day 47 Django 4的简单应用 创建简单的图书管理 (单表的增删改查)
前情提要
Django 已经学了大半.. 很多东西已经能够使用在生产环境当中
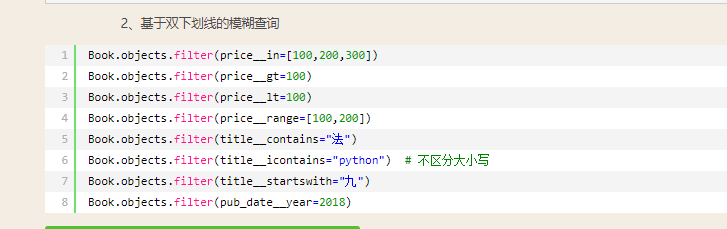
一:模糊查询
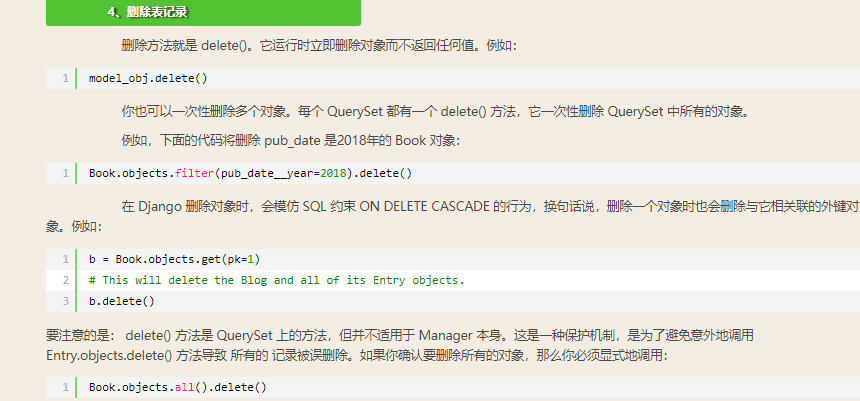
二:单表删除
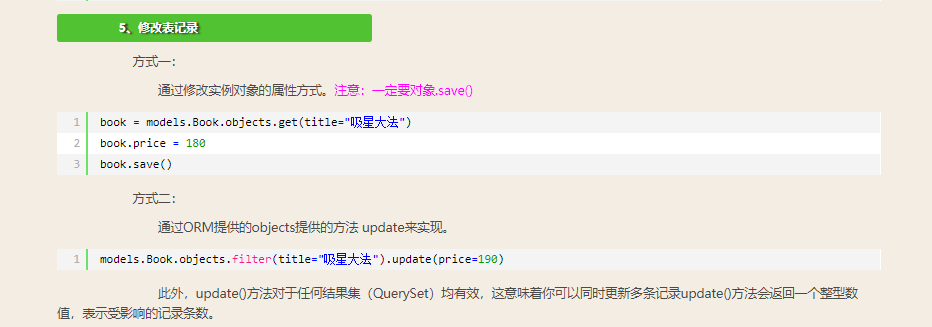
三:单表修改
四:图书管理
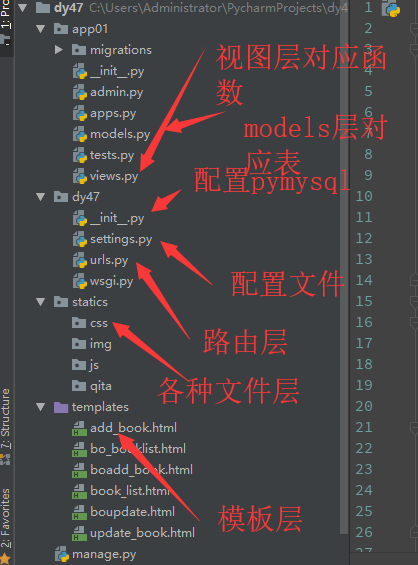
图书管理操作
视图结构
A:路由层
A :配置路由文件
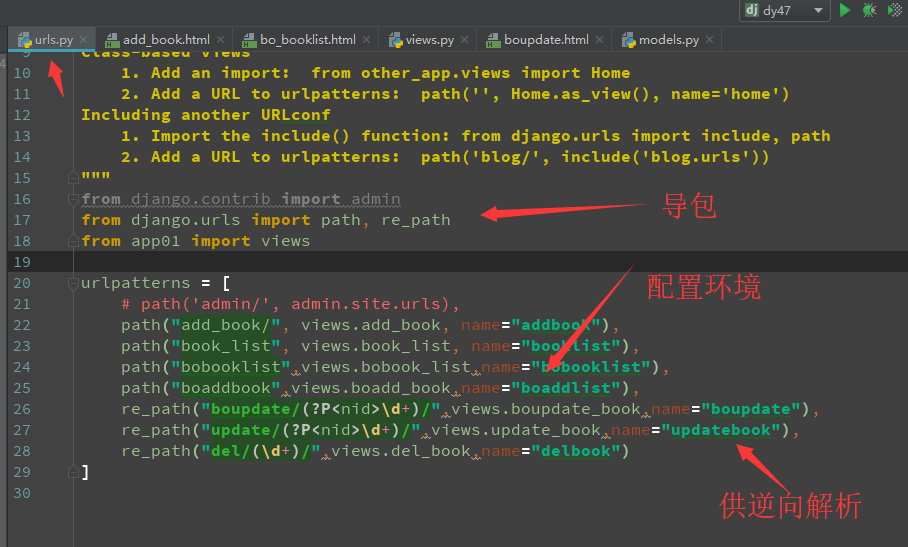
参数解析:
B :视图层
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse, redirect
from django.urls import reverse
from app01 import models # Create your views here.
