android NDK 神经网络API——是给tensorflow lite调用的底层API,应用开发者使用tensorflow lite即可
eural Networks API
In this document show more
- Understanding the Neural Networks API Runtime
- Neural Networks API Programming Model
- More About Operands
Related API reference
Related sample
Note: The Neural Networks API is available in Android 8.1 and higher system images. The header file is available in the latest version of the NDK. We encourage you to send us your feedback via the Android 8.1 Preview issue tracker.
The Android Neural Networks API (NNAPI) is an Android C API designed for running computationally intensive operations for machine learning on mobile devices. NNAPI is designed to provide a base layer of functionality for higher-level machine learning frameworks (such as TensorFlow Lite, Caffe2, or others) that build and train neural networks. The API is available on all devices running Android 8.1 (API level 27) or higher.
NNAPI supports inferencing by applying data from Android devices to previously trained, developer-defined models. Examples of inferencing include classifying images, predicting user behavior, and selecting appropriate responses to a search query.
On-device inferencing has many benefits:
- Latency: You don’t need to send a request over a network connection and wait for a response. This can be critical for video applications that process successive frames coming from a camera.
- Availability: The application runs even when outside of network coverage.
- Speed: New hardware specific to neural networks processing provide significantly faster computation than with general-use CPU alone.
- Privacy: The data does not leave the device.
- Cost: No server farm is needed when all the computations are performed on the device.
There are also trade-offs that a developer should keep in mind:
- System utilization: Evaluating neural networks involve a lot of computation, which could increase battery power usage. You should consider monitoring the battery health if this is a concern for your app, especially for long-running computations.
- Application size: Pay attention to the size of your models. Models may take up multiple megabytes of space. If bundling large models in your APK would unduly impact your users, you may want to consider downloading the models after app installation, using smaller models, or running your computations in the cloud. NNAPI does not provide functionality for running models in the cloud.
Understanding the Neural Networks API runtime
NNAPI is meant to be called by machine learning libraries, frameworks, and tools that let developers train their models off-device and deploy them on Android devices. Apps typically would not use NNAPI directly, but would instead directly use higher-level machine learning frameworks. These frameworks in turn could use NNAPI to perform hardware-accelerated inference operations on supported devices.
Based on the app’s requirements and the hardware capabilities on a device, Android’s neural networks runtime can efficiently distribute the computation workload across available on-device processors, including dedicated neural network hardware, graphics processing units (GPUs), and digital signal processors (DSPs).
For devices that lack a specialized vendor driver, the NNAPI runtime relies on optimized code to execute requests on the CPU.
The diagram below shows a high-level system architecture for NNAPI.
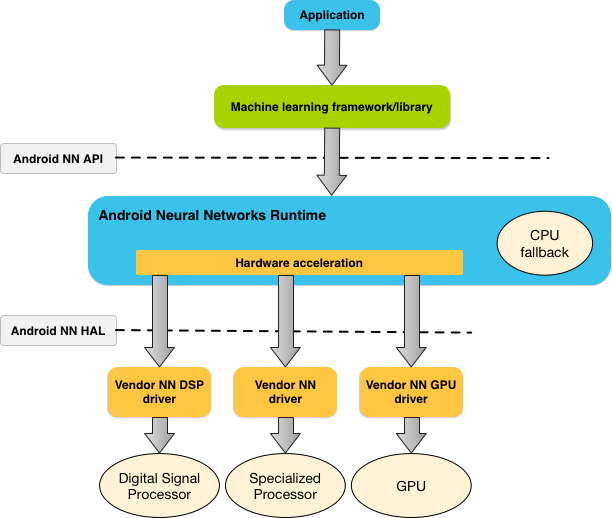 Figure 1. System architecture for Android Neural Networks API
Figure 1. System architecture for Android Neural Networks API
eural Networks API
In this document show more
- Understanding the Neural Networks API Runtime
- Neural Networks API Programming Model
- More About Operands
Related API reference
Related sample
Note: The Neural Networks API is available in Android 8.1 and higher system images. The header file is available in the latest version of the NDK. We encourage you to send us your feedback via the Android 8.1 Preview issue tracker.
The Android Neural Networks API (NNAPI) is an Android C API designed for running computationally intensive operations for machine learning on mobile devices. NNAPI is designed to provide a base layer of functionality for higher-level machine learning frameworks (such as TensorFlow Lite, Caffe2, or others) that build and train neural networks. The API is available on all devices running Android 8.1 (API level 27) or higher.
NNAPI supports inferencing by applying data from Android devices to previously trained, developer-defined models. Examples of inferencing include classifying images, predicting user behavior, and selecting appropriate responses to a search query.
On-device inferencing has many benefits:
- Latency: You don’t need to send a request over a network connection and wait for a response. This can be critical for video applications that process successive frames coming from a camera.
- Availability: The application runs even when outside of network coverage.
- Speed: New hardware specific to neural networks processing provide significantly faster computation than with general-use CPU alone.
- Privacy: The data does not leave the device.
- Cost: No server farm is needed when all the computations are performed on the device.
There are also trade-offs that a developer should keep in mind:
- System utilization: Evaluating neural networks involve a lot of computation, which could increase battery power usage. You should consider monitoring the battery health if this is a concern for your app, especially for long-running computations.
