78. Subsets(M) & 90. Subsets II(M) & 131. Palindrome Partitioning
Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets. Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. For example,
If nums = [,,], a solution is: [
[],
[],
[],
[,,],
[,],
[,],
[,],
[]
]
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums)
{
const size_t n = nums.size();
vector<int> v;
vector<vector<int> > result;
for (int i = ; i < <<n; ++i)
{
for (int j = ; j < n; ++j)
{
if(i & << j) v.push_back(nums[j]);
}
result.push_back(v);
v.clear();
}
return result;
}
};
3ms
迭代,增量构造.没看懂
http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/3451902.html
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
sort(S.begin(), S.end());
vector<vector<int> > result();
for (auto elem : S) {
result.reserve(result.size() * );
auto half = result.begin() + result.size();
copy(result.begin(), half, back_inserter(result));
for_each(half, result.end(), [&elem](decltype(result[]) &e){
e.push_back(elem);
});
}
return result;
}
};
3ms
位向量法
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
sort(S.begin(), S.end()); //
vector<vector<int> > result;
vector<bool> selected(S.size(), false);
subsets(S, selected, , result);
return result;
}
private:
static void subsets(const vector<int> &S, vector<bool> &selected, int step,
vector<vector<int> > &result) {
if (step == S.size()) {
vector<int> subset;
for (int i = ; i < S.size(); i++) {
if (selected[i]) subset.push_back(S[i]);
}
result.push_back(subset);
return;
}
//S[step]
selected[step] = false;
subsets(S, selected, step + , result);
//S[step]
selected[step] = true;
subsets(S, selected, step + , result);
}
};

6ms
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
sort(S.begin(), S.end()); //
vector<vector<int> > result;
vector<int> path;
subsets(S, path, , result);
return result;
}
private:
static void subsets(const vector<int> &S, vector<int> &path, int step,
vector<vector<int> > &result) {
if (step == S.size()) {
result.push_back(path);
return;
}
//S[step]
subsets(S, path, step + , result);
//S[step]
path.push_back(S[step]);
subsets(S, path, step + , result);
path.pop_back();
}
};

6ms
Iterative This problem can also be solved iteratively. Take [, , ] in the problem statement as an example. The process of generating all the subsets is like: Initially: [[]]
Adding the first number to all the existed subsets: [[], []];
Adding the second number to all the existed subsets: [[], [], [], [, ]];
Adding the third number to all the existed subsets: [[], [], [], [, ], [], [, ], [, ], [, , ]].
Have you got the idea :-) The code is as follows. class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> subs(, vector<int>());
for (int i = ; i < nums.size(); i++) {
int n = subs.size();
for (int j = ; j < n; j++) {
subs.push_back(subs[j]);
subs.back().push_back(nums[i]);
}
}
return subs;
}
};

// Recursion.
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > subsets(vector<int> &S) {
vector<vector<int> > res;
vector<int> out;
sort(S.begin(), S.end());
getSubsets(S, , out, res);
return res;
}
void getSubsets(vector<int> &S, int pos, vector<int> &out, vector<vector<int> > &res) {
res.push_back(out);
for (int i = pos; i < S.size(); ++i) {
//if (i != pos && S[i] == S[i-1]) continue;//subsets II
out.push_back(S[i]);
getSubsets(S, i + , out, res);
out.pop_back();
//while (S[i] == S[i + 1]) ++i; //subsets II
}
}
};

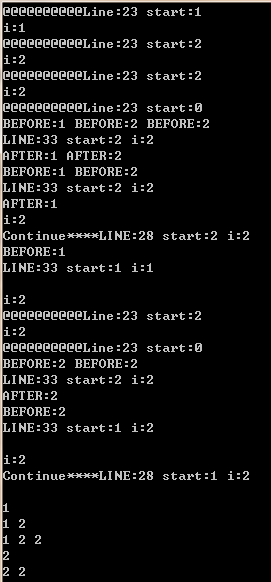
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int> > subsetsWithDup(vector<int> &S) {
sort(S.begin(), S.end()); // ????
