大数据处理算法--Bloom Filter布隆过滤
1. Bloom-Filter算法简介
Bloom-Filter,即布隆过滤器,1970年由Bloom中提出。它可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。
Bloom Filter(BF)是一种空间效率很高的随机数据结构,它利用位数组很简洁地表示一个集合,并能判断一个元素是否属于这个集合。它是一个判断元素是否存在集合的快速的概率算法。Bloom Filter有可能会出现错误判断,但不会漏掉判断。也就是Bloom Filter判断元素不再集合,那肯定不在。如果判断元素存在集合中,有一定的概率判断错误。因此,Bloom Filter不适合那些“零错误”的应用场合。而在能容忍低错误率的应用场合下,Bloom Filter比其他常见的算法(如hash,折半查找)极大节省了空间。
它的优点是空间效率和查询时间都远远超过一般的算法,缺点是有一定的误识别率和删除困难。
Bloom Filter的详细介绍:Bloom Filter
2、 Bloom-Filter的基本思想
Bloom-Filter算法的核心思想就是利用多个不同的Hash函数来解决“冲突”。
计算某元素x是否在一个集合中,首先能想到的方法就是将所有的已知元素保存起来构成一个集合R,然后用元素x跟这些R中的元素一一比较来判断是否存在于集合R中;我们可以采用链表等数据结构来实现。但是,随着集合R中元素的增加,其占用的内存将越来越大。试想,如果有几千万个不同网页需要下载,所需的内存将足以占用掉整个进程的内存地址空间。即使用MD5,UUID这些方法将URL转成固定的短小的字符串,内存占用也是相当巨大的。
于是,我们会想到用Hash table的数据结构,运用一个足够好的Hash函数将一个URL映射到二进制位数组(位图数组)中的某一位。如果该位已经被置为1,那么表示该URL已经存在。
Hash存在一个冲突(碰撞)的问题,用同一个Hash得到的两个URL的值有可能相同。为了减少冲突,我们可以多引入几个Hash,如果通过其中的一个Hash值我们得出某元素不在集合中,那么该元素肯定不在集合中。只有在所有的Hash函数告诉我们该元素在集合中时,才能确定该元素存在于集合中。这便是Bloom-Filter的基本思想。
原理要点:一是位数组, 而是k个独立hash函数。
1)位数组:
假设Bloom Filter使用一个m比特的数组来保存信息,初始状态时,Bloom Filter是一个包含m位的位数组,每一位都置为0,即BF整个数组的元素都设置为0。
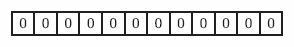
2)添加元素,k个独立hash函数
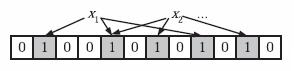
为了表达S={x1, x2,…,xn}这样一个n个元素的集合,Bloom Filter使用k个相互独立的哈希函数(Hash Function),它们分别将集合中的每个元素映射到{1,…,m}的范围中。
当我们往Bloom Filter中增加任意一个元素x时候,我们使用k个哈希函数得到k个哈希值,然后将数组中对应的比特位设置为1。即第i个哈希函数映射的位置hashi(x)就会被置为1(1≤i≤k)。
注意,如果一个位置多次被置为1,那么只有第一次会起作用,后面几次将没有任何效果。在下图中,k=3,且有两个哈希函数选中同一个位置(从左边数第五位,即第二个“1“处)。
3)判断元素是否存在集合
在判断y是否属于这个集合时,我们只需要对y使用k个哈希函数得到k个哈希值,如果所有hashi(y)的位置都是1(1≤i≤k),即k个位置都被设置为1了,那么我们就认为y是集合中的元素,否则就认为y不是集合中的元素。下图中y1就不是集合中的元素(因为y1有一处指向了“0”位)。y2或者属于这个集合,或者刚好是一个false positive。
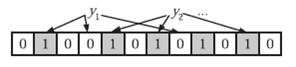
显然这 个判断并不保证查找的结果是100%正确的。
Bloom Filter的缺点:
1)Bloom Filter无法从Bloom Filter集合中删除一个元素。因为该元素对应的位会牵动到其他的元素。所以一个简单的改进就是 counting Bloom filter,用一个counter数组代替位数组,就可以支持删除了。 此外,Bloom Filter的hash函数选择会影响算法的效果。
2)还有一个比较重要的问题,如何根据输入元素个数n,确定位数组m的大小及hash函数个数,即hash函数选择会影响算法的效果。当hash函数个数k=(ln2)*(m/n)时错误率最小。在错误率不大于E的情况 下,m至少要等于n*lg(1/E) 才能表示任意n个元素的集合。但m还应该更大些,因为还要保证bit数组里至少一半为0,则m应 该>=nlg(1/E)*lge ,大概就是nlg(1/E)1.44倍(lg表示以2为底的对数)。
举个例子我们假设错误率为0.01,则此时m应大概是n的13倍。这样k大概是8个。
注意:
这里m与n的单位不同,m是bit为单位,而n则是以元素个数为单位(准确的说是不同元素的个数)。通常单个元素的长度都是有很多bit的。所以使用bloom filter内存上通常都是节省的。
一般BF可以与一些key-value的数据库一起使用,来加快查询。由于BF所用的空间非常小,所有BF可以常驻内存。这样子的话,对于大部分不存在的元素,我们只需要访问内存中的BF就可以判断出来了,只有一小部分,我们需要访问在硬盘上的key-value数据库。从而大大地提高了效率。
一个Bloom Filter有以下参数:
| m | bit数组的宽度(bit数) |
| n | 加入其中的key的数量 |
| k | 使用的hash函数的个数 |
| f | False Positive的比率 |
Bloom Filter的f满足下列公式:
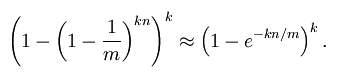
在给定m和n时,能够使f最小化的k值为:
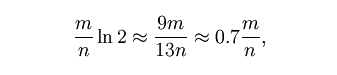
此时给出的f为:
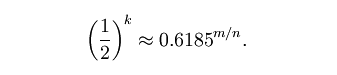
根据以上公式,对于任意给定的f,我们有:
3、 扩展 CounterBloom Filter
CounterBloom Filter
BloomFilter有个缺点,就是不支持删除操作,因为它不知道某一个位从属于哪些向量。那我们可以给Bloom Filter加上计数器,添加时增加计数器,删除时减少计数器。
但这样的Filter需要考虑附加的计数器大小,假如同个元素多次插入的话,计数器位数较少的情况下,就会出现溢出问题。如果对计数器设置上限值的话,会导致Cache Miss,但对某些应用来说,这并不是什么问题,如Web Sharing。
Compressed Bloom Filter
