hdu 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou bfs
The Donkey of Gui Zhou
Time Limit: 20 Sec
Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4740
Description
There was no donkey in the province of Gui Zhou, China. A trouble maker shipped one and put it in the forest which could be considered as an N×N grid. The coordinates of the up-left cell is (0,0) , the down-right cell is (N-1,N-1) and the cell below the up-left cell is (1,0)..... A 4×4 grid is shown below:
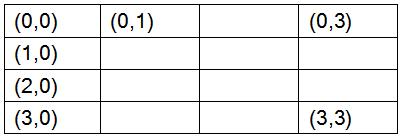
The donkey lived happily until it saw a tiger far away. The donkey had never seen a tiger ,and the tiger had never seen a donkey. Both of them were frightened and wanted to escape from each other. So they started running fast. Because they were scared, they were running in a way that didn't make any sense. Each step they moved to the next cell in their running direction, but they couldn't get out of the forest. And because they both wanted to go to new places, the donkey would never stepped into a cell which had already been visited by itself, and the tiger acted the same way. Both the donkey and the tiger ran in a random direction at the beginning and they always had the same speed. They would not change their directions until they couldn't run straight ahead any more. If they couldn't go ahead any more ,they changed their directions immediately. When changing direction, the donkey always turned right and the tiger always turned left. If they made a turn and still couldn't go ahead, they would stop running and stayed where they were, without trying to make another turn. Now given their starting positions and directions, please count whether they would meet in a cell.
Input
There are several test cases.
In each test case:
First line is an integer N, meaning that the forest is a N×N grid.
The second line contains three integers R, C and D, meaning that the donkey is in the cell (R,C) when they started running, and it's original direction is D. D can be 0, 1, 2 or 3. 0 means east, 1 means south , 2 means west, and 3 means north.
The third line has the same format and meaning as the second line, but it is for the tiger.
The input ends with N = 0. ( 2 <= N <= 1000, 0 <= R, C < N)
Output
For each test case, if the donkey and the tiger would meet in a cell, print the coordinate of the cell where they meet first time. If they would never meet, print -1 instead.
Sample Input
2
0 0 0
0 1 2
4
0 1 0
3 2 0
0
Sample Output
-1
1 3
HINT
题意
驴和老虎在n*n的格子里面跑呀跑,驴遇到障碍或者自己走过的路,就会往右转,而老虎往左转,问你最早在哪儿相遇。
注意,如果转一次还是不能走的话,就会停下来
题解:
啊,读懂题,用bfs搞一搞就好了……
模拟每一步
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
//freopen("D.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("D.out","w",stdout);
#define sspeed ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)
#define test freopen("test.txt","r",stdin)
const int maxn=;
#define mod 1000000009
#define eps 1e-9
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll infll = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
inline ll read()
{
ll x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
//************************************************************************************** int dy[]={,,-,};
int dx[]={,,,-};//这是驴++,老虎--
int vis1[][];
int vis2[][];
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF)
{
if(n==)
break;
memset(vis1,,sizeof(vis1));
memset(vis2,,sizeof(vis2));
int x=read(),y=read(),z=read();
int xx=read(),yy=read(),zz=read();
int flag=;
int flag1=,flag2=;
int flag11=,flag22=;
int tt=;
while(tt<)
{
flag1=,flag2=;
vis1[x][y]=;
vis2[xx][yy]=;
if(x==xx&&y==yy)
{
printf("%d %d\n",x,y);
flag=;
break;
}
int nowx=x,nowy=y,nowz=z;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
if(flag11==)
break;
int nextx=nowx,nexty=nowy,nextz=nowz;
nextz=(nowz+i+)%;
nextx+=dx[nextz];
nexty+=dy[nextz];
if(nextx<||nextx>=n)
continue;
if(nexty<||nexty>=n)
continue;
if(vis1[nextx][nexty])
continue;
flag1=;
x=nextx,y=nexty,z=nextz;
break;
}
nowx=xx,nowy=yy,nowz=zz;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
if(flag22==)
break;
int nextx=nowx,nexty=nowy,nextz=nowz;
nextz=(nowz-i+)%;
nextx+=dx[nextz];
nexty+=dy[nextz];
if(nextx<||nextx>=n)
continue;
if(nexty<||nexty>=n)
continue;
if(vis2[nextx][nexty])
continue;
flag2=;
xx=nextx,yy=nexty,zz=nextz;
break;
}
if(flag1==&&flag2==)
tt++;
if(flag1==)
flag11=;
if(flag2==)
flag22=;
}
if(!flag)
printf("-1\n");
}
}
hdu 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou bfs的更多相关文章
- hdu 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou(dfs模拟好题)
Problem Description There was no donkey ,) , the down-right cell ,N-) and the cell below the up-left ...
