一致性检验评价方法kappa
最近在做眼底图像的无监督分类,使用的数据集辣子kaggle的Diabetic Retinopathy,简称DR,中文称糖尿病型眼底疾病。
最后的评估方法是二次加权kappa。以前没接触过,网上也没有具体的介绍,在这里简单谈谈我的理解,如有错误欢迎指出。
简介
Kappa指数用来衡量两个模型对同一张图片进行判断时,判断结果一致的程度,结果范围从0~1,1表示评价完全相同,0表示评价完全相反。
一般用模型获得相同评价的数量与基于可能性的期望是否有差别来分析,当两个模型相同评价的数量和基于可能性期望的数量基本一样时,kappa的值就接近于1。
举个栗子,模型A和基准的kappa:
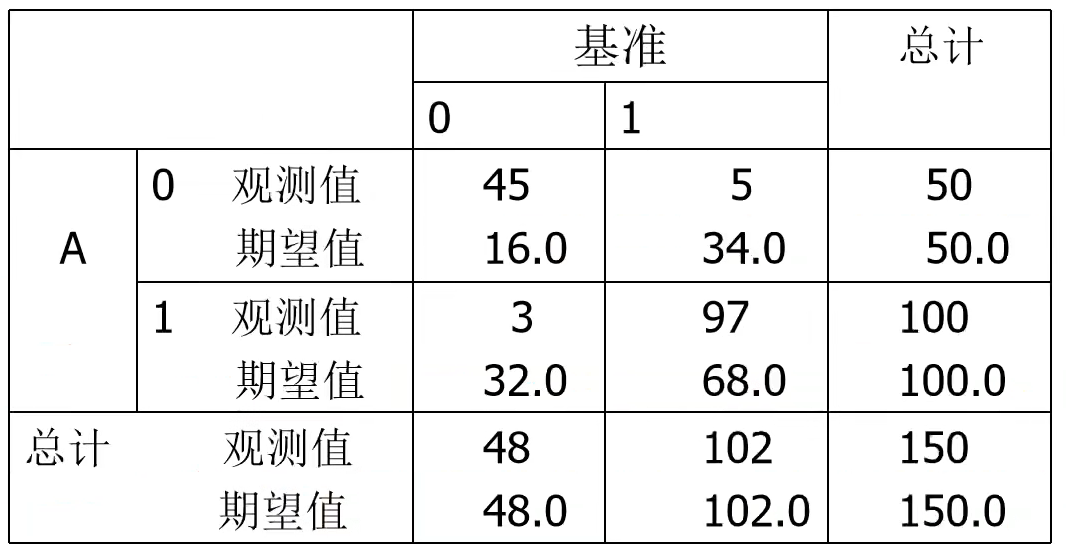
kappa = (p0-pe) / (n-pe)
其中,P0 = 对角线单元中观测值的总和;pe = 对角线单元中期望值的总和。
根据kappa的计算方法分为简单kappa(simple kappa)和加权kappa(weighted kappa),加权kappa又分为linear weighted kappa和quadratic weighted kappa。
weighted kappa
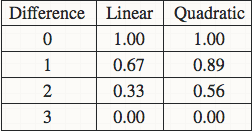
关于linear还是quadratic weighted kappa的选择,取决于你的数据集中不同class之间差异的意义。比如对于眼底图像识别的数据,class=0为健康,class=4为疾病晚期非常严重,所以对于把class=0预测成4的行为所造成的惩罚应该远远大于把class=0预测成class=1的行为,使用quadratic的话0->4所造成的惩罚就等于16倍的0->1的惩罚。如下图是一个四分类的两个计算方法的比较。
Python实现
参考:https://github.com/benhamner/Metrics/blob/master/Python/ml_metrics/quadratic_weighted_kappa.py
#! /usr/bin/env python2.7
import numpy as np
def confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the confusion matrix between rater's ratings
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
conf_mat = [[0 for i in range(num_ratings)]
for j in range(num_ratings)]
for a, b in zip(rater_a, rater_b):
conf_mat[a - min_rating][b - min_rating] += 1
return conf_mat
def histogram(ratings, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Returns the counts of each type of rating that a rater made
"""
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(ratings)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(ratings)
num_ratings = int(max_rating - min_rating + 1)
hist_ratings = [0 for x in range(num_ratings)]
for r in ratings:
hist_ratings[r - min_rating] += 1
return hist_ratings
def quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
quadratic_weighted_kappa calculates the quadratic weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
quadratic_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
rater_a = np.array(rater_a, dtype=int)
rater_b = np.array(rater_b, dtype=int)
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(min(rater_a), min(rater_b))
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(max(rater_a), max(rater_b))
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = pow(i - j, 2.0) / pow(num_ratings - 1, 2.0)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the linear weighted kappa
linear_weighted_kappa calculates the linear weighted kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
linear_weighted_kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
linear_weighted_kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
d = abs(i - j) / float(num_ratings - 1)
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def kappa(rater_a, rater_b, min_rating=None, max_rating=None):
"""
Calculates the kappa
kappa calculates the kappa
value, which is a measure of inter-rater agreement between two raters
that provide discrete numeric ratings. Potential values range from -1
(representing complete disagreement) to 1 (representing complete
agreement). A kappa value of 0 is expected if all agreement is due to
chance.
