2015 ACM-ICPC 亚洲区上海站 A - An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何)
题目链接:HDU 5572
Problem Description
On an infinite smooth table, there's a big round fixed cylinder and a little ball whose volume can be ignored.
Currently the ball stands still at point \(A\), then we'll give it an initial speed and a direction. If the ball hits the cylinder, it will bounce back with no energy losses.
We're just curious about whether the ball will pass point \(B\) after some time.
Input
First line contains an integer \(T\), which indicates the number of test cases.
Every test case contains three lines.
The first line contains three integers \(O_x\), \(O_y\) and \(r\), indicating the center of cylinder is \((O_x, O_y)\) and its radius is \(r\).
The second line contains four integers \(A_x\), \(A_y\), \(V_x\) and \(V_y\), indicating the coordinate of \(A\) is \((A_x, A_y)\) and the initial direction vector is \((V_x, V_y)\).
The last line contains two integers \(B_x\) and \(B_y\), indicating the coordinate of point \(B\) is \((B_x,B_y)\).
⋅ \(1 ≤ T ≤ 100.\)
⋅ \(|O_x|,|O_y|≤ 1000.\)
⋅ \(1 ≤ r ≤ 100.\)
⋅ \(|A_x|,|A_y|,|B_x|,|B_y|≤ 1000.\)
⋅ \(|V_x|,|V_y|≤ 1000.\)
⋅ \(V_x≠0 or V_y≠0.\)
⋅ both \(A\) and \(B\) are outside of the cylinder and they are not at same position.
Output
For every test case, you should output " Case #x: y", where \(x\) indicates the case number and counts from \(1\). \(y\) is " \(Yes\)" if the ball will pass point \(B\) after some time, otherwise \(y\) is " \(No\)".
Sample Input
2
0 0 1
2 2 0 1
-1 -1
0 0 1
-1 2 1 -1
1 2
Sample Output
Case #1: No
Case #2: Yes
Source
Solution
题意
在光滑平面上有一个圆,圆外有两点 \(a\),\(b\),给定 \(a\) 的方向向量,求 \(a\) 运动一段时间后能否到达 \(b\)(\(a\) 碰到圆后没有反弹没有能量损失)。
思路
分类讨论一下。
点 \(a\) 的运动在圆外或者与圆相切时直接判断。
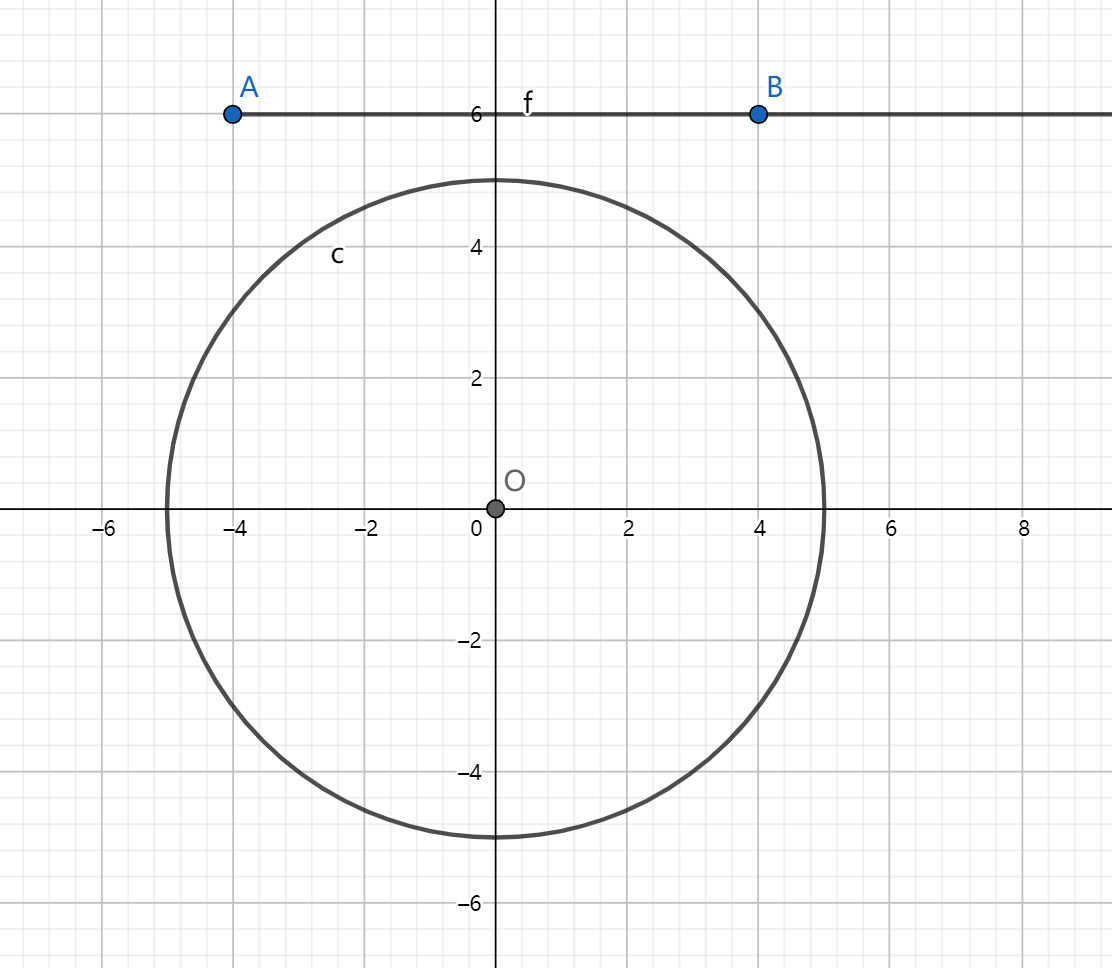
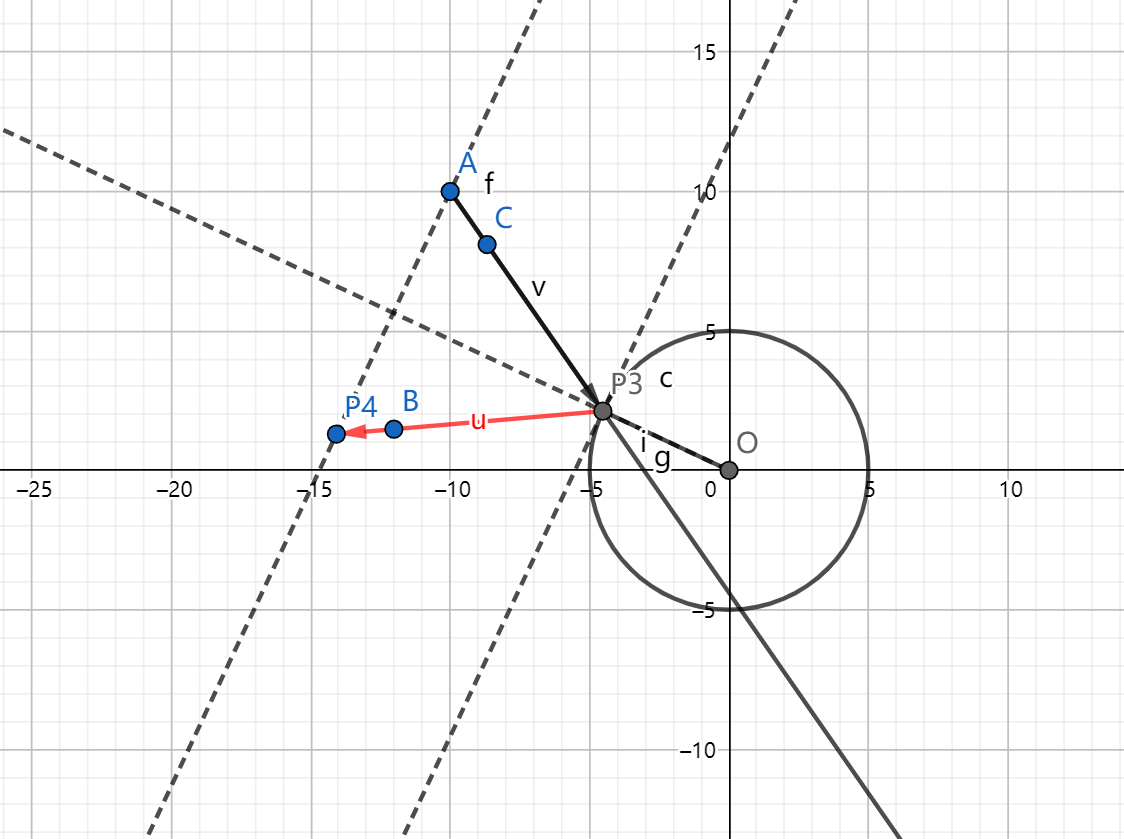
注意是射线,下图的情况是不行的。
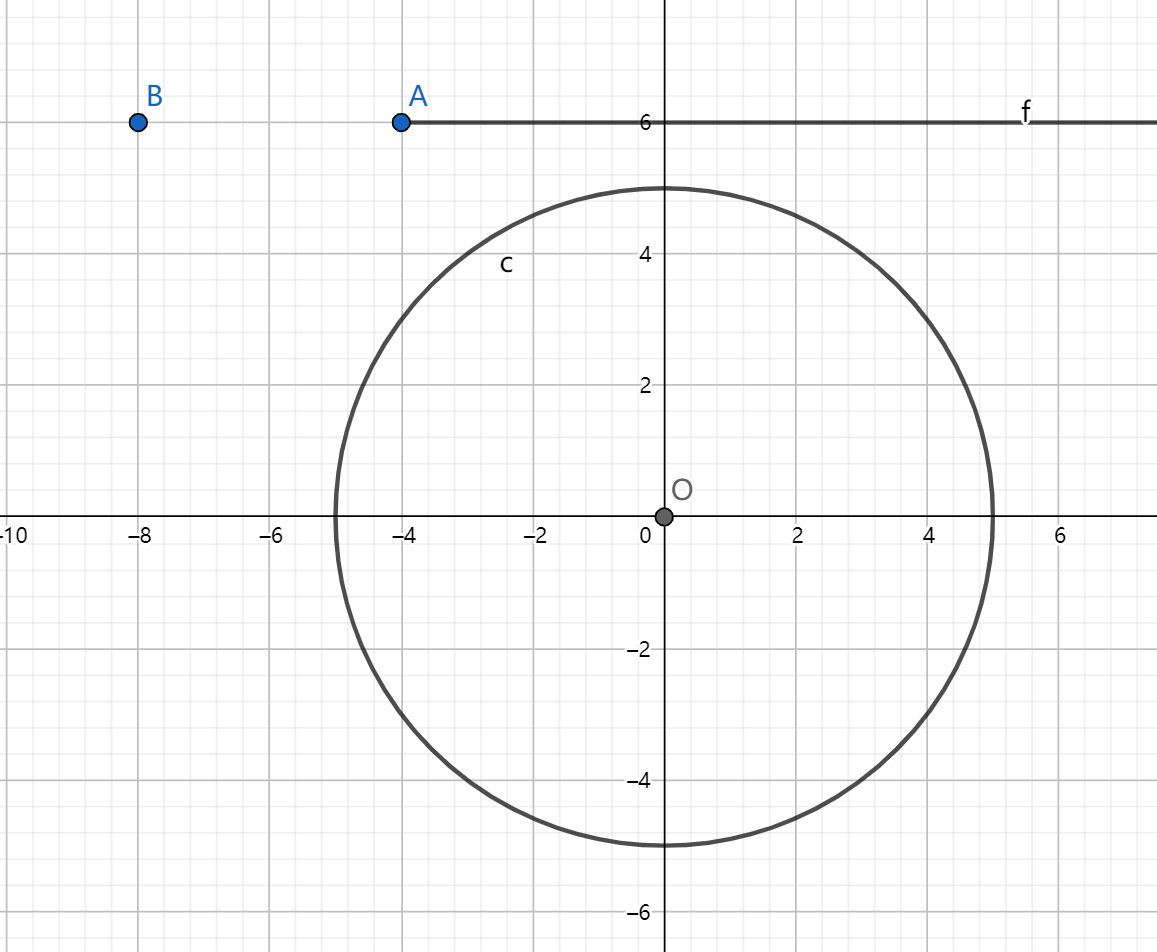
相交时如果点 \(b\) 在圆的另一边也是不行的。
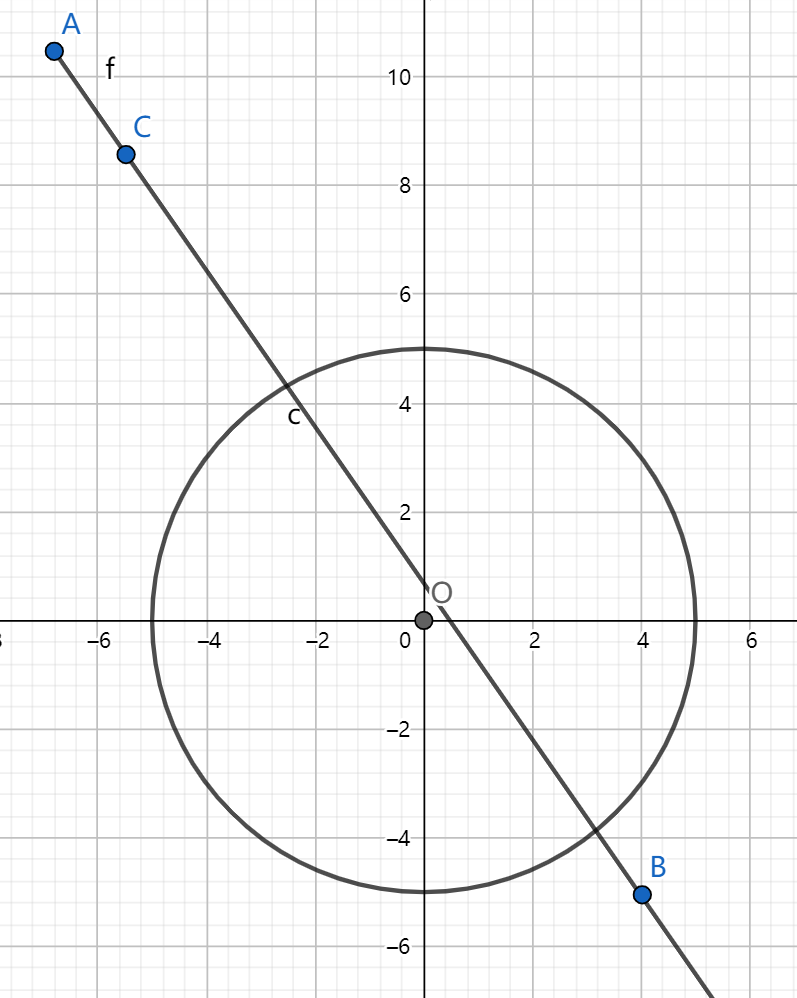
