Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) ABCDEF
最近打的比较少。。。就只有这么点题解了。
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a following process.
There is a platform with n columns. 1 × 1 squares are appearing one after another in some columns on this platform. If there are no squares in the column, a square will occupy the bottom row. Otherwise a square will appear at the top of the highest square of this column.
When all of the n columns have at least one square in them, the bottom row is being removed. You will receive 1 point for this, and all the squares left will fall down one row.
You task is to calculate the amount of points you will receive.
The first line of input contain 2 integer numbers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 1000) — the length of the platform and the number of the squares.
The next line contain m integer numbers c1, c2, ..., cm (1 ≤ ci ≤ n) — column in which i-th square will appear.
Print one integer — the amount of points you will receive.
3 9
1 1 2 2 2 3 1 2 3
2
题意:类似俄罗斯方块,不过每次只降下一个1*1的方块。给出列数,还有每次方块降下所在的列,求能消除几列。 题解:算每列方块数然后求最小值。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N=1e3+;
int a[N],n,m,d,minx;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&d);
a[d]++;
}
minx=INF;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
minx=min(minx,a[i]);
printf("%d\n",minx);
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Your friend Mishka and you attend a calculus lecture. Lecture lasts n minutes. Lecturer tells ai theorems during the i-th minute.
Mishka is really interested in calculus, though it is so hard to stay awake for all the time of lecture. You are given an array t of Mishka's behavior. If Mishka is asleep during the i-th minute of the lecture then ti will be equal to 0, otherwise it will be equal to 1. When Mishka is awake he writes down all the theorems he is being told — ai during the i-th minute. Otherwise he writes nothing.
You know some secret technique to keep Mishka awake for k minutes straight. However you can use it only once. You can start using it at the beginning of any minute between 1 and n - k + 1. If you use it on some minute i then Mishka will be awake during minutes j such that 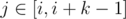 and will write down all the theorems lecturer tells.
and will write down all the theorems lecturer tells.
You task is to calculate the maximum number of theorems Mishka will be able to write down if you use your technique only once to wake him up.
The first line of the input contains two integer numbers n and k (1 ≤ k ≤ n ≤ 105) — the duration of the lecture in minutes and the number of minutes you can keep Mishka awake.
The second line of the input contains n integer numbers a1, a2, ... an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 104) — the number of theorems lecturer tells during the i-th minute.
The third line of the input contains n integer numbers t1, t2, ... tn (0 ≤ ti ≤ 1) — type of Mishka's behavior at the i-th minute of the lecture.
Print only one integer — the maximum number of theorems Mishka will be able to write down if you use your technique only once to wake him up.
6 3
1 3 5 2 5 4
1 1 0 1 0 0
16
In the sample case the better way is to use the secret technique at the beginning of the third minute. Then the number of theorems Mishka will be able to write down will be equal to 16.
题意:第一行给出长度为n的价值序列,以及第二行可否获取的01序列,你可以最多把01序列里面连续k个置为1,问最多能获得多少价值。
题解:可获取的序列a[i]直接加入贡献,并置a[i]为0。然后求a[i]前缀和pre[i],找一个最大的pre[i]-pre[i-k]加入贡献,这样的贡献即为答案。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+;
int a[N],t,n,m,d,maxn,k,ans,now;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",a+i);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&t);
if(t)
{
ans+=a[i];
a[i]=;
}
}
for(int i=;i<=k && i<=n;i++)
now+=a[i];
maxn=now;
for(int i=k+;i<=n;i++)
{
now-=a[i-k];
now+=a[i];
maxn=max(maxn,now);
}
ans+=maxn;
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ; }
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Magnus decided to play a classic chess game. Though what he saw in his locker shocked him! His favourite chessboard got broken into 4pieces, each of size n by n, n is always odd. And what's even worse, some squares were of wrong color. j-th square of the i-th row of k-th piece of the board has color ak, i, j; 1 being black and 0 being white.
Now Magnus wants to change color of some squares in such a way that he recolors minimum number of squares and obtained pieces form a valid chessboard. Every square has its color different to each of the neightbouring by side squares in a valid board. Its size should be 2n by2n. You are allowed to move pieces but not allowed to rotate or flip them.
The first line contains odd integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the size of all pieces of the board.
Then 4 segments follow, each describes one piece of the board. Each consists of n lines of n characters; j-th one of i-th line is equal to 1 if the square is black initially and 0 otherwise. Segments are separated by an empty line.
