关于Spring的配置文件的注解使用
从Spring3.0,@Configuration用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含有一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法,
这些方法将会AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,
初始化Spring容器。@Configuration标注在类上,相当于把该类作为spring的xml配置文件中的<beans>,作用为:配置spring容器(应用上下文)
当然也可为了便于分类配置多个类配置文件。
注意:@Configuration注解的配置类有如下要求:
- @Configuration不可以是final类型;
- @Configuration不可以是匿名类;
- 嵌套的configuration必须是静态类。
一、@Configuration配置spring并启动spring容器
@Configuration
public class TestConfiguration {
public TestConfiguration(){
System.out.println("spring容器启动初始化。。。");
}
}
相当于:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xmlns:jee="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee http://www.springframework.org/schema/jee/spring-jee-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task-4.0.xsd" default-lazy-init="false">
</beans>
主方法进行测试:
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//@Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
//如果加载spring-context.xml文件:
//ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml");
}
}
运行结果:

二、@Configuration启动容器+@Bean注册Bean,@Bean标注在方法上(返回某个实例的方法),等价于spring的xml配置文件中的<bean>,作用为:注册bean对象
bean类:
public class TestBean {
private String username;
private String url;
private String password;
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("TestBean sayHello...");
}
public String toString(){
return "username:"+this.username+",url:"+this.url+",password:"+this.password;
}
public void start(){
System.out.println("TestBean 初始化。。。");
}
public void cleanUp(){
System.out.println("TestBean 销毁。。。");
}
}
配置类:
@Configuration
public class TestConfiguration {
public TestConfiguration(){
System.out.println("spring容器启动初始化。。。");
} //@Bean注解注册bean,同时可以指定初始化和销毁方法
//@Bean(name="testBean",initMethod="start",destroyMethod="cleanUp")
@Bean
@Scope("prototype")
public TestBean testBean() {
return new TestBean();
}
}
主方法测试类:
package com.dxz.demo.configuration; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) { // @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class); // 如果加载spring-context.xml文件:
// ApplicationContext context = new
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml"); //获取bean
TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
}
}
@Bean下管理bean的生命周期
可以使用基于 Java 的配置来管理 bean 的生命周期。@Bean 支持两种属性,即 initMethod 和destroyMethod,这些属性可用于定义生命周期方法。在实例化 bean 或即将销毁它时,容器便可调用生命周期方法。生命周期方法也称为回调方法,因为它将由容器调用。使用 @Bean 注释注册的 bean 也支持 JSR-250 规定的标准 @PostConstruct 和 @PreDestroy 注释。如果您正在使用 XML 方法来定义 bean,那么就应该使用 bean 元素来定义生命周期回调方法。以下代码显示了在 XML 配置中通常使用 bean 元素定义回调的方法。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dxz.demo.configuration")
public class TestConfiguration {
public TestConfiguration() {
System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。");
} //@Bean注解注册bean,同时可以指定初始化和销毁方法
@Bean(name="testBean",initMethod="start",destroyMethod="cleanUp")
@Scope("prototype")
public TestBean testBean() {
return new TestBean();
}
}
启动类:
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
System.out.println(tb);
TestBean tb2 = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb2.sayHello();
System.out.println(tb2);
}
}
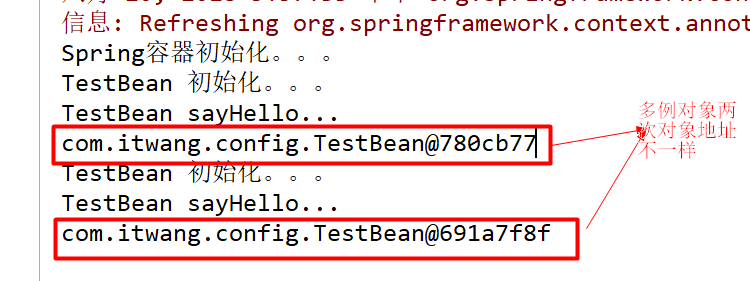
分析:
结果中的1:表明initMethod生效
结果中的2:表明@Scope("prototype")生效
注:
(1)、@Bean注解在返回实例的方法上,如果未通过@Bean指定bean的名称,则默认与标注的方法名相同;
(2)、@Bean注解默认作用域为单例singleton作用域,可通过@Scope(“prototype”)设置为原型作用域;
(3)、既然@Bean的作用是注册bean对象,那么完全可以使用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Ripository等注解注册bean,
当然需要配置@ComponentScan注解进行自动扫描。
三、@Configuration启动容器+@Component注册Bean
bean类:
package com.test.spring.configuration; //添加注册bean的注解
@Component
public class TestBean { public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("TestBean sayHello...");
} public String toString(){
return "username:"+this.username+",url:"+this.url+",password:"+this.password;
}
}
配置类:
@Configuration
//添加自动扫描注解,basePackages为TestBean包路径
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.test.spring.configuration")
public class TestConfiguration {
public TestConfiguration(){
System.out.println("spring容器启动初始化。。。");
} //取消@Bean注解注册bean的方式
//@Bean
//@Scope("prototype")
//public TestBean testBean() {
// return new TestBean();
//}
}
主方法测试获取bean对象:
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
//获取bean
TestBean tb = context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
}
}
sayHello()方法都被正常调用。
四、使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 注册 AppContext 类的两种方法
1. 配置类的注册方式是将其传递给 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 构造函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