def book_list(request):
if request.method == "GET":
book_list = models.Book.objects.all()
# print(book_list)
return render(request, "book_list.html", {
"booklist": book_list })
else:
add_title1 = request.POST.get("title1")
add_price1 = request.POST.get("price1") # price
add_publish1 = request.POST.get("publish1")
add_date1 = request.POST.get("date1")
models.Book.objects.create(title=add_title1,
price=add_price1,
publish=add_publish1,
pub_date=add_date1) print(add_title1, add_price1, add_publish1, )
return render(request, "book_list.html")
def bobook_list(request):
if request.method == "GET":
book_list = models.Book.objects.all()
# print(book_list)
return render(request, "bo_booklist.html", {
"booklist": book_list })
else:
add_title1 = request.POST.get("title1")
add_price1 = request.POST.get("price1") # price
add_publish1 = request.POST.get("publish1")
add_date1 = request.POST.get("date1")
models.Book.objects.create(title=add_title1,
price=add_price1,
publish=add_publish1,
pub_date=add_date1) print(add_title1, add_price1, add_publish1, )
return render(request, "bo_booklist.html") def add_book(request):
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, "add_book.html")
else:
add_title = request.POST.get("title") # title
add_price = request.POST.get("price") # price
add_publish = request.POST.get("publish")
add_date = request.POST.get("pub_date")
models.Book.objects.create(title=add_title,
price=add_price,
publish=add_publish,
pub_date=add_date)
return redirect(reverse("booklist"))
def boadd_book(request):
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, "boadd_book.html")
else:
add_title = request.POST.get("title") # title
add_price = request.POST.get("price") # price
add_publish = request.POST.get("publish")
add_date = request.POST.get("pub_date")
models.Book.objects.create(title=add_title,
price=add_price,
publish=add_publish,
pub_date=add_date)
return redirect(reverse("bobooklist")) def update_book(request, nid):
if request.method == "GET":
book = models.Book.objects.filter(nid=nid).first()
# print(book.title)
return render(request, "update_book.html", {"book": book})
else:
data = request.POST.dict()
del data['csrfmiddlewaretoken']
print(data)
models.Book.objects.filter(nid=nid).update(**data)
return redirect(reverse("booklist"))
def boupdate_book(request, nid):
if request.method == "GET":
book = models.Book.objects.filter(nid=nid).first()
# print(book.title)
return render(request, "boupdate.html", {"book": book})
else:
data = request.POST.dict()
del data['csrfmiddlewaretoken']
print(data)
models.Book.objects.filter(nid=nid).update(**data)
return redirect(reverse("bobooklist"))
def del_book(request,sid):
models.Book.objects.filter(nid=sid).delete()
return redirect(reverse("bobooklist"))
主要是单表练习.运用了跳转,. 逆向解析. 从html 获取内容,,,,将内容放到html,,从数据库获取内容,,将内容放到数据库,,
C模板层:
book_list
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> 三味书屋</h1>
<button><a href="{% url "addbook" %}">新增书籍</a></button>
<table border="">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>书名</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>出版商</th>
<th>日期</th>
<th>操作</th> </tr>
{% for book in booklist %}
<tr>
<td>{{forloop.counter}}</td>
<td>{{book.title}}</td>
<td>{{book.price}}</td>
<td>{{book.publish}}</td>
<td>{{ book.pub_date |date:"Y-m-d"}}</td>
<td><button value="" name=""><a href="{% url "updatebook" nid=book.nid %}">编辑</a></button>
<button value="" name=""><a href="{% url "delbook" book.nid %}">删除</a></button>
</td> </tr>
{% endfor %}
</table> <div>
<form action="{% url "booklist" %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<div> <span>书名 </span> <input type="text" name="title1" placeholder="请输入书名"><br>
<span>价格 </span> <input type="text" name="price1" placeholder="请输入价格"><br>