相交时有两种情况,一种是不经过反射就到达点 \(b\),另一种是经过反射才到达点 \(b\)。
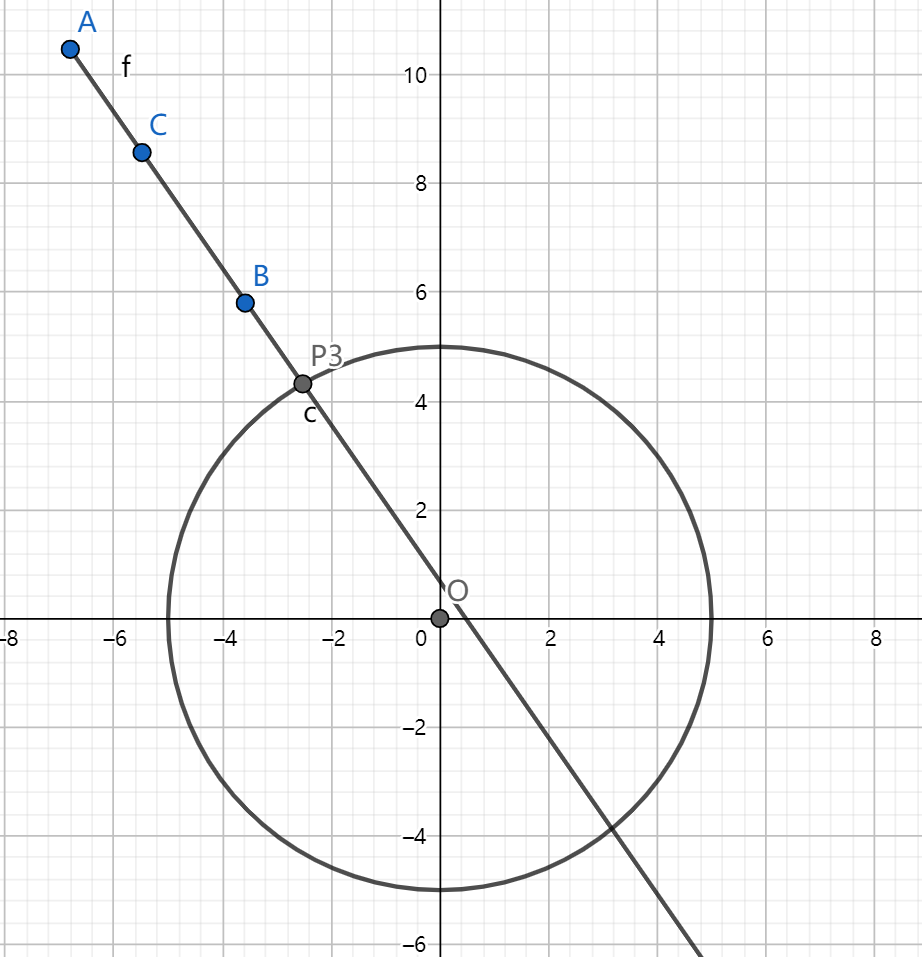
反射后的射线求一下对称点即可。(代码中的 P3 和 P4 点就是下图中的两点)
模板来自kuangbin的计算几何模板。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-8;
const db inf = 1e18;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(){}
Point(double _x,double _y){
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
void input(){
scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y);
}
bool operator == (Point b)const{
return dcmp(x-b.x) == 0 && dcmp(y-b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b)const{
return dcmp(x-b.x)== 0?dcmp(y-b.y)<0:x<b.x;
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
double operator ^(const Point &b)const{
return x*b.y - y*b.x;
}
double operator *(const Point &b)const{
return x*b.x + y*b.y;
}
double len(){
return hypot(x,y);
}
double len2(){
return x*x + y*y;
}
double distance(Point p){
return hypot(x-p.x,y-p.y);
}
db dis2(const Point a) {
return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);
}