//获取bean
TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
}
2.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的register 方法传入配置类来注册配置类
@Test
public void startSpringContext() {
AnnotationConfigRegistry ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(TestConfiguration.class);
}
3. 配置Web应用程序(web.xml中配置AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
过去,您通常要利用 XmlWebApplicationContext 上下文来配置 Spring Web 应用程序,即在 Web 部署描述符文件 web.xml 中指定外部 XML 上下文文件的路径。XMLWebApplicationContext 是 Web 应用程序使用的默认上下文类。以下代码描述了 web.xml 中指向将由 ContextLoaderListener 监听器类载入的外部 XML 上下文文件的元素。
<!-- 加载spring容器 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext-*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
现在,您要将 web.xml 中的上述代码更改为使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类。切记,XmlWebApplicationContext 是 Spring 为 Web 应用程序使用的默认上下文实现,因此您永远不必在您的web.xml 文件中显式指定这个上下文类。现在,您将使用基于 Java 的配置,因此在配置 Web 应用程序时,需要在web.xml 文件中指定 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类。上述代码将修改如下:
<context-param>
<param-name>contextClass</param-name>
<param-value> org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>
com.itwang.config.TestConfiguration //这里需要些你的配置类所在位置
</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
五、组合多个配置类
1. 在@configuration中引入spring的xml配置文件
@Configuration
@ImportResource("spring.xml")
public class WebConfig {
}
新建一个spring.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <bean id="testBean2" class="com.itwang.config.TestBean2"></bean>
</beans>
测试
@Test
public void testSpring() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(WebConfig.class);
TestBean2 testBean2 = (TestBean2) applicationContext.getBean("testBean2");
testBean2.sayHello();
}
结果:

2. 在@configuration中引入其它注解配置
@Configuration
@ImportResource("classpath:spring.xml")
@Import(TestConfiguration.class)
public class WebConfig {
}
测试:
public class TestMain2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(WebConfig.class);
// 如果加载spring-context.xml文件:
// ApplicationContext context = new
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context.xml");
// 获取bean
TestBean2 tb2 = (TestBean2) context.getBean("testBean2");
tb2.sayHello();
TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
}
}

3. @configuration嵌套(嵌套的Configuration必须是静态类)
通过配置类嵌套的配置类,达到组合多个配置类的目的。但注意内部类必须是静态类。
上代码:
@Component
public class TestBean { private String username;
private String url;
private String password; public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("TestBean sayHello...");
} public String toString() {
return "username:" + this.username + ",url:" + this.url + ",password:" + this.password;
} public void start() {
System.out.println("TestBean start");
} public void cleanUp() {
System.out.println("TestBean destory");
}
}
public class DataSource {
private String dbUser;
private String dbPass;
public String getDbUser() {
return dbUser;
}
public void setDbUser(String dbUser) {
this.dbUser = dbUser;
}
public String getDbPass() {
return dbPass;
}
public void setDbPass(String dbPass) {
this.dbPass = dbPass;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DataSource [dbUser=" + dbUser + ", dbPass=" + dbPass + "]";
}
}
//配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.dxz.demo.configuration3")
public class TestConfiguration {
public TestConfiguration() {
System.out.println("TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。");
} @Configuration
static class DatabaseConfig {
@Bean
DataSource dataSource() {
return new DataSource();
}
}
}
启动类:
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// @Configuration注解的spring容器加载方式,用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext替换ClassPathXmlApplicationContexts
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfiguration.class);
//bean
TestBean tb = (TestBean) context.getBean("testBean");
tb.sayHello();
DataSource ds = (DataSource) context.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(ds);
}
}
结果:
TestConfiguration容器启动初始化。。。
TestBean sayHello...
DataSource [dbUser=null, dbPass=null]
六、@EnableXXX注解
配合@Configuration使用,包括 @EnableAsync, @EnableScheduling, @EnableTransactionManagement, @EnableAspectJAutoProxy, @EnableWebMvc。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy---《spring AOP 之:@Aspect注解》
@EnableScheduling--《Spring 3.1新特性之二:@Enable*注解的源码,spring源码分析之定时任务Scheduled注解》
关于Spring的配置文件的注解使用的更多相关文章
- Spring的AOP配置文件和注解实例解析
1.1 Spring的AOP配置文件和注解实例解析 AOP它利用一种称为"横切"的技术,将那些与核心业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的逻辑或责任封装起来,便于减 ...