为了能在服务器之间更快地通过网络传输Bloom Filter,我们有方法能在已完成Bloom Filter之后,得到一些实际参数的情况下进行压缩。
将元素全部添加入Bloom Filter后,我们能得到真实的空间使用率,用这个值代入公式计算出一个比m小的值,重新构造Bloom Filter,对原先的哈希值进行求余处理,在误判率不变的情况下,使得其内存大小更合适。
4、 Bloom-Filter的应用
Bloom-Filter一般用于在大数据量的集合中判定某元素是否存在。例如邮件服务器中的垃圾邮件过滤器。在搜索引擎领域,Bloom-Filter最常用于网络蜘蛛(Spider)的URL过滤,网络蜘蛛通常有一个URL列表,保存着将要下载和已经下载的网页的URL,网络蜘蛛下载了一个网页,从网页中提取到新的URL后,需要判断该URL是否已经存在于列表中。此时,Bloom-Filter算法是最好的选择。
1.key-value 加快查询
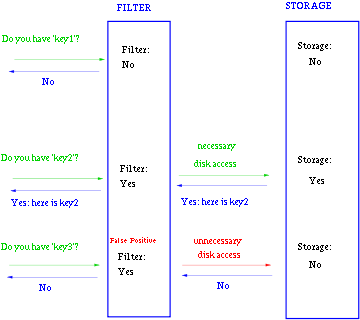
一般Bloom-Filter可以与一些key-value的数据库一起使用,来加快查询。
一般key-value存储系统的values存在硬盘,查询就是件费时的事。将Storage的数据都插入Filter,在Filter中查询都不存在时,那就不需要去Storage查询了。当False Position出现时,只是会导致一次多余的Storage查询。
由于Bloom-Filter所用的空间非常小,所有BF可以常驻内存。这样子的话,对于大部分不存在的元素,我们只需要访问内存中的Bloom-Filter就可以判断出来了,只有一小部分,我们需要访问在硬盘上的key-value数据库。从而大大地提高了效率。如图:
2 .Google的BigTable
Google的BigTable也使用了Bloom Filter,以减少不存在的行或列在磁盘上的查询,大大提高了数据库的查询操作的性能。
3. Proxy-Cache
在Internet Cache Protocol中的Proxy-Cache很多都是使用Bloom Filter存储URLs,除了高效的查询外,还能很方便得传输交换Cache信息。
4.网络应用
1)P2P网络中查找资源操作,可以对每条网络通路保存Bloom Filter,当命中时,则选择该通路访问。
2)广播消息时,可以检测某个IP是否已发包。
3)检测广播消息包的环路,将Bloom Filter保存在包里,每个节点将自己添加入Bloom Filter。
4)信息队列管理,使用Counter Bloom Filter管理信息流量。
5. 垃圾邮件地址过滤
像网易,QQ这样的公众电子邮件(email)提供商,总是需要过滤来自发送垃圾邮件的人(spamer)的垃圾邮件。
一个办法就是记录下那些发垃圾邮件的 email地址。由于那些发送者不停地在注册新的地址,全世界少说也有几十亿个发垃圾邮件的地址,将他们都存起来则需要大量的网络服务器。
如果用哈希表,每存储一亿个 email地址,就需要 1.6GB的内存(用哈希表实现的具体办法是将每一个 email地址对应成一个八字节的信息指纹,然后将这些信息指纹存入哈希表,由于哈希表的存储效率一般只有 50%,因此一个 email地址需要占用十六个字节。一亿个地址大约要 1.6GB,即十六亿字节的内存)。因此存贮几十亿个邮件地址可能需要上百 GB的内存。
而Bloom Filter只需要哈希表 1/8到 1/4 的大小就能解决同样的问题。
BloomFilter决不会漏掉任何一个在黑名单中的可疑地址。而至于误判问题,常见的补救办法是在建立一个小的白名单,存储那些可能别误判的邮件地址。
5、 Bloom-Filter的具体实现
c语言实现:
stdafx.h:
- #pragma once
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include "stdlib.h"
- #include <iostream>
- #include <time.h>
- using namespace std;
- #include "stdafx.h"
- #define ARRAY_SIZE 256 /*we get the 256 chars of each line*/
- #define SIZE 48000000 /* size should be 1/8 of max*/
- #define MAX 384000000/*the max bit space*/
- #define SETBIT(ch,n) ch[n/8]|=1<<(7-n%8)
- #define GETBIT(ch,n) (ch[n/8]&1<<(7-n%8))>>(7-n%8)
- unsigned int len(char *ch);/* functions to calculate the length of the url*/
- unsigned int RSHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int JSHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int PJWHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int ELFHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int BKDRHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int SDBMHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int DJBHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int DEKHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int BPHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int FNVHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int APHash(char* str, unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int HFLPHash(char* str,unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int HFHash(char* str,unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int StrHash( char* str,unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- unsigned int TianlHash(char* str,unsigned int len);/* functions to calculate the hash value of the url*/
