一个简单的C4.5算法,采用Python语言
Test1.py 主要是用来运行的 代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- from math import log
import operator
import treePlotter def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
"""
输入:数据集
输出:数据集的香农熵
描述:计算给定数据集的香农熵;熵越大,数据集的混乱程度越大
"""
# 数据集个数
numEntries = len(dataSet)
#print("dd",numEntries)
# 标签个数
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet:
# 获取每一行的结果 也就是yes or no
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
# print('e',currentLabel)
# 判断我获取的这个yes or no 在不在labelCounts字典中 如果不在创建新的设置为0
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
#print('r',labelCounts)
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
# 计算类别信息熵
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob, 2)
#print('----',shannonEnt)
return shannonEnt
# 分别按照这几个属性来计算信息熵 找出最大的,最后按照这一个来划分。
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
"""
输入:数据集,选择维度,选择值
输出:划分数据集
描述:按照给定特征划分数据集;去除选择维度中等于选择值的项
"""
retDataSet = []
# 这个时候 dataSet 还是完整的
for featVec in dataSet:
# print(axis,featVec)
# print('A',featVec[axis],"是不是等于",value)
if featVec[axis] == value:
reduceFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
# print("B",reduceFeatVec,"此时的维度:",axis)
reduceFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reduceFeatVec)
# print('GG',retDataSet)
return retDataSet def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
"""
输入:数据集
输出:最好的划分维度
描述:选择最好的数据集划分维度
"""
# 特征数量 也就是字段个数
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1
###################################################################
# (1)信息增益
# print('cc',numFeatures)
# 信息增益实际上是ID3算法中用来进行属性选择度量的。
# 它选择具有最高信息增益的属性来作为节点N的分裂属性。
# 该属性使结果划分中的元组分类所需信息量最小。
# 对D中的元组分类所需的期望信息为下式:
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) # 香农熵
# print('z',baseEntropy)
bestInfoGainRatio = 0.0 # 最好的熵
bestFeature = -1 # 最好的特征
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
# print('s',i,uniqueVals)
newEntropy = 0.0
splitInfo = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
# 划分数据集
# print("Bn",i,value)
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
#print("After",subDataSet,i,value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
# 现在假定按照属性A划分D中的元组,且属性A将D划分成v个不同的类。
# 在该划分之后,为了得到准确的分类还需要的信息由下面的式子度量
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
# 信息增益定义为原来的信息需求(即仅基于类比例)与新需求(即对A划分之后得到的)之间的差
splitInfo += -prob * log(prob, 2)
# 信息增益
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy
##########################################################################
if (splitInfo == 0): # 修复溢出错误
continue
#########################################################################
# (2)信息增益率
# 训练数据集D划分成对应于属性A测试的v个输出的v个划分产生的信息。信息增益率定义:
infoGainRatio = infoGain / splitInfo
# 选择具有最大增益率的属性作为分裂属性。
if (infoGainRatio > bestInfoGainRatio):
bestInfoGainRatio = infoGainRatio
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature def majorityCnt(classList):
"""
输入:分类类别列表
输出:子节点的分类
描述:数据集已经处理了所有属性,但是类标签依然不是唯一的,
采用少数服从多数的原则决定该子节点的分类
"""
''' 找出数量最多的分类 '''
# 分类字典
classCount = {}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
# 创建键值为classList中唯一值的数据字典,字典对象存储了classList中每个类标签出现的频率,最后利用operator操作键值排序字典,并返回出现次数最多的分类名称。
# iteritems:迭代器
# operator模块提供的itemgetter函数用于获取对象的哪些维的数据,参数为一些序号(即需要获取的数据在对象中的序号)
# sorted() 是Python内置的一个排序函数,它会从一个"迭代器"返回一个排好序的新列表。
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reversed=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
# 创建决策树 参数:数据集、标签
def createTree(dataSet, labels):
"""
输入:数据集,特征标签
输出:决策树
描述:递归构建决策树,利用上述的函数
