FATFS(A)
(一),什么是文件管理系统
答:数据在PC上是以文件的形式储存在磁盘中的,这些数据的形式一般为ASCII码或二进制形式。简单点说就是:管理磁盘上的文件的方法的代码!
如:我们写到SD卡上面的数据管理一下,更科学的方法来管理
http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html,官网介绍 Resources下面是源码
(二),我们在移植时主要是那些函数?
答:Device Control Interface(硬件接口函数)
- disk_status - Get device status 选择操纵的模块,此处用SD卡
- disk_initialize - Initialize device 初始化函数
- disk_read - Read sector(s) 读
- disk_write - Write sector(s) 写
- disk_ioctl - Control device dependent features
- get_fattime - Get current time
(三),例程:
1,我们用的是0.09版本的
2,CC936.c中文字体库
①新建工作区间
/* Register work area for each volume (Always succeeds regardless of disk status) */
f_mount(0,&fs); //(文件管理系统)注册一个工作区间,工作空间命名为0。
那么工作区间的命名范围是什么呢?
答:
FRESULT f_mount (
BYTE vol, /* Logical drive number to be mounted/unmounted */
FATFS *fs /* Pointer to new file system object (NULL for unmount)*/
)
{
FATFS *rfs; if (vol >= _VOLUMES) /* Check if the drive number is valid */
return FR_INVALID_DRIVE;
vol就是f_mount的第一个形参(命名),当他的值大于等于 _VOLUMES,就会返回错误
#define _VOLUMES 1 //can define 9
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. */
Parameters(官网)
- Drive
- Logical drive number (0-9) to register/unregister the work area.
- FileSystemObject
- Pointer to the work area (file system object) to be registered.
②然后再工作区间里面新建文件
/* function disk_initialize() has been called in f_open */ /* Create new file on the drive 0 */
res = f_open(&fnew, "0:newfile.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE );
OPEN的属性:
1.怎么打开呢?
FA_CREATE_ALWAYS 总是以创建总是新建的形式打开这个文件
FA_WRITE:此文件只能写
2.看下open函数
FRESULT f_open (
FIL* FileObject, /* Pointer to the blank file object structure */ 文件指针,把打开的文件关联到这个指针连
const TCHAR* FileName, /* Pointer to the file neme */ 文件名字
BYTE ModeFlags /* Mode flags */ 属性
);
属性:
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| FA_READ | Specifies read access to the object. Data can be read from the file. Combine with FA_WRITE for read-write access. |
| FA_WRITE | Specifies write access to the object. Data can be written to the file. Combine with FA_READ for read-write access. |
| FA_OPEN_EXISTING | Opens the file. The function fails if the file is not existing. (Default) |
| FA_OPEN_ALWAYS | Opens the file if it is existing. If not, a new file is created. To append data to the file, use f_lseek function after file open in this method. |
| FA_CREATE_NEW | Creates a new file. The function fails with FR_EXIST if the file is existing. |
| FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | Creates a new file. If the file is existing, it is truncated and overwritten. |
可以第一次打开用:FA_CREATE_NEW,之后打开用:FA_OPEN_EXISTING(已存在)就可以了
或者:总是打开,总是关闭
当用到:FA_CREATE_ALWAYS时,我们要将 #define _FS_READONLY 0 /* 0:Read/Write or 1:Read only */ 打开
3.对于返回值(Return Values):我们只测试:FR_OK(是否成功)
③往该文件内写数据
if ( res == FR_OK )
{
res = f_write(&fnew, textFileBuffer, sizeof(textFileBuffer), &bw);
f_close(&fnew); 写完之后,把该文件关掉
}
④关掉之后再打开它
res = f_open(&fnew, "0:newfile.txt", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ); // FA_READ:此时打开定义可读
⑤读取数据
res = f_read(&fnew, buffer, sizeof(buffer), &br);
⑥打印之后关闭
printf("\r\n %s ", buffer);
/* Close open files */
f_close(&fnew);
⑦在文件系统中注册掉刚才开辟的“0”工作区间
/* Unregister work area prior to discard it */
f_mount(0, NULL);
(四)文件管理系统与SD卡的关联!
