.NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Configuration(二)
文件型配置基本内容
上一篇文章讨论了Configuration的几个核心对象,本文继续讨论Configuration中关于文件型配置的相关内容。相比较而言,文件型配置的使用场景更加广泛,用户自定义配置扩展也可以基于文件型配置进行扩展。如果需要查看上一篇文章,可以点击移步。
.NET Core文件型配置中我们提供了三种主要的实现,分别是JSON、XML、INI,请查看下图
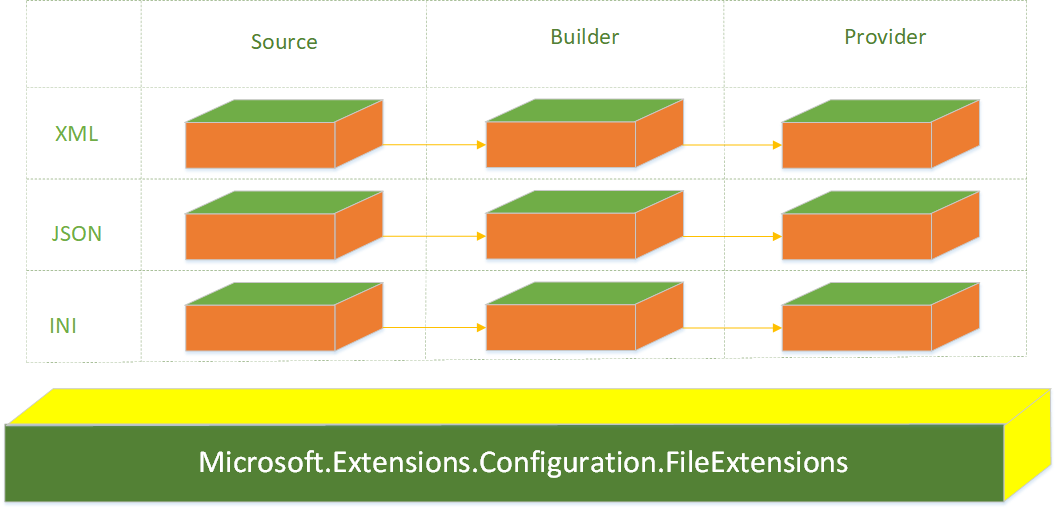
由图可知,这三种配置的实现方式是一样的,当然了其他的配置比如命令行配置、环境变量配置等也是大同小异,理解了改配置类型的实现方式,后面我们再扩展基于Consul或者ZK的实现,就非常简单了。
文件型配置的抽象扩展
文件型配置的抽象扩展位于Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.FileExtensions组件中,该扩展是一个基础实现。不过其命名空间是Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration,而Micros oft.Extensions.Configuration扩建本身又是整个.NET Core Configuration的基础实现。将File扩展独立于外部,体验了.NET Core的模块化设计。
FileConfigurationSource
Configuration.FileExtensions组件中,FileConfigurationSource是继承于IConfigurationSource的一个抽象类,包含了一个IConfigurationProvider类型的抽象方法,如下所示
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Builds the <see cref="IConfigurationProvider"/> for this source.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</param>
5: /// <returns>A <see cref="IConfigurationProvider"/></returns>
6: public abstract IConfigurationProvider Build(IConfigurationBuilder builder);
该抽象类中还包括了几个比较重要的参数,分别用于配置性行为、文件内容访问以及异常处理。
string Path:文件的路径
bool Optional:标识加载的文件是否是可选的
bool ReloadOnChange:如果文件发生修改,是否重新加载配置源
int ReloadDelay:加载延迟,单位是毫秒,默认是250毫秒
IFileProvider FileProvider:用于获取文件内容
Action<FileLoadExceptionContext> OnLoadException:文件加载异常处理
该类对FileProvider有特殊处理,就是如果没有提供FileProvider实例,则会基于绝对路径,在最近的现有目录中创建物理文件提供程序。源码如下,
1: /// <summary>
2: /// If no file provider has been set, for absolute Path, this will creates a physical file provider
3: /// for the nearest existing directory.
