CodeForces Round #548 Div2
http://codeforces.com/contest/1139
You are given a string s=s1s2…sns=s1s2…sn of length nn, which only contains digits 11, 22, ..., 99.
A substring s[l…r]s[l…r] of ss is a string slsl+1sl+2…srslsl+1sl+2…sr. A substring s[l…r]s[l…r] of ss is called even if the number represented by it is even.
Find the number of even substrings of ss. Note, that even if some substrings are equal as strings, but have different ll and rr, they are counted as different substrings.
The first line contains an integer nn (1≤n≤650001≤n≤65000) — the length of the string ss.
The second line contains a string ss of length nn. The string ss consists only of digits 11, 22, ..., 99.
Print the number of even substrings of ss.
4
1234
6
4
2244
10
In the first example, the [l,r][l,r] pairs corresponding to even substrings are:
- s[1…2]s[1…2]
- s[2…2]s[2…2]
- s[1…4]s[1…4]
- s[2…4]s[2…4]
- s[3…4]s[3…4]
- s[4…4]s[4…4]
In the second example, all 1010 substrings of ss are even substrings. Note, that while substrings s[1…1]s[1…1] and s[2…2]s[2…2] both define the substring "2", they are still counted as different substrings.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; int N;
string s; int main() {
cin >> N >> s;
int ans = ;
for(int i = ; i < N; i ++) {
if((s[i] - '') % == ) ans += (i + );
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return ;
}
You went to the store, selling nn types of chocolates. There are aiai chocolates of type ii in stock.
You have unlimited amount of cash (so you are not restricted by any prices) and want to buy as many chocolates as possible. However if you buy xixi chocolates of type ii (clearly, 0≤xi≤ai0≤xi≤ai), then for all 1≤j<i1≤j<i at least one of the following must hold:
- xj=0xj=0 (you bought zero chocolates of type jj)
- xj<xixj<xi (you bought less chocolates of type jj than of type ii)
For example, the array x=[0,0,1,2,10]x=[0,0,1,2,10] satisfies the requirement above (assuming that all ai≥xiai≥xi), while arrays x=[0,1,0]x=[0,1,0], x=[5,5]x=[5,5] and x=[3,2]x=[3,2] don't.
Calculate the maximum number of chocolates you can buy.
The first line contains an integer nn (1≤n≤2⋅1051≤n≤2⋅105), denoting the number of types of chocolate.
The next line contains nn integers aiai (1≤ai≤1091≤ai≤109), denoting the number of chocolates of each type.
Print the maximum number of chocolates you can buy.
5
1 2 1 3 6
10
5
3 2 5 4 10
20
4
1 1 1 1
1
In the first example, it is optimal to buy: 0+0+1+3+60+0+1+3+6 chocolates.
In the second example, it is optimal to buy: 1+2+3+4+101+2+3+4+10 chocolates.
In the third example, it is optimal to buy: 0+0+0+10+0+0+1 chocolates.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int maxn = 2e5 + ;
int N;
int a[maxn]; int main() {
scanf("%d", &N);
for(int i = ; i < N; i ++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]); long long ans = a[N - ];
int maxx = a[N - ];
for(int i = N - ; i >= ; i --) {
if(maxx == ) break;
if(a[i] < maxx) {
ans += a[i];
maxx = a[i];
} else {
ans += (maxx - );
maxx --;
} }
cout << ans << endl;
//printf("%lld\n", ans); return ;
}
You are given a tree (a connected undirected graph without cycles) of nn vertices. Each of the n−1n−1 edges of the tree is colored in either black or red.
You are also given an integer kk. Consider sequences of kk vertices. Let's call a sequence [a1,a2,…,ak][a1,a2,…,ak] good if it satisfies the following criterion:
- We will walk a path (possibly visiting same edge/vertex multiple times) on the tree, starting from a1a1 and ending at akak.
- Start at a1a1, then go to a2a2 using the shortest path between a1a1 and a2a2, then go to a3a3 in a similar way, and so on, until you travel the shortest path between ak−1ak−1 and akak.
- If you walked over at least one black edge during this process, then the sequence is good.
