HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (DFS枚举+最小生成树Prim)
Minimal Ratio Tree
Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 32768/32768K (Java/Other)
Total Submission(s) : 12 Accepted Submission(s) : 7
Font: Times New Roman | Verdana | Georgia
Font Size: ← →
Problem Description
Given a complete graph of n nodes with all nodes and edges weighted, your task is to find a tree, which is a sub-graph of the original graph, with m nodes and whose ratio is the smallest among all the trees of m nodes in the graph.
Input
All the weights of both nodes and edges (except for the ones on the diagonal of the matrix) are integers and in the range of [1, 100].
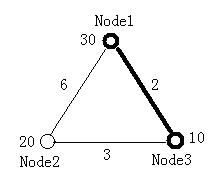
The figure below illustrates the first test case in sample input. Node 1 and Node 3 form the minimal ratio tree.
Output
Sample Input
3 2
30 20 10
0 6 2
6 0 3
2 3 0
2 2
1 1
0 2
2 0
0 0
Sample Output
1 3
1 2
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<climits>
using namespace std; int a[],f[],p[];
int mp[][];
bool vis[];
int i,j,n,m;
double ans;
void prim() //最小生成树
{
bool vis[];
int dis[];
int sumnode,sumedge=,k;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
vis[]=;
sumnode=p[a[]];
for(int i=;i<=m;i++) dis[i]=mp[a[]][a[i]];
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
{
int minn=INT_MAX;
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
{
if (!vis[j] && dis[j]<minn)
{
minn=dis[j];
k=j;
}
}
vis[k]=;
sumedge+=minn;
sumnode+=p[a[k]];
for(int j=;j<=m;j++)
if (!vis[j] && dis[j]>mp[a[k]][a[j]])
dis[j]=mp[a[k]][a[j]];
}
double w=sumedge*1.0/sumnode;
if (w<ans) //把最优解存放在f数组中
{
ans=w;
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
f[i]=a[i];
}
return;
}
void dfs(int k,int num)//dfs暴力枚举m个节点是哪几个存在a数组中
{
if (num==m)
{
prim();
return;
}
if (k>n) return; if (!vis[k])
{
vis[k]=;
a[num+]=k;
dfs(k+,num+);
vis[k]=;
}
dfs(k+,num);
return;
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m))
{
if (n== && m==) break;
for(i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&p[i]);
for(i=;i<=n;i++)
for(j=;j<=n;j++)
scanf("%d",&mp[i][j]);
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
ans=INT_MAX*1.0;
dfs(,);
for(i=;i<m;i++) printf("%d ",f[i]);
printf("%d\n",f[m]);
}
return ;
}
HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (DFS枚举+最小生成树Prim)的更多相关文章
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(dfs枚举+最小生成树)
想到枚举m个点,然后求最小生成树,ratio即为最小生成树的边权/总的点权.但是怎么枚举这m个点,实在不会.网上查了一下大牛们的解法,用dfs枚举,没想到dfs还有这么个作用. 参考链接:http:/ ...
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree (dfs+Prim最小生成树)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2489 Problem Description For a tree, which nodes and ...
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(暴力+最小生成树)(2008 Asia Regional Beijing)
Description For a tree, which nodes and edges are all weighted, the ratio of it is calculated accord ...
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 最小生成树+DFS
Minimal Ratio Tree Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- HDU 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree(prim+DFS)
Minimal Ratio Tree Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Other ...
- hdu 2489 Minimal Ratio Tree
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2489 这道题就是n个点中选择m个点形成一个生成树使得生成树的ratio最小.暴力枚举+最小生成树. #inclu ...
- hdu2489 Minimal Ratio Tree dfs枚举组合情况+最小生成树
#include <stdio.h> #include <set> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> u ...
- Minimal Ratio Tree HDU - 2489
Minimal Ratio Tree HDU - 2489 暴力枚举点,然后跑最小生成树得到这些点时的最小边权之和. 由于枚举的时候本来就是按照字典序的,不需要额外判. 错误原因:要求输出的结尾不能有 ...
- HDU2489 Minimal Ratio Tree 【DFS】+【最小生成树Prim】
Minimal Ratio Tree Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Other ...
随机推荐
- Python 邮件发送
python发送各类邮件的主要方法 python中email模块使得处理邮件变得比较简单,今天着重学习了一下发送邮件的具体做法,这里写写自己的的心得,也请高手给些指点. 一.相关模块介绍 ...
- python 日历
上章总结了python中time模块的使用,这次总结日历模块 calendar >>> import calendar >>> cal = calendar.mon ...
- wordpress建站过程1
使用wordpress我们需要理解一些概念: 1.WordPress是一种使用PHP语言开发的博客平台,它的程序是由php构成的,所以想要使用word press必须会php. 2.Wordpress ...
- 关于C++数组的几点讨论
数组名为何物? int main() { , , , , }; int *pnumber = number; cout << sizeof(number) << endl; c ...
- Chapter 1 First Sight——33
At that moment, the bell rang loudly, making me jump, and Edward Cullen was out of his seat. 在这个时候,铃 ...
- 第四十五节,logging日志模块
用于便捷记录日志且线程安全的模块 单文件日志 basicConfig()模块函数 功能:创建日志文件和写日志模式[有参] 使用方法:模块名称.basicConfig(filename="日志 ...
- LeetCode OJ 220.Contains Duplicate 3
Given an array of integers, find out whether there are two distinct indices i and j in the array suc ...
- dede 转 帝国
1.转换栏目 insert into ak_enewsclass (classid,bclassid,classname,myorder,classpath,intro,classpagekey) s ...
- ubuntu下 编译Caffe的Matlab接口
一般情况下不愿意使用Caffe的Matlab接口,总觉得Linux版的Matlab很难配置,但是现在搞目标检测,得到的源码是使用的Caffe的Matlab接口,只能硬着头皮上了. (1)修改caffe ...
- 使用SQL Server 2000索引视图提高性能
什么是索引视图? 许多年来,Microsoft? SQL Server? 一直都提供创建虚拟表(称为视图)的功能.在过去,这些视图主要有两种用途: 提供安全机制,将用户限制在一个或多个基表中的数据的某 ...