- spring 学习(二):spring bean 管理--配置文件和注解混合使用
spring 学习(二)spring bean 管理--配置文件和注解混合使用 相似的,创建 maven 工程,配置pom.xml 文件,具体可以参考上一篇博文: sprint 学习(一) 然后我们在 ...
- Struts2 整合Spring(Maven,注解版)
这两天正在试验Struts2与Spring框架的整合,和他们各自的“注解”.今天就总结一下这两个框架怎么用注解进行整合. 一,加入两者的依赖包,除了两者的必要依赖外,还需要导入struts2-spri ...
- Spring Shedule Task之注解实现 (两次启动Schedule Task 的解决方案)
在spring 中的新引入的task 命名空间.可以部分取代 quartz 功能,配置和API更加简单,并且支持注解方式. 第一步: 在Spring的相关配置文件中(applicationContex ...
- [Spring框架]Spring开发实例: XML+注解.
前言: 本文为自己学习Spring记录所用, 文章内容包括Spring的概述已经简单开发, 主要涉及IOC相关知识, 希望能够对新入门Spring的同学有帮助, 也希望大家一起讨论相关的知识. 一. ...
- Spring的配置文件
Web.xml将会配置Spring的配置文件位置: <servlet> <servlet-name>x</servlet-name> & ...
- 使用 Spring 2.5 基于注解驱动的 Spring MVC
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-spring25-mvc/ 概述 继 Spring 2.0 对 Spring MVC 进行重大升级后,Sp ...
- Spring+AOP+Log4j 用注解的方式记录指定某个方法的日志
一.spring aop execution表达式说明 在使用spring框架配置AOP的时候,不管是通过XML配置文件还是注解的方式都需要定义pointcut"切入点" 例如定义 ...
- 使用 Spring 2.5 基于注解驱动的 Spring MVC--转
概述 继 Spring 2.0 对 Spring MVC 进行重大升级后,Spring 2.5 又为 Spring MVC 引入了注解驱动功能.现在你无须让 Controller 继承任何接口,无需在 ...
随机推荐
- Silver Cow Party---poj3268(最短路,迪杰斯特拉)
Silver Cow Party Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:65536KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u De ...
- oracle(五)tkprof 使用 transient kernal profile 侧面 轮廓
1.show parameter sql_trace value是false表示系统当前不会产生trace文件 2.使产生trace文件 alter session set sql_trace = t ...
- javaScript高级教程(四) 复制对象
//返回新对象,双方互不影响 function clone(obj){ //alert('clone'); if(typeof(obj) != 'object') return obj; if(obj ...
- Mirror--如何在主库上增加文件
由于各种原因,如磁盘不空不足,需要对主库增加数据库文件到其他磁盘上,而镜像服务器上没有对应盘符,很多人会选择删除镜像,重新完备还原来搭建镜像,这种方式耗时耗力. 在做此类操作时,需要对主服务器和镜像服 ...
- linux下的字符界面和图形界面转换
linux下的字符界面和图形界面转换 linux下有六个虚拟终端按键ctrl+alt+F1-F6可以进入相应的虚拟终端永久的话修改/etc/inittab将id:5:initdefault:中的5改成 ...
- [py]约瑟夫问题-循环队列
约瑟夫问题(历史战争问题) 直观理解 老外视频讲解 模拟器演示 约瑟夫问题 数学姥公众号 讲的最清楚 背景及,推倒过程讲解得很清晰,旨在提高人们对数据的兴趣 简单说下: 几个人围成一圈(循环队列), ...
- CloudFlare防护下的破绽:寻找真实IP的几条途径
本文仅代表作者独立观点,本文提及的技术仅供安全研究和渗透测试用途 看Twitter发现CloudFlare总裁什么的最近很高调,北京.香港的跑着参加会议.发表演说什么的,CloudFlare似乎也没那 ...
- 【Win7 x64】+【annaconda3】+ 【python3.5.2】+【tensorflow-gpu】 [最终配置 gtx 940mx + Cuda8.0+cudnn v5.1 + tensorflow-gpu1.0.0 ]
1.安装cuda Toolkit 和cudnn (百度云可下载,版本需要对应) 2.配置环境变量: 3.安装cudnn(需要拷贝一些dll和lib来进行配置) 4.进入cmd,找到anaconda3的 ...
- 软件包管理:rpm命令管理-包命名与依赖性
rpm包的管理主要有两种方法:一种是rpm命令管理另一种是yum在线管理 注意软件包没有扩展名,写上只是为了好看,便于识别而已. 注意区别包名,包全名.之所以要区分,就是因为有些命令十分挑剔,需要跟正 ...
- Object之总结(一)
一.Object类中一共有12个方法.一个私有方法,两个保护方法,9个公共方法.另外还有一个静态代码块. 1.registerNatives方法.私有静态本地无参数无返回值. 2.finalize方法 ...
