NOIP模拟题 2017.11.6

题目大意 给定一个大小为n的数组,从中选出一个子集使得这个子集中的数的和能被n整除。
假设开始我没有做出来,那么我就random_shuffle一下,然后计算前缀和,有一个能被n整除,就输出答案。于是这道题就过了。(数据水得起飞)
考虑计算前缀和,如果存在两个前缀和在模n的意义同余,那么就有可以将两个前缀和相减得到的一段区间的和,它的和就是n的倍数。
考虑这么做的正确性,模n的意义下有n个数,但是前缀和总共有(n + 1)个数。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#ifdef WIN32
#define Auto "%I64d"
#else
#define Auto "%lld"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b)
#define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b)
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u) {
char x;
while(!isdigit(x = getchar()));
+ x - ');
}
int n;
int* a;
;
int L, R;
inline void init() {
readInteger(n);
a = )];
memset(a, -, ));
a[] = ;
, x; i <= n; i++) {
readInteger(x);
s = (s + x) % n;
) {
L = a[s] + , R = i;
return;
}
a[s] = i;
}
}
inline void solve() {
printf();
for(int i = L; i <= R; i++)
printf("%d ", i);
}
int main() {
freopen("set.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("set.out", "w", stdout);
init();
solve();
;
}


题目大意 有n本书,每次只能选择和上次种类不同的书阅读,问最少有多少本书看不了。
仔细分析题目可以得到一个信息:如果种类最多的那本书的数量大于n的一半,那么答案就是它的两倍减n减1。否则答案为0。
由于我只关心出现次数超过一半的众数的出现次数,因此有了以下三种解法(2骗分 + 1正解)
Solution 1 (抽样法I)
随机抽取一些位置,求出它们的众数,然后再带进原序列中求出现次数。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#ifdef WIN32
#define Auto "%I64d"
#else
#define Auto "%lld"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define ll long long
#define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b)
#define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b)
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u) {
char x;
while(!isdigit(x = getchar()));
+ x - ');
}
int m, k;
;
int *counter;
int *X, *Y, *Z, S;
int myrand() {
| rand();
}
inline void init() {
readInteger(m);
readInteger(k);
counter = )];
X = )];
Y = )];
Z = )];
S = ( << k) - ;
; i <= m; i++) {
readInteger(counter[i]);
n += counter[i];
}
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(X[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Y[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Z[i]);
}
;
int pos[randTime];
inline void solve() {
; i < randTime; i++)
pos[i] = myrand() % n;
sort(pos + , pos + randTime);
, pos + randTime) - pos;
, cnt = , id = -;
; i <= m && p < len; i++) {
last = X[i];
if(cnt == pos[p])
pos[p++] = last;
cnt++;
; j < counter[i]; j++, cnt++) {
last = (last * 1LL * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S;
if(cnt == pos[p])
pos[p++] = last;
}
}
pos[] = -;
sort(pos + , pos + len);
, maxcnt = ;
; i < len; i++) {
])
cmp = ;
if(++cmp > maxcnt)
maxcnt = cmp, id = pos[i];
}
cnt = ;
; i <= m; i++) {
cnt += (last = X[i]) == id;
; j < counter[i]; j++)
cnt += (last = (last * 1LL * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S) == id;
}
)
printf(");
else
printf( * cnt - n - );
}
int main() {
freopen("read.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("read.out", "w", stdout);
srand();
init();
solve();
;
}
read (Random I)
Solution 2 (抽样法II)
抽取每一段前10个,求出它们的众数,然后再带回原序列中求出现次数。
显然数据很水所以过了,然后求众数时,我没有排序,还是过了(这。。。)
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#ifdef WIN32
#define Auto "%I64d"
#else
#define Auto "%lld"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define ll long long
#define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b)
#define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b)
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u) {
char x;
while(!isdigit(x = getchar()));
+ x - ');
}
int m, k;
;
];
], Y[], Z[], S;
int myrand() {
| rand();
}
inline void init() {
readInteger(m);
readInteger(k);
S = ( << k) - ;
; i <= m; i++) {
readInteger(counter[i]);
n += counter[i];
}
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(X[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Y[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Z[i]);
}
];
inline void solve() {
;
; i <= m; i++) {
pos[++len] = X[i];
; j <= counter[i] && j < ; j++)
