struts2-第一章-基础用法3
一,结果类型配置
在之前servlet学习中,知道网页页面路径跳转有两种方式,内部跳转(请求转发)和外部跳转(重定向),两者的区别,内部跳转浏览器地址不会变化
可以保存上一次请求的数据
外部跳转浏览器地址会发生变化,但是不能保存上一次请求数据
struts2中也有上述两种跳转方式,但是需要我们进行指定,在struts.xml中action节点的result节点的type属性进行配置
type属性的取值:
(1)dispatcher :内部跳转,默认值,通常跳转jsp
(2)redirect:外部跳转,通常跳转jsp
(3)chain:内部跳转,通常跳转到action
(4)redirectAction:外部跳转,通常跳转到action
案例
(1)action1类
@Getter
@Setter
public class Demo1Action extends ActionSupport { private String name = "zhangsan"; //内部跳转jsp
public String dispatcher(){
System.out.println("Demo1Action.dispatcher...");
return "a";
}
//外部跳转jsp
public String redirect(){
System.out.println("Demo1Action.redirect...");
return "b";
}
//内部跳转action
public String chain(){
System.out.println("Demo1Action.chain...");
return "c";
}
//外部跳转action
public String redirectAction(){
System.out.println("Demo1Action.redirectAction...");
return "d";
} }
(2)struts.xml配置
<package name="default" namespace="/" extends="struts-default">
<action name="demo1Action" class="com.yujun.maven.action.Demo1Action">
<!-- 跳转到jsp,内部和外部 -->
<result name="a" type="dispatcher">/demo1.jsp</result>
<result name="b" type="redirect">/demo1.jsp</result> <!-- 跳转到action,内部和外部 -->
<result name="c" type="chain">
<!-- 指定跳转的action的名称 -->
<param name="actionName">demo2Action</param>
<!-- 指定action所在命名空间 -->
<param name="namespace">/</param>
<!-- 指定执行action的哪个方法 -->
<param name="method">m1</param>
</result>
<result name="d" type="redirectAction">
<!-- 指定跳转的action的名称 -->
<param name="actionName">demo2Action!m2.action</param>
<!-- 指定action所在命名空间 -->
<param name="namespace">/</param>
</result> </action> <action name="demo2Action" class="com.yujun.maven.action.Demo2Action">
<result>/demo2.jsp</result>
</action> </package>
(3)action2类
public class Demo2Action extends ActionSupport {
public String m1(){
System.out.println("Demo2Action.m1...");
return SUCCESS;
}
public String m2(){
System.out.println("Demo2Action.m2...");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
(4)demo1.jsp
<h3>
姓名:${name }
</h3>
(5)demo2.jsp
<h3>
this is demo2.jsp
</h3>
(6)index.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<base href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/ "/>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>
<a href="demo3Action!dispatcher.action">访问demo1Action的dispatcher方法</a>
</h4>
<h4>
<a href="demo3Action!redirect.action">访问demo1Action的redirect方法</a>
</h4>
<h4>
<a href="demo3Action!chain.action">访问demo1Action的chain方法</a>
</h4>
<h4>
<a href="demo3Action!redirectAction.action">访问demo1Action的redirectAction方法</a>
</h4> </body>
</html>
二,action中访问request,session,application
在struts2中的action有时需要访问servlet资源,比如会话,记录登录人信息,通常有三种
(1)使用ActionContext
(2)使用ServletActionContext
(3)action实现ServletRequestAware/ServletContextAware接口
1.ActionContext
表示action上下文,上下文看做一个容器(本质就是HashMap),存放的是action在执行时需要用到的对象,是一个线程安全类
(1)action类
public class Demo3Action extends ActionSupport {
public String m1(){
//都可以给当前请求中存放数据
//等效于request对象,但并不是request
ActionContext.getContext().put("name", "小明");
//真正的request对象
((Map)ActionContext.getContext().get("request")).put("name2", "小红");
//session对象
ActionContext.getContext().getSession().put("username", "admin");
//application对象
ActionContext.getContext().getApplication().put("count", 10);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
(2)struts.xml配置
<action name="demo3Action" class="com.yujun.maven.action.Demo3Action">
<result>/demo3.jsp</result>
</action>
(3)页面
<h3>
${name },${name2 },${username },${count }
</h3>
若想查看值栈的信息,可以使用struts2提供的debug标签

(4)访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/struts2-chapter1-3/demo3Action!m1.action
2.servletActionContext
public class ServletActionContext extend ActionContext implements StrutsStatics{
ServletActionContext类继承了ActionContext,因此此类也是一个线程安全类;该类提供了直接访问servlet容器对象(request、session、application)的功能
(1)action类
public class Demo4Action extends ActionSupport {
public String m1(){
//request对象
ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("abc", "abc123");
//session对象
ServletActionContext.getRequest().getSession().setAttribute("xyz", "xyz123");
//application对象
ServletActionContext.getServletContext().setAttribute("opq", "opq123");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
(2)struts.xml配置
<action name="demo4Action" class="com.yujun.maven.action.Demo4Action">
<result>/demo4.jsp</result>
</action>
(3)页面
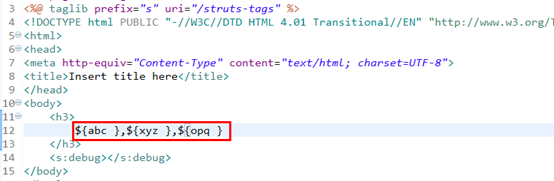
(4) 访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/struts2-chapter1-3/demo4Action!m1.action
3.实现接口的方式
(1)action类
public class Demo5Action extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware,ServletContextAware{
//成员变量保存servlet容器对象
private HttpServletRequest request;
private ServletContext application;
private HttpSession session;
//参数的request是struts2注入给我们的,我们可以直接保存起来
@Override
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
this.session = request.getSession();
}
@Override
public void setServletContext(ServletContext context) {
this.application = context;
}
public String m1(){
request.setAttribute("a", "a123");
session.setAttribute("b", "b123");
application.setAttribute("c", "c123");
return SUCCESS;
}
}
(2)struts.xml配置
<action name="demo5Action" class="com.yujun.maven.action.Demo5Action">
<result>/demo5.jsp</result>
</action>
(3)页面

(4)访问
http://127.0.0.1:8080/struts2-chapter1-3/demo5Action!m1.action
struts2-第一章-基础用法3的更多相关文章
- struts2第一章-基本用法
一.struts简介 1.回顾 MVC M-model模型层 V-view 视图层 前端界面 C-controller 控制层 struts2: Apache提供的开源的控制层框架,相当于servl ...