vector<vector<int> > result;
vector<int> path;
dfs(S, S.begin(), path, result);
for (int i = ; i < result.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = ; j < result[i].size(); ++j) {
printf("%d ", result[i][j]);
}printf("\n");
}
return result;
}
private:
static void dfs(const vector<int> &S, vector<int>::iterator start,
vector<int> &path, vector<vector<int> > &result) {
result.push_back(path);
printf("@@@@@@@@@@Line:%d start:%d\n", __LINE__, *start);
for (auto i = start; i < S.end(); i++) {
printf("i:%d\n", *i);
if (i != start && *i == *(i-))
{
printf("Continue****LINE:%d start:%d i:%d\n", __LINE__, *start, *i);
continue;
}
path.push_back(*i);
dfs(S, i + , path, result); for(auto xx : path) printf("BEFORE:%d ", xx);
printf("\nLINE:%d start:%d i:%d\n", __LINE__, *start, *i);
path.pop_back(); for (auto xx : path) printf("AFTER:%d ", xx); printf("\n");
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
vector<int> v{,,};
Solution sn;
sn.subsetsWithDup(v);
//printf("%d %d\n",v[0],v.size());
return ;
}
This structure might apply to many other backtracking questions, but here I am just going to demonstrate Subsets, Permutations, and Combination Sum.
Subsets : https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, );
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list , List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, int start){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, i + );
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
Subsets II (contains duplicates) : https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, );
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, int start){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){
if(i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-]) continue; // skip duplicates
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, i + );
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
Permutations : https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
// Arrays.sort(nums); // not necessary
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums){
if(tempList.size() == nums.length){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
} else{
for(int i = ; i < nums.length; i++){
if(tempList.contains(nums[i])) continue; // element already exists, skip
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums);
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
}
Permutations II (contains duplicates) : https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, new boolean[nums.length]);
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, boolean [] used){
if(tempList.size() == nums.length){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
} else{
for(int i = ; i < nums.length; i++){
if(used[i] || i > && nums[i] == nums[i-] && !used[i - ]) continue;
used[i] = true;
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, used);
used[i] = false;
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
}
Combination Sum : https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, target, );
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, int remain, int start){
if(remain < ) return;
else if(remain == ) list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
else{
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, remain - nums[i], i); // not i + 1 because we can reuse same elements
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
}
Combination Sum II (can't reuse same element) : https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), nums, target, );
return list;
}
private void backtrack(List<List<Integer>> list, List<Integer> tempList, int [] nums, int remain, int start){
if(remain < ) return;
else if(remain == ) list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
else{
for(int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){
if(i > start && nums[i] == nums[i-]) continue; // skip duplicates
tempList.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(list, tempList, nums, remain - nums[i], i + );
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
}
Palindrome Partitioning : https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(list, new ArrayList<>(), s, );
return list;
}
public void backtrack(List<List<String>> list, List<String> tempList, String s, int start){
if(start == s.length())
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tempList));
else{
for(int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){
if(isPalindrome(s, start, i)){
tempList.add(s.substring(start, i + ));
backtrack(list, tempList, s, i + );
tempList.remove(tempList.size() - );
}
}
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s, int low, int high){
while(low < high)
if(s.charAt(low++) != s.charAt(high--)) return false;
return true;
}
/*Without any crap! Hit the road! Since we have to collect all the possible sets that meet the requirements -> a palindrome; so traversing the whole possible paths will be definitely the case -> using DFS and backtracking seems to be on the table. try from the start index of the string till any index latter and then check its validity - a palindrome? from the start index till the ending?
if so, we need to store it in a stack for latter collection and then traverse further starting from the previous ending index exclusively and begin the checking again and on and on till the start index is beyond the string;
at that time we are to collect the palindromes along the paths.