db dis(const Point a) {
return sqrt(dis2(a));
}
Point operator +(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
Point operator *(const double &k)const{
return Point(x*k,y*k);
}
Point operator /(const double &k)const{
return Point(x/k,y/k);
}
double rad(Point a,Point b){
Point p = *this;
return fabs(atan2( fabs((a-p)^(b-p)),(a-p)*(b-p) ));
}
Point trunc(double r){
double l = len();
if(!dcmp(l))return *this;
r /= l;
return Point(x*r,y*r);
}
};
struct Line{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e){
s = _s;
e = _e;
}
void input(){
s.input();
e.input();
}
void adjust(){
if(e < s)swap(s,e);
}
double length(){
return s.distance(e);
}
double angle(){
double k = atan2(e.y-s.y,e.x-s.x);
if(dcmp(k) < 0)k += pi;
if(dcmp(k-pi) == 0)k -= pi;
return k;
}
int relation(Point p){
int c = dcmp((p-s)^(e-s));
if(c < 0)return 1;
else if(c > 0)return 2;
else return 3;
}
double dispointtoline(Point p){
return fabs((p-s)^(e-s))/length();
}
// 点 p 在直线上的投影
Point lineprog(Point p){
return s + ( ((e-s)*((e-s)*(p-s)))/((e-s).len2()) );
}
// 点 p 关于直线的对称点
Point symmetrypoint(Point p){
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2*q.x-p.x,2*q.y-p.y);
}
};
struct Circle{
Point p;
double r;
Circle(){}
Circle(Point _p,double _r){
p = _p;
r = _r;
}
void input(){
p.input();
scanf("%lf",&r);
}
int relationline(Line v){
double dst = v.dispointtoline(p);
if(dcmp(dst-r) < 0)return 2;
else if(dcmp(dst-r) == 0)return 1;
return 0;
}
// 直线和圆的交点
int pointcrossline(Line v,Point &p1,Point &p2){
if(!(*this).relationline(v))return 0;
Point a = v.lineprog(p);
double d = v.dispointtoline(p);
d = sqrt(r*r-d*d);
if(dcmp(d) == 0){
p1 = a;
p2 = a;
return 1;
}
p1 = a + (v.e-v.s).trunc(d);
p2 = a - (v.e-v.s).trunc(d);
return 2;
}
};
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
int kase = 0;
while(T--) {
Circle o;
o.input();
Point a, b, c;
a.input();
Point v;
v.input(); // 方向向量
b.input();
c = a + v;
Line l = Line(a, c); // 射线ac代表a运动的方向
Point p1, p2, p3;
