Apache Phoenix on CDH 5
We are happy to announce the inclusion of Apache Phoenix in Cloudera Labs.
[Update: A new package for Apache Phoenix 4.7.0 on CDH 5.7 was released in June 2016.]
Apache Phoenix is an efficient SQL skin for Apache HBase that has created a lot of buzz. Many companies are successfully using this technology, including Salesforce.com, where Phoenix first started.

With the news that Apache Phoenix integration with Cloudera’s platform has joined Cloudera Labs, let’s take a closer look at a few key questions surrounding Phoenix: What does it do? Why does anyone want to use it? How does it compare to existing solutions? Do the benefits justify replacing existing systems and infrastructure?
In this post, we’ll try to answers those questions by briefly introducing Phoenix and then discussing some of its unique features. I’ll also cover some use cases and compare Phoenix to existing solutions.
What is Apache Phoenix?
Phoenix adds SQL to HBase, the distributed, scalable, big data store built on Hadoop. Phoenix aims to ease HBase access by supporting SQL syntax and allowing inputs and outputs using standard JDBC APIs instead of HBase’s Java client APIs. It lets you perform all CRUD and DDL operations such as creating tables, inserting data, and querying data. SQL and JDBC reduce the amount of code users need to write, allow for performance optimizations that are transparent to the user, and opens the door to leverage and integrate lots of existing tooling.
Internally, Phoenix takes your SQL query, compiles it into a series of native HBase API calls, and pushes as much work as possible onto the cluster for parallel execution. It automatically creates a metadata repository that provides typed access to data stored in HBase tables. Phoenix’s direct use of the HBase API, along with coprocessors and custom filters, results in performance on the order of milliseconds for small queries, or seconds for tens of millions of rows.
Use Cases
Phoenix is good for fast HBase lookups. Its secondary indexing feature supports many SQL constructs and make lookup via non-primary key fields more efficient than full table scans. It simplifies the creation and management of typed row-centric data by providing composite row keys and by enforcing constraints on data when written using the Phoenix interfaces.
Phoenix provides a way to transparently salt the row key, which helps in avoiding the RegionServerhotspotting often caused by monotonically increasing rowkeys. It also provides multi-tenancy via a combination of multi-tenant tables and tenant-specific connections. With tenant-specific connections, tenants can only access data that belongs to them, and with multi-tenant tables, they can only see their own data in those tables and all data in regular tables.
Regardless of these helpful features, Phoenix is not a drop-in RDBMS replacement. There are some limitations:
- Phoenix doesn’t support cross-row transactions yet.
- Its query optimizer and join mechanisms are less sophisticated than most COTS DBMSs.
- As secondary indexes are implemented using a separate index table, they can get out of sync with the primary table (although perhaps only for very short periods.) These indexes are therefore not fully-ACID compliant.
- Multi-tenancy is constrained—internally, Phoenix uses a single HBase table.
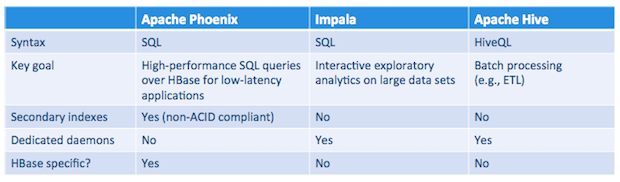
Comparisons to Hive and Impala
The other well known SQL alternatives to Phoenix on top of HBase are Apache Hive and Impala. There is significant overlap in the functionality provided by these products. For example, all of them follow SQL-like syntax and provide a JDBC driver.
Unlike Impala and Hive, however, Phoenix is intended to operate exclusively on HBase data; its design and implementation are heavily customized to leverage HBase features including coprocessors and skip scans.
Some other considerations include:
- The main goal of Phoenix is to provide a high-performance relational database layer over HBase for low-latency applications. Impala’s primary focus is to enable interactive exploration of large data sets by providing high-performance, low-latency SQL queries on data stored in popular Hadoop file formats. Hive is mainly concerned with providing data warehouse infrastructure, especially for long-running batch-oriented tasks.