Print one number — minimum number of squares Magnus should recolor to be able to obtain a valid chessboard.
1
0 0 1 0
1
3
101
010
101 101
000
101 010
101
011 010
101
010
2
题意:有一个黑白相间的棋盘碎成4个n*n的块,而且其上的颜色沾污了,不一定是黑白相间的。现在让你把这4个块染色,给块中一格染色需要付出代价1。现在让你求使得这四块能拼成一个黑白相间的棋盘所需付出的最小代价。
题解:每个块染色后都有两种样式,分别对应左上角为黑或白。我们把每块变为这两种样式所需代价求出,然后枚举所有的4个块拼成棋盘的组合,找出最小的代价即为答案。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+;
int need[][],n,m,ans;
char s[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
{
scanf("%s",s);
for(int k=;k<n;k++)
{
m=s[k]-'';
need[i][(k&)^(j&)^m]++;
}
}
}
ans=INF;
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
for(int j=;j<=;j++)
if(j!=i)
for(int k=;k<=;k++)
if(k!=j && k!=i)
for(int l=;l<=;l++)
if(l!=k && l!=j && l!=i)
{
ans=min(ans,need[i][]+need[j][]+need[k][]+need[l][]);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given n points on Cartesian plane. Every point is a lattice point (i. e. both of its coordinates are integers), and all points are distinct.
You may draw two straight lines (not necessarily distinct). Is it possible to do this in such a way that every point lies on at least one of these lines?
The first line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of points you are given.
Then n lines follow, each line containing two integers xi and yi (|xi|, |yi| ≤ 109)— coordinates of i-th point. All n points are distinct.
If it is possible to draw two straight lines in such a way that each of given points belongs to at least one of these lines, print YES. Otherwise, print NO.
5
0 0
0 1
1 1
1 -1
2 2
YES
5
0 0
1 0
2 1
1 1
2 3
NO
In the first example it is possible to draw two lines, the one containing the points 1, 3 and 5, and another one containing two remaining points.
题意:给你一堆整数点,然后让你判断是否能最多只画两条直线,使得这两条直线经过所有点。
题解:先找到互不在同一直线上的三个点。然后枚举其中两个点连线,为其中一条直线。另外一个点找不在这条直线上的另一个点连线(用向量积),构成另外一条直线。然后检查所有点是不是在这两条线上,如果是的话就输出YES反之输出NO。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+;
struct node{
int x,y;
}p[maxn];
int res[];
int n;
void Read(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
}
}
bool judge(int a,int b){
int ans=;
while(ans==a||ans==b) ans++;
int y1=p[res[b]].y-p[res[a]].y;
int x1=p[res[b]].x-p[res[a]].x;
int x2,y2;
bool flag=true;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++){
int y=p[i].y-p[res[a]].y;
int x=p[i].x-p[res[a]].x;
if(1LL*y1*x==1LL*x1*y)continue;
y=p[i].y-p[res[ans]].y;
x=p[i].x-p[res[ans]].x;
if(flag&&i!=res[ans]){
y2=y;x2=x;flag=false;
}
else{
if(y2*x==x2*y)continue;
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
Read();
if(n<=){
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
int y1=p[].y-p[].y;
int x1=p[].x-p[].x;
int flag=;
int i=;
for(;i<=n;i++){
int y=p[i].y-p[].y;
int x=p[i].x-p[].x;
if(1LL*y1*x==1LL*x1*y)
continue;
else{
flag=;
break;
}
}
if(!flag){
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
res[]=,res[]=,res[]=i;
for(i=;i<;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<;j++)
if(judge(i,j)){
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
One day Polycarp decided to rewatch his absolute favourite episode of well-known TV series "Tufurama". He was pretty surprised when he got results only for season 7 episode 3 with his search query of "Watch Tufurama season 3 episode 7 online full hd free". This got Polycarp confused — what if he decides to rewatch the entire series someday and won't be able to find the right episodes to watch? Polycarp now wants to count the number of times he will be forced to search for an episode using some different method.
TV series have n seasons (numbered 1 through n), the i-th season has ai episodes (numbered 1 through ai). Polycarp thinks that if for some pair of integers x and y (x < y) exist both season x episode y and season y episode x then one of these search queries will include the wrong results. Help Polycarp to calculate the number of such pairs!
The first line contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of seasons.