- int main()
- {
- int i,num,num2=0; /* the number to record the repeated urls and the total of it*/
- unsigned int tt=0;
- int flag; /*it helps to check weather the url has already existed */
- char buf[257]; /*it helps to print the start time of the program */
- time_t tmp = time(NULL);
- char file1[100],file2[100];
- FILE *fp1,*fp2;/*pointer to the file */
- char ch[ARRAY_SIZE];
- char *vector ;/* the bit space*/
- vector = (char *)calloc(SIZE,sizeof(char));
- printf("Please enter the file with repeated urls:\n");
- scanf("%s",&file1);
- if( (fp1 = fopen(file1,"rb")) == NULL) { /* open the goal file*/
- printf("Connot open the file %s!\n",file1);
- }
- printf("Please enter the file you want to save to:\n");
- scanf("%s",&file2);
- if( (fp2 = fopen(file2,"w")) == NULL) {
- printf("Connot open the file %s\n",file2);
- }
- strftime(buf,32,"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S",localtime(&tmp));
- printf("%s\n",buf); /*print the system time*/
- for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++) {
- vector[i]=0; /*set 0*/
- }
- while(!feof(fp1)) { /* the check process*/
- fgets(ch,ARRAY_SIZE,fp1);
- flag=0;
- tt++;
- if( GETBIT(vector, HFLPHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,HFLPHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if( GETBIT(vector, StrHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,StrHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if( GETBIT(vector, HFHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,HFHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if( GETBIT(vector, DEKHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,DEKHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if( GETBIT(vector, TianlHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,TianlHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if( GETBIT(vector, SDBMHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX) ) {
- flag++;
- } else {
- SETBIT(vector,SDBMHash(ch,len(ch))%MAX );
- }
- if(flag<6)
- num2++;
- else
- fputs(ch,fp2);
- /* printf(" %d",flag); */
- }
- /* the result*/
- printf("\nThere are %d urls!\n",tt);
- printf("\nThere are %d not repeated urls!\n",num2);
- printf("There are %d repeated urls!\n",tt-num2);
- fclose(fp1);
- fclose(fp2);
- return 0;
- }
- /*functions may be used in the main */
- unsigned int len(char *ch)
- {
- int m=0;
- while(ch[m]!='\0') {
- m++;
- }
- return m;
- }
- unsigned int RSHash(char* str, unsigned int len) {
- unsigned int b = 378551;
- unsigned int a = 63689;
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i=0; i<len; str++, i++) {
- hash = hash*a + (*str);
- a = a*b;
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of RS Hash Function */
- unsigned int JSHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 1315423911;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i=0; i<len; str++, i++) {