- Phoenix is a good choice, for example, in CRUD applications where you need the scalability of HBase along with the facility of SQL access. In contrast, Impala is a better option for strictly analytic workloads and Hive is well suited for batch-oriented tasks like ETL.
- Phoenix is comparatively lightweight since it doesn’t need an additional server.
- Phoenix supports advanced functionality like multiple secondary-index implementations optimized for different workloads, flashback queries, and so on. Neither Impala nor Hive have any provision for supporting secondary index lookups yet.
The following table summarizes what we’ve discussed so far:
Installation
To install Phoenix, you will need HBase 1.0, which ships as part of CDH 5.4). Source code is available here.
- Find the Phoenix parcels here.
- Install the parcel into Cloudera Manager as explained here. This operation adds a new parcel repository to your Cloudera Manager configuration. Download, distribute, and activate the Phoenix parcel, following the instructions here.
- In case you are planning to use secondary indexing feature, please add the following to
hbase-site.xmlbefore restarting the HBase service.1234<property><name>hbase.regionserver.wal.codec</name><value>org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.wal.IndexedWALEditCodec</value></property> After you activate the Phoenix parcel, confirm that the HBase service is restarted.
Phoenix Command-line Tools
Important Phoenix command-line tools are located in /usr/bin. Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to your JDK installation directory before using the command-line.tools and ensure that java is available in PATH. For example:
|
1
2
|
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_67-cloudera
export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
|
- phoenix-sqlline.py is terminal interface to execute SQL from the command line. To start it, you need to specify the Apache ZooKeeper quorum of the corresponding HBase cluster (for example,
phoenix-sqlline.py zk01.example.com:2181). To execute SQL scripts from the command line, you can include a SQL file argument such assqlline.py zk01.example.com:2181 sql_queries.sql. - phoenix-psql.py is for loading CSV data and/or executing SQL scripts (example:
phoenix-psql.py zk01.example.com:2181 create_stmts.sql data.csv sql_queries.sql). - phoenix-performance.py is a script for creating as many rows as you want and running timed queries against them (example:
phoenix-psql.py zk01.example.com:2181 100000).
Future Work
The Phoenix project is investigating integration with transaction managers such as Tephra (from Cask). It is also trying to incorporate query optimizations based on the size and cardinality of the data. Although Phoenix supports tracing now, more work is needed to round out its monitoring and management capabilities.
Conclusion
Phoenix offers some unique functionality for a certain set of HBase use cases. As with everything else in Cloudera Labs, Phoenix integration is not supported yet and it’s for experimentation only. If you have any feedback or comments, let us know via the Cloudera Labs discussion forum.
Srikanth Srungarapu is a Software Engineer at Cloudera, and an HBase committer.
Apache Phoenix on CDH 5的更多相关文章
- [saiku] 使用 Apache Phoenix and HBase 结合 saiku 做大数据查询分析
saiku不仅可以对传统的RDBMS里面的数据做OLAP分析,还可以对Nosql数据库如Hbase做统计分析. 本文简单介绍下一个使用saiku去查询分析hbase数据的例子. 1.phoenix和h ...
- Apache Phoenix JDBC 驱动和Spring JDBCTemplate的集成
介绍:Phoenix查询引擎会将SQL查询转换为一个或多个HBase scan,并编排运行以生成标准的JDBC结果集. 直接使用HBase API.协同处理器与自己定义过滤器.对于简单查询来说,其性能 ...
- phoenix 报错:type org.apache.phoenix.schema.types.PhoenixArray is not supported
今天用phoenix报如下错误: 主要原因: hbase的表中某字段类型是array,phoenix目前不支持此类型 解决方法: 复制替换phoenix包的cursor文件 # Copyright 2 ...
- Mapreduce atop Apache Phoenix (ScanPlan 初探)
利用Mapreduce/hive查询Phoenix数据时如何划分partition? PhoenixInputFormat的源码一看便知: public List<InputSplit> ...