kappa(rater_a, rater_b), where rater_a and rater_b
each correspond to a list of integer ratings. These lists must have the
same length.
The ratings should be integers, and it is assumed that they contain
the complete range of possible ratings.
kappa(X, min_rating, max_rating), where min_rating
is the minimum possible rating, and max_rating is the maximum possible
rating
"""
assert(len(rater_a) == len(rater_b))
if min_rating is None:
min_rating = min(rater_a + rater_b)
if max_rating is None:
max_rating = max(rater_a + rater_b)
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(rater_a, rater_b,
min_rating, max_rating)
num_ratings = len(conf_mat)
num_scored_items = float(len(rater_a))
hist_rater_a = histogram(rater_a, min_rating, max_rating)
hist_rater_b = histogram(rater_b, min_rating, max_rating)
numerator = 0.0
denominator = 0.0
for i in range(num_ratings):
for j in range(num_ratings):
expected_count = (hist_rater_a[i] * hist_rater_b[j]
/ num_scored_items)
if i == j:
d = 0.0
else:
d = 1.0
numerator += d * conf_mat[i][j] / num_scored_items
denominator += d * expected_count / num_scored_items
return 1.0 - numerator / denominator
def mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=None):
"""
Calculates the mean of the quadratic
weighted kappas after applying Fisher's r-to-z transform, which is
approximately a variance-stabilizing transformation. This
transformation is undefined if one of the kappas is 1.0, so all kappa
values are capped in the range (-0.999, 0.999). The reverse
transformation is then applied before returning the result.
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas), where kappas is a vector of
kappa values
mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights), where weights is a vector
of weights that is the same size as kappas. Weights are applied in the
z-space
"""
kappas = np.array(kappas, dtype=float)
if weights is None:
weights = np.ones(np.shape(kappas))
else:
weights = weights / np.mean(weights)
# ensure that kappas are in the range [-.999, .999]
kappas = np.array([min(x, .999) for x in kappas])
kappas = np.array([max(x, -.999) for x in kappas])
z = 0.5 * np.log((1 + kappas) / (1 - kappas)) * weights
z = np.mean(z)
return (np.exp(2 * z) - 1) / (np.exp(2 * z) + 1)
def weighted_mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(solution, submission):
predicted_score = submission[submission.columns[-1]].copy()
predicted_score.name = "predicted_score"
if predicted_score.index[0] == 0:
predicted_score = predicted_score[:len(solution)]
predicted_score.index = solution.index
combined = solution.join(predicted_score, how="left")
groups = combined.groupby(by="essay_set")
kappas = [quadratic_weighted_kappa(group[1]["essay_score"], group[1]["predicted_score"]) for group in groups]
weights = [group[1]["essay_weight"].irow(0) for group in groups]
return mean_quadratic_weighted_kappa(kappas, weights=weights)
一致性检验评价方法kappa的更多相关文章
- 多准则决策模型-TOPSIS评价方法-源码
? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 ...
- 自动文档摘要评价方法:Edmundson,ROUGE
自动文档摘要评价方法大致分为两类: (1)内部评价方法(Intrinsic Methods):提供参考摘要,以参考摘要为基准评价系统摘要的质量.系统摘要与参考摘要越吻合, 质量越高. (2)外部评价方 ...
- 全参考视频质量评价方法(PSNR,SSIM)以及与MOS转换模型
转载处:http://blog.csdn.NET/leixiaohua1020/article/details/11694369 最常用的全参考视频质量评价方法有以下2种: PSNR(峰值信噪比):用 ...