- hash ^= ((hash<<5) + (*str) + (hash>>2));
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of JS Hash Function */
- unsigned int PJWHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- const unsigned int BitsInUnsignedInt = (unsigned int)(sizeof(unsigned int) * 8);
- const unsigned int ThreeQuarters = (unsigned int)((BitsInUnsignedInt * 3) / 4);
- const unsigned int OneEighth = (unsigned int)(BitsInUnsignedInt / 8);
- const unsigned int HighBits = (unsigned int)(0xFFFFFFFF) << (BitsInUnsignedInt - OneEighth);
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int test = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i=0;i<len; str++, i++) {
- hash = (hash<<OneEighth) + (*str);
- if((test = hash & HighBits) != 0) {
- hash = ((hash ^(test >> ThreeQuarters)) & (~HighBits));
- }
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of P. J. Weinberger Hash Function */
- unsigned int ELFHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int x = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash = (hash << 4) + (*str);
- if((x = hash & 0xF0000000L) != 0) {
- hash ^= (x >> 24);
- }
- hash &= ~x;
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of ELF Hash Function */
- unsigned int BKDRHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int seed = 131; /* 31 131 1313 13131 131313 etc.. */
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++)
- {
- hash = (hash * seed) + (*str);
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of BKDR Hash Function */
- unsigned int SDBMHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash = (*str) + (hash << 6) + (hash << 16) - hash;
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of SDBM Hash Function */
- unsigned int DJBHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 5381;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + (*str);
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of DJB Hash Function */
- unsigned int DEKHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = len;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash = ((hash << 5) ^ (hash >> 27)) ^ (*str);
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of DEK Hash Function */
- unsigned int BPHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash = hash << 7 ^ (*str);
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of BP Hash Function */
- unsigned int FNVHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- const unsigned int fnv_prime = 0x811C9DC5;
- unsigned int hash = 0;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash *= fnv_prime;
- hash ^= (*str);
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of FNV Hash Function */
- unsigned int APHash(char* str, unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int hash = 0xAAAAAAAA;
- unsigned int i = 0;
- for(i = 0; i < len; str++, i++) {
- hash ^= ((i & 1) == 0) ? ( (hash << 7) ^ (*str) * (hash >> 3)) :
- (~((hash << 11) + (*str) ^ (hash >> 5)));
- }
- return hash;
- }