"""
# 截取dataSet的最后一行
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
# 数据集都是同一类的情况
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
# 遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的
#print('bb',dataSet[1])
# 如果数据集只有一个特征的情况
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
# 最大增益率的属性作为分裂属性
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) # 最好的特征
# print('bestFeat',bestFeat) # 0 2 当选择0(outlook)之后 剩下的012中选择2(windy)中
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] # 最好的分类
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
# print(myTree) # {'outlook': {}} {'windy': {}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
# 得到列表包括节点所有的属性值
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
# print('featValues',featValues)
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
# print('uniqueVals',uniqueVals)
for value in uniqueVals:
# 去掉前面标签之后剩下的标签
subLabels = labels[:]
# print('subLabels',subLabels)
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), subLabels)
# print('myTree',myTree)
return myTree def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec):
"""
输入:决策树,分类标签,测试数据
输出:决策结果
描述:跑决策树
"""
firstStr = list(inputTree.keys())[0]
# print('t2',firstStr)
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
#print('t3',secondDict)
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
# print('t4',featIndex)
for key in secondDict.keys():
#print('key',key)
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
#print('testVec[featIndex]',testVec[featIndex])
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = secondDict[key]
# print('t5',classLabel)
return classLabel
# 通过输入的决策树和对应的标签 来对测试集合 进行预测
def classifyAll(inputTree, featLabels, testDataSet):
"""
输入:决策树,分类标签,测试数据集
输出:决策结果
描述:跑决策树
"""
# 空列表
classLabelAll = []
for testVec in testDataSet:
# print('t1',testVec)
# 将预测结果插入到classLabelAll中
classLabelAll.append(classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec))
# print("t6",classLabelAll)
return classLabelAll # 训练集
def createDataSet():
"""
天气情况 outlook-> sunny | overcast | rain
温度情况 temperature-> hot | mild | cool
湿度情况 humidity-> high | normal
风力情况 windy-> false | true
"""
######## no or yes is play golf ???
dataSet = [["sunny", "hot", "high", "false", 'no'],
["sunny", "hot", "high", "true", 'no'],
["overcast", "hot", "high", "false", 'yes'],
["rain", "mild", "high", "false", 'yes'],
["rain", "cool", "normal", "false", 'yes'],
["rain", "cool", "normal", "true", 'no'],
["overcast","cool", "normal", "true", 'no'],
["rain", "hot", "high", "true", 'yes'],
["sunny", "mild", "high", "true", 'no'],
["rain", "hot", "normal", "true", 'yes'],
["overcast","mild", "high", "false", 'no']]
# 对应的标签
labels = ['outlook', 'temperature', 'humidity', 'windy']
return dataSet, labels
# 测试集
def createTestSet():
testSet = [["sunny", "mild", "high", "false"],
["sunny", "cool", "normal", "false"],
["rain", "mild", "normal", "false"],
["sunny", "mild", "normal", "true"],
["overcast","mild", "high", "true"],
["rain", "hot", "normal", "true"],
["sunny", "mild", "normal", "false"],
["rain", "hot", "high", "true"],
["sunny", "mild", "high", "true"],
["rain", "hot", "normal", "true"],
["overcast", "mild", "high", "false"],
["rain", "mild", "high", "true"]]
return testSet
#主函数 定义
def main():
dataSet, labels = createDataSet()
labels_tmp = labels[:] # 拷贝 labels
Tree = createTree(dataSet, labels_tmp)
print('Tree:\n', Tree)
treePlotter.createPlot(Tree)
print('------------------------------')
