and the original source IP address of 192.168.1.10 into the destination IP address field.
The client receives the reply packet it expects, and the connection is established.
However, the web server only ever sees a source IP address of 192.168.1.1 for all requests from internal clients regardless of the internal client's real IP address. There is no way to avoid this without either using a router that can do application level DNS inspection and can rewrite A records accordingly, or a split DNS server that serves the internal clients the internal server IP address and external clients the external server IP address.
This is called - among other terms - hair pin NAT because the traffic flow has clients enter the router through the same interface it leaves through, which when drawn looks like a hair pin.
RouterOS 设定NAT loopback (Hairpin NAT)回流的更多相关文章
- Linux 与 CONE NAT 和 Symmetric NAT
http://alexanderlaw.blog.hexun.com/31883661_d.html 1. NAT 的划分 RFC3489 中将 NAT 的实现分为四大类: 1. Full Cone ...
- 静态NAT、动态NAT
静态NAT.动态NAT 实验拓扑: 实验目的:熟悉网络地址转换协议 掌握静态NAT 和动态NAT的配置 分析静态NAT 和动态NAT的区别 使用show命令来检查NAT的运行情况 实验要求:按拓扑图来 ...
- 运营商级NAT(Carrier-grade NAT)
运营商级NAT(Carrier-grade NAT) 运营商级(Carrier-grade)NAT,是用于缓解是IPV4地址枯竭的一种方法,通过这种方法,原来被分配公网ip的端点.家庭网络等可以被 ...
- CONE NAT 和 Symmetric NAT
CONE NAT 和 Symmetric NAT 1. NAT 的划分 RFC3489 中将 NAT 的实现分为四大类: Full Cone NAT 完全锥形 NAT Restricted Cone ...
- 什么叫NAT,设置NAT的两个方法
NAT是网络地址翻译就是把公网IP翻译成私有地址, 又叫端口映射或端口转发. 采用路由方式是指ADSL拥有一个动态或固定的公网IP,ADSL直接接在HUB或交换机上,所有的电脑共享上网.这时ADSL的 ...
- NAT and Traversal NAT(TURN/STUN/ICE)
http://www.cnblogs.com/whyandinside/archive/2010/12/08/1900492.html -------------------------------- ...
- 静态NAT、动态NAT、PAT(端口多路复用)的配置
静态NAT.动态NAT.PAT(端口多路复用)的配置 NAT的实现方式有三种,即静态转换Static Nat.动态转换Dynamic Nat 和 端口多路复用OverLoad. 静态转换 ( ...
- NAT原理与NAT穿越
最近在看东西的时候发现很多网络程序中都需要NAT穿越,特意在此总结一下. 先做一个约定: 内网A中有:A1(192.168.0.8).A2(192.168.0.9)两用户 网关X1(一个NAT设备)有 ...
- NAT与FULL NAT的区别
LVS 当前应用主要采用 DR 和 NAT 模式,但这 2 种模式要求 RealServer 和 LVS在同一个 vlan中,导致部署成本过高:TUNNEL 模式虽然可以跨 vlan,但RealSer ...
随机推荐
- DevExpress v17.2新版亮点—WinForms篇(三)
用户界面套包DevExpress v17.2终于正式发布,本站将以连载的形式为大家介绍各版本新增内容.开篇介绍了DevExpress WinForms v17.2 Data Grid Control ...
- TV-B-Gone Kit - Universal v1.2
- mdadm 创建md 删除md步骤
最近在使用mdadm创建和删除RAID设备.但是在创建和删除过程中会出现创建md0重启后变成md127,删除md127重启后又重新出现的状况.在网上搜索了一下,总结如下: 创建: 1. mdad ...
- APP测试重点罗列
1.安装和卸载 应用是否可以在IOS不同系统版本或android不同系统版本上安装(有的系统版本过低,应用不能适配) 软件安装后是否可以正常运行,安装后的文件夹及文件是否可以写到指定的目录里. 安装过 ...
- 【c++基础】判断是否到文件末尾-eof函数
前言 读取文件内容时,需要判断是否到文件末尾,此时用到eof函数. 函数定义 Check whether eofbit is set Returns true if theeofbiterror st ...
- 【opencv基础】imread-第二个参数
问题1: 显示的是灰色的界面,不能正常显示图像. 解决方法:在imshow之后加上waitKey即可.原因here: Note:This function should be followed by ...
- (2)流程控制(for循环、if...else判断、while循环)
for循环 for item in names: #结构语法 print(item) for循环嵌套for循环 for循环配合range()可以直接指定要打印的数量 例:打印一个金字塔 for i ...
- Linux下rsync命令使用总结
一.rsync的概述 rsync是类unix系统下的数据镜像备份工具,从软件的命名上就可以看出来了——remote sync.rsync是Linux系统下的文件同步和数据传输工具,它采用“rsync” ...
- sleep和 wait
- 多个sshkey 指定key来clone仓库
Something like this should work (suggested by orip): ssh-agent bash -c 'ssh-add /somewhere/yourkey; ...
