zynq QSPI flash分区设置&启动配置
需求:
一款基于zynq架构的产品,只有qspi flash,并没有其他的存储设备,
现在的要求固化某个应用程序app,设置开机启动,
但是根据厂家提供的sdk,编译出的镜像重启后,文件系统的内容都会还原,
之前的方案是每次都要把程序放到buildroot下,
然后重新编译,将rootfs、内核镜像、设备树打包到image.ub.bin中,
然后用jtag重新烧录到flash中。
这很不合理,所以要我们需要对flash进行分区,
然后将需要固化的程序通过flashcp烧写到flash中,然后在用dd命令导出该文件。
0. MTD基础
该操作依赖linux的MTD子系统。
MTD(Memory Technology Device)是内存技术设备,它为原始闪存设备(例如NAND,OneNAND,NOR 等)提供了一个抽象层。
这些不同类型的Flash都可以使用相同的API。
通常内核都默认支持MTD驱动。
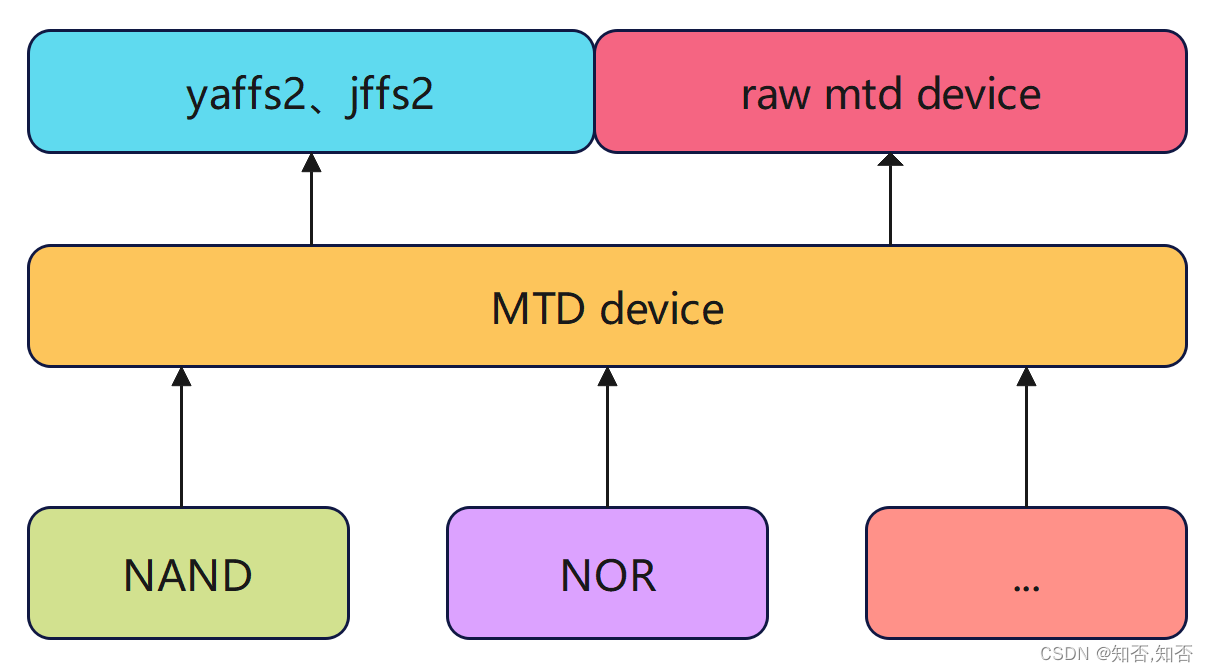
MTD字符设备-通常称为/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd1等。
这些字符设备提供对原始闪存的I/O访问。
它们支持许多ioctl调用,用于擦除擦除块,将其标记为不良或检查擦除块是否不良,获取有关MTD设备的信息等。
sysfs接口,它提供有关系统中每个MTD设备的完整信息。 此接口易于扩展,并且鼓励开发人员尽可能使用sysfs接口,而不是较旧的ioctl或/proc/mtd接口。
mtd子系统的sysfs接口已在内核中进行了说明,当前可在Documentation/ABI/ testing/sysfs-class-mtd中找到。
/proc/mtd proc文件系统文件提供常规的MTD信息。 这是旧版界面,而sysfs界面提供了更多信息。
MTD子系统支持带有软件和硬件ECC的 raw NAND闪存,OneNAND闪存,CFI(通用闪存接口)NOR闪存以及其他类型的闪存。
1. 查看qspi flash大小
进入uboot
fmsh> sf probe 0
SF: Detected n25q256 with page size 256 Bytes, erase size 4 KiB, total 32 MiB
该命令式查看设备信息。
可以看到qspi flash容量为32MB,即0x1E84800
2. 需要固化镜像分区地址设置
一口君使用的平台需要固化2个文件:cfg(存储配置信息)、app(可执行程序)
加上必须烧录的boot.bin、image.ub.bin,一共有4个文件,
所以我们需要配置4个分区。
1) boot.bin、image.ub.bin地址
其中boot.bin包含了fpga的ip核和启动必要的文件信息,地址固定为0
image.ub.bin的地址通常厂家也会给出默认地址,
进入uboot打印环境信息:
fmsh> printenv
fit_size=0x153f000
flash_off=0x500000
load_addr=0x2000000
qspiboot=echo Copying FIT from SPI flash to RAM...
&& sf probe && sf read ${load_addr} ${flash_off} ${fit_size} && bootm ${load_addr}
echo Copying FIT from SPI flash to RAM... :
打印提示信息
sf probe:
查看设备硬件信息
sf read ${load_addr} ${flash_off} ${fit_size},
从flash地址flash_off开始读取fit_size个字节到ram地址load_addr
bootm ${load_addr}:
启动内核
可以看到flash地址是flash_off:0x500000
2) 分区划分
那现在我们就可以给这4个文件设置分区信息了
| 镜像 | 文件实际大小(hex) | 起始地址 | offset | 块数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| boot.bin | 3D0900 | 0x00000 | 0x500000 | 61-80 |
| image.ub.bin | D59F80 | 0x500000 | 0x1100000 | 214-272 |
