Call stack Structure
The stack frame at the top of the stack is for the currently executing routine. The stack frame usually includes at least the following items (in push order):
- the arguments (parameter values) passed to the routine (if any);
- the return address back to the routine's caller (e.g. in the
DrawLinestack frame, an address intoDrawSquare's code); and - space for the local variables of the routine (if any).
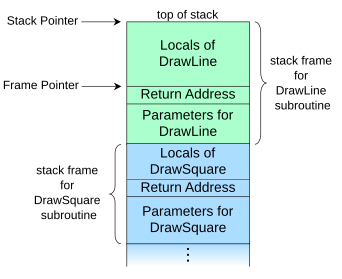
Call stack layout
Stack and frame pointers[edit]
When stack frame sizes can differ, such as between different functions or between invocations of a particular function, popping a frame off the stack does not constitute a fixed decrement of the stack pointer. At function return, the stack pointer is instead restored to the frame pointer, the value of the stack pointer just before the function was called. Each stack frame contains a stack pointer to the top of the frame immediately below. The stack pointer is a mutable register shared between all invocations. A frame pointer of a given invocation of a function is a copy of the stack pointer as it was before the function was invoked.[2]
The locations of all other fields in the frame can be defined relative either to the top of the frame, as negative offsets of the stack pointer, or relative to the top of the frame below, as positive offsets of the frame pointer. The location of the frame pointer itself must inherently be defined as a negative offset of the stack pointer.
Storing the address to the caller's frame[edit]
In most systems a stack frame has a field to contain the previous value of the frame pointer register, the value it had while the caller was executing. For example, the stack frame of DrawLine would have a memory location holding the frame pointer value that DrawSquare uses (not shown in the diagram above). The value is saved upon entry to the subroutine and restored upon return. Having such a field in a known location in the stack frame enables code to access each frame successively underneath the currently executing routine's frame, and also allows the routine to easily restore the frame pointer to the caller's frame, just before it returns.
Lexically nested routines[edit]
Programming languages that support nested subroutines also have a field in the call frame that points to the stack frame of the latest activation of the procedure that most closely encapsulates the callee, i.e. the immediate scope of the callee. This is called an access link or static link (as it keeps track of static nesting during dynamic and recursive calls) and provides the routine (as well as any other routines it may invoke) access to the local data of its encapsulating routines at every nesting level. Some architectures, compilers, or optimization cases store one link for each enclosing level (not just the immediately enclosing), so that deeply nested routines that access shallow data do not have to traverse several links; this strategy is often called a "display".[3]
Access links can be optimized away when an inner function does not access any (non-constant) local data in the encapsulation, as is the case with pure functions communicating only via arguments and return values, for example. Some historical computers, such as the Burroughs large systems, had special "display registers" to support nested functions, while compilers for most modern machines (such as the ubiquitous x86) simply reserve a few words on the stack for the pointers, as needed.
Overlap[edit]
For some purposes, the stack frame of a subroutine and that of its caller can be considered to overlap, the overlap consisting of the area where the parameters are passed from the caller to the callee. In some environments, the caller pushes each argument onto the stack, thus extending its stack frame, then invokes the callee. In other environments, the caller has a preallocated area at the top of its stack frame to hold the arguments it supplies to other subroutines it calls. This area is sometimes termed the outgoing arguments area or callout area. Under this approach, the size of the area is calculated by the compiler to be the largest needed by any called subroutine.
Call stack Structure的更多相关文章
- 线性数据结构之栈——Stack
Linear data structures linear structures can be thought of as having two ends, whose items are order ...
- 【LeetCode OJ】Evaluate Reverse Polish Notation
Problem link: http://oj.leetcode.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/ According to the wik ...
- MakeObjectInstance的前世今生(关键是ECX的何时入栈以及Self指针何时存储的)
高手们的文章有很大启发,但是总有些小错,也有没交代清楚的,以下是我的理解: 编译器编译MainWndProc的时候,它是一个正常Delphi普通函数,MakeObjectInstance对它做变换是运 ...
- java建立二叉树,递归/非递归先序遍历,递归/非递归中序遍历,层次遍历
import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Stack; //structure of binary ...
- [转] iOS ABI Function Call Guide
source: apple ARMv6 Function Calling Conventions When functions (routines) call other functions (sub ...
- iOS - Block底层解析
Block是iOS开发中一种比较特殊的数据结构,它可以保存一段代码,在合适的地方再调用,具有语法简介.回调方便.编程思路清晰.执行效率高等优点,受到众多猿猿的喜爱.但是Block在使用过程中,如果对B ...
- allego 输出报告说明
List of Available Reports Assigned Function Report Lists all assigned functions, sorted by function ...
- SECD machine
SECD machine 对程序语言理论的理解 程序语言理论主要研究语法.语义及语言的实现.编程语言有语法,各种数学逻辑.结构化数据都有语法.乔姆斯基的语言体系及巴科斯范式是语法分析的基础,语法分析将 ...
- 【deep learning精华部分】稀疏自编码提取高阶特征、多层微调完全解释及代码逐行详解
我们前面已经讲了如何训练稀疏自编码神经网络,当我们训练好这个神经网络后,当有新的样本输入到这个训练好的稀疏自编码器中后,那么隐藏层各单元的激活值组成的向量就可以代表(因为根据稀疏自编码,我们可以用来恢 ...
随机推荐
- Objective-C 2.0 基础要点归纳
本文的阅读基本条件: 具备C/C++基础知识,了解面向对象特征 阅读过<Objective-C 2.0 程序设计(第二版)>.<Objective-C 程序设计 第6版>或相关 ...
- 模式识别之ocr---文字识别Tesseract-OCR 进行文字识别 VS2010
近日做铸件文字识别的项目,需要识别铸件上的字符和数字,找到开源的识别库Tesseract,下面简单记录下怎么使用. 首先在项目主页http://code.google.com/p/tesseract- ...
- iOS 多线程,ARC
iOS自己创建的线程需要自己定时的创建autorelease pools,否则对象不能及时自动释放. 方法1是不对的,while中的对象会无法及时释放. 1:-(void)Thread{ @autor ...
- 函数计算 触发式计算 日志 MP3 图片 合成视频
函数计算 触发式计算 日志 MP3 图片 合成视频 [start_time]:20120511 06:59:11 [20120511 06:59:11_0.4950568322522534]: ...
- HDU 5855Less Time, More profit
Less Time, More profit Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/O ...
- 美国诚实签经验——IMG全球医疗险,TODO
那么,诚实签最关键的4个要点 是什么呢? 第一,证明你有一定的经济实力. 可能需要房产.存款等证明,也需要银行信用卡或借记卡半年流水证明(让人信服的每月进帐和消费能力). 这些是为了证明,你可以支付在 ...
- hdu 5782(kmp+hash)
Cycle Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- bzoj1047
二维单调队列 rmq很明显会超时,如果这个序列是一维的,很明显就是个单调队列,现在就是把一维的单调队列转换为二维单调队列. 先求出每一列的窗口极值,然后对于每一行做单调队列,值就是之前求出每个位置结尾 ...
- Hadoop 分布式环境slave节点重启忽然不好使了
Hadoop 分布式环境slaves节点重启: 忽然无法启动DataNode和NodeManager处理: 在master节点: vim /etc/hosts: 修改slave 节点的IP (这个时候 ...
- js moment.js日期操作类 datetime,日期操作,dayjs
http://momentjs.com/ JS时间处理插件MomentJS https://juejin.im/post/5a2bdc55f265da432b4abf5e Day.js 2kB超轻量时 ...