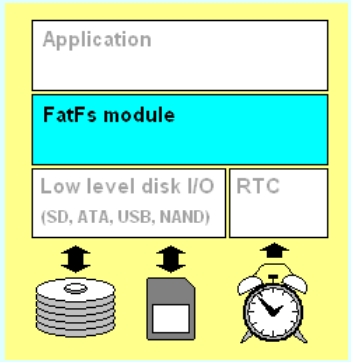
1,Application:就是我们主函数中使用的那些上层函数
2,中间是文件系统模块,文件系统要操纵底层SD卡的时候呢还需要 Low level disk I/O,这一部分驱动,这一部分驱动需要我们自己写
/*-------------------------- SD Init ----------------------------- */
Status = SD_Init();
if (Status!=SD_OK )
{
return STA_NOINIT;
}
else
{
return RES_OK;
} }
和
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Return Disk Status */ DSTATUS disk_status (
BYTE drv /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
)
{
return RES_OK;
}
底层的磁盘的读/写
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Read Sector(s) */ DRESULT disk_read (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE *buff, /* Data buffer to store read data */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to read (1..255) */
)
{ if (count > 1) //多个磁盘
{
SD_ReadMultiBlocks(buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE, count); /* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitReadOperation(); //循环查询dma传输是否结束 /* Wait until end of DMA transfer */
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK);
}
else //单个磁盘
{ SD_ReadBlock(buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE); /* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitReadOperation(); //循环查询dma传输是否结束 /* Wait until end of DMA transfer */
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK); }
return RES_OK;
} /*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Write Sector(s) */ #if _READONLY == 0
DRESULT disk_write (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
const BYTE *buff, /* Data to be written */
DWORD sector, /* Sector address (LBA) */
BYTE count /* Number of sectors to write (1..255) */
)
{ if (count > 1)
{
SD_WriteMultiBlocks((uint8_t *)buff, sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE, count); /* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitWriteOperation(); //等待dma传输结束
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK); //等待sdio到sd卡传输结束
}
else
{
SD_WriteBlock((uint8_t *)buff,sector*BLOCK_SIZE, BLOCK_SIZE); /* Check if the Transfer is finished */
SD_WaitWriteOperation(); //等待dma传输结束
while(SD_GetStatus() != SD_TRANSFER_OK); //等待sdio到sd卡传输结束
}
return RES_OK;
}
#endif /* _READONLY */
IO控制为空(直接返回OK)
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* Miscellaneous Functions */ DRESULT disk_ioctl (
BYTE drv, /* Physical drive nmuber (0..) */
BYTE ctrl, /* Control code */
void *buff /* Buffer to send/receive control data */
)
{
return RES_OK;
}
嵌入式初学者,看到此文的大神们,有什么错误的地方多多意见啊!
FATFS(A)的更多相关文章
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(终)-配合内存管理来遍历SD卡
[STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 [STM3 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(八)-认识内存管理
[STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 [STM3 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(七)-准备移植FatFs
[STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 [STM3 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(六)-FatFs使用的思路介绍
[STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 [STM3 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(五)-文件管理初步介绍
其他链接 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡
由于一张SD卡要能读写,涉及到的技术有些多,我打算分以下几篇博客 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍
其他链接 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(三)-SD卡的操作流程
其他链接 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 ...
- 【STM32】使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(四)-介绍库函数,获取一些SD卡的信息
其他链接 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(一)-初步认识SD卡 [STM32]使用SDIO进行SD卡读写,包含文件管理FatFs(二)-了解SD总线,命令的相关介绍 ...
随机推荐
- python3学习笔记(1)_string
#python学习笔记 17/07/07 # !/usr/bin/evn python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #r"" 引号当中的字符串不转义 #练习 # ...
- a loosely strongly typed language
JavaScript: The Definitive Guide, Sixth Edition by David Flanagan As explained above, the following ...
- 系统之锹sysdig:Linux服务器监控和排障利器
当你需要追踪某个进程产生和接收的系统调用时,首先浮现在你脑海中的是什么?你可能会想到strace,那么你是对的.你会使用什么样的命令行工具来监控原始网络通信呢?如果你想到了tcpdump,你又作出了一 ...
- iOS多线程编程之线程间的通信(转载)
一.简单说明 线程间通信:在1个进程中,线程往往不是孤立存在的,多个线程之间需要经常进行通信 线程间通信的体现 1个线程传递数据给另1个线程 在1个线程中执行完特定任务后,转到另1个线程继续执行任务 ...
- 洛谷P3389 高斯消元 / 高斯消元+线性基学习笔记
高斯消元 其实开始只是想搞下线性基,,,后来发现线性基和高斯消元的关系挺密切就一块儿在这儿写了好了QwQ 先港高斯消元趴? 这个算法并不难理解啊?就会矩阵运算就过去了鸭,,, 算了都专门为此写个题解还 ...
- CentOS VmwareTools安装
1. 虚拟机菜单栏--虚拟机--安装VMware tools 2. CentOS系统中弹出的VMware tools窗口中--右击VMwaretools.tar.gz--Extract到桌面 3.打开 ...
- hibernate注解(三)1+N问题
一.什么时候会遇到1+N的问题? 前提:Hibernate默认表与表的关联方法是fetch="select",不是fetch="join",这都是为了懒加载而准 ...
- SRM 619
easy: 假设每堆石头不全为1,那么每次我们总能取一堆石头分给另外两堆,堆数-1.而且新的局面肯定有一堆的个数大于1. 于是,假设每堆石头数都为1 -> lose.否则的话推断堆数奇偶就可以 ...
- Spring和Spring MVC包扫描
在Spring整体框架的核心概念中,容器是核心思想,就是用来管理Bean的整个生命周期的,而在一个项目中,容器不一定只有一个,Spring中可以包括多个容器,而且容器有上下层关系,目前最常见的一种场景 ...
- [py]django强悍的数据库接口(QuerySet API)-增删改查
django强悍的数据库接口(QuerySet API) 4种方法插入数据 获取某个对象 filter过滤符合条件的对象 filter过滤排除某条件的对象- 支持链式多重查询 没找到排序的 - 4种方 ...