# 获取测试集 进行预测
testSet = createTestSet()
print('classifyResult:\n', classifyAll(Tree, labels, testSet))
# 调用主函数
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
treePlotter.py 用来画决策树。 代码如下所示:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义文本框和箭头格式
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
# 绘制带箭头的注释
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', \
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', \
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args)
''' 获得决策树的叶节点数 '''
def getNumLeafs(myTree):
numLeafs = 0
# fistStr获得字典的键 代表树根
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] # 头结点
# print('firstStr',firstStr)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr] # 取出头结点的的字典
for key in secondDict.keys(): # 测试节点的数据类型是否为字典
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key])
else:
numLeafs += 1
return numLeafs
''' 求树的深度 '''
def getTreeDepth(myTree):
maxDepth = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] # 头结点
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in secondDict.keys(): # 测试节点的数据类型是否为字典
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) + 1
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > maxDepth:
maxDepth = thisDepth
return maxDepth
''' 在父子节点之间填充文本信息 '''
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
''' 根节点坐标 '''
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) # 子节点数量
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) # 深度
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] # 根节点的key
'''X坐标=节点的x偏移量 + 叶节点数距离
所有该节点下子叶子节点的距离:numLeafs / plotTree.totalW
但是坐标在叶子节点的中心:numLeafs / 2 / plotTree.totalW
又因为xOff初始坐标点在原点的左边:numLeafs / 2 / plotTree.totalW + 0.5 / plotTree.totalW ,这是偏移量
那么x = numLeafs / 2 / plotTree.totalW + 0.5 / plotTree.totalW + plotTree.xOff
'''
# 根节点坐标
# 叶子节点距离
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalw, plotTree.yOff)
# 标记子节点属性值
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalw
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
# plot构建树
def createPlot(inTree):
# figure语法 创建自定义图像 定义了一个框架
# num:图像编号或名称,数字为编号
# facecolor:背景颜色
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
#plt.close()将完全关闭图形窗口
# plt.clf()将清除图形-您仍然可以在其上绘制另一个绘图。
fig.clf()
# xticks是一个列表,其中的元素就是x轴上将显示的坐标
# yticks是y轴上显示的坐标,这里空列表则不显示坐标
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
# 这里定义一个子图窗口
# 第一个参数xyz含义是,将框架划分为x行y列窗口,ax1代表其第z个窗口。
# ps:111 就是一行一列第一个窗口
# frameon = False将隐藏坐标轴
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
# plotTree.totalW是决策树的叶子树,也代表宽度
plotTree.totalw = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
# plotTree.totalD是决策树的深度
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
# 方便后面加上 1.0 / plotTree.totalW 后位置刚好在中间
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalw
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
# 调用函数plotTree(),绘制整棵决策树,最后显示出来。
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()
运行结果如下所示:

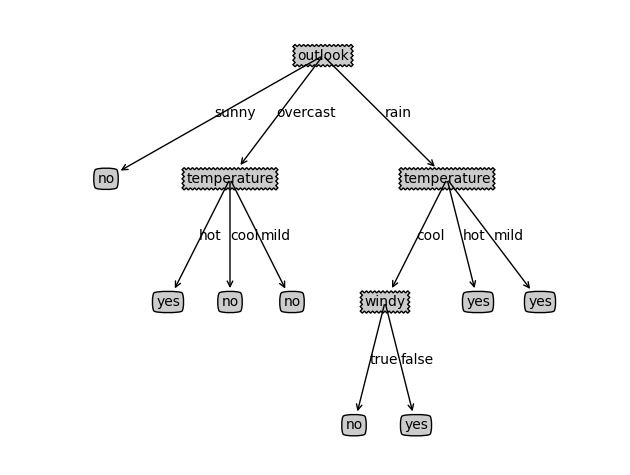
一个简单的C4.5算法,采用Python语言的更多相关文章
- 实现一个简单的邮箱地址爬虫(python)
我经常收到关于email爬虫的问题.有迹象表明那些想从网页上抓取联系方式的人对这个问题很感兴趣.在这篇文章里,我想演示一下如何使用python实现一个简单的邮箱爬虫.这个爬虫很简单,但从这个例子中你可 ...
- 实现一个简单的虚拟demo算法
假如现在你需要写一个像下面一样的表格的应用程序,这个表格可以根据不同的字段进行升序或者降序的展示. 这个应用程序看起来很简单,你可以想出好几种不同的方式来写.最容易想到的可能是,在你的 JavaScr ...
- 通过创建一个简单的骰子游戏来探究 Python
在我的这系列的第一篇文章 中, 我已经讲解如何使用 Python 创建一个简单的.基于文本的骰子游戏.这次,我将展示如何使用 Python 模块 Pygame 来创建一个图形化游戏.它将需要几篇文章才 ...
- day-7 一个简单的决策树归纳算法(ID3)python编程实现
本文介绍如何利用决策树/判定树(decision tree)中决策树归纳算法(ID3)解决机器学习中的回归问题.文中介绍基于有监督的学习方式,如何利用年龄.收入.身份.收入.信用等级等特征值来判定用户 ...