| cfg.bin | 200 | 0x1600000 | 0x10000 | 1 |
| app.bin | 7800 | 0x1610000 | 0x30000 | 3 |
注意:
offset大小必须是 0x10000整数倍,这个是擦除的最小单位-块。
每个分区大小结合要固化的程序,合理分配,既要考虑后面程序升级需要预留足够空间,也不要太大,造成浪费
分区划分不能超过flash最大值32M
3. 设备树
flash分区设备树说明如下:
Documentation\devicetree\bindings\mtd\partition.txt
Fixed Partitions
================
Partitions can be represented by sub-nodes of a flash device. This can be used
on platforms which have strong conventions about which portions of a flash are
used for what purposes, but which don't use an on-flash partition table such
as RedBoot.
The partition table should be a subnode of the flash node and should be named
'partitions'. This node should have the following property:
- compatible : (required) must be "fixed-partitions"
Partitions are then defined in subnodes of the partitions node.
For backwards compatibility partitions as direct subnodes of the flash device are
supported. This use is discouraged.
NOTE: also for backwards compatibility, direct subnodes that have a compatible
string are not considered partitions, as they may be used for other bindings.
#address-cells & #size-cells must both be present in the partitions subnode of the
flash device. There are two valid values for both:
<1>: for partitions that require a single 32-bit cell to represent their
size/address (aka the value is below 4 GiB)
<2>: for partitions that require two 32-bit cells to represent their
size/address (aka the value is 4 GiB or greater).
Required properties:
- reg : The partition's offset and size within the flash
Optional properties:
- label : The label / name for this partition. If omitted, the label is taken
from the node name (excluding the unit address).
- read-only : This parameter, if present, is a hint to Linux that this
partition should only be mounted read-only. This is usually used for flash
partitions containing early-boot firmware images or data which should not be
clobbered.