Several stuff should be specified: checking whether a string is palindrome is quite simple in C using pointer;
using DP might not help a lot since the checking process is quite fast while DP will require extra work to record and space allocation and so on.
In the end, let's check its space and time consumption: space cost O(n*2^n) -> one set of palindrome will take about O(n) but the amount of sets is dependent on the original string itself.
time cost O(n*2^n) -> collecting them while using the space to store them so the space and time cost should be linearly proportional; since the range can be varied a lot depending on the actual provided string so the performance might not be a problem. by LHearen
4ms in us. 72ms in cn.
*/ void traverse(char* s, int len, int begin, char** stack, int top, char**** arrs, int** colSizes, int* returnSize)
{
if(begin == len) //there is nothing left, collect the strings of a set;
{
*returnSize += ;
*colSizes = (int*)realloc(*colSizes, sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int size = top+;
(*colSizes)[*returnSize-] = size;
*arrs = (char***)realloc(*arrs, sizeof(char**)*(*returnSize));
(*arrs)[*returnSize-] = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*)*size);
for(int i = ; i < size; i++)
(*arrs)[*returnSize-][i] = stack[i];
return ;
}
for(int i = begin; i < len; i++) //check each string that begin with s[begin];
{
int l=begin, r=i;
while(l<r && s[l]==s[r]) l++, r--;
if(l >= r) //it's a palindrome;
{
int size = i-begin+;
char *t = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(size+));
*t = '\0';
strncat(t, s+begin, size);
stack[top+] = t;
traverse(s, len, i+, stack, top+, arrs, colSizes, returnSize); //collect the left;
}
}
} char*** partition(char* s, int** colSizes, int* returnSize)
{
if(!*s) return NULL;
int len = strlen(s);
*returnSize = ;
*colSizes = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char));
char*** arrs = (char***)malloc(sizeof(char**));
char** stack = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*)*len);
int top = -;
traverse(s, strlen(s), , stack, top, &arrs, colSizes, returnSize);
return arrs;
}
public class Solution {
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[s.length()][s.length()];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (i - j <= 2 || dp[j+1][i-1])) {
dp[j][i] = true;
}
}
}
helper(res, new ArrayList<>(), dp, s, 0);
return res;
}
private void helper(List<List<String>> res, List<String> path, boolean[][] dp, String s, int pos) {
if(pos == s.length()) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = pos; i < s.length(); i++) {
if(dp[pos][i]) {
path.add(s.substring(pos,i+1));
helper(res, path, dp, s, i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
}
/*
The normal dfs backtracking will need to check each substring for palindrome, but a dp array can be used to record the possible break for palindrome before we start recursion.
Edit:
Sharing my thought process:
first, I ask myself that how to check if a string is palindrome or not, usually a two point solution scanning from front and back. Here if you want to get all the possible palindrome partition, first a nested for loop to get every possible partitions for a string, then a scanning for all the partitions. That's a O(n^2) for partition and O(n^2) for the scanning of string, totaling at O(n^4) just for the partition. However, if we use a 2d array to keep track of any string we have scanned so far, with an addition pair, we can determine whether it's palindrome or not by justing looking at that pair, which is this line if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j) && (i - j <= 2 || dp[j+1][i-1])). This way, the 2d array dp contains the possible palindrome partition among all.