- /* End Of AP Hash Function */
- unsigned int HFLPHash(char *str,unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned int n=0;
- int i;
- char* b=(char *)&n;
- for(i=0;i<strlen(str);++i) {
- b[i%4]^=str[i];
- }
- return n%len;
- }
- /* End Of HFLP Hash Function*/
- unsigned int HFHash(char* str,unsigned int len)
- {
- int result=0;
- char* ptr=str;
- int c;
- int i=0;
- for (i=1;c=*ptr++;i++)
- result += c*3*i;
- if (result<0)
- result = -result;
- return result%len;
- }
- /*End Of HKHash Function */
- unsigned int StrHash( char *str,unsigned int len)
- {
- register unsigned int h;
- register unsigned char *p;
- for(h=0,p=(unsigned char *)str;*p;p++) {
- h=31*h+*p;
- }
- return h;
- }
- /*End Of StrHash Function*/
- unsigned int TianlHash(char *str,unsigned int len)
- {
- unsigned long urlHashValue=0;
- int ilength=strlen(str);
- int i;
- unsigned char ucChar;
- if(!ilength) {
- return 0;
- }
- if(ilength<=256) {
- urlHashValue=16777216*(ilength-1);
- } else {
- urlHashValue = 42781900080;
- }
- if(ilength<=96) {
- for(i=1;i<=ilength;i++) {
- ucChar=str[i-1];
- if(ucChar<='Z'&&ucChar>='A') {
- ucChar=ucChar+32;
- }
- urlHashValue+=(3*i*ucChar*ucChar+5*i*ucChar+7*i+11*ucChar)%1677216;
- }
- } else {
- for(i=1;i<=96;i++)
- {
- ucChar=str[i+ilength-96-1];
- if(ucChar<='Z'&&ucChar>='A')
- {
- ucChar=ucChar+32;
- }
- urlHashValue+=(3*i*ucChar*ucChar+5*i*ucChar+7*i+11*ucChar)%1677216;
- }
- }
- return urlHashValue;
- }
- /*End Of Tianl Hash Function*/
网上找到的php简单实现:
- <?php
- /**
- * Implements a Bloom Filter
- */
- class BloomFilter {
- /**
- * Size of the bit array
- *
- * @var int
- */
- protected $m;
- /**
- * Number of hash functions
- *
- * @var int
- */
- protected $k;
- /**
- * Number of elements in the filter
- *
- * @var int
- */
- protected $n;
- /**
- * The bitset holding the filter information
- *
- * @var array
- */
- protected $bitset;
- /**
- * 计算最优的hash函数个数:当hash函数个数k=(ln2)*(m/n)时错误率最小
- *
- * @param int $m bit数组的宽度(bit数)
- * @param int $n 加入布隆过滤器的key的数量
- * @return int
- */
- public static function getHashCount($m, $n) {
- return ceil(($m / $n) * log(2));
- }
- /**
- * Construct an instance of the Bloom filter
- *
- * @param int $m bit数组的宽度(bit数) Size of the bit array
- * @param int $k hash函数的个数 Number of different hash functions to use
- */
- public function __construct($m, $k) {
- $this->m = $m;
- $this->k = $k;
- $this->n = 0;
- /* Initialize the bit set */
- $this->bitset = array_fill(0, $this->m - 1, false);
- }
- /**
- * False Positive的比率:f = (1 – e-kn/m)k
- * Returns the probability for a false positive to occur, given the current number of items in the filter
- *
- * @return double
- */
- public function getFalsePositiveProbability() {
- $exp = (-1 * $this->k * $this->n) / $this->m;
- return pow(1 - exp($exp), $this->k);
- }
- /**
- * Adds a new item to the filter
- *
- * @param mixed Either a string holding a single item or an array of
- * string holding multiple items. In the latter case, all
- * items are added one by one internally.
