Spring基础学习(二)—详解Bean(上)
在Spring配置文件中,用户不但可以将String、int等字面值注入Bean中,还可以将集合、Map等类型注入Bean中,此外还可以注入配置文件中其他定义的Bean。
一、字面值
(1)可用字符串表示的值,可以通过<value>元素标签或value属性进行注入。
(2)基本数据类型及其封装类、Stting类型都可以采用字面值注入的方式。
(3)若字面值包含特殊字符,可以使用<![CDATA[]]>把字面值包裹起来。
<bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" >
<value><![CDATA[BMW&x5]]></value>
</property>
<property name="color" value="Black"/>
<property name="price" value="800000"/>
<property name="maxSpeed" value="200"/>
</bean>
由于brand属性包含了一个XML的特殊符号,因此特意在属性值外添加一个XML特殊处理标签<![CDATA[]]>,这个标签的作用就是让XML解析器将标签中的字符串当作普通文本对待,以防止某些字符对XML格式造成破坏。
二、引用其他Bean
(1)要使Bean能相互访问,就必须在Bean的配置文件中指定对Bean的引用。
(2)在Bean的配置文件中,可以通过<ref>属性或元素配置。
(3)也可以在属性内部包含Bean的声明,这样的Bean称为内部Bean。
(4)内部Bean不能被外部使用。
Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
private Car car;
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", car=" + car + "]";
}
//省略get set...
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW"/>
<property name="color" value="Black"/>
<property name="price" value="800000"/>
<property name="maxSpeed" value="200"/>
</bean> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom"/>
<property name="age" value="26"/> <!-- 使用ref属性建立bean之间的引用关系 -->
<property name="car" ref="car"/> </bean> </beans>
Test.java
@Test
public void testCar(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Person person = (Person)context.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
结果:
Person [name=Tom, age=26, car=Car [brand=BMW, color=Black, price=800000.0, maxSpeed=200]]
如果不引用外部的Bean,可以在内部声明一个内部Bean,这个内部Bean不能被其他外部Bean引用。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="800000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="200" />
</bean> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom" />
<property name="age" value="26" /> <!-- 定义一个内部bean,内部bean外面不能引用 -->
<property name="car">
<bean class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="Audi" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="300000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="250" />
</bean>
</property> </bean> </beans>
结果:
Person [name=Tom, age=26, car=Car [brand=Audi, color=Black, price=300000.0, maxSpeed=250]]
也可以为级联属性赋值。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="800000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="200" />
</bean> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom" />
<property name="age" value="26" />
<property name="car" ref="car"/>
<!-- 为级联属性赋值,前提是属性先初始化然后才可以为其级联属性赋值 -->
<property name="car.maxSpeed" value="250"/> </bean> </beans>
结果:
Person [name=Tom, age=26, car=Car [brand=BMW, color=Black, price=800000.0, maxSpeed=250]]
三、集合属性
1.List和Set
(1)配置List需要指定<list>标签,标签里包含一些元素,这些元素可以通过<value>指定简单的常量值,也可以使用<ref>指定对其他Bean的引用。
(2)配置set需要使用<set>标签,其他属性和List一样。
Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
private List<Car> cars;
//省略get set...
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="800000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="300" />
</bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="Audi" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="400000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="250" />
</bean> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom" />
<property name="age" value="26" />
<!-- 配置集合属性List -->
<property name="cars"> <list>
<ref bean="car"/>
<ref bean="car2"/>
</list> </property>
</bean> </beans>
结果:
Person [name=Tom, age=26, cars=[Car [brand=BMW, color=Black, price=800000.0, maxSpeed=300], Car [brand=Audi, color=Black, price=400000.0, maxSpeed=250]]]
2.Map
(1)通过<map>标签定义,子标签使用<entry>标签。
(2)在<entry>标签里可以使用key、key-ref、value、value-ref属性。
Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private int age;
private Map<String,Car> cars;
//省略get set...
