【Cocos2d-Js基础教学(2)类的使用和面向对象】
类的使用和面向对象
大家都知道在cocos2d-x 底层是C++编写的,那么就有类的概念和继承机制。
但是在JS中,是没有类这个概念的,没有提供类,没有C++的类继承机制。
那么JS是通过什么方式实现简单的继承呢?JS是通过对象的原型实现继承。
我们来看一下这段代码:
var baselayer = cc.Layer.extend({
ctor:function(){
this._super();
cc.log("baselayer ctor read");
},
init:function(){
this._super();
cc.log("baselayer init read");
}
});
我们申明了baseLayer对象 ,并且利用cc.Layer.extend,继承了CClayer。
那么问题来了?他究竟是怎么实现的呢?我们按住crtl跟进去看看cc.Layer.extend的实现;
ClassManager.compileSuper.ClassManager = ClassManager; /* Managed JavaScript Inheritance
* Based on John Resig's Simple JavaScript Inheritance http://ejohn.org/blog/simple-javascript-inheritance/
* MIT Licensed.
* 在这里申明了,实现JS继承的方式 是参考了 John Resig's 的一个例子来实现的;并且有原文地址,有兴趣的同学可以去看看原版实现方式
*/
(function () {
var fnTest = /\b_super\b/;
var config = cc.game.config;
var releaseMode = config[cc.game.CONFIG_KEY.classReleaseMode];
if(releaseMode) {
console.log("release Mode");
} /**
* The base Class implementation (does nothing)
* @class
*/
cc.Class = function () {
}; /**
* Create a new Class that inherits from this Class
* @static
* @param {object} props
* @return {function}
*/
cc.Class.extend = function (props) {
//声明_super对象,并赋值为原型
var _super = this.prototype; // Instantiate a base Class (but only create the instance,
// don't run the init constructor) //实例化创建prototype这个基类,只是创建实例,并没有跑init构造函数
var prototype = Object.create(_super); //给这个class复制ID标识,并且将_super对象添加到ClassManager类管理器中
var classId = ClassManager.getNewID();
ClassManager[classId] = _super;
// Copy the properties over onto the new prototype. We make function
// properties non-eumerable as this makes typeof === 'function' check
// unneccessary in the for...in loop used 1) for generating Class()
// 2) for cc.clone and perhaps more. It is also required to make
// these function properties cacheable in Carakan.
//进行函数的验证检测,以及设置他使用基本设置
var desc = { writable: true, enumerable: false, configurable: true }; //单例模式的基础申明
prototype.__instanceId = null; // The dummy Class constructor
//创建Class这个类
function Class() {
this.__instanceId = ClassManager.getNewInstanceId();
// All construction is actually done in the init method
//如果这个类他存在.ctor方法,那么就默认的使用执行这个方法
//ctor在JS中就相当于构造函数
if (this.ctor)
this.ctor.apply(this, arguments);
} //给ID复制
Class.id = classId;
// desc = { writable: true, enumerable: false, configurable: true,
// value: XXX }; Again, we make this non-enumerable.
desc.value = classId;
Object.defineProperty(prototype, '__pid', desc); // Populate our constructed prototype object
//把我们原型对象赋值
Class.prototype = prototype; // Enforce the constructor to be what we expect
//将整个类赋值给desc.value
desc.value = Class;
//并且将类里构造的对象赋值
Object.defineProperty(Class.prototype, 'constructor', desc); // Copy getter/setter
//模拟get/set的方式,使用cc.clone函数来拷贝
this.__getters__ && (Class.__getters__ = cc.clone(this.__getters__));
this.__setters__ && (Class.__setters__ = cc.clone(this.__setters__)); for(var idx = 0, li = arguments.length; idx < li; ++idx) {
var prop = arguments[idx];
for (var name in prop) {
var isFunc = (typeof prop[name] === "function");
var override = (typeof _super[name] === "function");
var hasSuperCall = fnTest.test(prop[name]); if (releaseMode && isFunc && override && hasSuperCall) {
desc.value = ClassManager.compileSuper(prop[name], name, classId);
Object.defineProperty(prototype, name, desc);
} else if (isFunc && override && hasSuperCall) {
desc.value = (function (name, fn) {
return function () {
var tmp = this._super; // Add a new ._super() method that is the same method
// but on the super-Class
//如果在新的对象方法里面添加._super(),他会继承父类的_super方法