- lock : Do not unlock the partition at initialization time (not supported on
all devices)
我们只需要关注分区的子节点说明即可:
reg
描述某个flash分区的offset和size
label(可选)
分区名字
read-only(可选)
该分区只读
根据前面所有分析内容,最终我们修改设备信息如下:
&qspi0 {
status = "okay";
flash0: s25fl256s@0 {
compatible = "spi-flash","spansion,s25fl256s1", "jedec,spi-nor";
reg = <0>; /* chip select */
spi-max-frequency = <50000000>;
m25p,fast-read;
page-size = <256>;
block-size = <16>; /* 2^16, 64KB */
cdns,read-delay = <2>;
cdns,tshsl-ns = <0>;
cdns,tsd2d-ns = <0>;
cdns,tchsh-ns = <0>;
cdns,tslch-ns = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
partition@boot {
label = "boot";
reg = <0x0000000 0x500000>;
};
partition@uimage.ub {
label = "uimage.ub";
reg = <0x500000 0x1100000>;
};
partition@prm {
label = "cfg";
reg = <0x1600000 0x10000>;
};
partition@kk_ap {
label = "app";
reg = <0x1610000 0x30000>;
};
};
};
重新编译rootfs打包后重新启动即可。
4. 查看分区信息
# cat /proc/mtd
dev: size erasesize name
mtd0: 00500000 00010000 "boot"
mtd1: 01100000 00010000 "uimage.ub"
mtd2: 00010000 00010000 "cfg"
mtd3: 00030000 00010000 "app"
# ls /dev/mtd* -l
crw------- 1 root root 90, 0 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd0
crw------- 1 root root 90, 1 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd0ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 2 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd1
crw------- 1 root root 90, 3 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd1ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 4 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd2
crw------- 1 root root 90, 5 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd2ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 6 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd3
crw------- 1 root root 90, 7 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd3ro
brw------- 1 root root 31, 0 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock0
brw------- 1 root root 31, 1 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock1
brw------- 1 root root 31, 2 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock2
brw------- 1 root root 31, 3 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock3
/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd0ro,/dev/mtdblock0代表的是同一个MTD分区,但是/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd0ro都是字符设备,其中/dev/mtd0ro是只读字符设备,/dev/mtdblock0是块设备。
常见的mtd-utils,nand_write等工具只能操作/dev/mtdX字符设备,因为只有字符设备才支持ioctl操作。
5. 拷贝读取 MTD 分区
查看 MTD 分区
cat /proc/mtd
擦除 MTD 分区
flash_eraseall /dev/mtdX
擦除/dev/mtd0分区的第1块数据。
flash_erase /dev/mtd0 0x0 1
写 MTD 分区 NOR Flash
flashcp /tmp/mtd.bin /dev/mtdX
写 MTD 分区 NAND Flash
nandwrite /tmp/image.bin /dev/mtdX
读 MTD 分区
