Python基础(函数-递归)
本章内容:
- 深浅拷贝
- 函数(全局与局部变量)
- 内置函数
- 文件处理
- 三元运算
- lambda 表达式
- 递归(斐波那契数列)
- 冒泡排序
深浅拷贝
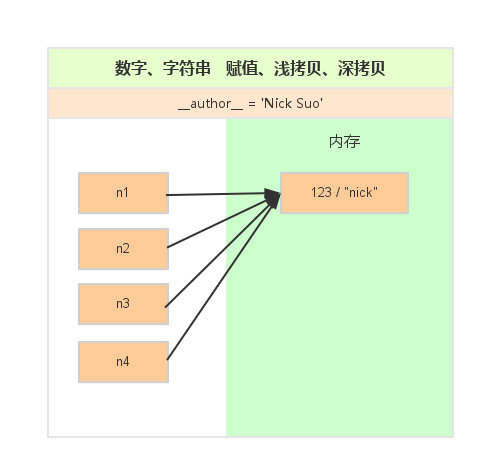
一、数字和字符串
对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import copy#定义变量 数字、字符串n1 = 123#n1 = 'nick'print(id(n1))#赋值n2 = n1print(id(n2))#浅拷贝n3 = copy.copy(n1)print(id(n3))#深拷贝n4 = copy.deepcopy(n1)print(id(n4)) |
二、字典、元祖、列表
对于字典、元祖、列表 而言,进行赋值、浅拷贝和深拷贝时,其内存地址的变化是不同的。
1、赋值
创建一个变量,该变量指向原来内存地址
|
1
2
|
n1 = {"k1": "nick", "k2": 123, "k3": ["jenny", 666]}n2 = n1 |

2、浅拷贝
在内存中只额外创建第一层数据
|
1
2
3
4
|
import copy n1 = {"k1": "nick", "k2": 123, "k3": ["jenny", 666]}n2 = copy.copy(n1) |

3、深拷贝
在内存中将所有的数据重新创建一份(排除最后一层,即:python内部对字符串和数字的优化)
|
1
2
3
4
|
import copy n1 = {"k1": "nick", "k2": 123, "k3": ["jenny", 666]}n2 = copy.deepcopy(n1) |

函数
一、定义和使用
函数式编程最重要的是增强代码的重用性和可读性
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
def 函数名(参数): ... 函数体 ... 返回值 |
函数的定义主要有如下要点:
- def:表示函数的关键字
- 函数名:函数的名称,日后根据函数名调用函数
- 函数体:函数中进行一系列的逻辑计算
- 参数:为函数体提供数据
- 返回值:当函数执行完毕后,可以给调用者返回数据。
1、返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
def 发送邮件(): 发送邮件的代码... if 发送成功: return True else: return False while True: # 每次执行发送邮件函数,都会将返回值自动赋值给result # 之后,可以根据result来写日志,或重发等操作 result = 发送邮件() if result == False: 记录日志,邮件发送失败... |
2、参数
函数的有三中不同的参数:
- 普通参数
- 默认参数
- 动态参数
#定义函数
#n 叫做函数 name 的形式参数,简称:形参 def name(n):
print(n) #执行函数
#'nick' 叫做函数 name 的实际参数,简称:实参 name('nick')
def func(name, age = 18):
print("%s:%s")%(name,age) # 指定参数
func('nick', 19)
# 使用默认参数
func('nick') 注:默认参数需要放在参数列表最后
def func(*args):
print args # 执行方式一
func(11,22,33,55,66) # 执行方式二
li = [11,22,33,55,66]
func(*li)
def func(**kwargs):
print kwargs # 执行方式一
func(name='nick',age=18) # 执行方式二
li = {'name':'nick', age:18, 'job':'pythoner'}
func(**li)
def hi(a,*args,**kwargs):
print(a,type(a))
print(args,type(args))
print(kwargs,type(kwargs))
hi(11,22,33,k1='nick',k2='jenny')
#发送邮件实例
def mail(主题,邮件内容='test',收件人='630571017@qq.com'):
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
from email.utils import formataddr msg = MIMEText(邮件内容, 'plain', 'utf-8')
msg['From'] = formataddr(["发件人", '发件人地址'])
msg['To'] = formataddr(["收件人", '630571017@qq.com'])
msg['Subject'] = 主题 server = smtplib.SMTP("smtp.126.com", 25)
server.login("登录邮箱账号", "邮箱密码")
server.sendmail('发件邮箱地址账号', [收件人地址, ], msg.as_string())
server.quit() mail('我是主题',收件人='630571017@qq.com',邮件内容='邮件内容')
mail(主题='我是主题',)
3、全局与局部变量
全局变量在函数里可以随便调用,但要修改就必须用 global 声明
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
############### 全 局 与 局 部 变 量 ###############全局变量P = 'nick'def name(): global P #声明修改全局变量 P = 'jenny' #局部变量 print(P)def name2(): print(P)name()name2() |
内置函数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
|
