Spring学习(二)Spring的bean管理(XML)
Bean的实例化方式
1、在Spring里面通过配置文件创建对象
2、bean实例化的三种方式
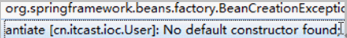
第一种:使用类的无参数构造函数创建(最常用的方式,第2种和第3种方法一般不用)
如果类里面没有无参的构造函数,将会出现异常
第二种:使用静态工厂创建
(1)创建类的静态方法,返回类对象
第三种:使用实例工厂创建
(2)创建不是静态的方法,返回类的对象

3、bean标签常用属性
(1)id
id表示为该类起一个名字,id属性值一般为小写的类名id=user
id属性值,不能有特殊符号,为一个单独的单词(user_1错误)
根据id值得到配置对象
(2)class:创建对象所在类的全路径 (3)name:功能和id属性是一样的(现在name属性已经不用了,为了针对整合struts1)
但是id睡醒不可以有特殊符号,name可以有特殊符号

(4)scope:
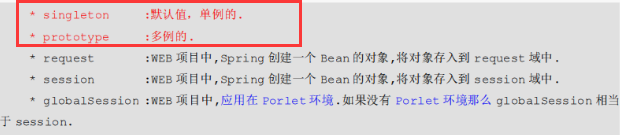
默认是单实例的,可以不写,也可以写:

多实例必须要写scope="prototype",多实例的应用场景:配置action

4、属性注入方法:
4.1 JAVA的属性注入方法:
(1)创建对象的时候,向类里面的属性设置值
(2)属性注入的介绍(3种方式)
方法一:set方式(用的最多)
public class User{
private String name;
public void setName(String name){
this.name=name;
}
} 实现:User user=new User();
user,setName("Zhangsan"); 方法二:有参构造
public class user{
private String name;
public User(String name){
this.name=name;
}
} 实现:
User user=new User("ZhangSan");
第三种:使用接口注入
public interface Dao{
public void delete(String name);
}
public class DaoImpl implements Dao{
private String name;
public void delete(String name){
this.name=name
}
}
4.2、在Spring框架中只支持(1)set方法注入和(2)有参的构造注入
(1)set
Book类:
package cn.itcast.property;
public class Book {
private String bookname;
public void setBookname(String bookname) {
this.bookname = bookname;
}
public void demobook(){
System.out.println("booknmae="+bookname);
}
}
配置文件:
<!-- 使用set方法注入属性 -->
<bean id="book" class="cn.itcast.property.Book">
<!-- 注入属性值 name:类里面定义的属性名称 value:设置具体的值
-->
<property name="bookname" value="JAVA"></property>
</bean>
(2)有参构造
类:
package cn.itcast.property;
public class PropertyDemo1 {
private String username;
public PropertyDemo1(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void test1() {
System.out.println("username....."+username);
}
}
配置文件:
<bean id="demo" class="cn.itcast.property.PropertyDemo1">
<constructor-arg name="username" value="小王"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
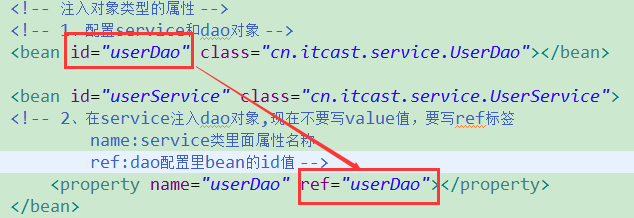
4.3 注入对象类型的属性********重点掌握
1、创建service类和dao类
在service中得到dao的对象
2、具体实现过程
在service里面把dao作为类属性
生成dao类型属性的set方法
配置文件中注入关系
UserDao类:
package cn.itcast.service;
public class UserDao {
public void add(){
System.out.println("dao.....");
}
}
UserService类:
package cn.itcast.service;
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add(){
System.out.println("service.....");
//在service中得到到对象,才能调用dao里面的方法
// UserDao dao=new UserDao();
// dao.add();
userDao.add();
}
}
配置文件:
P名称空间注入:(很少用)
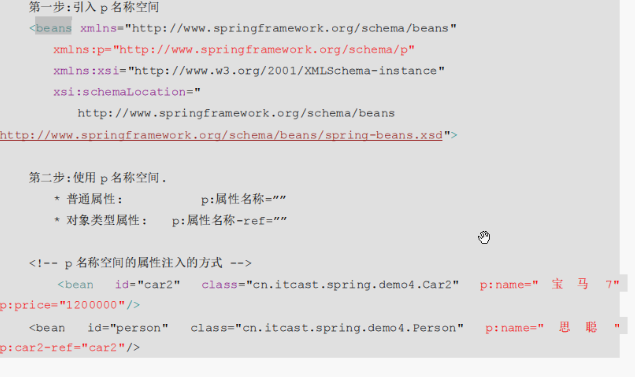
注入复杂类型的属性:
1、数组
2、list集合
3、Map集合
4、Properties类型
<bean id="user" class="cn.itcast.property.Person">
<!--数组-->
<property name="arrs">
<list>
<value>张三</value>
<value>李四</value>
<value>王五</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--list-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>张三list</value>
<value>李四list</value>
<value>王五list</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--map-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="a" value="lucy"></entry>
<entry key="b" value="tom"></entry>
<entry key="c" value="kate"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--properties-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="driverclass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="pwd">123</prop>
</list>
</property> </bean>
Ioc和DI区别:
Ioc:控制反转,把对象的创建交给spring进行配置
DI:依赖注入,向类里面的属性中,设置值
Ioc与DI的关系,依赖注入不可以单独存在,需要在Ioc的基础之上来完成依赖注入的操作
Spring的bean管理(注解)
注解介绍:
- 代码里面特殊的标记,使用注解可以完成功能
- 注解写法 @注解名称(属性名称=属性值),例如单元测试@Test
- 注解用在什么地方:类、方法、属性都可以使用注解
spring注解开发准备工作
- 1、导入jar包
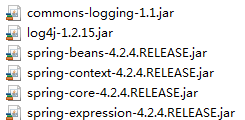
(1)导入基本jar包
(2)导入aop的jap包
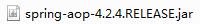
- 2、创建类,创建方法
- 3、创建Spring配置文件
(1)不用注解方式,引入约束 beans,即
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
(2)引入新的约束