//并且实现方法里面的所有对象及方法的赋值
this._super = _super[name]; // The method only need to be bound temporarily, so we
// remove it when we're done executing
var ret = fn.apply(this, arguments);
this._super = tmp; return ret;
};
})(name, prop[name]);
Object.defineProperty(prototype, name, desc);
} else if (isFunc) {
desc.value = prop[name];
Object.defineProperty(prototype, name, desc);
} else {
prototype[name] = prop[name];
} if (isFunc) {
// Override registered getter/setter
//如果是方法,那么重载里面的属性,并且实现get,set方法可以直接使用
var getter, setter, propertyName;
if (this.__getters__ && this.__getters__[name]) {
propertyName = this.__getters__[name];
for (var i in this.__setters__) {
if (this.__setters__[i] === propertyName) {
setter = i;
break;
}
}
cc.defineGetterSetter(prototype, propertyName, prop[name], prop[setter] ? prop[setter] : prototype[setter], name, setter);
}
if (this.__setters__ && this.__setters__[name]) {
propertyName = this.__setters__[name];
for (var i in this.__getters__) {
if (this.__getters__[i] === propertyName) {
getter = i;
break;
}
}
cc.defineGetterSetter(prototype, propertyName, prop[getter] ? prop[getter] : prototype[getter], prop[name], getter, name);
}
}
}
} // And make this Class extendable
// 可以使用Class.extend来实现类的继承
Class.extend = cc.Class.extend; //add implementation method
//添加要实现的方法
Class.implement = function (prop) {
for (var name in prop) {
prototype[name] = prop[name];
}
};
return Class;
};
})();
重点看3个点:
// The dummy Class constructor
//创建Class这个类
function Class() {
this.__instanceId = ClassManager.getNewInstanceId();
// All construction is actually done in the init method
//如果这个类他存在.ctor方法,那么就默认的使用执行这个方法
//ctor在JS中就相当于构造函数
if (this.ctor)
this.ctor.apply(this, arguments);
}
第一,这个是在JS中的实现构造函数的方法,如果在自定义类中,存在有ctor:function()这个方法,那么他会
默认执行,默认成为构造函数;
desc.value = (function (name, fn) {
return function () {
var tmp = this._super;
// Add a new ._super() method that is the same method
// but on the super-Class
//如果在新的对象方法里面添加._super(),他会继承父类的_super方法
//并且实现方法里面的所有对象及方法的赋值
this._super = _super[name];
// The method only need to be bound temporarily, so we
// remove it when we're done executing
var ret = fn.apply(this, arguments);
this._super = tmp;
return ret;
};
})(name, prop[name]);
第二,desc.value在这个for循环中的赋值,实现了this._super()的原理,它会为派生类实完成对父类的实现;
通俗点来说,就是,如果我们想要继承并实现父类的方法,那么就需要在方法里面调用this._super()这个方法!
// And make this Class extendable
// 可以使用Class.extend来实现类的继承
Class.extend = cc.Class.extend;
第三,讲cc.Class.extend赋值给Class.extend,就可以使用Class.extend来实现自定义类的继承;
OK,梳理完毕下面看看我们来学习一下怎么实现自定义类和自定义的继承:
var myLayer = baselayer.extend({
ctor:function(){
this._super();
cc.log("myLayer ctor read");
},
init:function(){
this._super();
cc.log("myLayer init read");
}
});
这段代码中我从myLayer继承了父类baselayer,注意用法就是刚才我们Review底层代码时看到的
var myLayer = baselayer.extend({});
然后继续续实现ctor构造方法函数,和自定义方法函数init;
并且日志输出一下;
最终我们需要在MainScene中调用;
如下:
var MainScene = cc.Scene.extend({
onEnter:function(){
this._super();
var layer = new myLayer();
this.addChild(layer);
}
});
我们首先只调用
var layer = new myLayer();
看看最终输出是什么?
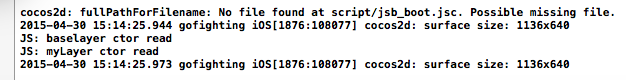
从输出可以看出他先调用了baselayer,再调用了myLayer;
那么就可以理解为我们直接new myLayer() 会直接自动实现调用我们写的ctor构造函数方法;
而且是先调用父类,然后再调用我们的派生类自定义类;
他并没有主动调用init:function()这个方法,因为他是我们自定义的,所以需要我们手动去调用
layer.init();
OK,我们加上手动调用后再来看一下输出是什么?
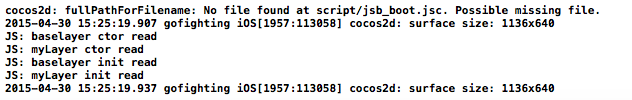
我们可以看到了前两行输出都是 ctor 先执行;
init 函数后执行;
而且调用也是 先执行baseLayer 我们的父类的init函数 再执行我们的自定义init方法!
现在就非常清晰了,我们的myLayer.init方法继承了baseLayer.init的属性方法;
而且实现的原理就是通过this._super()来实现的!
我们再修改一下代码来看看是不是这样,将myLayer类里面的init方法里面的this._super();这句话去掉!