- */
- public function add($key) {
- if (is_array($key)) {
- foreach ($key as $k) {
- $this->add($k);
- }
- return;
- }
- $this->n++;
- foreach ($this->getSlots($key) as $slot) {
- $this->bitset[$slot] = true;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Queries the Bloom filter for an element
- *
- * If this method return FALSE, it is 100% certain that the element has
- * not been added to the filter before. In contrast, if TRUE is returned,
- * the element *may* have been added to the filter previously. However with
- * a probability indicated by getFalsePositiveProbability() the element has
- * not been added to the filter with contains() still returning TRUE.
- *
- * @param mixed Either a string holding a single item or an array of
- * strings holding multiple items. In the latter case the
- * method returns TRUE if the filter contains all items.
- * @return boolean
- */
- public function contains($key) {
- if (is_array($key)) {
- foreach ($key as $k) {
- if ($this->contains($k) == false) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- foreach ($this->getSlots($key) as $slot) {
- if ($this->bitset[$slot] == false) {
- return false;
- }
- }
- return true;
- }
- /**
- * Hashes the argument to a number of positions in the bit set and returns the positions
- *
- * @param string Item
- * @return array Positions
- */
- protected function getSlots($key) {
- $slots = array();
- $hash = self::getHashCode($key);
- mt_srand($hash);
- for ($i = 0; $i < $this->k; $i++) {
- $slots[] = mt_rand(0, $this->m - 1);
- }
- return $slots;
- }
- /**
- * 使用CRC32产生一个32bit(位)的校验值。
- * 由于CRC32产生校验值时源数据块的每一bit(位)都会被计算,所以数据块中即使只有一位发生了变化,也会得到不同的CRC32值。
- * Generates a numeric hash for the given string
- *
- * Right now the CRC-32 algorithm is used. Alternatively one could e.g.
- * use Adler digests or mimick the behaviour of Java's hashCode() method.
- *
- * @param string Input for which the hash should be created
- * @return int Numeric hash
- */
- protected static function getHashCode($string) {
- return crc32($string);
- }
- }
- $items = array("first item", "second item", "third item");
- /* Add all items with one call to add() and make sure contains() finds
- * them all.
- */
- $filter = new BloomFilter(100, BloomFilter::getHashCount(100, 3));
- $filter->add($items);
- //var_dump($filter); exit;
- $items = array("firsttem", "seconditem", "thirditem");
- foreach ($items as $item) {
- var_dump(($filter->contains($item)));
- }
- /* Add all items with multiple calls to add() and make sure contains()
- * finds them all.
- */
- $filter = new BloomFilter(100, BloomFilter::getHashCount(100, 3));
- foreach ($items as $item) {
- $filter->add($item);
- }
- $items = array("fir sttem", "secondit em", "thir ditem");
- foreach ($items as $item) {
- var_dump(($filter->contains($item)));
- }
问题实例】 给你A,B两个文件,各存放50亿条URL,每条URL占用64字节,内存限制是4G,让你找出A,B文件共同的URL。如果是三个乃至n个文件呢?
根据这个问题我们来计算下内存的占用,4G=2^32大概是40亿*8大概是340亿bit,n=50亿,如果按出错率0.01算需要的大概是650亿个bit。 现在可用的是340亿,相差并不多,这样可能会使出错率上升些。另外如果这些urlip是一一对应的,就可以转换成ip,则大大简单了。
大数据处理算法--Bloom Filter布隆过滤的更多相关文章
- 海量数据处理算法—Bloom Filter
海量数据处理算法—Bloom Filter 1. Bloom-Filter算法简介 Bloom-Filter,即布隆过滤器,1970年由Bloom中提出.它可以用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中. Bl ...
- 【转】海量数据处理算法-Bloom Filter
1. Bloom-Filter算法简介 Bloom Filter(BF)是一种空间效率很高的随机数据结构,它利用位数组很简洁地表示一个集合,并能判断一个元素是否属于这个集合.它是一个判断元素是否存在于 ...
- 【转】Bloom Filter布隆过滤器的概念和原理
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/jiaomeng/article/details/1495500 之前看数学之美丽,里面有提到布隆过滤器的过滤垃圾邮件,感觉到何其的牛,竟然有这么高效的 ...