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="800000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="300" />
</bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="Audi" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="400000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="250" />
</bean> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom" />
<property name="age" value="26" /> <!-- 配置集合属性Map -->
<property name="cars">
<map>
<entry key="1" value-ref="car"/>
<entry key="2" value-ref="car2"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean> </beans>
结果:
Person [name=Tom, age=26, cars={1=Car [brand=BMW, color=Black, price=800000.0, maxSpeed=300], 2=Car [brand=Audi, color=Black, price=400000.0, maxSpeed=250]}]
3.Properties
Properties类型可以看作Map类型的特例,Map元素的键和值可以是任何类型的对象,而Properties的键和值只能是字符串。
Boss.java
public class Boss{
private Properties mails;
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Boss [mails=" + mails + "]";
}
public Properties getMails(){
return mails;
}
public void setMails(Properties mails){
this.mails = mails;
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<bean name="boss" class="com.kiwi.domain.Boss">
<property name="mails">
<props>
<prop key="jobMail">123@126.com</prop>
<prop key="lifeMail">789@qq.com</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
结果:
Boss [mails={lifeMail=789@qq.com, jobMail=123@126.com}]
4.配置集合类型的Bean
(1)使用基本集合标签定义集合时,不能将集合作为独立的Bean定义,导致其他Bean无法引用该集合,所以无法在不同Bean直接共享集合。
(2)如果希望配置一个集合类型的Bean,而非一个集合类型的属性,则可以通过util命名空间进行配置。
(3)必须先引用util命名空间才能使用。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="BMW" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="800000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="300" />
</bean> <bean id="car2" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car">
<property name="brand" value="Audi" />
<property name="color" value="Black" />
<property name="price" value="400000" />
<property name="maxSpeed" value="250" />
</bean> <!-- 定义一个公共的Map其他Bean能够直接引用它 -->
<util:map id="cars">
<entry key="1" value-ref="car"/>
<entry key="2" value-ref="car2"/>
</util:map> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="Tom" />
<property name="age" value="26" />
<!-- 引用公共的Map -->
<property name="cars" ref="cars"/>
</bean> </beans>
四、使用p命名空间
为了简化XML文件的配置,越来越多的XML文件采用属性而非子元素配置信息。
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car"
p:brand="AuDi" p:color="Silver"
p:price="500000" p:maxSpeed="3000"/> <bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person"
p:name="Tom" p:age="27" p:car-ref="car"/> </beans>
这样写省略了<property>的子标签,使配置文件更加简洁。
五、自动装配
<bean>元素提供了一个指定自动装配类型的属性:atuowire。Spring提供了4种自动装配类型。
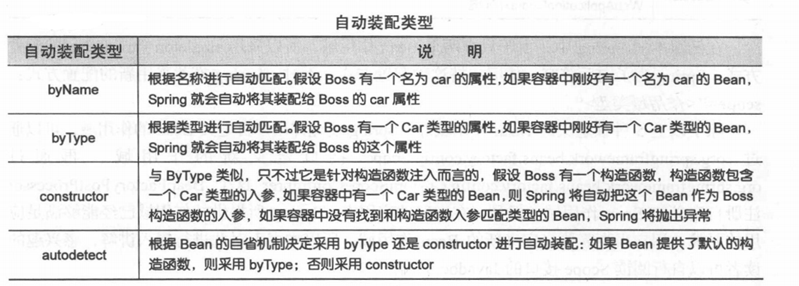
Person.java
public class Person{
private String name;
private Car car;
private Address address;
//...
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd"> <bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car"
p:brand="LandRover"
p:price="1200000"
/> <bean id="address" class="com.kiwi.domain.Address"
p:province="BJ"
p:city="CangPing"
/> <!--
可以使用autowire属性指定自动装配的方式 。
byName: 根据名称自动装配,必须将目标bean的名称和属性名设置的完全相同。
byType: 根据类型自动装配,若IOC容器中有多个与目标 bean类型一致的 bean,
在这种情况下,Spring 将无法判定哪个bean最合适该属性,所以不能执行自动装配。
-->
<bean id="person" class="com.kiwi.domain.Person"
p:name="Tom"
autowire="byName"
/> </beans>
结果:
Person [name=Tom, car=Car [brand=LandRover, price=1200000.0], address=Address [province=BJ, city=CangPing]]
一般情况下,在实际的项目中很少使用自动装配功能,因为和自动装配功能所带来的好处比起来,明确清晰的配置文档更有说服力一些。
六、Bean之间的关系
Bean直接存在两种关系: 继承、依赖。
1.继承
(1)Spring允许继承bean的配置,被继承的bean称为父bean。
(2)子bean从父bean继承配置,包括属性配置,也可以覆盖父bean的配置。
(3)若只想把父bean作为模板,可以设置其属性abstract属性为true,这样Spring将不会实例化这个bean。
(4)并不是<bean>所有的属性都会被继承,比如:autowire、abstract。
applicationContext.xml
<bean id="address" class="com.kiwi.domain.Address"
p:province="BJ"
p:city="CangPingQu"
/> <bean id="address2" parent="address"
p:city="HaiDianQu"
/>
结果:
Address [province=BJ, city=CangPingQu]
Address [province=BJ, city=HaiDianQu]
2.依赖
depend-on: 表示一个bean的实例化依靠另一个bean先实例化。如果在一个bean A上定义了depend-on B那么就表示:A 实例化前先实例化 B。这种情况下,A可能根本不需要持有一个B对象。
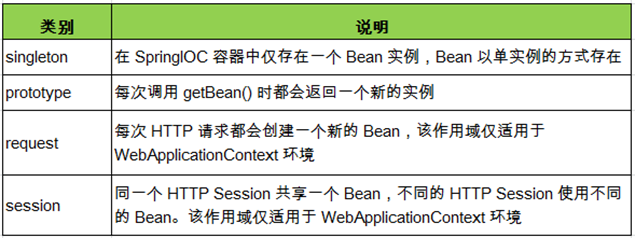
七、Bean的作用域
(1)在Spring中,可以在<bean>元素的scope属性设置Bean的作用域。
(2)默认情况下,Spring只为每个IOC容器里声明Bean创建唯一的一个实例,整个IOC容器都能共享该实例,该作用域为默认的singleton。
applicationContext.xml
<!--
使用bean的scope属性来配置bean的作用域
singleton: 默认值。容器初始化时创建bean实例,在整个容器生命周期内只创建这一个bean,单例的。
prototype: 容器初始化时不创建bean的实例,而在每次getBean()时都创建一个实例。
-->
<bean id="car" class="com.kiwi.domain.Car"
p:brand="LandRover"
p:price="1200000"
scope="singleton"
/>
Test.java
@Test
public void testCar(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Car car = (Car)context.getBean("car");
Car car2 = (Car)context.getBean("car");
System.out.println(car == car2);
}
结果:
true
如果修改为scope="prototype",结果将返回false。
Spring基础学习(二)—详解Bean(上)的更多相关文章
- Spring基础学习(三)—详解Bean(下)
一.Bean的生命周期 1.概述 Spring IOC容器可以管理Bean的生命周期,Spring 允许在Bean的生命周期的特定点执行定制的任务. Spring IOC容器对Be ...