看看我们的baseLayer.init方法会不会被调用
var myLayer = baselayer.extend({
ctor:function(){
this._super();
cc.log("myLayer ctor read");
},
init:function(){
cc.log("myLayer init read");
}
});
看看输出:

【Cocos2d-Js基础教学(2)类的使用和面向对象】的更多相关文章
- js基础回顾-数据类型和typeof怎么用
js的基本数据类型有六种,undefined.null.number.string.boolean.object. 未定义 空 数字 字符串 布尔 ...
- 前端工程师面试问题归纳(一、问答类html/css/js基础)
一.参考资源 1.前端面试题及答案整理(一) 2.2017年前端面试题整理汇总100题 3.2018最新Web前端经典面试试题及答案 4.[javascript常见面试题]常见前端面试题及答案 5.W ...
- 【Cocos2d-Js基础教学 入门目录】
本教程视地址频在: 九秒课堂 完全免费 从接触Cocos2dx-Js以来,它的绽放的绚丽让我无法不对它喜欢.我觉得Js在不断带给我们惊喜:在开发过程中,会大大提升我们对原型开发的利用率,使用Js语言做 ...
- js 基础
js基础知识点总结 如何在一个网站或者一个页面,去书写你的js代码:1.js的分层(功能):jquery(tool) 组件(ui) 应用(app),mvc(backboneJs)2.js的规划():避 ...
- JS基础知识总结
js基础知识点总结 如何在一个网站或者一个页面,去书写你的js代码:1.js的分层(功能):jquery(tool) 组件(ui) 应用(app),mvc(backboneJs)2.js的规划() ...
- js基础篇——call/apply、arguments、undefined/null
a.call和apply方法详解 call方法: 语法:call([thisObj[,arg1[, arg2[, [,.argN]]]]]) 定义:调用一个对象的一个方法,以另一个对象替换当前对象 ...
- js基础知识总结(2016.11.1)
js基础知识点总结 如何在一个网站或者一个页面,去书写你的js代码:1.js的分层(功能):jquery(tool) 组件(ui) 应用(app),mvc(backboneJs)2.js的规划():避 ...
- JS表单验证类HTML代码实例
以前用的比较多的一个JS表单验证类,对于个人来说已经够用了,有兴趣的可以在此基础上扩展成ajax版本.本表单验证类囊括了密码验证.英文4~10个 字符验证. 中文非空验证.大于10小于100的数字.浮 ...
- 【 js 基础 】Javascript “继承”
是时候写一写 "继承"了,为什么加引号,因为当你阅读完这篇文章,你会知道,说是 继承 其实是不准确的. 一.类1.传统的面向类的语言中的类:类/继承 描述了一种代码的组织结构形式. ...
随机推荐
- 多重背包问题:悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——珍惜现在,感恩生活(HDU 2191)(二进制优化)
悼念512汶川大地震遇难同胞——珍惜现在,感恩生活 HDU 2191 一道裸的多重背包问题: #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #i ...
- h5专题应该兼容那些浏览器?
本人做专题还不算很多,但是也很腻烦了.一般一个专题制作也就3天,可是调试得4/5天.除了销售客户各种无休止的改改改.还有一点很重要就是浏览器的兼容性.刚开始做专题的时候天真的以为苹果只要兼容到ipho ...
- [leetcode 23]Merge k Sorted Lists
1 题目 Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexi ...
- 无线安全专题_破解篇02--kali破解pin码
最近项目有点紧,所以本应该上周发的文章,拖到了本周三,在此说声抱歉.无线安全专题,我打算系统地写六个部分,分别为破解篇,攻击篇,欺骗篇,路由篇,移动篇和蓝牙篇,当然在发布的过程中,可能还会掺杂着发布f ...
- Dynamic CRM 2013学习笔记(七)追踪、监控及性能优化
本文将介绍CRM的三个内容追踪.监控及性能优化.追踪是CRM里一个很有用的功能,它能为我们的CRM调试或解决错误.警告提供有价值的信息:我们可以用window的性能监控工具来了解CRM的性能状况:最后 ...
- spring配置entitymangerfactory
<bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerE ...
- jdbc实现简单的增删改查
先是Book类. 略 然后一个主页,写一个表单,提交Book的信息到AddBook. 略 AddBook.jsp连接jdbc,并向Book表插入. <%@ page language=" ...
- H5图片裁剪升级版(手机版)
前段时间做了个跟裁剪相关的活动<用H5中的Canvas等技术制作海报>,这次公司要做个与奥运相关的活动,扫车牌赢奖. 于是我就在上一个活动的基础上,将代码重新封装一下,并且将计算方式写的更 ...
- bundle与package区别与联系
转:http://blog.csdn.net/lmbda/article/details/17895619 bundle是Apple提供的软件安装的便捷方法. bundle为用户和开发者提供了一个简单 ...
- Liferay7 BPM门户开发之26: 集成Activiti到Liferay7
开发顺序: 实战任务1,开发BPM管理后台(用于在Liferay管理中心管理Activiti模型上传) 一个熟悉Portlet操作的项目,为开发打好基础. http://www.cnblogs.com ...