###### 求绝对值 #######a = abs(-95)print(a)###### 只有一个为假就为假 ########a = all([True,True,False])print(a)###### 只有一个为真就为真 ########a = any([False,True,False])print(a)####### 返回一个可打印的对象字符串方式表示 ########a = ascii('0x\10000')b = ascii('b\x19')print(a,b)######### 将整数转换为二进制字符串 ############a = bin(95)print(a)######### 将一个数字转化为8进制 ##############a = oct(95)print(a)######### 将一个数字转化为10进制 #############a = int(95)print(a)######### 将整数转换为16进制字符串 ##########a = hex(95)print(a)######### 转换为布尔类型 ###########a = bool('')print(a)######### 转换为bytes ########a = bytes('索宁',encoding='utf-8')print(a)######## chr 返回一个字符串,其ASCII码是一个整型.比如chr(97)返回字符串'a'。参数i的范围在0-255之间。 #######a = chr(88)print(a)######## ord 参数是一个ascii字符,返回值是对应的十进制整数 #######a = ord('X')print(a)######## 创建数据字典 ########dict({'one': 2, 'two': 3})dict(zip(('one', 'two'), (2, 3)))dict([['two', 3], ['one', 2]])dict(one=2, two=3)###### dir 列出某个类型的所有可用方法 ########a = dir(list)print(a)###### help 查看帮助文档 #########help(list)####### 分别取商和余数 ######a = divmod(9,5)print(a)##### 计算表达式的值 #####a = eval('1+2*2')print(a)###### exec 用来执行储存在字符串或文件中的Python语句 ######exec(print("Hi,girl."))exec("print(\"hello, world\")")####### filter 过滤 #######li = [1,2,3,4,5,6]a = filter(lambda x:x>3,li)for i in a:print(i)##### float 浮点型 #####a = float(1)print(a)###### 判断对象是不是属于int实例 #########a = 5b = isinstance(a,int)print(b)######## globals 返回全局变量 ################ locals 返回当前局部变量 ######name = 'nick'def hi(): a = 1 print(locals())hi()print(globals())########## map 遍历序列,对序列中每个元素进行操作,最终获取新的序列。 ##########li = [11,22,33]def func1(arg): return arg + 1 #这里乘除都可以new_list = map(func1,li) #这里map调用函数,函数的规则你可以自己指定,你函数定义成什么他就做什么操作!for i in new_list:print(i)###### max 返回集合中的最大值 ############ min 返回集合中的最小值 ######a = [1,2,3,4,5]s = max(a)print(s)n = min(a)print(n)####### pow 返回x的y次幂 ########a = pow(2,10)print(a)a = pow(2,10,100) #等于2**10%100,取模print(a)######## round 四舍五入 ########a = round(9.5)print(a)######## sorted 队集合排序 ########char=['索',"123", "1", "25", "65","679999999999", "a","B","nick","c" ,"A", "_", "ᒲ",'a钱','孙','李',"余", '佘',"佗", "㽙", "铱", "啊啊啊啊"]new_chat = sorted(char)print(new_chat)for i in new_chat: print(bytes(i, encoding='utf-8'))######## sum 求和的内容 ########a = sum([1,2,3,4,5])print(a)a = sum(range(6))print(a)######## __import__ 通过字符串的形式,导入模块 ######### 通过字符串的形式,导入模块。起个别名ccascomm = input("Please:")ccas = __import__(comm)ccas.f1()# 需要做拼接时后加 fromlist=Truem = __import__("lib."+comm, fromlist=True) |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
lt(a, b) 相当于 a < ble(a,b) 相当于 a <= beq(a,b) 相当于 a == bne(a,b) 相当于 a != bgt(a,b) 相当于 a > bge(a, b)相当于 a>= b |
zip函数接受任意多个(包括0个和1个)序列作为参数,返回一个tuple列表。具体意思不好用文字来表述,直接看示例: 1.示例1: 复制代码
x = [1, 2, 3] y = [4, 5, 6] z = [7, 8, 9] xyz = zip(x, y, z) print xyz
复制代码
运行的结果是: [(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)] 从这个结果可以看出zip函数的基本运作方式。 2.示例2: x = [1, 2, 3]
y = [4, 5, 6, 7]
xy = zip(x, y)
print xy
运行的结果是: [(1, 4), (2, 5), (3, 6)] 从这个结果可以看出zip函数的长度处理方式。 3.示例3: x = [1, 2, 3]