dd if=/dev/mtdX of=/tmp/mtd.bin
a) 烧写cfg.bin文件到mtd2
首先需要下载文件导开发板,可以用sd卡、网口(tftp)、串口(rz命令),根据自己的开发板资源。
执行下面命令烧录:
flash_erase /dev/mtd2 0x0 1
flashcp cfg.bin /dev/mtd2
导出分区文件
dd if=/dev/mtd2 of=/mnt/cfg.bin
b) 烧写app.bin到mtd3
flash_erase /dev/mtd3 0x0 3
flashcp app /dev/mtd3
导出分区文件
dd if=/dev/mtd3 of=/mnt/app.bin
6. 还原文件
注意导出的文件除了我们烧录的文件之外,
尾部还有多余FF,所以还需要去掉这些多余的部分,
所以我们必须要还原文件。
如下图所示:

【文件必须以二进制形式打开才能看到,彭老师用的Hex Editor Neo】

下载地址:
https://hhdsoftware.com/free-hex-editor
还原文件有很多方法,一口君自己写了个小程序,
原理:
逐字节读取文件,然后判断是否是0xFF,连续读取到16个0xff(防止文件中也由多个0XFF出现),
则认为读到了有效文件尾部,记录有效文件长度,然后根据该长度,复制成最终文件,该文件就是我们所需要的最终文件。
源码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int fd_p;
int fdw_p;
unsigned char c;
int count = 0;
int pos = 0;
int i;
if(argc != 3)
{
printf("argument error\n");
for(int i = 0; i < argc ; i++)
{
printf("argv[%d] = %s\n", i, argv[i]);
}
}
fd_p = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if(fd_p < 0){
printf("open file %s failed\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
fdw_p = open(argv[2], O_RDWR | O_CREAT);
if(fdw_p < 0){
printf("open file %s failed\n", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
while(1){
read(fd_p, &c, 1);
if(c == 0xff){
count++;
if(count >= 16){
break;
}
}
else{
count = 0;
}
pos++;
}
lseek(fd_p, SEEK_SET, 0);
for(i=0; i<pos-15; i++){
read(fd_p, &c, 1);
write(fdw_p, &c, 1);
}
return 0;
}
测试:

可见写入到分区的文件和我们从分区读取后再还原的文件时一致的。
重启后,再验证

从MD5校验码可知,可执行程序还原正确。
7. 开机自动还原文件
要想开机后自动还原该文件,并启动程序app,步骤如下:
- 将exportimg拷贝文件系统/mnt下,(目录有执行权限即可)
- 设置开机子启动脚本
sdk/buildroot-xxxxxx/output/target/etc/init.d/rcS
文件尾部添加:
dd if=/dev/mtd2 of=/mnt/cfg.bin
dd if=/dev/mtd3 of=/mnt/app.bin
touch /mnt/app
touch /mnt/cfg
chmod 777 /mnt/app
chmod 777 /mnt/cfg
/mnt/exportimg /mnt/app.bin /mnt/app
/mnt/exportimg /mnt/cfg.bin /mnt/cfg
rm /mnt/cfg.bin
rm /mnt/app.bin
/mnt/app &
本例在复旦微fmsh平台测试通过。
zynq平台应该也没问题。
zynq QSPI flash分区设置&启动配置的更多相关文章
- 设计模式(一)单例模式:创建模式 ASPNET CORE WEB 应用程序的启动 当项目中 没有STARTUP.CS 类如何设置启动 配置等等
设计模式(一)单例模式:创建模式 先聊一下关于设计的几个原则(1)单一原则(SRP):一个类应该仅有一个引起它变化的原因 :意思就是 (一个类,最好只负责一件事情,并且只有一个引起它变化的原因(2)开 ...
- AspNet Core Web 应用程序的启动(有关 Program.cs类/ Startup.cs类 ) 当项目中干掉 Startup.cs 类如何设置启动 配置等等
.有关怎么创建Core MVC/API 这里就不说了,前段时间的博客有说过: 1. 项目生成后会有如图所示两个类 Program类Startup类 2. Startup类 初始内容 public ...
- AspNet Core Web 应用程序的启动 当项目中 没有Startup.cs 类如何设置启动 配置等等
感叹: Core 16年6月1号 在中国宣布上线 到现在已经快经历两年时间了,目前版本已经到了2.0 就目前的前景来看,个人感觉 到2020年才可能有所起色,等到Core更成熟 个人看法:在.net这 ...
- 【设计经验】3、ISE中烧录QSPI Flash以及配置mcs文件的加载速度与传输位宽
一.软件与硬件平台 软件平台: 操作系统:Windows 7 64-bit 开发套件:ISE14.7 硬件平台: FPGA型号:XC6SLX45-CSG324 QSPI Flash型号:W25Q128 ...
- VM配置Centos(第十三步分区设置)
1.点击开启此虚拟机之后,选择第一个 (注意:如果鼠标不显示出来,按alt+ctrl键) 2.然后选择skip跳过检测,如果选择了ok就会有很长时间的检测 3.然后选择NEXT 4.选择中文,然后点击 ...
