Python自动化办公--Pandas玩转Excel【一】
相关文章:
Python自动化办公--Pandas玩转Excel数据分析【二】
Python自动化办公--Pandas玩转Excel数据分析【三】_汀、的博客-CSDN博客
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(含实战)【一】
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(含实战)【二】
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(数据筛选、公式操作、单元格拆分合并、冻结窗口、图表绘制等)【三】
python入门之后须掌握的知识点(模块化编程、时间模块)【一】
python入门之后须掌握的知识点(excel文件处理+邮件发送+实战:批量化发工资条)【二】
pandas玩转excel码源.zip-数据挖掘文档类资源-CSDN下载 码源
1.基础温故【Pandas】
1.1 创建文件
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame()
df.to_excel('001.xlsx') #可以指定路径
#df.to_excel('H:\\Anaconda\\001.xlsx')
df = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3],'name':['a','b','c']})
df.to_excel('001-data.xlsx')
df = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3],'name':['a','b','c']})
df = df.set_index('id')
df.to_excel('001-data-index.xlsx')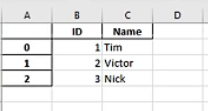
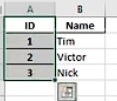
第一幅图索引默认在A列,通过set_index把ID设置为索引。
1.2 读取excel中的数据

脏数据处理:第一行错误数据,或者没有数据
import pandas as pd
people = pd.read_excel('people001.xlsx')
print(people.shape)
print(people.columns)
# 默认打印3行
print(people.head())
print(people.head(3))
# 默认打印5行
print(people.tail())
#脏数据处理:第一行错误数据,或者没有数据
#存在空行会自动识别并跳过,获取列名
people = pd.read_excel('people002.xlsx',header=1)
print(people.columns)
#脏数据处理:第一行没有列名,添加列名
people = pd.read_excel('people003.xlsx',header=None)
people.columns = ['ID', 'Type', 'Title', 'FirstName', 'MiddleName', 'LastName']
people = people.set_index('ID',inplace=True)
people.to_excel('output.xlsx')
其中在colums中是把列名和索引区别的,
people = people.set_index('ID',inplace=True)
#设置完index后,
print(people.columns)
#显示
'Type', 'Title', 'FirstName', 'MiddleName', 'LastName'再次读取时:id还是会当作列

这时候在读取的时候需要设置index,即可。
import pandas as pd
people = pd.read_excel('people001.xlsx',index_col="ID")
1.3 生成列、行、单元格(Series)
Series和python中的字典类似,下面是几种创建方法:
import pandas as pd
d = {
'x':100,
'y':200,
'z':300,
}
print(d.values())
print(d.keys())
s1 = pd.Series(d)
print(s1.index)
L1 = [100,200,300]
L2 = ['x','y','z']
s2 = pd.Series(L1,index=L2)
print(s2.index)
s3 = pd.Series([100,200,300],index=['x','y','z'])
print(s3.index)
创建一个简单的列表:行列不同形式添加。



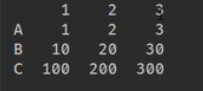
index是默认对齐的方式,如果不相同会用NaN填充。

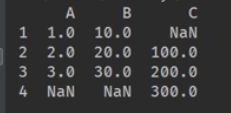
1.4 自动填充功能【数据区域读取填充数字】
1.4.1 数值填充
原始数据:只有name(书名)进行填充数据

数据区域不是定格,无法自动识别
import pandas as pd
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None)
#usecols='C,D,E,F',填充完再设置index_col
print(books)
#NaN填充的dtype是float64
import pandas as pd
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
print(books)
为了显示为整型,先把类型设置为str
import pandas as pd
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
print(books)
import pandas as pd
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
print(books)
import pandas as pd
from datetime import date, timedelta
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
start=date(2018,1,1)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books["Date"].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
print(books)

月份相加需要计算一下,定义个子函数
import pandas as pd
from datetime import date, timedelta
def add_month[d, md):
yd=md/12
m=d.month+md%12
if m!= 12:
yd+=m/12
m=m%12
return date(d.year + yd,m, d.day)
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
start=date(2018,1,1)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books["Date"].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
#books["Date"].at[i]=add_month(start,i)
#print(books)
books.set_index("ID",inplace=True)
books.to_excel("output/xlsx")

还有一种写法不改series直接改单元格写法如下:
for i in books.index:
booksat[i,"ID"]]=i+1
books.at[i,"InStroe"]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books.at[i,"Date"]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
#books["Date"].at[i]=add_month(start,i)
#print(books)1.4.2 计算填充(列操作)