- 通过编写一个简单的漏洞扫描程序学习Python基本语句
今天开始读<Python绝技:运用Python成为顶级黑客>一书,第一章用一个小例子来讲解Python的基本语法和语句.主要学习的内容有:1. 安装第三方库.2. 变量.字符串.列表.词典 ...
- 算法课上机实验(一个简单的GUI排序算法比较程序)
(在家里的电脑上Linux Deepin截的图,屏幕大一点的话,deepin用着还挺不错的说) 这个应该是大二的算法课程上机实验时做的一个小程序,也是我的第一个GUI小程序,实现什么的都记不清了,只记 ...
- C++写一个简单的解析器(分析C语言)
该方案实现了一个分析C语言的词法分析+解析. 注意: 1.简单语法,部分秕.它可以在本文法的基础上进行扩展,此过程使用自上而下LL(1)语法. 2.自己主动能达到求First 集和 Follow 集. ...
- 【学习笔记】PYTHON语言程序设计(北理工 嵩天)
1 Python基本语法元素 1.1 程序设计基本方法 计算机发展历史上最重要的预测法则 摩尔定律:单位面积集成电路上可容纳晶体管数量约2年翻倍 cpu/gpu.内存.硬盘.电子产品价格等都遵 ...
- 一个简单的多机器人编队算法实现--PID
用PID进行领航跟随法机器人编队控制 课题2:多机器人编队控制研究对象:两轮差动的移动机器人或车式移动机器人研究内容:平坦地形,编队的保持和避障,以及避障和队形切换算法等:起伏地形,还要考虑地形情况对 ...
- 一个简单的mock server
在前后端分离的项目中, 前端无需等后端接口提供了才调试, 后端无需等第三方接口提供了才调试, 基于“契约”,可以通过mock server实现调试, 下面是一个简单的mock server,通过pyt ...
随机推荐
- Spring的依赖注入方式(set及constructor)
Bean的依赖注入方式: set方法注入 P命名空间注入本质也是set方法注入,但比起上面的set方法进行注入更加方便,主要体现在配置文件中,如下: 首先,引入P命名空间: xmlns:p=" ...
- python打包方法
在Python中,要编写setup.py文件,用于构建和打包你的Python项目,你可以遵循以下步骤: 创建项目目录结构:首先,你需要创建项目的目录结构,包括源代码文件.资源文件等.一个常见的项目结构 ...
- Avalonia项目在OpenKylin运行踩坑
Avalonia项目在OpenKylin运行踩坑 本篇博客记录OpenKylin开源操作系统中运行Avalonia项目遇到的各种问题,会一直更新,最新的内容请点击文末的链接跳转到我的博客原文地址查看. ...
- 2021-6-16 TcpIp
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.T ...
- Angular:修改启动端口号
目标 修改预先设定的4200端口号,改为4100 解决方案 在启动命令中添加 --port 4100.参数 --open,会在启动时自动打开浏览器. ng serve --open --port 41 ...
- Django CSRF cookie not set.
错误原因 由于django框架的settings.py配置了中间件,为了防止跨站请求伪造,form表单POST方式会导致出现报错 解决办法: 将'django.middleware.csrf.Csrf ...
- 记一次使用pagehelper的坑(返回的total和size每页条数一致的问题)
问题描述 众所周知,pagehelper使用时应该在dao查询语句的前一句加上PageHelper.startPage,所以标题的问题由此引出-- 原因 PageHelper.startPage使用后 ...
- 在不修改代码情况下解决 Chrome 浏览器跨域
前言: 在前后台分离的项目,跨域是经常遇到的问题了.是实际解决方案中,大部分采用服务端配置,而如果只是调试,可以通过配置 Chrome 浏览器实现跨域,以下以 NodeJs 服务为例. 开始: 1. ...
- 避坑 | OI排雷新生态
可持久化线段树 query 的时候两结点的 sz 相减的时候一定是左儿子相减. 可持久化线段树建新点要将原来的不更改的节点连接上. 动态规划也可以倒着考虑. P3957的单调队列是先加入后删除,否则加 ...
- 配置DHCP
配置DHCP 条件:关闭防火墙 和selinux 1,安装dhcp服务 [root@localhost ~]#yum install dhcp -y#安装dhcp服务 2,查看配置文件 [root@l ...