- 基于反熔丝FPGA、QSPI FLASH的高可靠程序存储、启动控制系统
1 涉及术语解释 1.1 三模冗余 三模冗余系统简称TMR(Triple Modular Redundancy),是最常用的一种容错设计技术.三个模块同时执行相同的操作,以多数相同的 ...
- (三)修改内核大小,适配目标板Nand flash分区配置
一. 修改内核大小 1. 在你的配置文件下uboot/include/config/xxx.h 里面有一个宏定义 #define MTDPARTS_DEFAULT "mtdparts=jz2 ...
- S03_CH12_基于UDP的QSPI Flash bin文件网络烧写
S03_CH12_基于UDP的QSPI Flash bin文件网络烧写 12.1概述 为了满足不同的需求,本例程在"基于TCP的QSPI Flash bin文件网络烧写"上进行修改 ...
- S03_CH11_基于TCP的QSPI Flash bin文件网络烧写
S03_CH11_基于TCP的QSPI Flash bin文件网络烧写 11.1概述 针对ZYNQ中使用QSPI BOOT的应用,将BOOT.bin文件烧写至QSPI Flash基本都是通过USB C ...
- DNW烧写FL2440 NAND Flash分区
转自 calvinlee1984 Subject:DNW烧写FL2440 NAND Flash分区 Date: 2-Mar-2011 By: Calvinlee1984@163 ...
随机推荐
- .NET Core WebApi接口ip限流实践
.NET Core WebApi接口ip限流实践 前言 之前一直想实现接口限流,但一直没去实现,然后刚好看到一篇文章是基于AspNetCoreRateLimit 组件的限流策略.这个组件不做多的介绍, ...
- Android案例分享,基于瑞芯微RK3568国产平台!
开发环境说明 Windows开发环境:Windows7 64bit.Windows10 64bit 虚拟机:VMware15.5.5 AndroidSDK编译环境:Ubuntu18.04.4 64bi ...
- RK3588J + 麒麟系统,“软硬件”全国产——让您的产品更具竞争力!
银河麒麟嵌入式操作系统简介 银河麒麟嵌入式操作系统V10是面向物联网及工业互联网场景的安全实时嵌入式操作系统,具备信息安全.多域隔离.云边端协同.多样性算力支持等特点,可满足嵌入式场景对操作系统小型化 ...
- 嵌入式工业开发板基础测试手册——基于NXP iMX6ULL开发板(1)
前 言 本文档适用开发环境: Windows开发环境:Windows 7 64bit.Windows 10 64bit 虚拟机:VMware15.1.0 Linux开发环境:Ubuntu18.04.4 ...
- Linux Mint操作系统安装
1,Linux 发行版 什么是Linux 发行版呢?这要从Linux 来源说起.Unix操作系统后期,开始收费和商业闭源了.一个叫Richard Stallman 的人就发起 GNU 计划,想模仿U ...
- Mac Docker设置国内镜像加速器
安装docker 点我直达 设置国内加速镜像 { "experimental": false, "features": { "buildkit&quo ...
- JavaSE 常见时间日期
java.util包提供了Date类来封装当前的⽇期和时间 构造函数 //当前时间 Date() //从1970年1⽉1⽇起的毫秒数作为参数 Date(long millisec) 常见方法 //返回 ...
- oeasy教您玩转vim - 005 - # 程序本质
程序本质 回忆上次内容 py 的程序是按照顺序 一行行挨排解释执行的 我们可以 python3 -m pdb hello.py 来对程序调试 调试的目的是去除 bug 别害怕 bug bug 会有 ...
- SMU Summer 2024 Contest Round 1(7.8)zhaosang
A-A http://162.14.124.219/contest/1005/problem/A 一道数学问题,求概率. 要求成功的概率,有两个色子, 一个用来抛正反面,一个用来控制得分大小,当超过某 ...
- Python 基于pymongo操作Mongodb学习总结
实践环境 Python 3.6.4 pymongo 4.1.1 pymongo-3.12.3-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl 下载地址:https://pypi.org/simple ...