- Application size: Pay attention to the size of your models. Models may take up multiple megabytes of space. If bundling large models in your APK would unduly impact your users, you may want to consider downloading the models after app installation, using smaller models, or running your computations in the cloud. NNAPI does not provide functionality for running models in the cloud.
Understanding the Neural Networks API runtime
NNAPI is meant to be called by machine learning libraries, frameworks, and tools that let developers train their models off-device and deploy them on Android devices. Apps typically would not use NNAPI directly, but would instead directly use higher-level machine learning frameworks. These frameworks in turn could use NNAPI to perform hardware-accelerated inference operations on supported devices.
Based on the app’s requirements and the hardware capabilities on a device, Android’s neural networks runtime can efficiently distribute the computation workload across available on-device processors, including dedicated neural network hardware, graphics processing units (GPUs), and digital signal processors (DSPs).
For devices that lack a specialized vendor driver, the NNAPI runtime relies on optimized code to execute requests on the CPU.
The diagram below shows a high-level system architecture for NNAPI.
 Figure 1. System architecture for Android Neural Networks API
Figure 1. System architecture for Android Neural Networks API
参考:https://developer.android.com/ndk/guides/neuralnetworks/index.html
android NDK 神经网络API——是给tensorflow lite调用的底层API,应用开发者使用tensorflow lite即可的更多相关文章
- Android NDK 初探,生成so文件以及调用so文件方法
因为最近业务上涉及安全的问题 然后有一些加密解密的方法和key的存储问题 本来想存储到手机里面,但是网上说一般敏感信息不要存储到手机Sdcard上 而且我这个如果从网络建立通信获取的话,又太耗时,所以 ...
- Android NDK学习(五):Java调用Native代码流程总结
编写一个Java类,并且在某个方法签名的修饰符中加上native修饰符. 使用Javac命令编译第一步中的Java类,使之成为一个class文件. 使用Javah -jni 包名.类名 生成Jni接口 ...
- TensorFlow Lite demo——就是为嵌入式设备而存在的,底层调用NDK神经网络API,注意其使用的tf model需要转换下,同时提供java和C++ API,无法使用tflite的见后
Introduction to TensorFlow Lite TensorFlow Lite is TensorFlow’s lightweight solution for mobile and ...
- 【译】Android NDK API 规范
[译]Android NDK API 规范 译者按: 修改R代码遇到Lint tool的报错,搜到了这篇文档,aosp仓库地址:Android NDK API Guidelines. 975a589 ...
- Android NDK开发初识
神秘的Android NDK开发往往众多程序员感到兴奋,但又不知它为何物,由于近期开发应用时,为了是开发的.apk文件不被他人解读(反编译),查阅了很多资料,其中有提到使用NDK开发,怀着好奇的心理, ...
- 初识Android NDK
本文介绍Windows环境下搭建Android NDK开发环境,并创建一个简单的使用Native代码的Android Application. 一.环境搭建 二.JNI函数绑定 三.例子 一.环境搭建 ...
- Android NDK开发入门实例
AndroidNDK是能使Android应用开发者把从c/c++编译而来的本地代码嵌入到应用包中的一系列工具的组合. 注意: AndroidNDK只能用于Android1.5及以上版本中. I. An ...
- [原]如何用Android NDK编译FFmpeg
我们知道在Ubuntu下直接编译FFmpeg是很简单的,主要是先执行./configure,接着执行make命令来编译,完了紧接着执行make install执行安装.那么如何使用Android的ND ...
- android ndk环境配置(转)
转载自:http://jingyan.baidu.com/article/3ea51489e7a9bd52e61bbac7.html android sdk 更新到 r23 时,eclipse 自带 ...
随机推荐
- 安卓发送图片文字,java后台接收
安卓使用retrofit2 和rxjava2 url: @Multipart @POST(UrlTools.STORYUPLOAD) Observable<Result> saveRepo ...
- 探索java世界中的日志奥秘
java日志简单介绍 对于一个应用程序来说日志记录是必不可少的一部分.线上问题追踪,基于日志的业务逻辑统计分析等都离不日志.JAVA领域存在多种日志框架,目前常用的日志 ...
- CSS3设计炫目字体
阴影 .text-shadow{ text-shadow:#FF0000 0 0 10px; color:white; font-size:60px } 描边 <style> .text- ...
- ipc (进程间通信
进程间通信(IPC,Inter-Process Communication),指至少两个进程或线程间传送数据或信号的一些技术或方法.进程是计算机系统分配资源的最小单位(严格说来是线程).每个进程都有自 ...
- node里读取命令行参数
一.process.env process.env属性返回一个包含用户环境信息的对象. 最常见的需求,前端需要根据不同的环境(dev,prd),来调用不同的后端接口.如果用webpack,是这么做的: ...
- copy contents of file with variable number in Matlab
input : transient.case output: transient_1.case, transient_2.case, transient_3.case ... ************ ...
- CodeForces - 357D - Xenia and Hamming
先上题目: D. Xenia and Hamming time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input st ...
- [UOJ#35] [UOJ后缀数组模板题] 后缀排序 [后缀数组模板]
后缀数组,解决字符串问题的有利工具,本题代码为倍增SA算法 具体解释详见2009年国家集训队论文 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> ...
- hdu_1859_最小长方形_201402282048
最小长方形 Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- Spring for Apache Kafka @KafkaListener使用及注意事项
官方文档: https://docs.spring.io/spring-kafka/reference/html/ @KafkaListener The @KafkaListener annota ...