- 图像质量评价方法PSNR+SSIM&&评估指标SROCC,PLCC
update:2018-04-07 今天发现ssim的计算里面有高斯模糊,为了快速计算,先对每个小块进行计算,然后计算所有块的平均值.可以参考源代码实现,而且代码实现有近似的在里面!matlab中中图 ...
- 机器学习评价方法 - Recall & Precision
刚开始看这方面论文的时候对于各种评价方法特别困惑,还总是记混,不完全统计下,备忘. 关于召回率和精确率,假设二分类问题,正样本为x,负样本为o: 准确率存在的问题是当正负样本数量不均衡的时候: 精心设 ...
- 视频质量评价方法:VQM
如何确定一个视频质量的好坏一直以来都是个棘手的问题.目前常用的方法就是通过人眼来直接观看,但是由于人眼的主观性及观看人员的单体差异性,对于同样的视频质量,不同的人的感受是不一样的.为此多个研究机构提出 ...
- 多标签图像分类任务的评价方法-mAP
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9db078090102whzw.html 多标签图像分类(Multi-label Image Classification)任务中图片的 ...
- logistic regression评价方法
1.sensitivity,也叫recall,true positive rate,含义是预测为正向的case中对的(true positive)和所有事实为正向的case的比例. 2.specifi ...
- 【一致性检验指标】Kappa(cappa)系数
1 定义 百度百科的定义: 它是通过把所有地表真实分类中的像元总数(N)乘以混淆矩阵对角线(Xkk)的和,再减去某一类地表真实像元总数与被误分成该类像元总数之积对所有类别求和的结果,再除以总像元数的平 ...
随机推荐
- 第8章 File I/O,File类操作文件的属性
1.文件 1.1.什么是文件? 答:文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合 1.2.文件- -般存储在哪里? 答: 磁盘,硬盘,文件夹 1.3.JAVA程序如何访向文件属性? JAVA API:i ...
- 使用Sinopia部署私有npm仓库
使用Sinopia部署私有npm仓库 [root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname --static npm-server [root@npm-server ...
- Spring高级特性之三:@Enable*注解的工作原理
Spring Boot中阐述热插拔技术的时候,简单地提及@Enable*注解.随着多种框架的应用及深入了解,@Enable*这个注解在各种框架中应用相当普及. 那么@Enable*注解工作原理是怎么样 ...
- GitLab API使用小结
GitLab API使用小结 背景描述 需求描述: 最近因为工作上的需求,需要对GitLab进行大批量的操作,又因为服务器不在境内,所以所有的操作都需要连接VPN来进行FQ访问.目前大概有6000多个 ...
- 第六题 Z字走法
我和答案第一种解法是很相似的 但是时间 和空间都被大部分人击败了. 思路就是用一个标记 为0就竖着走 为1就斜着走 把二维数组填满 我觉得难点在于PHYTON如何创建一个二维数组 而且是不定长的 ...
- SaaS平台是什么,为什么字节、腾讯等大厂都在抢相关人才
SaaS平台很多人可能没听说是什么,但是从事TO B公司的员工来说,SaaS平台应该都有所耳闻.从2016年开始,腾讯开始发力TO B算起,到处在挖TO B公司的骨干人才,而熟悉SaaS平台的人才竞 ...
- 零售BI:为什么说零售行业非上一套企业BI系统不可?
如果你要问为什么现在越来越多的零售企业都会在公司上一套企业BI系统,这边文章就能解答你的疑惑. 2016年10月,马云在云栖大会上提出了"新零售"概念.在新零售时代,数字化转型打通 ...
- pycharm创建模板
用pycharm构造作者模板 模板,就是创建一个文件时自动生成模板内容. 这里用pycharm创建作者模板,步骤如下: File-->Settings Editor-->File and ...
- SPYEYE手机远程监控和官方SPYEYE间谍软件最新下载方式
听起来远程控制手机好像很高级的样子,但是实现起来其实非常简单.实现原理如下: 运行程序,让程序不停地读取数据 用手机给手机发送邮件 判断是否读取到指定主题的手机,如果有,则获取手机内容 根据邮件内容, ...
- 【C#设计模式】里氏替换原则
今天,我们再来学习 SOLID 中的"L"对应的原则:里式替换原则. 里氏替换原则 里氏替换原则(Liskov Substitution Principle):派生类(子类)对象能 ...