x = zip(x)
print x
运行的结果是: [(1,), (2,), (3,)] 从这个结果可以看出zip函数在只有一个参数时运作的方式。 4.示例4: x = zip()
print x
运行的结果是: [] 从这个结果可以看出zip函数在没有参数时运作的方式。 5.示例5: 复制代码
x = [1, 2, 3] y = [4, 5, 6] z = [7, 8, 9] xyz = zip(x, y, z) u = zip(*xyz) print u
复制代码
运行的结果是: [(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6), (7, 8, 9)] 一般认为这是一个unzip的过程,它的运行机制是这样的: 在运行zip(*xyz)之前,xyz的值是:[(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)] 那么,zip(*xyz) 等价于 zip((1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)) 所以,运行结果是:[(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6), (7, 8, 9)] 注:在函数调用中使用*list/tuple的方式表示将list/tuple分开,作为位置参数传递给对应函数(前提是对应函数支持不定个数的位置参数) 6.示例6: x = [1, 2, 3]
r = zip(* [x] * 3)
print r
运行的结果是: [(1, 1, 1), (2, 2, 2), (3, 3, 3)] 它的运行机制是这样的: [x]生成一个列表的列表,它只有一个元素x [x] * 3生成一个列表的列表,它有3个元素,[x, x, x] zip(* [x] * 3)的意思就明确了,zip(x, x, x)
文件处理
open函数,该函数用于文件处理
一、打开文件
|
1
|
文件句柄 = open('文件路径', '模式') |
打开文件时,需要指定文件路径和以何等方式打开文件,打开后,即可获取该文件句柄,日后通过此文件句柄对该文件操作。
打开文件的模式有:
- r ,只读模式【默认】
- w,只写模式【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则清空内容】
- x, 只写模式【不可读;不存在则创建,存在则报错】
- a, 追加模式【不可读;不存在则创建;存在则只追加内容】
"+" 表示可以同时读写某个文件
- r+, 读写【可读,可写】
- w+,写读【可读,可写】
- x+ ,写读【可读,可写】
- a+, 写读【可读,可写】
"b"表示以字节的方式操作
- rb 或 r+b
- wb 或 w+b
- xb 或 w+b
- ab 或 a+b
注:以b方式打开时,读取到的内容是字节类型,写入时也需要提供字节类型
二、操作
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
####### r 读 #######f = open('test.log','r',encoding='utf-8')a = f.read()print(a)###### w 写(会先清空!!!) ######f = open('test.log','w',encoding='utf-8')a = f.write('car.\n索宁')print(a) #返回字符####### a 追加(指针会先移动到最后) ########f = open('test.log','a',encoding='utf-8')a = f.write('girl\n索宁')print(a) #返回字符####### 读写 r+ ########f = open('test.log','r+',encoding='utf-8')a = f.read()print(a)f.write('nick')##### 写读 w+(会先清空!!!) ######f = open('test.log','w+',encoding='utf-8')a = f.read()print(a)f.write('jenny')######## 写读 a+(指针先移到最后) #########f = open('test.log','a+',encoding='utf-8')f.seek(0) #指针位置调为0a = f.read()print(a)b = f.write('nick')print(b)####### rb #########f = open('test.log','rb')a = f.read()print(str(a,encoding='utf-8'))# ######## ab #########f = open('test.log','ab')f.write(bytes('索宁\ncar',encoding='utf-8'))f.write(b'jenny')##### 关闭文件 ######f.close()##### 内存刷到硬盘 #####f.flush()##### 获取指针位置 #####f.tell()##### 指定文件中指针位置 #####f.seek(0)###### 读取全部内容(如果设置了size,就读取size字节) ######f.read()f.read(9)###### 读取一行 #####f.readline()##### 读到的每一行内容作为列表的一个元素 #####f.readlines() |
class file(object)
def close(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
关闭文件
"""
close() -> None or (perhaps) an integer. Close the file. Sets data attribute .closed to True. A closed file cannot be used for
further I/O operations. close() may be called more than once without
error. Some kinds of file objects (for example, opened by popen())
may return an exit status upon closing.