- .net架构设计读书笔记--第一章 基础
第一章 基础 第一节 软件架构与软件架构师 简单的说软件架构即是为客户构建一个软件系统.架构师随便软件架构应运而生,架构师是一个角色. 2000年9月ANSI和IEEE发布了<密集性软件架构建 ...
- Laxcus大数据管理系统2.0(2)- 第一章 基础概述 1.1 基于现状的一些思考
第一章 基础概述 1.1 基于现状的一些思考 在过去十几年里,随着互联网产业的普及和高速发展,各种格式的互联网数据也呈现爆炸性增长之势.与此同时,在数据应用的另一个重要领域:商业和科学计算,在各种新兴 ...
- Linux系统shell编程自学_第一章基础
第一章 基础shell的优势在于处理操作系统底层的业务,Python,php的优势在于开发运维工具,web界面的管理工具以及web业务开发.处理一键安装.优化.报警脚本shell又叫命令解释器,它能识 ...
- wpf(第一章 基础知识)
wpf第一章基础知识:通过vs2015创建wpf程序会在引用里面多出3个核心程序集PresentationCore.PresentationFramework.WindowsBase.并且会在解决方案 ...
- 《openssl编程》:第一章基础知识
第一章 基础知识 1.1 对称算法 对称算法使用一个密钥.给定一个明文和一个密钥,加密产生密文,其长度和明文大致相同.解密时,使用读密钥与加密密钥相同. 对称算法主要有四种加密模式: (1) 电子密码 ...
- Python第一章-基础知识
第一章:基础知识 1.1 安装python. 直接官网下载最新的python然后默认安装就可以了,然后开始菜单里找到pyhton *.*.* Shell.exe运行python的交互shell ...
- 【SSH三框架】Struts2第一章的基础:第一次写Struts2规划
今年八月,当已经SSH三架完成学业.然后,他感动Android开展.三个框架已经很长的时间做无用的东西.所以,如果你想花三四天的时间来复习一下,写在博客. 附带SSH整个jar包网盘下载:http:/ ...
- 《Python基础教程(第二版)》学习笔记 -> 第一章 基础知识
写笔记的原因:书也看了一遍,视频也看了,但总是感觉效果不好,一段时间忘记了,再看又觉得有心无力,都是PDF的书籍,打开了就没有心情了,上班一天了,回家看这些东西,真的没多大精力了,所以,我觉得还是把p ...
- TypeScript学习指南第一章--基础数据类型(Basic Types)
基础数据类型(Basic Types) 为了搭建应用程序,我们需要使用一些基础数据类型比如:numbers,strings,structures,boolean等等. 在TypeScript中除了Ja ...
随机推荐
- 【ML】从特征分解,奇异值分解到主成分分析
1.理解特征值,特征向量 一个对角阵\(A\),用它做变换时,自然坐标系的坐标轴不会发生旋转变化,而只会发生伸缩,且伸缩的比例就是\(A\)中对角线对应的数值大小. 对于普通矩阵\(A\)来说,是不是 ...
- C语言函数-strcat
strcat: 将两个char类型连接. char d[20]="GoldenGlobal"; char *s="View"; strcat(d,s); 结果放 ...
- [AH2017/HNOI2017]大佬
题目描述 人们总是难免会碰到大佬.他们趾高气昂地谈论凡人不能理解的算法和数据结构,走到任何一个地方,大佬的气场就能让周围的人吓得瑟瑟发抖,不敢言语. 你作为一个 OIER,面对这样的事情非常不开心,于 ...
- logstash配置多入多出并互相隔离
需求:需要利用同一logstash进程采集不同日志,输出到es的不同index,各输入输出隔离: 主要需要解决如下两个问题: 1.如何加载多个配置文件? 普通启动方式:nohup bin/logsta ...
- (八)控件介绍,QLable
Radio单选框 默认互斥,加GroupBox进行分组可以解决这个 checkBox复选 ListWidget TableWIdget:有表头 #include "widget.h" ...
- BAT面试经验分享——iOS高级开发工程师的自我总结!
序言 目前形势,参加到iOS队伍的人是越来越多,甚至已经到供过于求了. 今年,找过工作人可能会更深刻地体会到今年的就业形势不容乐观,随着各大公司秋招的开始,很多小伙伴都行动起来了,我也有幸获得了一份不 ...
- keras使用
一.pad_sequences from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences keras只能接受长度相同的序列输入.因此如果目前序列长度 ...
- Kubernetes之dashboard
部署dashboard $ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommen ...
- Hadoop高可用集群
1.简介 若HDFS集群中只配置了一个NameNode,那么当该NameNode所在的节点宕机,则整个HDFS就不能进行文件的上传和下载. 若YARN集群中只配置了一个ResourceManager, ...
- Aras 发布Web Services
https://blog.csdn.net/plm888/article/details/10890173