- 4、开启注解扫描
<!-- 开启注解扫描
(1)到包里面扫描类、方法、睡醒上面是否有注解
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast"></context:component-scan>
- 使用注解创建对象(可以替换配置文件,但是不可以完全脱离配置文件)
1、在创建对象的类上面使用注解实现
@Component(value="user")
public class User {
}
测试代码:
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
User user=(User) context.getBean("user");
System.out.println("user==="+user);
user.add();
2、spring中提供的注解方式除了
(1)@Component 还有三个衍注解,是为了让标注类本身的用途更加的清晰
(2)@Controller WEB 层
(3)@Service 业务层
(4)@Repository 持久层
这四个注解的功能是一样的
3、创建对象的单实例还是多实例
@Component(value="user")
@Scope(value="prototype")//singleton
public class User {
}
- 注解方式来注入属性
(配置文件只有一行:<context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast"></context:component-scan>)
1、创建service类,创建dao类,在service中得到dao的类
注入属性第一个注解@Autowired(用的不多):不需要指定类
注入属性第二个注解@Resource(name="userDao"):要指定用的name
@Component(value="userDao")
public class UserDao {
public void add(){
System.out.println("dao ....");
}
}
UserService类
@Service(value="userService")
public class UserService {
//得到dao 对象
//1、在service中定义dao类型属性
// 在dao属性上面使用注解来完成对象注入
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
//2、使用注解,不用set方法
public void add(){
System.out.println("service......");
userDao.add();
}
}
第二种属性注入方式
@Service(value="userService")
public class UserService {
//得到dao 对象
//1、在service中定义dao类型属性
// 在dao属性上面使用注解来完成对象注入
@Resource(name="userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
//2、使用注解,不用set方法
public void add(){
System.out.println("service......");
userDao.add();
}
}
测试代码:
public void testDemo(){
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
UserService user=(UserService) context.getBean("userService");
System.out.println("user==="+user);
user.add();
}
配置文件和注解混合使用
1、创建对象的操作使用配置文件方式实现
2、注入属性操作注解方式实现
3、例子在BookService中使用BookDao类和OrdersDao类
BookDao类
package cn.itcast.xmlann0;
public class BookDao {
public void book(){
System.out.println("bookDao....");
}
}
OrdersDao类
package cn.itcast.xmlann0;
public class OrdersDao {
public void buy(){
System.out.println("ordersbuy....");
}
}
BookService类
package cn.itcast.xmlann0;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
public class BookService {
@Resource(name="bookDao")
private BookDao bookDao;
@Resource(name="ordersDao")
private OrdersDao ordersDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("service....");
bookDao.book();
ordersDao.buy();
}
}
bean2.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- bean definitions here -->
<!-- 开启注解扫描
(1)到包里面扫描类、方法、睡醒上面是否有注解
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.itcast"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 配置对象 -->
<bean id="bookDao" class="cn.itcast.xmlann0.BookDao"></bean>
<bean id="ordersDao" class="cn.itcast.xmlann0.OrdersDao"></bean>
<bean id="bookService" class="cn.itcast.xmlann0.BookService"></bean>
</beans>
测试代码:
@Test
public void testxmlanno(){
ApplicationContext context =new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