<span>出版商</span> <input type="text" name="publish1" placeholder="请输入出版商"><br>
<span>日期 </span> <input type="date" name="date1" placeholder="请输入日期"><br>
</div>
<div>
<button type="submit"><a href="">新增提交</a></button>
</div>
</form>
</div> </body>
</html>
add_book
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>add_book</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<form action="" method="post">
{%csrf_token %}
<div> <span>书名 </span> <input type="text" name="title" placeholder="请输入书名"><br>
<span>价格 </span> <input type="text" name="price" placeholder="请输入价格"><br>
<span>出版商</span> <input type="text" name="publish" placeholder="请输入出版商"><br>
<span>日期 </span> <input type="date" name="pub_date" placeholder="请输入日期"><br>
</div>
<div>
<button type="submit" name=""><a href="">新增提交</a></button>
</div>
</form>
</div> </body>
</html>
update_book
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<p>书名 <input type="text" placeholder="{{book.title}}" value="" name="title"></p>
<p>价格 <input type="text" placeholder="{{book.price}}" value="" name="price"></p>
<p>出版商 <input type="text" placeholder="{{book.publish}}" value="" name="publish"></p>
<p>日期 <input type="date" placeholder="{{book.pub_date}}" value="" name="pub_date"></p>
<button type="submit">修改</button>
</form> </body>
</html>
D: 参数文件配置
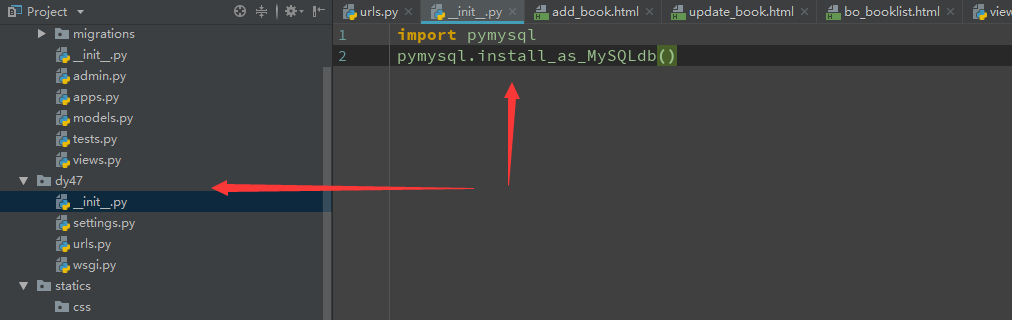
setting
"""
Django settings for dy47 project. Generated by 'django-admin startproject' using Django 2.1.. For more information on this file, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/settings/ For the full list of settings and their values, see
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/
""" import os # Build paths inside the project like this: os.path.join(BASE_DIR, ...)
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) # Quick-start development settings - unsuitable for production
# See https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/howto/deployment/checklist/ # SECURITY WARNING: keep the secret key used in production secret!
SECRET_KEY = '($z1^$1*b9gi7ydy(=tr7n85v^v7&ks5_pb_kxj)6u3ef12qi@' # SECURITY WARNING: don't run with debug turned on in production!
DEBUG = True ALLOWED_HOSTS = [] # Application definition INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'app01.apps.App01Config',
] MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
] ROOT_URLCONF = 'dy47.urls' TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')]
,
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
] WSGI_APPLICATION = 'dy47.wsgi.application' # Database
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/#databases DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
"NAME": "book2",
"HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"PROT": ,
"USER": "root",
"PASSWORD": ""
}
} # Password validation
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/ref/settings/#auth-password-validators AUTH_PASSWORD_VALIDATORS = [
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.UserAttributeSimilarityValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.MinimumLengthValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.CommonPasswordValidator',
},
{
'NAME': 'django.contrib.auth.password_validation.NumericPasswordValidator',
},
] # Internationalization
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/i18n/ LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' TIME_ZONE = 'UTC' USE_I18N = True USE_L10N = True USE_TZ = True # Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/howto/static-files/ STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "statics")
]
day 47 Django 4的简单应用 创建简单的图书管理 (单表的增删改查)的更多相关文章
- python全栈开发day61-django简单的出版社网站展示,添加,删除,编辑(单表的增删改查)
day61 django内容回顾: 1. 下载: pip install django==1.11.14 pip install -i 源 django==1.11.14 pycharm 2. 创建项 ...