4: /// </summary>
5: public void ResolveFileProvider()
6: {
7: if (FileProvider == null &&
8: !string.IsNullOrEmpty(Path) &&
9: System.IO.Path.IsPathRooted(Path))
10: {
11:
var directory = System.IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(Path);
12: var pathToFile = System.IO.Path.GetFileName(Path);
13: while (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(directory) && !Directory.Exists(directory))
14: {
15: pathToFile = System.IO.Path.Combine(System.IO.Path.GetFileName(directory), pathToFile);
16: directory = System.IO.Path.GetDirectoryName(directory);
17: }
18: if (Directory.Exists(directory))
19: {
20: FileProvider = new PhysicalFileProvider(directory);
21: Path = pathToFile;
22: }
23: }
24: }
FileConfigurationProvider
该类是继承于ConfigurationProvider的抽象类,是从文件系统加载配置的基类,同时还继承了IDisposable,其抽象方法是Load方法,用于从当前的Provider中以Stream方式加载数据
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Loads this provider's data from a stream.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="stream">The stream to read.</param>
5: public abstract void Load(Stream stream);
该类还重写了ConfigurationProvider的Load方法,并对文件加载中的异常做了处理,Data属性在前文有提到过,此处不再做其他说明。方法源码如下所示:
1: private void Load(bool reload)
2: {
3: var file = Source.FileProvider?.GetFileInfo(Source.Path);
4: if (file == null || !file.Exists)
5: {
6: if (Source.Optional || reload) // Always optional on reload
7: {
8: Data = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
9: }
10: else
11: {
12: var error = new StringBuilder($"The configuration file '{Source.Path}' was not found and is not optional.");
13: if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(file?.PhysicalPath))
14: {
15: error.Append($" The physical path is '{file.PhysicalPath}'.");
16: }
17: HandleException(new FileNotFoundException(error.ToString()));
18: }
19: }
20: else
21: {
22: // Always create new Data on reload to drop old keys
23: if (reload)
24: {
25: Data = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
26: }
27: using (var stream = file.CreateReadStream())
28: {
29: try
30: {
31: Load(stream);
32: }
33: catch (Exception e)
34: {
35: HandleException(e);
36: }
37: }
38: }
39: // REVIEW: Should we raise this in the base as well / instead?,通过注释,我们可以知道OnReload()方法可能会在新版中发生变化
40: OnReload();
41: }
42:
43: /// <summary>
44: /// Loads the contents of the file at <see cref="Path"/>.
45: /// </summary>
46: /// <exception cref="FileNotFoundException">If Optional is <c>false</c> on the source and a
47: /// file does not exist at specified Path.</exception>
48: public override void Load()
49: {
50: Load(reload: false);
51: }
另外它还有一个特殊方法,就是参数类型为FileConfigurationSource的构造函数,其主要功能是监控文件,并在FileConfigurationSource.ReloadDelay设置的时间里重新加载文件并返回一个IDisposable类型的值,以下是该构造函数的源码:
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Initializes a new instance with the specified source.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="source">The source settings.</param>
5: public FileConfigurationProvider(FileConfigurationSource source)
6: {
7: if (source == null)
8: {
9: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(source));
10: }
11: Source = source;
12:
13: if (Source.ReloadOnChange && Source.FileProvider != null)
14: {
15: _changeTokenRegistration = ChangeToken.OnChange(
16: () => Source.FileProvider.Watch(Source.Path),
17: () => {
18: Thread.Sleep(Source.ReloadDelay);
19: Load(reload: true);
20: });
21: }
22: }
FileConfigurationExtensions
该类是一个静态类,其提供了的多个扩展方法,主要基于
- IConfigurationBuilder
- IFileProvider
- Action<FileLoadExceptionContext>
包括主要用于设置或获取IFileProvider对象,前文有介绍过,是存储于字典之中,需要注意的是,在Get的时候如果字典中并不存在IFileProvider对象,则会实例化一个PhysicalFileProvider对象出来,该类位于Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders.PhysicalFileProvider
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Sets the default <see cref="IFileProvider"/> to be used for file-based providers.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/> to add to.</param>
5: /// <param name="fileProvider">The default file provider instance.</param>
6: /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</returns>
7: public static IConfigurationBuilder SetFileProvider(this IConfigurationBuilder builder, IFileProvider fileProvider)
8: {
9: if (builder == null)
10: {
11: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
12: }
13:
14: builder.Properties[FileProviderKey] = fileProvider ?? throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(fileProvider));
15: return builder;
16: }
17:
18: /// <summary>
19: /// Gets the default <see cref="IFileProvider"/> to be used for file-based providers.