second, based on the prescanned palindrome partitions saved in dp array, a simple backtrack does the job. Java DP + DFS solution by yfcheng
*/
bool isPalin(char* s, int end);
void helper(char* s, char*** ret, int** colS, int* retS, char** cur, int k ); char*** partition(char* s, int** colS, int* retS)
{
*retS = ;
if(s == NULL || !strcmp(s, "")) return NULL; /* I know ... I hate static mem alloc as well */
*colS = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*);
char*** ret = (char***)malloc(sizeof(char**) * );
int len = strlen(s)+; char** cur = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * );
for(int i = ; i<; i++)
cur[i] = (char*)malloc(len); /* backtracking starting from s[0] */
helper(s, ret, colS, retS, cur, ); return ret;
} void helper(char* s, char*** ret, int** colS, int* retS, char** cur, int k )
{
/* termination if already at the end of string s
we found a partition */
if(*s == )
{
ret[*retS] = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*)*k);
for(int i = ; i<k; i++)
{
ret[*retS][i] = (char*)malloc(strlen(cur[i]) + );
strcpy(ret[*retS][i], cur[i]);
}
(*colS)[(*retS)++] = k;
return;
} /* explore next */
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i = ; i < len; i++)
{
if(isPalin(s, i))
{
/* put it into the cur list */
strncpy(cur[k], s, i+);
cur[k][i+] = '\0'; /* backtracking */
helper(s+i+, ret, colS, retS, cur, k+);
}
}
} bool isPalin(char* s, int end)
{
/* printf("error: start %d, end %d\n", start, end); */
if(end < ) return false;
int start = ;
while(end > start)
{
if(s[start] != s[end]) return false;
start++; end--;
}
return true;
} // by zcjsword Created at: September 11, 2015 5:12 AM
char*** result;
int head; int check(char* s,int left,int right){
while(s[left]==s[right]){
left++,right--;
}
return left>=right;
} int getResult(char* s,int left,int right,int path[],int index,int* colSize){
//printf("%d %d\n",left,right);
if(left>right){
char** list=(char**)malloc(sizeof(char*));
int h=; for(int i=index-;i>;i--){
char* tmp=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(path[i-]-path[i]+));
int count=;
for(int j=path[i];j<path[i-];j++){
tmp[count++]=s[j];
}
tmp[count]='\0';
list[h++]=tmp;
list=(char**)realloc(list,sizeof(char*)*(h+));
}
colSize[head]=h;
result[head++]=list;
result=(char***)realloc(result,sizeof(char**)*(head+)); }
for(int i=right;i>=left;i--){
if(check(s,i,right)){
path[index]=i;
getResult(s,left,i-,path,index+,colSize);
}
}
return ;
} char*** partition(char* s, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
result=(char***)malloc(sizeof(char**));
head=;
int path[];
*columnSizes=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*);
path[]=strlen(s);
getResult(s,,path[]-,path,,*columnSizes);
*returnSize=head;
return result;
}
// 28ms example
#define MAXCOL 1000
void DFS(char *s,int startIndex,char **temp_result,char ***result,
int len,int** columnSizes, int* returnSize)
{
int i,j;
if(startIndex >= len)
{
for(i = ;i < (*columnSizes)[*returnSize];i ++)
{
for(j = ;temp_result[i][j] != '\0';j ++)
{
result[*returnSize][i][j] = temp_result[i][j];
}
result[*returnSize][i][j] = '\0';
}
*returnSize += ;
(*columnSizes)[*returnSize] = (*columnSizes)[*returnSize-];
}
for(i = startIndex;i < len;i ++)
{
int left = startIndex;
int right = i;
while(left <= right && s[left]==s[right])
{
left ++;
right --;
}
if(left >= right)
{
strncpy(temp_result[(*columnSizes)[*returnSize]],s+startIndex,i - startIndex + );
temp_result[(*columnSizes)[*returnSize]][i - startIndex + ] = '\0';
(*columnSizes)[*returnSize] += ;
//printf("OK\n");
DFS(s,i+,temp_result,result,len,columnSizes,returnSize);
(*columnSizes)[*returnSize] -= ;
}
}
} char*** partition(char* s, int** columnSizes, int* returnSize) {
int i,j,k;
int len = strlen(s);
char ***result = malloc(MAXCOL*sizeof(char**));
for(i = ;i < MAXCOL;i ++)
{
result[i] = malloc(len*sizeof(char*));
for(j = ;j < len;j ++)
{
result[i][j] = malloc(len*sizeof(char));
}
}
char **temp_result = malloc(len*sizeof(char*));
for(i = ;i < len;i ++)
{
temp_result[i] = malloc(len*sizeof(char));
}
*columnSizes = calloc(MAXCOL,sizeof(int));
*returnSize = ;
DFS(s,,temp_result,result,len,columnSizes,returnSize);
return result;