The second line contains n integers separated by space a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — number of episodes in each season.
Print one integer — the number of pairs x and y (x < y) such that there exist both season x episode y and season y episode x.
5
1 2 3 4 5
0
3
8 12 7
3
3
3 2 1
2
Possible pairs in the second example:
- x = 1, y = 2 (season 1 episode 2
 season 2 episode 1);
season 2 episode 1); - x = 2, y = 3 (season 2 episode 3
 season 3 episode 2);
season 3 episode 2); - x = 1, y = 3 (season 1 episode 3
 season 3 episode 1).
season 3 episode 1).
In the third example:
- x = 1, y = 2 (season 1 episode 2
 season 2 episode 1);
season 2 episode 1); - x = 1, y = 3 (season 1 episode 3
 season 3 episode 1).
season 3 episode 1).
题意,给出一些季度和每季度的最高章节数,现在让你找存在总点对数。其中如若存在第x季度的第y章节及第y季度的第x章节(x<y),那么(x,y)算作一对。
题解:写一个主席树,对于每个i,在a[i](a[i]若>n,a[i]=n)处权值+1。然后对于每个i,查询其第i+1~a[i]棵树间[i,n]的权值总和,加入答案。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LL long long
using namespace std;
const int N=2e5+;
struct seg
{
int l,r;
int sum;
int lt,rt;
}tree[N<<];
int root[N],cnt,n,a[N];
LL ans;
void init(int &i,int l,int r)
{
tree[++cnt]=(seg){l,r};
i=cnt;
if(l==r)
return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>;
init(tree[i].lt,l,mid);
init(tree[i].rt,mid+,r);
return ;
}
void update(int &i,int pos,int val)
{
tree[++cnt]=tree[i];
i=cnt;
tree[i].sum+=val;
if(tree[i].l==tree[i].r)
return ;
int mid=(tree[i].l+tree[i].r)>>;
if(pos<=mid)
update(tree[i].lt,pos,val);
else
update(tree[i].rt,pos,val);
return ;
}
int query(int &i,int &j,int l,int r)
{
if(tree[i].l>=l && tree[i].r<=r)
return tree[j].sum-tree[i].sum;
int mid=(tree[i].l+tree[i].r)>>;
int ans=;
if(l<=mid)
ans+=query(tree[i].lt,tree[j].lt,l,r);
if(r>mid)
ans+=query(tree[i].rt,tree[j].rt,l,r);
return ans;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
init(root[],,n);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",a+i);
if(a[i]>n) a[i]=n;
update(root[i]=root[i-],a[i],);
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i]>i)
{
ans+=1LL*query(root[i],root[a[i]],i,n);
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return ;
}
4 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a string s consisting of n lowercase Latin letters.
Let's denote k-substring of s as a string subsk = sksk + 1..sn + 1 - k. Obviously, subs1 = s, and there are exactly 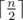 such substrings.
such substrings.
Let's call some string t an odd proper suprefix of a string T iff the following conditions are met:
- |T| > |t|;
- |t| is an odd number;
- t is simultaneously a prefix and a suffix of T.
For evey k-substring (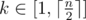 ) of s you have to calculate the maximum length of its odd proper suprefix.
) of s you have to calculate the maximum length of its odd proper suprefix.
The first line contains one integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 106) — the length s.
The second line contains the string s consisting of n lowercase Latin letters.
Print 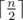 integers. i-th of them should be equal to maximum length of an odd proper suprefix of i-substring of s (or - 1, if there is no such string that is an odd proper suprefix of i-substring).
integers. i-th of them should be equal to maximum length of an odd proper suprefix of i-substring of s (or - 1, if there is no such string that is an odd proper suprefix of i-substring).