- Bloom Filter 布隆过滤器
Bloom Filter 是由伯顿.布隆(Burton Bloom)在1970年提出的一种多hash函数映射的快速查找算法.它实际上是一个很长的二进制向量和一些列随机映射函数.应用在数据量很大的情况下 ...
- 海量信息库,查找是否存在(bloom filter布隆过滤器)
Bloom Filter(布隆过滤器) 布隆过滤器用于测试某一元素是否存在于给定的集合中,是一种空间利用率很高的随机数据结构(probabilistic data structure),存在一定的误识 ...
- Bloom Filter布隆过滤器原理和实现(1)
引子 <数学之美>介绍布隆过滤器非常经典: 在日常生活中,包括设计计算机软件时,经常要判断一个元素是否在一个集合中.比如: 在字处理软件中,需要检查一个英语单词是否拼写正确(也就是要判断它 ...
- Bloom Filter(布隆过滤器)的概念和原理
Bloom filter 适用范围:可以用来实现数据字典,进行数据的判重,或者集合求交集 基本原理及要点: 对于原理来说很简单,位数组+k个独立hash函数.将hash函数对应的值的位数组置1,查找时 ...
- 海量数据处理之Bloom Filter详解
前言 : 即可能误判 不会漏判 一.什么是Bloom Filter Bloom Filter是一种空间效率很高的随机数据结构,它的原理是,当一个元素被加入集合时,通过K个Hash函 ...
- 浅谈布隆过滤器Bloom Filter
先从一道面试题开始: 给A,B两个文件,各存放50亿条URL,每条URL占用64字节,内存限制是4G,让你找出A,B文件共同的URL. 这个问题的本质在于判断一个元素是否在一个集合中.哈希表以O(1) ...
随机推荐
- apigateway-kong(七)配置说明
这一部分应该在最开始介绍,但是我觉得在对kong有一定了解后再回头看下配置,会理解的更深刻.接下来对这个配置文件里的参数做个详细的解释便于更好的使用或优化kong网关. 目录 一.配置加载 二.验证配 ...
- (大数 string) Integer Inquiry hdu1047
Integer Inquiry Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- Linux网络协议栈(一)——Socket入门(2)
转自: http://www.cnblogs.com/hustcat/archive/2009/09/17/1568765.html 3.套接字的实现套接字最先是在UNIX的BSD版本实现的,所以也叫 ...
- java中BorderLayout的使用方法
相关设置: 使用BorderLayout布局上下左右中布局5个按键,单击中间的那个按键时就关闭窗口 代码: /**** *java中BorderLayout的使用方法 * 使用BorderLayout ...
- 记一次B站答题经历
第一题部分:社区规范卷 --------- ------------ 第二题:社区规范第二部分 -------------------- 第三部分自由选择题 --------------------- ...
- Linux下Shell去除空行的方法
1.用grep命令 grep -v “^$” 文件名 2.用sed命令 cat 文件名 | sed ‘/^$/d' 3.用awk命令 cat 文件名 | awk ‘{if($0!=”")pr ...
- 面向对象【day07】:新式类和经典类(八)
本节内容 1.概述 2.类的多继承 3.经典类VS新式类 4.总结 一.概述 在python还支持多继承,但是一般我们很少用,有些语言干脆就不支持多继承,有多继承,就会带来两个概念,经典类和新式类,下 ...
- 8、Python-函数
定义 def printInfo(): print("人生苦短,我用Python") 调用 def printInfo(): print("人生苦短,我用Python&q ...
- Vue.js 模板指令
1. 数据渲染:v-text.v-html(保存了html结构).{{}}(自动更新): 2. 控制模块隐藏:v-if:直接不渲染 DOM 元素: v-show:css 里的 display:none ...
- java实现获取当前年月日 小时 分钟 秒 毫秒
java代码实现如下 view source print? /** * 英文简写(默认)如:2010-12-01 */ public static String F ...