""" def fileno(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
文件描述符
"""
fileno() -> integer "file descriptor". This is needed for lower-level file interfaces, such os.read().
"""
return 0 def flush(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
刷新文件内部缓冲区
""" flush() -> None. Flush the internal I/O buffer. """
pass def isatty(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
判断文件是否是同意tty设备
""" isatty() -> true or false. True if the file is connected to a tty device. """
return False def next(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取下一行数据,不存在,则报错
""" x.next() -> the next value, or raise StopIteration """
pass def read(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取指定字节数据
"""
read([size]) -> read at most size bytes, returned as a string. If the size argument is negative or omitted, read until EOF is reached.
Notice that when in non-blocking mode, less data than what was requested
may be returned, even if no size parameter was given.
"""
pass def readinto(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取到缓冲区,不要用,将被遗弃
""" readinto() -> Undocumented. Don't use this; it may go away. """
pass def readline(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
仅读取一行数据
"""
readline([size]) -> next line from the file, as a string. Retain newline. A non-negative size argument limits the maximum
number of bytes to return (an incomplete line may be returned then).
Return an empty string at EOF.
"""
pass def readlines(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
读取所有数据,并根据换行保存值列表
"""
readlines([size]) -> list of strings, each a line from the file. Call readline() repeatedly and return a list of the lines so read.
The optional size argument, if given, is an approximate bound on the
total number of bytes in the lines returned.
"""
return [] def seek(self, offset, whence=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
指定文件中指针位置
"""
seek(offset[, whence]) -> None. Move to new file position. Argument offset is a byte count. Optional argument whence defaults to
(offset from start of file, offset should be >= 0); other values are 1
(move relative to current position, positive or negative), and 2 (move
relative to end of file, usually negative, although many platforms allow
seeking beyond the end of a file). If the file is opened in text mode,
only offsets returned by tell() are legal. Use of other offsets causes
undefined behavior.
Note that not all file objects are seekable.
"""
pass def tell(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
获取当前指针位置
""" tell() -> current file position, an integer (may be a long integer). """
pass def truncate(self, size=None): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
截断数据,仅保留指定之前数据
"""
truncate([size]) -> None. Truncate the file to at most size bytes. Size defaults to the current file position, as returned by tell().
"""
pass def write(self, p_str): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
写内容
"""
write(str) -> None. Write string str to file. Note that due to buffering, flush() or close() may be needed before
the file on disk reflects the data written.
"""
pass def writelines(self, sequence_of_strings): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
将一个字符串列表写入文件
"""
writelines(sequence_of_strings) -> None. Write the strings to the file. Note that newlines are not added. The sequence can be any iterable object
producing strings. This is equivalent to calling write() for each string.
"""
pass def xreadlines(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
可用于逐行读取文件,非全部
"""
xreadlines() -> returns self. For backward compatibility. File objects now include the performance
optimizations previously implemented in the xreadlines module.
"""
pass
class TextIOWrapper(_TextIOBase):
"""
Character and line based layer over a BufferedIOBase object, buffer. encoding gives the name of the encoding that the stream will be
decoded or encoded with. It defaults to locale.getpreferredencoding(False). errors determines the strictness of encoding and decoding (see
help(codecs.Codec) or the documentation for codecs.register) and
defaults to "strict". newline controls how line endings are handled. It can be None, '',
'\n', '\r', and '\r\n'. It works as follows: * On input, if newline is None, universal newlines mode is
enabled. Lines in the input can end in '\n', '\r', or '\r\n', and
these are translated into '\n' before being returned to the
caller. If it is '', universal newline mode is enabled, but line
endings are returned to the caller untranslated. If it has any of
the other legal values, input lines are only terminated by the given
string, and the line ending is returned to the caller untranslated. * On output, if newline is None, any '\n' characters written are
translated to the system default line separator, os.linesep. If
newline is '' or '\n', no translation takes place. If newline is any
of the other legal values, any '\n' characters written are translated
to the given string. If line_buffering is True, a call to flush is implied when a call to
write contains a newline character.