pos[++len] = (pos[len - ] * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S;
}
pos[] = -;
, id, maxcnt = , cnt, last;
; i < len; i++) {
])
cmp = ;
if(++cmp > maxcnt)
maxcnt = cmp, id = pos[i];
}
cnt = ;
; i <= m; i++) {
cnt += (last = X[i]) == id;
; j < counter[i]; j++)
cnt += (last = (last * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S) == id;
}
)
printf(");
else
printf( * cnt - n - );
}
int main() {
freopen("read.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("read.out", "w", stdout);
// srand(233);
init();
solve();
;
}
read (Random II)
Solution 3 (求和法)
因为它出现次数大于一半,所以考虑用一个 cnt 和一个 id
枚举序列中每个数,如果 cnt == ,那么就将 id 赋值为当前枚举的这个数,并将cnt置为1。
否则,如果当前的这个数和 id 相等,就将 cnt 的值加1,否则减1。
这个算法完成后,我们会得到一个是出现次数超过n的一半的众数或者一个诡异的数,最后再把得到的id带回去求次数。
这么做的正确性显然(虽然解释不了但是觉得显然正确啊)。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#ifdef WIN32
#define Auto "%I64d"
#else
#define Auto "%lld"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define ll long long
#define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b)
#define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b)
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u) {
char x;
while(!isdigit(x = getchar()));
+ x - ');
}
int m, k;
;
int *counter;
int *X, *Y, *Z, S;
inline void init() {
readInteger(m);
readInteger(k);
counter = )];
X = )];
Y = )];
Z = )];
S = ( << k) - ;
; i <= m; i++) {
readInteger(counter[i]);
n += counter[i];
}
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(X[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Y[i]);
; i <= m; i++)
readInteger(Z[i]);
}
, id;
inline void add(int x) {
)
id = x, cnt = ;
else if(id == x)
cnt++;
else
cnt--;
}
inline void solve() {
int last;
; i <= m; i++) {
add(last = X[i]);
; j < counter[i]; j++)
add(last = (last * 1LL * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S);
}
cnt = ;
; i <= m; i++) {
cnt += (last = X[i]) == id;
; j < counter[i]; j++)
cnt += (last = (last * 1LL * Y[i] + Z[i]) & S) == id;
}
)
printf(");
else
printf( * cnt - n - );
}
int main() {
freopen("read.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("read.out", "w", stdout);
init();
solve();
;
}


题目大意 (题目太简洁,无法概括大意)
因为涉及到了可恶的位运算,为了更好地处理它们,所以想到Trie树。
如果Trie树的一个非叶节点在两天中表示的名次在a ~ b之间,设它的两棵子树的大小分别为s1和s2。
那么左子树表示的区间就是a ~ (a + s1 - 1)和(a + s2) ~ b,右子树同理。
因为最终到了叶节点,表示的区间都变成a ~ a的形式,并且我们关心的只是平方和。
所以考虑如何维护所有开始端点的平方和。
写写式子发现:
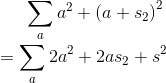
由于然后发现再维护一下所有左端点的和就可以搞定了。
写代码的时候可以用黑科技优化,不建Trie树就可以直接搞答案。先将A数组排序,然后对于每一层都进行二分查找这一位0和1的分界位置。
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <cctype>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#ifdef WIN32
#define Auto "%I64d"
#else
#define Auto "%lld"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define ll long long
#define smin(_a, _b) _a = min(_a, _b)
#define smax(_a, _b) _a = max(_a, _b)
template<typename T>
inline void readInteger(T& u) {
static char x;
while(!isdigit(x = getchar()));
+ x - ');
}
;
int n, m;
;
ll S;
int* A;
inline void init() {
readInteger(n);
readInteger(m);
A = )];
S = (1ll << (m - ));
; i <= n; i++)
readInteger(A[i]);
}
void dfs(int dep, int L, int R, ll sum, ll sum2) {
if(L == R) {
ans ^= (sum2 % M);
return;
}
int l = L, r = R;
while(l <= r) {
;
<< dep)) r = mid - ;
;
}
, s2 = R - r;
, L, r, sum + S * s2, sum2 + (ll)sum * s2 + S * s2 * s2);
, r + , R, sum + S * s1, sum2 + (ll)sum * s1 + S * s1 * s1);
}
inline void solve() {
sort(A + , A + n + );
dfs(m - , , n, , );
printf("%d", ans);
}
int main() {
freopen("race.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("race.out", "w", stdout);
init();
solve();
;
}
NOIP模拟题 2017.11.6的更多相关文章
- NOIP模拟题 2017.7.3 - 模拟 - 贪心 - 记忆化搜索
直接暴力模拟,注意判数据结构为空时的取出操作. Code #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<ctime> # ...
- noip模拟题 2017.10.28 -kmp -Tarjan -鬼畜的优化
题目大意 给定A串,选择A串的前lB个字符作为B串,再在B串后增加一个字符,问最长的相等的A串前缀和B串的后缀. Solution 1(KMP) 用1个奇怪的字符连接A串和B串,再用KMP求最长公共前 ...