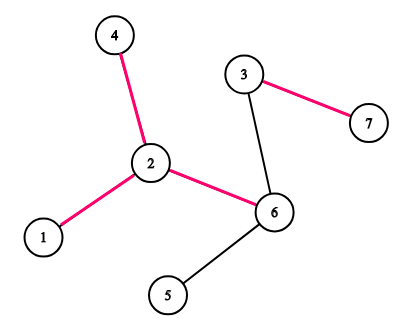
Consider the tree on the picture. If k=3k=3 then the following sequences are good: [1,4,7][1,4,7], [5,5,3][5,5,3] and [2,3,7][2,3,7]. The following sequences are not good: [1,4,6][1,4,6], [5,5,5][5,5,5], [3,7,3][3,7,3].
There are nknk sequences of vertices, count how many of them are good. Since this number can be quite large, print it modulo 109+7109+7.
The first line contains two integers nn and kk (2≤n≤1052≤n≤105, 2≤k≤1002≤k≤100), the size of the tree and the length of the vertex sequence.
Each of the next n−1n−1 lines contains three integers uiui, vivi and xixi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤ui,vi≤n, xi∈{0,1}xi∈{0,1}), where uiui and vivi denote the endpoints of the corresponding edge and xixi is the color of this edge (00 denotes red edge and 11 denotes black edge).
Print the number of good sequences modulo 109+7109+7.
4 4
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 1
252
4 6
1 2 0
1 3 0
1 4 0
0
3 5
1 2 1
2 3 0
210
In the first example, all sequences (4444) of length 44 except the following are good:
- [1,1,1,1][1,1,1,1]
- [2,2,2,2][2,2,2,2]
- [3,3,3,3][3,3,3,3]
- [4,4,4,4][4,4,4,4]
In the second example, all edges are red, hence there aren't any good sequences.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int mod = 1e9 + ;
const int maxn = 1e5 + ;
int N, K;
int num;
vector<int> v[maxn];
int vis[maxn]; long long Pow(long long a, long long b) {
long long ans1 = ; a = a % mod; while(b) {
if(b % ) {
ans1 = (ans1 * a) % mod;
b --;
} else {
a = (a * a) % mod;
b /= ;
}
}
return ans1;
} void dfs(int st) {
if(v[st].size() == ) {
num ++;
return ;
} for(int i = ; i < v[st].size(); i ++) {
if(vis[v[st][i]] == ) {
vis[v[st][i]] = ;
num ++;
dfs(v[st][i]);
}
}
} int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &N, &K);
memset(vis, , sizeof(vis));
for(int i = ; i < N - ; i ++) {
int st, en, col;
scanf("%d%d%d", &st, &en, &col);
if(col == ) {
v[st].push_back(en);
v[en].push_back(st);
}
} long long ans = ;
for(int i = ; i <= N; i ++) {
if(vis[i]) continue;
num = ;
dfs(i);
ans = (ans + Pow(num, K)) % mod;
ans %= mod;
} ans = (Pow(N, K) - ans + mod) % mod;
cout << ans << endl; return ;
}
There are nn students and mm clubs in a college. The clubs are numbered from 11 to mm. Each student has a potential pipi and is a member of the club with index cici. Initially, each student is a member of exactly one club. A technical fest starts in the college, and it will run for the next dd days. There is a coding competition every day in the technical fest.
Every day, in the morning, exactly one student of the college leaves their club. Once a student leaves their club, they will never join any club again. Every day, in the afternoon, the director of the college will select one student from each club (in case some club has no members, nobody is selected from that club) to form a team for this day's coding competition. The strength of a team is the mex of potentials of the students in the team. The director wants to know the maximum possible strength of the team for each of the coming dddays. Thus, every day the director chooses such team, that the team strength is maximized.
The mex of the multiset SS is the smallest non-negative integer that is not present in SS. For example, the mex of the {0,1,1,2,4,5,9}{0,1,1,2,4,5,9} is 33, the mex of {1,2,3}{1,2,3} is 00 and the mex of ∅∅ (empty set) is 00.
The first line contains two integers nn and mm (1≤m≤n≤50001≤m≤n≤5000), the number of students and the number of clubs in college.
The second line contains nn integers p1,p2,…,pnp1,p2,…,pn (0≤pi<50000≤pi<5000), where pipi is the potential of the ii-th student.