"""
def close(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
关闭文件
pass def fileno(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
文件描述符
pass def flush(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
刷新文件内部缓冲区
pass def isatty(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
判断文件是否是同意tty设备
pass def read(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
读取指定字节数据
pass def readable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
是否可读
pass def readline(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
仅读取一行数据
pass def seek(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
指定文件中指针位置
pass def seekable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
指针是否可操作
pass def tell(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
获取指针位置
pass def truncate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
截断数据,仅保留指定之前数据
pass def writable(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
是否可写
pass def write(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
写内容
pass def __getstate__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass @staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass def __next__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Implement next(self). """
pass def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass buffer = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default closed = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default encoding = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default errors = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default line_buffering = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default name = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default newlines = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default _CHUNK_SIZE = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default _finalizing = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
三、管理上下文
为了避免打开文件后忘记关闭,可以通过管理上下文,即:
|
1
2
3
|
with open('log','r') as f: ... |
如此方式,当with代码块执行完毕时,内部会自动关闭并释放文件资源。
在Python 2.7 及以后,with又支持同时对多个文件的上下文进行管理,即:
|
1
2
|
with open('log1') as obj1, open('log2') as obj2: pass |
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
###### 从一文件挨行读取并写入二文件 #########with open('test.log','r') as obj1 , open('test1.log','w') as obj2: for line in obj1: obj2.write(line) |
三元运算
三元运算(三目运算),是对简单的条件语句的缩写。
|
1
2
3
|
result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 # 如果条件成立,那么将 “值1” 赋值给result变量,否则,将“值2”赋值给result变量 |
|
1
2
3
|
########## 三 元 运 算 ############name = "nick" if 1==1 else "jenny"print(name) |
lambda函数
对于简单的函数,存在一种简便的表示方式,即:lambda表达式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
######## 普 通 函 数 ######### 定义函数(普通方式)def func(arg): return arg + 1 # 执行函数result = func(123) ######## lambda 表 达 式 ######## # 定义函数(lambda表达式)my_lambda = lambda arg : arg + 1 # 执行函数result = my_lambda(123) |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
##### 列表重新判断操作排序 #####li = [11,15,9,21,1,2,68,95]s = sorted(map(lambda x:x if x > 11 else x * 9,li))print(s)######################ret = sorted(filter(lambda x:x>22, [55,11,22,33,]))print(ret) |
递归
- 递归就是在过程或函数里调用自身。
- 在使用递归策略时,必须有一个明确的递归结束条件,称为递归出口。
- 递归算法解题通常显得很简洁,但递归算法解题的运行效率较低。所以一般不提倡用递归算法设计程序。
- 在递归调用的过程当中系统为每一层的返回点、局部量等开辟了栈来存储。递归次数过多容易造成栈溢出等。所以一般不提倡用递归算法设计程序。
利用函数编写如下数列:
斐波那契数列指的是这样一个数列 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233,377,610,987,1597,2584,4181,6765,10946,17711,28657,46368...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
def func(arg1,arg2): if arg1 == 0: print arg1, arg2 arg3 = arg1 + arg2 print arg3 func(arg2, arg3) func(0,1) |

|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#写函数,利用递归获取斐波那契数列中的第 10 个数#方法一def fie(n): if n == 0 or n == 1: return n else: return (fie(n-1)+fie(n-2))ret = fie(10)print(ret)#方法二def num(a,b,n): if n == 10: return a print(a) c = a + b a = num(b,c,n + 1) return as = num(0,1,1)print(s) |
冒泡排序

将一个不规则的数组按从小到大的顺序进行排序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
data = [10,4,33,21,54,8,11,5,22,2,17,13,3,6,1,]print("before sort:",data)for j in range(1,len(data)): for i in range(len(data) - j): if data[i] > data[i + 1]: temp = data[i] data[i] = data[i + 1] data[i + 1] = temp print(data)print("after sort:",data) |
| 深浅拷贝 |
Python基础(函数-递归)的更多相关文章
- python基础-函数递归
函数递归 概念:直接或间接地重复调用函数本身,是一种函数嵌套调用的表现形式. 直接调用:在函数内部,直接调用函数本身 def foo(): print("这是foo函数") foo ...
- 十四. Python基础(14)--递归
十四. Python基础(14)--递归 1 ● 递归(recursion) 概念: recursive functions-functions that call themselves either ...
- python基础,函数,面向对象,模块练习
---恢复内容开始--- python基础,函数,面向对象,模块练习 1,简述python中基本数据类型中表示False的数据有哪些? # [] {} () None 0 2,位和字节的关系? # ...
- python基础——函数的参数
python基础——函数的参数 定义函数的时候,我们把参数的名字和位置确定下来,函数的接口定义就完成了.对于函数的调用者来说,只需要知道如何传递正确的参数,以及函数将返回什么样的值就够了,函数内部的复 ...