- org.apache.phoenix.exception.PhoenixIOException: SYSTEM:CATALOG
Error: SYSTEM:CATALOG (state=08000,code=101)org.apache.phoenix.exception.PhoenixIOException: SYSTEM: ...
- phoenix连接hbase数据库,创建二级索引报错:Error: org.apache.phoenix.exception.PhoenixIOException: Failed after attempts=36, exceptions: Tue Mar 06 10:32:02 CST 2018, null, java.net.SocketTimeoutException: callTimeou
v\:* {behavior:url(#default#VML);} o\:* {behavior:url(#default#VML);} w\:* {behavior:url(#default#VM ...
- apache phoenix 安装试用
备注: 本次安装是在hbase docker 镜像的基础上配置的,主要是为了方便学习,而hbase搭建有觉得 有点费事,用镜像简单. 1. hbase 镜像 docker pull har ...
- How to use DBVisualizer to connect to Hbase using Apache Phoenix
How to use DBVisualizer to connect to Hbase using Apache Phoenix Article DB Visualizer is a popular ...
- 关于Apache Phoenix和Cloudera结合
1. 安装: phoenix的官网最新版4.13.2是有parcle版本的,并不需要从cloudera的labs(实验室)中下载.安装完成后,可以运行一下phoenix的shell来简单验证一下:/o ...
随机推荐
- Effective C++ 改善55个方法
美·Scott Meyers 候捷 电子工业 2011 刚才看到个会议时间有点晚,3.25论文都提交了 谷歌去广告的插件, 最后投了这个会议,刚刚好正合适.我说金钱与时间 ACCUSTOMING YO ...
- MVC 和 MVR 的区别分析
MVC模式中,可以将路由绑定到控制器上.MVR是一对一的.路由和控制器是一个东西. 优点是需要被迫处理路由.缺点是不能在控制器被绑定到路由之前复用控制器. [1] node.js - Differen ...
- Docker部署Nginx应用(2)
Docker部署Nginx应用(2) 1.拉取Nginx镜像 [root@localhost ~]# docker pull nginx Using default tag: latest lates ...
- sql server 保留小数,向上保留指定位数的小数,仅记录,勿看。
比如 4.05 要取成 4.1 , 4.16 取成 4.2 ,4.5 取成 4.5 ,意思就是小数部分第二位不管是多少都丢掉然后加0.1,但是如果是 4.5 这样完整的就不需要处理. 可以像下面这么写 ...
- (转)python time模块和datetime模块详解
python time模块和datetime模块详解 原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/tkqasn/p/6001134.html 一.time模块 time模块中时间表现的格式主要 ...
- dfs.replication、dfs.replication.min/max及dfs.safemode.threshold.pct
一.参数含义 dfs.replication:设置数据块应该被复制的份数: dfs.replication.min:所规定的数据块副本的最小份数: dfs.replication.max:所规定的数据 ...
- 【ExtJS】FormPanel 布局(二)
周末2天好好学习了下布局,现在都给实现了吧. 5.border布局: Border布局将容器分为五个区域:north.south.east.west和center.除了center区域外,其他区域都需 ...
- jquery metadata 详解
1.0的版本是这样的$.meta 2.0的版本是这样的$.metadata 很多插件的编写都用到了这个插件,个人感觉这个东西应该是jquery官方的.推荐使用2.0的版本, 因为现在官方上就是2.0的 ...
- unity接入安卓sdk (unity调用安卓工程)
1.安装jdk 并且配置环境,这个网上资料很多,这里不说了 2.安卓开发软件eclipse集成环境版 下载地址 http://tools.android-studio.org/index.php/ad ...
- FocusBI: 总线矩阵(原创)
关注微信公众号:FocusBI 查看更多文章:加QQ群:808774277 获取学习资料和一起探讨问题. <商业智能教程>pdf下载地址 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/ ...