列相乘,操作符重载【不用循环计算更方便】

循环:【不从头到尾计算,部分区域计算采用单元格计算】




价格加2 使用apply

lambda:

1.5 排序,多重排序


ascending默认从小到大排序:【true 从大到小 false从小到大】

1.6 数据筛选、过滤

找出年龄【18,30】分数【60,90】之间的
import pandas as pd
def validate_age(a):
return 18 <= a <= 30 #pandas特有写法
def level_b(s):
return 60 <= s < 90
students = pd.read_excel('Students.xlsx', index_col='ID')#id作为index
students = students.loc[students['Age'].apply(validate_age)].loc[students.Score.apply(level_b)] # 两
种语法
students = students.loc[students.Age.apply(validate_age)].loc[students.Score.apply(level_b)] # 两
种语法
print(students)loc与iloc功能介绍:数据切片。通过索引来提取数据集中相应的行数据or列数据(可以是多行or多列)总结不同:
1. loc函数通过调用index名称的具体值来取数据
2. iloc函数通过行序号来取数据
3.取多行数据时iloc不包含末尾
4.对数据进行筛选使用loc函数,当使用loc函数时, 如果index不具有特定意义,而且重复,那么提取的数据需要进一步处理,可用.reset index()函数重置index相同: .
5.【】中无逗号时,默认取行
筛选出来的结果:
Name Age Score
ID
4 Student_004 27 73
8 Student_008 21 61
9 Student_009 18 85
19 Student_019 19 86换一种写法:lambda
import pandas as pd
# def validate_age(a):
# return 18 <= a <= 30
# def level_b(s):
# return 60 <= s < 90
students = pd.read_excel('Students.xlsx', index_col='ID')
students = students.loc[students['Age'].apply(
lambda a:18 <= a <= 30)] .loc[students.Score.apply(lambda s:60 <= s < 90)] # 两种语法
print(students)2.数据可视化
2.1 柱状图
| Field | Number |
| Agriculture | 12,318 |
| Business and Management | 200,312 |
| Education | 19,483 |
| Engineering | 216,932 |
| Fine and Applied Arts | 59,736 |
| Health Professions | 33,947 |
| Humanities | 17,664 |
| Mathematics and Computer Sciences | 141,651 |
| Other/Unspecified Subject Areas | 185,107 |
| Physical and Life Sciences | 75,385 |
| Social Sciences | 81,304 |
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students1.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='Number', inplace=True, ascending=False)
students.index = range(0, len(students))
print(students)
plt.bar(students['Field'], students['Number'], color='orange', width=0.7)#
plt.xticks(students['Field'], rotation='90') #rotation旋转
plt.title('International Student by Field', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Field')
plt.ylabel('Number')
plt.tight_layout() #j紧凑型,避免下标显示不全
plt.show()
pandas中inplace参数在很多函数中都会有,它的作用是:是否在原对象基础上进行修改
inplace = True:不创建新的对象,直接对原始对象进行修改;
inplace = False:对数据进行修改,创建并返回新的对象承载其修改结果。
默认是False,即创建新的对象进行修改,原对象不变, 和深复制和浅复制有些类似。


或者直接用pandas自带的:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('C:/Temp/Students.xlsx')
students.sort_values('Number', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(students)
students.plot.bar(x='Field', y='Number', color='blue', title='International Students by Field')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()2.2 分组柱图深度优化(比较图)
| Field | 2016 | 2017 |
| Agriculture | 12,318 | 12,602 |
| Business and Management | 200,312 | 200,754 |
| Communications and Journalism | 21,160 | 21,913 |
| Education | 19,483 | 17,993 |
| Engineering | 216,932 | 230,711 |
| Fine and Applied Arts | 59,736 | 61,506 |
| Humanities | 17,664 | 17,561 |
| Intensive English | 40,877 | 30,309 |
| Legal Studies and Law Enforcement | 15,077 | 15,306 |
| Math and Computer Science | 141,651 | 167,180 |
| Physical and Life Sciences | 75,385 | 76,838 |
| Social Sciences | 81,304 | 83,046 |
| Other Fields of Study | 81,318 | 87,577 |
| Undeclared | 26,675 | 21,131 |
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students2.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='2017', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(students)
students.plot.bar('Field', ['2016', '2017'], color=['orange', 'Red'])
plt.title('International Students by Field', fontsize=16,fontweight="bold")
plt.xlabel('Field', fontweight='bold')
plt.ylabel('Number', fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
ax = plt.gca() #坐标轴移动修改
ax.set_xticklabels(students['Field'], rotation=40, ha='right') #默认中心旋转
plt.gcf().subplots_adjust(left=0.2, bottom=0.42) #画布大小调整
plt.show()
推荐第一个
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students2.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='2017', inplace=True, ascending=False)
students.index = range(0, len(students))
print(students)
bar_width = 0.7
x_pos = np.arange(len(students) * 2, step=2)
plt.bar(x_pos, students['2016'], color='green', width=bar_width)
plt.bar(x_pos + bar_width, students['2017'], color='blue', width=bar_width)
plt.legend()
plt.xticks(x_pos + bar_width / 2, students['Field'], rotation='90')
plt.title('International Student by Field', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Field')
plt.ylabel('Number')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
2.3 叠加柱状图