}
// 52ms example
78. Subsets(M) & 90. Subsets II(M) & 131. Palindrome Partitioning的更多相关文章
- leetcode 131. Palindrome Partitioning 、132. Palindrome Partitioning II
131. Palindrome Partitioning substr使用的是坐标值,不使用.begin()..end()这种迭代器 使用dfs,类似于subsets的题,每次判断要不要加入这个数 s ...
- Leetcode 22. Generate Parentheses Restore IP Addresses (*) 131. Palindrome Partitioning
backtracking and invariant during generating the parathese righjt > left (open bracket and cloas ...
- leetcode 78. Subsets 、90. Subsets II
第一题是输入数组的数值不相同,第二题是输入数组的数值有相同的值,第二题在第一题的基础上需要过滤掉那些相同的数值. level代表的是需要进行选择的数值的位置. 78. Subsets 错误解法: cl ...
- 131. Palindrome Partitioning(回文子串划分 深度优先)
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all ...
- [LeetCode] 131. Palindrome Partitioning 回文分割
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all ...
- Leetcode 131. Palindrome Partitioning
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all ...
- 131. Palindrome Partitioning
题目: Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return ...
- [leetcode]131. Palindrome Partitioning字符串分割成回文子串
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all ...
- 【LeetCode】131. Palindrome Partitioning
Palindrome Partitioning Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is ...
随机推荐
- SQL 追踪
SQL追踪(SQL Trace)是一个轻量级的追踪工具,按照事件(Events)记录数据库发生的消息,几乎对数据库性能没有什么影响.SQL Server内置一个Trace,称作默认追踪(Default ...
- CMake与MSVC工程化实践
CMake与MSVC工程化实践 CMake基础 cmake无疑是最流行的c++跨平台构建工具之一,关于cmake入门指南这里不再赘述,官方文档是最好的参考,这里通过一个例子简述构建一个工程常用的函数和 ...
- mysql学习(4)python操作数据库
整理了一下前面3期学的内容后,现在练习使用python去操作数据库 #!python3# coding:utf-8import pymysqlclass mysql_option(): def __i ...
- PAT甲题题解-1001. A+B Format (20)-字符串处理,水
计算A+B的和,并且按标准格式处理,每3个就要有个逗号 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm ...
- win10下装上virtualbox 以及在virtualbox上装上 ubuntu 12.04
首先要下载virtual 在win10下可能第一步你就遇到了麻烦 首先刚开始我装的是最新版本的virtualbox 5.0.24.8355 (直接百度就可搜到) 然后可以按照这个教程 http://j ...
- mysql 列转行处理
CREATE TABLE `table1` ( `id` ) DEFAULT NULL, `name` ) CHARACTER SET utf8 DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=MyISA ...
- 如何有效地让一个“ParentFont = False”子控件使用与父母相同的字体名称?
如何有效地让一个“ParentFont = False”子控件使用与父母相同的字体名称?(How to efficiently let a `ParentFont = False` child con ...
- MyBatis关联查询,一对一关联查询
数据库E-R关系 实体类 public class City { Long id; String name; Long countryId; Date lastUpdate; } public cla ...
- Asp.Net Mvc的几个小问题
突然想到一些小问题,对写代码影响不大,当是又很实用. MVC 中视图中的model的大小写问题,什么时候用大写,什么时候用小写? 所谓强类型视图,就是通过@model指令指明当前Model(属性)的具 ...
- UVa 572 油田 (dfs)
The GeoSurvComp geologic survey company is responsible for detecting underground oil deposits. GeoSu ...