- Django学习笔记(10)——Book单表的增删改查页面
一,项目题目:Book单表的增删改查页面 该项目主要练习使用Django开发一个Book单表的增删改查页面,通过这个项目巩固自己这段时间学习Django知识. 二,项目需求: 开发一个简单的Book增 ...
- django模型层 关于单表的增删改查
关于ORM MTV或者MVC框架中包括一个重要的部分,就是ORM,它实现了数据模型与数据库的解耦,即数据模型的设计不需要依赖于特定的数据库, 通过简单的配置就可以轻松更换数据库,这极大的减轻了开发人员 ...
- Django中对单表的增删改查
之前的简单预习,重点在后面 方式一: # create方法的返回值book_obj就是插入book表中的python葵花宝典这本书籍纪录对象 book_obj=Book.objects.creat ...
- django 利用ORM对单表进行增删改查
牛小妹上周末,一直在尝试如何把数据库的数据弄到界面上.毕竟是新手,搞不出来,文档也看不懂.不过没关系,才刚上大学.今晚我们就来解释下,要把数据搞到界面的第一步.先把数据放到库里,然后再把数据从库里拿出 ...
- Django学习笔记--数据库中的单表操作----增删改查
1.Django数据库中的增删改查 1.添加表和字段 # 创建的表的名字为app的名称拼接类名 class User(models.Model): # id字段 自增 是主键 id = models. ...
- $Django 模板层(模板导入,继承)、 单表*详(增删改查,基于双下划线的查询)、static之静态文件配置
0在python脚本中使用django环境 import osif __name__ == '__main__': os.environ.setdefault("DJANGO_SETT ...
- Django之单表的增删改查
books/urls.py """books URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to vi ...
- Django --- 单表的增删改查
随机推荐
- vue路由组件传参
在组件中使用 $route 会使之与其对应路由形成高度耦合,从而使组件只能在某些特定的 URL 上使用,限制了其灵活性. 使用 props 将组件和路由解耦: 取代与 $route 的耦合 const ...
- 使用JConsole监控HBase内存状态
使用JConsole或者VisualVM等工具监控HBase状态时,需要修改HBase的配置文件,以解决随机端口问题. 文件名:hbase-env.sh export HBASE_JMX_BASE=& ...
- AJAX初尝试——ACM/ICPC类比赛气球管理系统
很早之前做过一个,白板没界面,20秒暴力刷新,数据库每个team一个n列的对应n个题目的标记项,只能对单个比赛暴力把全部user_id导入单独的气球表(也就是cid=1000用这个表的话,cid100 ...
- 一文读懂:超详细正态分布方差等于o的推导
(uv)' = [(u+△u)(v+△v) - uv] /△x = (v△u+u△v +△u△v)/△x = v(△u/△x) + u(△v/△x) +(△u△v)/△x =u'v+uv'
- POJ 3686 The Windy's (最小费用流或最佳完全匹配)
题意:有n个订单m个车间,每个车间均可以单独完成任何一个订单.每个车间完成不同订单的时间是不同的.不会出现两个车间完成同一个订单的情况.给出每个订单在某个车间完成所用的时间.问订单完成的平均时间是多少 ...
- passwd: Have exhausted maximum number of retries for service
使用命令passwd修改密码时,遇到如下问题:# echo 'utf8'|passwd zhangsan --stdinChanging password for user zhangsan.pass ...
- Linux 用 sftp scp命令 互传文件
sftp它类似于 ftp, 但它进行加密传输,比FTP有更高的安全性. sftp 是SSH服务的子程序 常用命令 pwd 查看当前工作目录 ls 查看远程当前目录下的所以文件或者目录信息 lls 查看 ...
- ios开发 ad hoc怎么用
简单的说就是这样 ad hoc 方式是苹果用来给未上线的app做测试用的,首先你要在苹果开发平台上申请一个ad hoc的证书,再在profile中生成一个ad hoc 的profile文件(只需要在生 ...
- openfire消息发送
找了一些demo,做了一些示例,演示了基于xmpp协议的openfire的客户端之间消息的发送. 代码需要两个包,smack.jar ,smackx.jar. 第一个代码,只是点对点发送消息的,不涉及 ...
- CodeFirst迁移注意点
Context构造函数不检查__MigrationHistory 取消当数据库模型发生改变时删除当前数据库重建新数据库的设置.Database.SetInitializer<Context> ...