15
bcabcabcabcabca
9 7 5 3 1 -1 -1 -1
24
abaaabaaaabaaabaaaabaaab
15 13 11 9 7 5 3 1 1 -1 -1 1
19
cabcabbcabcabbcabca
5 3 1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 -1 -1
The answer for first sample test is folowing:
- 1-substring: bcabcabcabcabca
- 2-substring: cabcabcabcabc
- 3-substring: abcabcabcab
- 4-substring: bcabcabca
- 5-substring: cabcabc
- 6-substring: abcab
- 7-substring: bca
- 8-substring: c
POI2012的一道原题Prefixuffix差不多,题解就不多说了,拿hash写写就能过了。
蟹蟹clairs的提点。顺便学了字符串hash。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
//usually mod num is 1004535809 99824435 1000000007
#define pnum 233
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+;
int f[N],power[N][],hashx[N][],mod[]={,};
inline int gethashx(int l,int r,int x)
{
return (hashx[r][x]-(LL)hashx[l-][x]*power[r-l+][x]%mod[x]+mod[x])%mod[x];
}
inline bool check(int x,int y,int len)
{
return gethashx(x,x+len-,)==gethashx(y,y+len-,) && gethashx(x,x+len-,)==gethashx(y,y+len-,);
}
int n,ans;
char s[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",s);
power[][]=power[][]=;
hashx[][]=hashx[][]=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=;j<;j++)
{
power[i][j]=(LL)power[i-][j]*pnum%mod[j];
hashx[i][j]=((LL)hashx[i-][j]*pnum+(s[i-]-'a'))%mod[j];
}
for(int i=(n+)/;i>=;i--)
{
f[i]=min(f[i+]+,n-*i+);
if(!(f[i]&))
f[i]--;
while(f[i]> && !check(i,n-i-f[i]+,f[i])) f[i]-=;
}
for(int i=;i<=(n+)/;i++)
printf("%d ",f[i]);
printf("\n");
return ;
}
另外一种方法就是求后缀数组+LCP+ST,这个麻烦点。两者区别就在于求子串相等部分的处理。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define clr(x) memset(x,0,sizeof(x))
#define clr_1(x) memset(x,-1,sizeof(x))
#define LL long long
#define mod 1000000007
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define F(x) ((x) / 3 + ((x) % 3 == 1 ? 0 : tb))
#define G(x) ((x) < tb ? (x) * 3 + 1 : ((x) - tb) * 3 + 2)
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+;
int wa[N],wb[N],backet[N],order[N],sa[N*];
int ranked[N],height[N],s[N*],n,f[N];
char str[N];
int c0(int *r,int a,int b)
{
return r[a]==r[b]&&r[a+]==r[b+]&&r[a+]==r[b+];
}
int c12(int k,int *r,int a,int b)
{
if(k==) return r[a]<r[b]||r[a]==r[b]&&c12(,r,a+,b+);
else return r[a]<r[b]||r[a]==r[b]&&order[a+]<order[b+];
}
void sorted(int *r,int *a,int *b,int n,int m)
{
int i;
for(i=;i<n;i++) order[i]=r[a[i]];
for(i=;i<m;i++) backet[i]=;
for(i=;i<n;i++) backet[order[i]]++;
for(i=;i<m;i++) backet[i]+=backet[i-];
for(i=n-;i>=;i--) b[--backet[order[i]]]=a[i];
return;
}
void dc3(int *r,int *sa,int n,int m)
{
int i,j,*san=sa+n,ta=,tb=(n+)/,tbc=,p;
int *rn=r+n;
r[n]=r[n+]=;
for(i=;i<n;i++) if(i%!=) wa[tbc++]=i;
sorted(r+,wa,wb,tbc,m);
sorted(r+,wb,wa,tbc,m);
sorted(r,wa,wb,tbc,m);
for(p=,rn[F(wb[])]=,i=;i<tbc;i++)
rn[F(wb[i])]=c0(r,wb[i-],wb[i])?p-:p++;
if(p<tbc) dc3(rn,san,tbc,p);
else for(i=;i<tbc;i++) san[rn[i]]=i;
for(i=;i<tbc;i++) if(san[i]<tb) wb[ta++]=san[i]*;
if(n%==) wb[ta++]=n-;
sorted(r,wb,wa,ta,m);
for(i=;i<tbc;i++) order[wb[i]=G(san[i])]=i;
for(i=,j=,p=;i<ta && j<tbc;p++)
sa[p]=c12(wb[j]%,r,wa[i],wb[j])?wa[i++]:wb[j++];
for(;i<ta;p++) sa[p]=wa[i++];
for(;j<tbc;p++) sa[p]=wb[j++];
return;
}
void calheight(int *r, int *sa, int n) {
int i, j, k = ;
for (i = ; i <= n; i++) ranked[sa[i]] = i;
for (i = ; i < n; height[ranked[i++]] = k)
for (k ? k-- : , j = sa[ranked[i] - ]; r[i + k] == r[j + k]; k++);
return ;
}
int st[N][];
void calmin(int n)
{
int t=,k,divk;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
st[i][]=height[i+];
for(k=,t=,divk=;k<=n;k<<=,divk<<=,t++)