20: /// </summary>
21: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</param>
22: /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</returns>
23: public static IFileProvider GetFileProvider(this IConfigurationBuilder builder)
24: {
25: if (builder == null)
26: {
27: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
28: }
29:
30: if (builder.Properties.TryGetValue(FileProviderKey, out object provider))
31: {
32: return provider as IFileProvider;
33: }
34:
35: return new PhysicalFileProvider(AppContext.BaseDirectory ?? string.Empty);
36: }
为指定路径的物理文件设置文件型Provider,该方法同样基于PhysicalFileProvider,并返回IConfigurationBuilder对象
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Sets the FileProvider for file-based providers to a PhysicalFileProvider with the base path.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/> to add to.</param>
5: /// <param name="basePath">The absolute path of file-based providers.</param>
6: /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</returns>
7: public static IConfigurationBuilder SetBasePath(this IConfigurationBuilder builder, string basePath)
8: {
9: if (builder == null)
10: {
11: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
12: }
13:
14: if (basePath == null)
15: {
16: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(basePath));
17: }
18:
19: return builder.SetFileProvider(new PhysicalFileProvider(basePath));
20: }
以及异常处理,可以看到其异常处理也会存放于字典中,如果字典中找不到,就会返回空,这个地方如果直接使用,需要注意空指针问题。
1: /// <summary>
2: /// Sets a default action to be invoked for file-based providers when an error occurs.
3: /// </summary>
4: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/> to add to.</param>
5: /// <param name="handler">The Action to be invoked on a file load exception.</param>
6: /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</returns>
7: public static IConfigurationBuilder SetFileLoadExceptionHandler(this IConfigurationBuilder builder, Action<FileLoadExceptionContext> handler)
8: {
9: if (builder == null)
10: {
11: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
12: }
13:
14: builder.Properties[FileLoadExceptionHandlerKey] = handler;
15: return builder;
16: }
17:
18: /// <summary>
19: /// Gets the default <see cref="IFileProvider"/> to be used for file-based providers.
20: /// </summary>
21: /// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</param>
22: /// <returns>The <see cref="IConfigurationBuilder"/>.</returns>
23: public static Action<FileLoadExceptionContext> GetFileLoadExceptionHandler(this IConfigurationBuilder builder)
24: {
25: if (builder == null)
26: {
27: throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(builder));
28: }
29:
30: if (builder.Properties.TryGetValue(FileLoadExceptionHandlerKey, out object handler))
31: {
32: return handler as Action<FileLoadExceptionContext>;
33: }
34:
return null;
35: }
该类还有两个静态私有变量,指定了文件Provider的Key以及文件加载异常处理Key。
1: private static string FileProviderKey = "FileProvider";
2: private static string FileLoadExceptionHandlerKey = "FileLoadExceptionHandler";