- NOIP模拟题汇总(加厚版)
\(NOIP\)模拟题汇总(加厚版) T1 string 描述 有一个仅由 '0' 和 '1' 组成的字符串 \(A\),可以对其执行下列两个操作: 删除 \(A\)中的第一个字符: 若 \(A\)中 ...
- 【入门OJ】2003: [Noip模拟题]寻找羔羊
这里可以复制样例: 样例输入: agnusbgnus 样例输出: 6 这里是链接:[入门OJ]2003: [Noip模拟题]寻找羔羊 这里是题解: 题目是求子串个数,且要求简单去重. 对于一个例子(a ...
- 9.9 NOIP模拟题
9.9 NOIP模拟题 T1 两个圆的面积求并 /* 计算圆的面积并 多个圆要用辛普森积分解决 这里只有两个,模拟计算就好 两圆相交时,面积并等于中间两个扇形面积减去两个三角形面积 余弦定理求角度,算 ...
- 8.22 NOIP 模拟题
8.22 NOIP 模拟题 编译命令 g++ -o * *.cpp gcc -o * *.c fpc *.pas 编译器版本 g++/gcc fpc 评测环境 位 Linux, .3GHZ CPU ...
- NOIP模拟赛-2018.11.7
NOIP模拟赛 如果用命令行编译程序可以发现没加头文件之类的错误. 如果用命令行编译程序可以发现没加头文件之类的错误. 如果用命令行编译程序可以发现没加头文件之类的错误. 编译之前另存一份,听说如果敲 ...
- NOIP模拟赛-2018.11.6
NOIP模拟赛 今天想着反正高一高二都要考试,那么干脆跟着高二考吧,因为高二的比赛更有技术含量(我自己带的键盘放在这里). 今天考了一套英文题?发现阅读理解还是有一些困难的. T1:有$n$个点,$m ...
- NOIP模拟题17.9.26
B 君的任务(task)[题目描述]与君初相识,犹如故人归.B 君看到了Z 君的第一题,觉得很难.于是自己出了一个简单题.你需要完成n 个任务,第i 任务有2 个属性ai; bi.其中ai 是完成这个 ...
随机推荐
- vuex使用一
至于为什么使用vuex在这里就不过多的解释了,直接进入正题 1.vuex的安装 cnpm install vuex -S 2.然后在main.js中引入 import Vue from 'vue' i ...
- caffe-ssd运行create_data.sh的时候报错:SSD from caffe.proto import caffe_pb2 ImportError: No module named caffe.proto
在用voc2007和voc2012的数据训练基于caffe的SSD模型的时候,我们需要将图片数据转换成lmdb格式,运行脚本文件是SSD源码里面提供的create_data.sh(具体位置在$CAFF ...
- ubuntu安装python-mysqldb
前期准备: sudo apt-get install libmysqld-dev sudo apt-get install libmysqlclient-dev sudo apt-get insta ...
- html5-css渐变应用小实例,按钮
.but1{ padding: 10px 20px; font-size: 16px; text-shadow: 2px 2px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.8); bo ...
- B树,B+树,B*树以及R树的介绍
https://blog.csdn.net/peterchan88/article/details/52248714 作者:July.weedge.Frankie.编程艺术室出品. 说明:本文从B树开 ...
- JavaScript--常用的输出方式
1.alert("要输出的内容"); 在浏览器中弹出一个对话框,然后把要输出的内容展示出来 2.document.write("要输出的内容"); ...
- uva 1322 Minimizing Maximizer
题意: 有n个数,m个排序器,每个排序器可以把区间ai到bi的数从小到大排序.这m个排序器的输出就是m个排序之后的第n个数. 现在发现有些排序器是多余的.问至少需要多少个排序器可以使得输出不变.排序器 ...
- C#基础知识整理
年时,北风吹雁雪纷纷,一条秋裤冻上头.冷的连手都懒得动,就随便翻翻书,也没有更新博客,如今年已过,开始投入到正常的工作状态中,趁现在需求还没有来,把C#基础知识梳理一下,其实一直以来就想这样做的,对于 ...
- jsp页面报错 javax.servlet cannot be resolved to a type
需要引入 Tomcat 中的两个 jar 包: servlet-api jsp-api.jar
- python 将文件描述符包装成文件对象
有一个对应于操作系统上一个已打开的I/O 通道(比如文件.管道.套接字等)的整型文件描述符,你想将它包装成一个更高层的Python 文件对象. 一个文件描述符和一个打开的普通文件是不一样的.文件描述符 ...