- 框架基础学习之--详解web+maven+spring+mybatis+struts框架文件夹作用
详解web+maven+spring+mybatis+struts框架文件夹作用 1.程序名 2.Mybatis,mybatis是数据持久层,就是和对象类有关系的东西 3.存放java文件,xml,p ...
- C#基础表达式语句详解(上)
本节内容: 1.表达式的定义: 2.各类表达式概览: 3.语句的定义: 4.语句详解: 1.表达式的定义: 1.1什么是表达式: (定义见下图)各类编程语言对表达式的实现不尽相同,但大体上都符合这个定 ...
- Spring框架系列(8) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之Bean实例化(生命周期,循环依赖等)
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:以及Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的:容器中存放的是Bean的定义即Be ...
- Spring第三天,详解Bean的生命周期,学会后让面试官无话可说!
点击下方链接回顾往期 不要再说不会Spring了!Spring第一天,学会进大厂! Spring第二天,你必须知道容器注册组件的几种方式!学废它吊打面试官! 今天讲解Spring中Bean的生命周期. ...
- iOS 开发之照片框架详解之二 —— PhotoKit 详解(上)
转载自:http://kayosite.com/ios-development-and-detail-of-photo-framework-part-two.html 一. 概况 本文接着 iOS 开 ...
- spring框架 AOP核心详解
AOP称为面向切面编程,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等待,Struts2的拦截器设计就是基于AOP的思想,是个比较经典的例子. 一 AOP的基本概念 (1)Asp ...
- Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC体系结构设计
在对IoC有了初步的认知后,我们开始对IOC的实现原理进行深入理解.本文将帮助你站在设计者的角度去看IOC最顶层的结构设计.@pdai Spring框架系列(6) - Spring IOC实现原理详解 ...
- Spring框架系列(7) - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构:紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的. ...
随机推荐
- Linux-7.2+LNMP+zabbix-3.2.1
LNMP+zabbix-3.2.1 一.zabbix服务端部署 1.解压 yum –y install bzip2 tar -xf nginx-1.10.1.tar.gz tar -xf php-5. ...
- 安装MongoDB x86_64
1.下载MongoDB 下载mongodb的windows版本,有32位和64位版本,根据系统情况下载,下载地址:http://www.mongodb.org/downloads 2.安装MongoD ...
- 最新虚拟机SAP ECC6.0 EHP7带示例数据IDES版+BW740
学习SAP,需要虚拟机,请联系QQ:858-048-581 版本:ECC6.0 EHP7.虚拟机操作系统:windows server 2008 64bit..数据库:SQL2008 R2.系统已经做 ...
- C# TCP多线程服务器示例
前言 之前一直很少接触多线程这块.这次项目中刚好用到了网络编程TCP这块,做一个服务端,需要使用到多线程,所以记录下过程.希望可以帮到自己的同时能给别人带来一点点收获- 关于TCP的介绍就不多讲,神马 ...
- Hibernate框架Criteria查询
本文章适合一些初学者 一.使用Criteria查询数据 1.条件查询 1.1:使用Criteria查询的步骤 1.使用Sess ...
- java线程学习(一)
1.简介 java基础知识部分线程创建的三种方式.线程执行的样例. 代码地址:http://git.oschina.net/blue_phantom/javaj 包位置:package com.blu ...
- Bat再次小试
继<Bat小试牛刀>之后,今天又需要一个小的bat文件.需求是这样的,有一个windows服务(服务名:xxxx,进程映像名:xxxx.exe)被数据库拖慢了,但目前又没时间调整代码,所以 ...
- grpc-gateway:grpc对外提供http服务的解决方案
我所在公司的项目是采用基于Restful的微服务架构,随着微服务之间的沟通越来越频繁,就希望可以做成用rpc来做内部的通讯,对外依然用Restful.于是就想到了google的grpc. 使用grpc ...
- 锋利的jQuery事件
一:事件 1.鼠标事件 (1)$()是$(document)的简写,默认参数是document. $(function(){}是$(document).ready(function(){})的简写. ...
- WeMall微商城源码投票插件Vote的主要源码
WeMall微信商城源码投票插件Vote,用于商城的签到系统,分享了部分比较重要的代码,供技术员学习参考 AdminController.class.php <?php namespace Ad ...