The third line contains nn integers c1,c2,…,cnc1,c2,…,cn (1≤ci≤m1≤ci≤m), which means that ii-th student is initially a member of the club with index cici.
The fourth line contains an integer dd (1≤d≤n1≤d≤n), number of days for which the director wants to know the maximum possible strength of the team.
Each of the next dd lines contains an integer kiki (1≤ki≤n1≤ki≤n), which means that kiki-th student lefts their club on the ii-th day. It is guaranteed, that the kiki-th student has not left their club earlier.
For each of the dd days, print the maximum possible strength of the team on that day.
5 3
0 1 2 2 0
1 2 2 3 2
5
3
2
4
5
1
3
1
1
1
0
5 3
0 1 2 2 1
1 3 2 3 2
5
4
2
3
5
1
3
2
2
1
0
5 5
0 1 2 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
4
2
3
5
4
1
1
1
1
Consider the first example:
On the first day, student 33 leaves their club. Now, the remaining students are 11, 22, 44 and 55. We can select students 11, 22 and 44 to get maximum possible strength, which is 33. Note, that we can't select students 11, 22 and 55, as students 22 and 55 belong to the same club. Also, we can't select students 11, 33 and 44, since student 33 has left their club.
On the second day, student 22 leaves their club. Now, the remaining students are 11, 44 and 55. We can select students 11, 44 and 55 to get maximum possible strength, which is 11.
On the third day, the remaining students are 11 and 55. We can select students 11 and 55 to get maximum possible strength, which is 11.
On the fourth day, the remaining student is 11. We can select student 11 to get maximum possible strength, which is 11.
On the fifth day, no club has students and so the maximum possible strength is 00.
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int maxn = ;
int N, M, Q;
int vis[maxn], see[maxn], sz[maxn], mp[maxn];
int p[maxn], c[maxn];
vector<int> v[maxn];
int ans = INT_MIN;
vector<int> s; int mex(vector<int> &v) {
int szz = v.size();
if(szz == ) return ;
memset(see, , sizeof(see));
for(int i = ; i < szz; i ++)
see[v[i]] = ;
int temp = ;
for(int i = ; i <= maxn; i ++) {
if(!see[i]) {
temp = i;
break;
}
}
return temp;
} vector<vector<int> > out;
void dfs(int step, vector<int> &s) {
if(step == M + ) {
if(mex(s) >= ans)
ans = mex(s);
//out.push_back(s);
return ;
} if(sz[step] == ) dfs(step + , s);
for(int i = ; i < v[step].size(); i ++) {
if(!vis[v[step][i]]) {
vis[v[step][i]] = ;
s.push_back(p[v[step][i]]);
dfs(step + , s);
s.pop_back();
vis[v[step][i]] = ;
}
}
} int main() {
memset(sz, , sizeof(sz));
scanf("%d%d", &N, &M);
for(int i = ; i <= N; i ++)
scanf("%d", &p[i]);
for(int i = ; i <= N; i ++) {
scanf("%d", &c[i]);
v[c[i]].push_back(i);
sz[c[i]] ++;
mp[i] = c[i];
}
memset(vis, , sizeof(vis));
scanf("%d", &Q);
while(Q --) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
vis[x] = ;
sz[mp[x]] --;
ans = INT_MIN;
out.clear();
vector<int> b;
dfs(, s);
//for(int i = 0; i < out.size(); i ++) {
//for(int j = 0; j <out[i].size(); j ++)
// printf("%d ", out[i][j]);
//printf("@@@@ %d\n", mex(out[i]));
// ans = max(ans, mex(out[i]));
//}
printf("%d\n", ans);
} /*scanf("%d", &N);
vector<int> zlr;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
zlr.push_back(x);
}
printf("%d\n", mex(zlr));*/
return ;
} //3 16 0 14 2 15 1
花了两个来小时你给我 TLE 改了无数遍还是不行 事实证明并不能暴力出奇迹 所以查了题解搞出来一个匈牙利算法也是看的一脸懵了 所以先把 TLE 的贴出来(我不管 就算 TLE 也要贴 毕竟这是我的一下午了。。。)
CodeForces Round #548 Div2的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #539 div2
Codeforces Round #539 div2 abstract I 离散化三连 sort(pos.begin(), pos.end()); pos.erase(unique(pos.begin ...