for(int i=;i<=n-k+;i++)
st[i][t]=min(min(st[i][t-],st[i+divk][t-]),height[i+divk]);
return ;
}
int getmin(int u,int v)
{
u=ranked[u];
v=ranked[v];
if(u>v) swap(u,v);
int p=v-u+,k=;
while(p)
{
p>>=;
k++;
}
return min(st[u][k-],st[v-(<<k-)+][k-]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",str);
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
s[i]=str[i]-'a'+;
}
s[n]=;
dc3(s,sa,n+,);
calheight(s,sa,n);
calmin(n);
int t;
for(int i=(n-)/;i>=;i--)
{
f[i]=min(f[i+]+,n-*i-);
if(!(f[i]&))
f[i]--;
while(f[i]> && getmin(i,n-i-f[i])<f[i])
f[i]-=;
}
for(int i=;i<=(n-)/;i++)
printf("%d ",f[i]);
return ;
}
Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) ABCDEF的更多相关文章
- Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2)F. k-substrings
题意比较麻烦略 题解:枚举前缀的中点,二分最远能扩展的地方,lcp来check,然后线段树维护每个点最远被覆盖的地方,然后查询线段树即可 //#pragma GCC optimize(2) //#pr ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2)(A~D)
由于之前打过了这场比赛的E题,而后面两道题太难,所以就手速半个多小时A了前4题. 就当练手速吧,不过今天除了C题数组开小了以外都是1A A Tetris 题意的抽象解释可以在Luogu里看一下(话说现 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2)
这场没打又亏疯了!!! A - Tetris : 类似俄罗斯方块,模拟一下就好啦. #include<bits/stdc++.h> #define fi first #define se ...
- D. Pair Of Lines( Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2))
#include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; ty ...
- C. Chessboard( Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2))
//暴力 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string> using namespace st ...
- B. Lecture Sleep( Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2))
前缀后缀和搞一搞,然后枚举一下区间,找出最大值 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; ; ...
- 【Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) D】Pair Of Lines
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 如果点的个数<=3 那么直接输出有解. 否则. 假设1,2最后会在一条直线上,则把这条直线上的点都删掉. 看看剩余的点是否在同 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2) D. Pair Of Lines (几何,随机)
D. Pair Of Lines time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard in ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 57 (Rated for Div. 2) ABCDEF题解
题目总链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1096 A. Find Divisible 题意: 给出l,r,在[l,r]里面找两个数x,y,使得y%x==0,保证有解. ...
随机推荐
- 【51NOD-0】1118 机器人走方格
[算法]DP #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; ,maxn=; int f[maxn][max ...
- jquery的基础语法、选取元素、操作元素、加事件、挂事件及移除事件
jquery基础知识 1.jquery文件的引入,所有的js代码要写在下面那段代码下面. <script src="../jquery-1.11.2.min.js">& ...
- ...args剩余参数用法
剩余参数语法允许我们将一个不定数量的参数表示为一个数组. function sum(...theArgs) { return theArgs.reduce((previous, current) ...
- webpack_配置和使用教程
webpack是一个模块打包的工具,它的作用是把互相依赖的模块处理成静态资源. webpack 可以使用 loader 来预处理文件.这允许你打包除 JavaScript 之外的任何静态资源.你可以使 ...
- Python switch-case语句的实现 -- 字典模拟实现
static void print_asru_status(int status, char *label) { char *msg = NULL; switch (status) { : msg = ...
- net_device->uc_promisc
如果设备不支持单播过滤,并且要监听多个单播地址时,就要使用net_device->uc_count和net_device->uc_promisc来设置混杂模式,具体见__dev_set_r ...
- wait与waitpid
1. 函数原型: #include <sys/wait.h> pid_t wait(int *statloc); pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *statloc ...
- C# 笔记——覆盖和重写
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace Cons ...
- LeetCode解题报告—— Swap Nodes in Pairs & Divide Two Integers & Next Permutation
1. Swap Nodes in Pairs Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. For e ...
- Highcharts创建一个简单的柱状图
新建一个html文件,将highcharts引入到你的页面后,通过两个步骤我们就可以创建一个简单的图表了. 1.创建div容器 在页面的 body部分创建一个div,并指定div 的 id,高度和宽度 ...