- python基础—函数嵌套与闭包
python基础-函数嵌套与闭包 1.名称空间与作用域 1 名称空间分为: 1 内置名称空间 内置在解释器中的名称 2 全局名称空间 顶头写的名称 3 局部名称空间 2 找一个名称的查找顺序: ...
- python基础—函数装饰器
python基础-函数装饰器 1.什么是装饰器 装饰器本质上是一个python函数,它可以让其他函数在不需要做任何代码变动的前提下增加额外功能. 装饰器的返回值是也是一个函数对象. 装饰器经常用于有切 ...
- Python基础-函数参数
Python基础-函数参数 写在前面 如非特别说明,下文均基于Python3 摘要 本文详细介绍了函数的各种形参类型,包括位置参数,默认参数值,关键字参数,任意参数列表,强制关键字参数:也介绍了调用函 ...
- python基础之递归,匿名,内置函数
递归函数: 什么是递归函数? 函数递归调用:在调用一个函数的过程中,又直接或间接地调用了该函数本身. 递归必须要有两个明确的阶段: ①递推:一层一层递归调用下去,强调:每进入下一层问题规模减少 ②回溯 ...
- Python基础-函数篇
本节内容 1. 函数基本语法及特性 2. 参数与局部变量 3. 返回值 嵌套函数 4.递归 5.匿名函数 6.函数式编程介绍 7.高阶函数 8.内置函数 函数与函数式编程 1.面向对象: 华山派-- ...
- 第三章:Python基础の函数和文件操作实战
本課主題 Set 集合和操作实战 函数介紹和操作实战 参数的深入介绍和操作实战 format 函数操作实战 lambda 表达式介绍 文件操作函数介紹和操作实战 本周作业 Set 集合和操作实战 Se ...
随机推荐
- 深入浅出了解OCR识别票据原理(Applying OCR Technology for Receipt Recognition)
原文:Applying OCR Technology for Receipt Recognition 译文:深入浅出了解OCR识别票据原理 英文票据识别技术, 非中文票据识别技术, 中文情况的ocr更 ...
- Go a lot of way but I go back to the original point
I try a lot of blog platform and even construct my blog website. But I have to say I just want to ha ...
- 笔记:XML-解析文档
要处理XML文档,就要先解析(parse)他,解析器时这样一个程序,读入一个文件,确认整个文件具有正确的格式,然后将其分解成各种元素,使得程序员能够访问这些元素,Java库提供了两种XML解析器: 像 ...
- Spring Boot应用的后台运行配置
酱油一篇,整理一下关于Spring Boot后台运行的一些配置方式.在介绍后台运行配置之前,我们先回顾一下Spring Boot应用的几种运行方式: 运行Spring Boot的应用主类 使用Mave ...
- C++基于范围循环(range-based for loop)的陷阱
C++的基于范围的循环是C++11出现的新特性,很方便,一定程度上替代了使用迭代器的for循环用法.不过基于范围的for循环有一个隐藏的陷阱,如果不注意可能会出现严重的内存错误. 举例说明 看下面这个 ...
- 【Django】 rest-framework和RestfulAPI的设计
[rest-framework] 这是一个基于django才能发挥作用的组件,专门用于构造API的. 说到API,之前在其他项目中我也做过一些小API,不过那些都是玩票性质,结构十分简单而且要求的设计 ...
- Flash Builder4.7安装破解
引用自CSDN博客,日后我会上传FlashBuilder到百度网盘谢谢 http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/391036327
- 用Python登录好友QQ空间点赞
记得之前跟我女票说过,说要帮她空间点赞,点到999就不点了.刚开始还能天天记得,但是后来事情一多,就难免会忘记,前两天点赞的时候忽然觉得这样好枯燥啊,正好也在学Python,就在想能不能有什么方法能自 ...
- mycat入门_介绍与安装
利用闲暇时间接触了下mycat. 一.介绍 1.概述: 国内最活跃的.性能最好的开源数据库中间件,可以理解为数据库和应用层之间的一个代理组件. 2.作用: 读写分离.分表分库.主从切换. 3.原理: ...
- [知识梳理]课本1&2.1-2.5
面向对象的语言 出发点:更直接地描述客观世界中存在的事物(对象)以及它们之间的关系. 特点: 是高级语言. 将客观事物看作具有属性和行为的对象. 通过抽象找出同一类对象的共同属性和行为,形成类. 通过 ...