总结
文件型配置还依赖于.NET Core的其他组件Microsoft.Extensions.FileProviders和Microsoft.Extensions.Primitives。
FileProviders组件提供了文件处理的一般方法,Primitives组件提供了监控机制,同时还包括两个比较重要的结构体StringValues和StringSegment,本文暂时不做讨论,有兴趣的朋友,可以自行查看该组件源码。
.NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Configuration(二)的更多相关文章
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Configuration(一)
Configuration总体介绍 微软在.NET Core里设计出了全新的配置体系,并以非常灵活.可扩展的方式实现.从其源码来看,其运行机制大致是,根据其Source,创建一个Builder实例,并 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解HttpClientFactory(二)
写在前面 上一篇文章讨论了通过在ConfigureServices中调用services.AddHttpClient()方法,并基于此进一步探讨了DefaultHttpClientFactory是 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Host(二)
写在前面 停了近一个月的技术博客,随着正式脱离996的魔窟,接下来也正式恢复了.本文从源码角度进一步讨论.NET Core 3.0 中关于Host扩展的一些技术点,主要讨论Long Run Pro ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Configuration(三)
写在前面 上一篇文章讨论了文件型配置的基本内容,本篇内容讨论JSON型配置的实现方式,理解了这一种配置类型的实现方式,那么其他类型的配置实现方式基本可以触类旁通.看过了上一篇文章的朋友,应该看得出 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Startup的注册及运行
原文:.NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Startup的注册及运行 写在前面 开发.NET Core应用,直接映入眼帘的就是Startup类和Program类,它们是.NET Core应用程 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Kestrel的集成与应用(一)
写在前面 ASP.NET Core 的 Web 服务器默认采用Kestrel,这是一个基于libuv(一个跨平台的基于Node.js异步I/O库)的跨平台.轻量级的Web服务器. 在开始之前,先回 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解Kestrel的集成与应用(二)
前言 前一篇文章主要介绍了.NET Core继承Kestrel的目的.运行方式以及相关的使用,接下来将进一步从源码角度探讨.NET Core 3.0中关于Kestrel的其他内容,该部分内容,我们 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解ObjectPool(一)
写在前面 对象池是一种比较常用的提高系统性能的软件设计模式,它维护了一系列相关对象列表的容器对象,这些对象可以随时重复使用,对象池节省了频繁创建对象的开销. 它使用取用/归还的操作模式,并重复执行这些 ...
- .NET Core 3.0之深入源码理解HealthCheck(一)
写在前面 我们的系统可能因为正在部署.服务异常终止或者其他问题导致系统处于非健康状态,这个时候我们需要知道系统的健康状况,而健康检查可以帮助我们快速确定系统是否处于正常状态.一般情况下,我们会提供公开 ...
随机推荐
- c++中vector向量几种情况的总结(向量指针,指针的向量)
1.标准库vector类型 vector 是同一种类型的对象的集合.每一个对象都有一个相应的整数索引值.标准库将负责管理与存储元素相关的内存.我们把 vector 称为容器,是由于它能够包括其它对象. ...
- MySQL的字符编码体系(一)——数据存储编码
安装MySQL好多次了,每次都会纠结于数据库的字符编码配置,所以我决定这一次彻底把它理清. MySQL的字符编码结构比較细,它慷慨向分为两个部分:数据存储编码和传输数据编码.本篇讨论数据存储编码部分, ...
- booth乘法器原理
在微处理器芯片中,乘法器是进行数字信号处理的核心,同一时候也是微处理器中进行数据处理的wd=%E5%85%B3%E9%94%AE%E9%83%A8%E4%BB%B6&hl_tag=textli ...
- getElementByID,getElementsByName,getElementsByTagName
<input type="checkbox" name="hobby" id="hobby1"> 音乐 <input ty ...
- iOS多线程编程指南
iOS多线程编程指南(拓展篇)(1) 一.Cocoa 在Cocoa上面使用多线程的指南包括以下这些: (1)不可改变的对象一般是线程安全的.一旦你创建了它们,你可以把这些对象在线程间安全的传递.另一方 ...
- iOS开发之---判断是否是手机号
iOS开发之---判断是否是手机号
- Cocos Console命令总结
1. 工程创建 使用Cocos Console创建工程非常简单,安装完cocos命令之后,只需要在需要创建工程的目标目录下打开终端或命令行工具,输入下面的命令即可: cocos new -l js P ...
- Hibernate的一些使用技巧
1.Hibernate是如今最流行的开源对象关系映射(ORM)持久化框架,SSH框架组合是很多JavaEE工程的首选,java持久化框架(JPA)的设计师是Hibernate的作者,因此对于Hiber ...
- 使用iconv的包装类CharsetConverter进行编码转换的示例
GitHub地址https://github.com/BuYishi/charset_converter_test charset_converter_test.cpp #include <io ...
- Android:在子线程中更新UI的三种方式
①使用Activity中的runOnUiThread(Runnable) ②使用Handler中的post(Runnable) 在创建Handler对象时,必须先通过Context的getMainLo ...