用户总量从大到小排序:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
users = pd.read_excel('Users.xlsx')
users['Total'] = users['Oct'] + users['Nov'] + users['Dec']
users.sort_values(by='Total', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(users)
users.plot.bar(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)
# users.plot.barh(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)#水平柱状图堆积
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()


users.sort_values(by='Total', inplace=True, ascending=Ture)
users.plot.barh(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)#水平柱状图堆积
2.4 饼图

其中2016 2017是字符串,避免pandas误认为数字。
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students3.xlsx', index_col='From')
print(students)
# counterclock顺逆时针,startangle开始点确认
students['2017'].plot.pie(fontsize=8, counterclock=False, startangle=-270)
plt.title('Source of International Students', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.ylabel('2017', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
plt.show()
2.5 折现趋势图,叠加区域图

import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
weeks = pd.read_excel('Orders.xlsx', index_col='Week')
print(weeks)
weeks.plot(y=['Accessories', 'Bikes', 'Clothing', 'Components'])
weeks.plot.area(y=['Accessories', 'Bikes', 'Clothing', 'Components'])
plt.title('Sales Trends', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.xticks(weeks.index, fontsize=8)
plt.show()


2.6 散点图直方图密度图

import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pd.options.display.max_columns = 999#所有列都会显示
homes = pd.read_excel('home_data.xlsx')
# print(homes.head())
print(homes.corr())#相关性
homes.plot.scatter(x='sqft_living', y='price')
plt.figure()
homes.sqft_living.plot.kde() #密度图
plt.figure()
homes.sqft_living.plot.hist(bins=100) #区间设置
plt.xticks(range(0, max(homes.sqft_living), 500), fontsize=8, rotation=90) #面积
# homes.price.plot.hist(bins=200)
# plt.xticks(range(0, max(homes.price), 100000), fontsize=8, rotation=90) #房价
plt.show()

密度图:

相关性:corr()
id price bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living \
id 1.000000 -0.016762 0.001286 0.005160 -0.012258
price -0.016762 1.000000 0.308350 0.525138 0.702035
bedrooms 0.001286 0.308350 1.000000 0.515884 0.576671
bathrooms 0.005160 0.525138 0.515884 1.000000 0.754665
sqft_living -0.012258 0.702035 0.576671 0.754665 1.000000
sqft_basement -0.005151 0.323816 0.303093 0.283770 0.435043
sqft_lot -0.132109 0.089661 0.031703 0.087740 0.172826
floors 0.018525 0.256794 0.175429 0.500653 0.353949
yr_built 0.021380 0.054012 0.154178 0.506019 0.318049
sqft_basement sqft_lot floors yr_built
id -0.005151 -0.132109 0.018525 0.021380
price 0.323816 0.089661 0.256794 0.054012
bedrooms 0.303093 0.031703 0.175429 0.154178
bathrooms 0.283770 0.087740 0.500653 0.506019
sqft_living 0.435043 0.172826 0.353949 0.318049
sqft_basement 1.000000 0.015286 -0.245705 -0.133124
sqft_lot 0.015286 1.000000 -0.005201 0.053080
floors -0.245705 -0.005201 1.000000 0.489319
yr_built -0.133124 0.053080 0.489319 1.000000Python自动化办公--Pandas玩转Excel【一】的更多相关文章
- Python数据分析:pandas玩转Excel (二)
1 对Excel文件的操作 方法一: 使用xlrd库或者xlwt库进行对excel表格的操作读与写: 方法二: pandas库同样支持excel的读写操作:且更加简便. 2 pd.read_excel ...
- Python数据分析:pandas玩转Excel (一)
目录 1 pandas简介 2 导入 3 使用 4 读取.写入 1 pandas简介 1.Pandas是什么? Pandas是一个强大的分析结构化数据的工具集: 它的使用基础是Numpy(提供高性能的 ...
- Python数据分析:pandas玩转Excel(三)
将对象写入Excel工作表. 要将单个对象写入 Excel .xlsx 文件,只需指定目标文件名即可.要写入多个工作表,必须创建具有目标文件名的ExcelWriter对象,并在文件中指定要写入的工作表 ...
- Python自动化办公知识点整理汇总
知乎上有人提问:用python进行办公自动化都需要学习什么知识呢? 很多人学习python,不知道从何学起.很多人学习python,掌握了基本语法过后,不知道在哪里寻找案例上手.很多已经做案例的人,却 ...
- 20210105 - python自动化办公简介
新的一年开始了, 计划每周至少更新三篇博客. 人生苦短,如果不做改变,人生很快会过去!2021年寻求改变,加油! python自动化办公: 1.相关工具与环境的安装概要: 需要用到python(一种开 ...
- Python自动化办公:将文本文档内容批量分类导入Excel表格
序言 (https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=GmeRhIX0) 它来了,它又来了. 本文实现用Python将文本文件自动保存到Excel表格里面去. 需求 将锦江区.t ...
- Python自动化办公:27行代码实现将多个Excel表格内容批量汇总合并到一个表格
序言 (https://jq.qq.com/?_wv=1027&k=GmeRhIX0) 老板最近越来越过分了,快下班了发给我几百个表格让我把内容合并到一个表格内去.还好我会Python,分分钟 ...
- Python自动化办公之操作Excel文件
模块导入 import openpyxl 读取Excel文件 打开Excel文件 workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook("test.xlsx") 输出 ...
- 《Python编程快速上手 —让繁琐工作自动化》|百度网盘免费下载|Python自动化办公
Python编程快速上手—让繁琐工作自动化 提取码:u8vj 如今,人们面临的大多数任务都可以通过编写计算机软件来完成. Python 是一种解释型.面向对象.动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言.通过 P ...
- Python自动化办公第三方库xlwt
Python向excel表格写入内容,首先安装第三方库: pip3 install xlwt 代码实例(结合xlrd): #!usr/bin/env python3 #!-*-coding=utf-8 ...
随机推荐
- python 内置命名空间、标准库、模块相关概念
内置命名空间 python 解释器启动后就可以直接使用一些函数,常量,类型,异常等.保存这些数据的空间统称内置命名空间. 内置命名空间中包含的数据如下: 对于内置命名空间中最常用的就是内置函数. 内置 ...
- 基于C++11特性的线程池
写在前面:本文学习自基于C++11实现线程池,代码部分均属于该博主,自己只是想记录以下自己的认知,并以这种方式加深一下自己对于多线程的理解 1 前置知识 RAII管理机制 简单来说RAII机制是一种对 ...
- Java 使用 slf4j + log4j 写日志
没有SpringBoot等框架的情况下 pom.xml: <properties> <slf4j.version>1.7.26</slf4j.version> &l ...
- Qt 如何配置CLion标准控制台输出?
CMake 相关问题: 即CMakeLists.txt文件中,在add_executable添加了WIN32.即当使用了WIN32标识后,就去掉了控制台,那么自然就没有信息打印出来了. # for e ...
- 【LibCurl】C++使用libcurl实现HTTP POST和GET、PUT
libcurl简介 libcurl是一个跨平台的网络协议库,支持http, https, ftp, gopher, telnet, dict, file, 和ldap 协议.libcurl同样支持HT ...
- FastDFS 海量小文件存储解决之道
作者:vivo互联网服务器团队-Zhou Changqing 一.FastDFS原理介绍 FastDFS是一个C语言实现的开源轻量级分布式文件系统 . 支持 Linux.FreeBSD.AID 等Un ...
- 基于 HTML5 WebGL + WebVR 的 3D 虚拟现实可视化培训系统
前言 2019 年 VR, AR, XR, 5G, 工业互联网等名词频繁出现在我们的视野中,信息的分享与虚实的结合已经成为大势所趋,5G 是新一代信息通信技术升级的重要方向,工业互联网是制造业转型升级 ...
- 面试重点:webpack
webpack 熟练掌握Webpack的常用配置,能够自己构建前端环境,并进行项目优化; 001.谈谈你对webpack的看法: webpack是一个模块打包工具,可以使用它管理项目中的模块依赖,并编 ...
- TortoiseSVN 中文手册下载
TortoiseSVN 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1wAxZST9wKc_HebOrBiewjw 提取码:3gjq
- hdu 5234
题意:求在不超过k的情况下,最多可以得到多少价值. 三维dp,结合01背包,第三维就是用来保存在不同的背包容量下能得到的最大价值,也就是第三维有很多状态. #include<iostream&g ...