- Codeforces Round 548 (Div. 2)
layout: post title: Codeforces Round 548 (Div. 2) author: "luowentaoaa" catalog: true tags ...
- 【前行】◇第3站◇ Codeforces Round #512 Div2
[第3站]Codeforces Round #512 Div2 第三题莫名卡半天……一堆细节没处理,改一个发现还有一个……然后就炸了,罚了一啪啦时间 Rating又掉了……但是没什么,比上一次好多了: ...
- Codeforces Round#320 Div2 解题报告
Codeforces Round#320 Div2 先做个标题党,骗骗访问量,结束后再来写咯. codeforces 579A Raising Bacteria codeforces 579B Fin ...
- Codeforces Round #564(div2)
Codeforces Round #564(div2) 本来以为是送分场,结果成了送命场. 菜是原罪 A SB题,上来读不懂题就交WA了一发,代码就不粘了 B 简单构造 很明显,\(n*n\)的矩阵可 ...
- Codeforces Round #361 div2
ProblemA(Codeforces Round 689A): 题意: 给一个手势, 问这个手势是否是唯一. 思路: 暴力, 模拟将这个手势上下左右移动一次看是否还在键盘上即可. 代码: #incl ...
- Codeforces Round #626 Div2 D,E
比赛链接: Codeforces Round #626 (Div. 2, based on Moscow Open Olympiad in Informatics) D.Present 题意: 给定大 ...
- CodeForces Round 192 Div2
This is the first time I took part in Codeforces Competition.The only felt is that my IQ was contemp ...
- Codeforces Round #359 div2
Problem_A(CodeForces 686A): 题意: \[ 有n个输入, +\space d_i代表冰淇淋数目增加d_i个, -\space d_i表示某个孩纸需要d_i个, 如果你现在手里 ...
随机推荐
- May 29. 2018 Week 22nd Tuesday
Nothing is more terrible than ignorance in action. 最可怕的事情莫过于无知而行动. In today's digital age, we can ru ...
- MVC+EF 序列化类型为“System.Data.Entity.DynamicProxies.__的对象时检测到循环引用
用MVC+EF做简单查询时,返回json格式数据出现问题 原代码: public ActionResult JSon({ NorthwindEntities db = new NorthwindEnt ...
- python3编写网络爬虫19-app爬取
一.app爬取 前面都是介绍爬取Web网页的内容,随着移动互联网的发展,越来越多的企业并没有提供Web页面端的服务,而是直接开发了App,更多信息都是通过App展示的 App爬取相比Web端更加容易 ...
- jq stop()和:is(":animated")用法区别
stop(true,true): 表示停止匹配元素正在进行的动画并跳转到末状态,清空未执行完的动画队列.常用于”解决光标移入移出得过快导致的动画效果与光标动作不一致“问题! jQuery stop() ...
- PHP 缓存技术(一)
移除光盘
- 计划任务执行bat
@echo offtaskkill /f /t /im ControlKJmen.exetaskkill /f /t /im KJMen.exetaskkill /f /t /im DisplayLo ...
- 【angularjs】使用ionic+angular 搭建移动端项目,字体适配
解析: 首先,rem是以html为基准. 一般的,各大主流浏览器的font-size默认值为16px,此时1rem=16px.如果此时将rem与px进行换算很麻烦,比如0.75rem=12px. 为了 ...
- 最长上升子序列(LIS)
(我先扯些没用的) 我这个笨孩子 学点东西好慢好慢的 我还贪玩 于是 将自己陷入了一个超级超级超级差的境地 可 我还傻乎乎的保有着天真的梦想(理想?) 所以现在我要加倍的努力努力再努力了 只能嘎油了 ...
- [Micropython] TPYBoard STM32F407开发板运行第一个脚本
从这篇教程开始将动手在TPYBoard STM32F407开发板上运行 Python 脚本,下面教大家拿到这个开发板后怎么用!(该款开发板某宝上有售) 1 连接开发板 通过 USB 线连接你的 PC ...
- Java IO(四)——字符流
一.字符流 字节流提供了处理任何类型输入/输出操作的功能(因为对于计算机而言,一切都是0和1,只需把数据以字节形式表示就够了),但它们不可以直接操作Unicode字符,因为一个Unicode字符占用2 ...