- hdu 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou(暴力搜索)
题目地址:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4740 [题意]: 森林里有一只驴和一只老虎,驴和老虎互相从来都没有见过,各自自己走过的地方不能走第二次 ...
- HDU 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou (模拟)
由于一开始考虑的很不周到,找到很多bug.....越改越长,不忍直视. 不是写模拟的料...................... 反正撞墙或者碰到已经走过的点就会转向,转向后还碰到这两种情况就会傻站 ...
- hdu 4740 The Donkey of Gui Zhou
1.扯犊子超多if else 判断的代码,华丽丽的TLE. #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #define N 1010 int ma ...
- The Donkey of Gui Zhou
Problem Description There was no donkey in the province of Gui Zhou, China. A trouble maker shipped ...
- HDU 1312 Red and Black --- 入门搜索 BFS解法
HDU 1312 题目大意: 一个地图里面有三种元素,分别为"@",".","#",其中@为人的起始位置,"#"可以想象 ...
- hdu 3247 AC自动+状压dp+bfs处理
Resource Archiver Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 100000/100000 K (Java/Ot ...
- HDU 1430 魔板(康托展开+BFS+预处理)
魔板 Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submis ...
- HDU 5025:Saving Tang Monk(BFS + 状压)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5025 Saving Tang Monk Problem Description <Journey to ...
随机推荐
- C++ STL知识点小结
1.capacity(容量)与size(长度)的区别. size(长度)指容器当前拥有的元素个数. capacity(容量)指容器在必须分配新存储空间之前可以存储的元素总数.
- Android基于XMPP Smack openfire 开发的聊天室
Android基于XMPP Smack openfire 开发的聊天室(一)[会议服务.聊天室列表.加入] http://blog.csdn.net/lnb333666/article/details ...
- Microsoft Office 2010 requires 的 MSXML 版本 6.10.1129.0 be 已安装在您计算机的安装"的基于 Windows 7 的计算机上安装 Office 2010 时出现错误消息
https://support.microsoft.com/zh-cn/kb/2290714
- Linux基本命令(8)网络操作的命令
网络操作命令 命令 功能 命令 功能 ftp 传送文件 telnet 远端登陆 bye 结束连线并结束程序 rlogin 远端登入 ping 检测主机 netstat 显示网络状态 8.1 ftp命令 ...
- 【转】linux之fsck命令
转自:http://www.linuxso.com/command/fsck.html 使用权限 : 超级使用者 使用方式 : fsck [-sACVRP] [-t fstype] [--] [fsc ...
- 【LeetCode】66 & 67- Plus One & Add Binary
66 - Plus One Given a non-negative number represented as an array of digits, plus one to the number. ...
- WCF_Config頁面常用配置
右键点击App.config文件,选中Edit WCF Configuration进行编辑,我们添加2个baseAddress,一个是基于HTTP协议的:一个是基于TCP协议的.同时添加2个bindi ...
- 45个有新意的Photoshop教程和技巧
图形制作者和网页设计师已经准备好迎接新的Adobe Photoshop 教程了.在大家喜欢背后有许多它的理由,诸如Adobe Photoshop很容易操作,学习起来十分简单,但最重要的一点是这款软件能 ...
- pku1273 Drainage Ditches
http://poj.org/problem?id=1273 网络流,Dinic #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include ...
- 关于python all(itrable)的使用 和列表表达式使用以及复习一下短路效应。
其实现在来看 并不是什么高级特性. 但是当时看到