BookService bookService=(BookService) context.getBean("bookService");
bookService.add();
}
结果:
service....
bookDao....
ordersbuy....
Spring学习(二)Spring的bean管理(XML)的更多相关文章
- Spring学习二----------IOC及Bean容器
© 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处 接口 用于沟通的中介物的抽象化 实体把自己提供给外界的一种抽象化说明,用以由内部操作分离出外部沟通方法,使其能被修改内部而不影响外界其他实体与其交互的 ...
- Spring学习笔记三:Bean管理
转载请注明原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ygj0930/p/6775827.html 一:如何使用Spring获取对象 1:定义bean类:要按照注入方式来定义对应的bea ...
- Spring学习(十一)-----Spring使用@Required注解依赖检查
Spring学习(九)-----Spring依赖检查 bean 配置文件用于确定的特定类型(基本,集合或对象)的所有属性被设置.在大多数情况下,你只需要确保特定属性已经设置但不是所有属性.. 对于这种 ...
- Spring学习(六)-----Spring使用@Autowired注解自动装配
Spring使用@Autowired注解自动装配 在上一篇 Spring学习(三)-----Spring自动装配Beans示例中,它会匹配当前Spring容器任何bean的属性自动装配.在大多数情况下 ...
- IoC容器-Bean管理XML方式(创建对象和set注入属性,有参构造注入属性)
Ioc操作Bean管理 1,什么是Bean管理 (0)Bean管理指的是两个操作 (1)Spring创建对象 (2)Spring注入属性 2,Bean管理操作有两种方式 (1)基于xml配置文件方式实 ...
- Spring基础学习(二)—详解Bean(上)
在Spring配置文件中,用户不但可以将String.int等字面值注入Bean中,还可以将集合.Map等类型注入Bean中,此外还可以注入配置文件中其他定义的Bean. 一.字面值 ...
- Spring学习(二)--装配Bean
一.Spring装配机制 Spring提供了三种主要的装配机制: 1.在XML中进行显示配置 2.在Java中进行显示配置 3.隐式的bean发现机制和自动装配--自动化装配bean Spring可以 ...
- Spring学习二:Spring Bean 定义
Bean 定义 被称作 bean 的对象是构成应用程序的支柱也是由 Spring IoC 容器管理的.bean 是一个被实例化,组装,并通过 Spring IoC 容器所管理的对象.这些 bean 是 ...
- Spring学习(二):Spring支持的5种Bean Scope
序言 Scope是定义Spring如何创建bean的实例的.Spring容器最初提供了两种bean的scope类型:singleton和prototype,但发布2.0以后,又引入了另外三种scope ...
- Spring学习(5)---Bean的定义及作用域的注解实现
Bean管理的注解实现 Classpath扫描与组件管理 类的自动检测与注册Bean <context:annotation-config/> @Component,@Repository ...
随机推荐
- ZOJ1610(经典线段树涂色问题)
Description Painting some colored segments on a line, some previously painted segments may be covere ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(五十):ActionBar(3):搜索条
目录(?)[-] ActionBar中的搜索条 通过Menu item上定义search view 进行Searchable的配置 在activity中将search view关联searchable ...
- java用write()拷贝一个文本文件
总结:灵活运用循环语句,或条件判断语句.每一种流的正确使用方法: 这里是两种方法: package com.ds; import java.io.*; public class tyut { /*pu ...
- modbus读输入状态与读线圈状态的区别?
01 读线圈状态 描述 读从机离散量输出口的 ON/OFF 状态,不支持广播.附录B列出由不同控制器型号支持最大的参数清单. 查询 查询信息规定了要读的起始线圈和线圈量,线圈的起始地址为零,1-16个 ...
- WEB 项目中的全局异常处理
在web 项目中,遇到异常一般有两种处理方式:try.....catch....:throw 通常情况下我们用try.....catch.... 对异常进行捕捉处理,可是在实际项目中随时的进行异常捕捉 ...
- 【255】◀▶IEW-Unit20
Unit 20 Environment: Tourism I.定语从句及分词在雅思写作中的运用 定语从句: 1. 先行词 2. 关系词:关系代词.关系副词 3. 非限制性定语从句 4. 分词和定语从句 ...
- 转:JMeter整合InfluxDB,Grafana让测试结果实时显示
软件版本: apache-jmeter-2.13.tgz grafana-2.1.1-1.x86_64.rpm influxdb-0.8.8-1.x86_64.rpm 虽然官方不在支持influxdb ...
- 9、IPA通路分析相关网页教程
IPA FAQ: http://ingenuity.force.com/ipa/IPATutorials# ####有各种相关教程和帮助文件. IPA 分析结果展示: http://www.lucid ...
- 面试问题 - SQL 中存储过程与函数的区别
SQL 中的存储过程与函数没有本质上的区别 函数 -> 只能返回一个变量. 函数可以嵌入到sql中使用, 可以在select 中调用, 而存储过程不行. 但函数也有着更多的限制,比如不能使用临 ...
- ubuntu-12.04.5安装cacti笔记
坑啊,磨磨蹭蹭按了一个星期.按了3个版本. 第一次:cacti-0.8.7e.tar.gz 安装完之后,Host: Localhost->Memory Usage...四张图始终出不了.点击进去 ...