int cnt = o.pointcrossline(l, p1, p2); // 求直线ac与圆的交点
if(cnt == 2) { // 判断交点在线段外还是线段内
if((p1 - a)*(c - a) < 0) {
cnt = 0;
}
}
if(cnt == 0 || cnt == 1) { // 没有交点或者直线ac与圆相切
// 判断射线ac是否经过点b
if(dcmp((b - a)^(c - a)) == 0 && dcmp((b - a)*(c - a)) > 0) {
printf("Case #%d: Yes\n", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: No\n", ++kase);
continue;
}
} else {
// 找从圆外进入圆内的一个交点 p3
if(p1.dis2(a) < p2.dis2(a)) {
p3 = p1;
} else {
p3 = p2;
}
// 判断点b是否在线段ap3上
if(dcmp((b - a)^(c - a)) == 0 && dcmp((b - a)*(c - a)) > 0) {
if((p3 - a)*(p3 - b) < 0) {
printf("Case #%d: No\n", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: Yes\n", ++kase);
continue;
}
}
// 反弹的情况
Line tmp = Line(o.p, p3);
Point p4 = tmp.symmetrypoint(a); // 反射后的一个点 点a关于圆心到交点p3所在直线的对称点
// 判断反射后能否到达点b
if(dcmp((b - p3)^(p4 - p3)) == 0 && dcmp((b - p3)*(p4 - p3)) > 0) {
printf("Case #%d: Yes\n", ++kase);
continue;
} else {
printf("Case #%d: No\n", ++kase);
continue;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
2015 ACM-ICPC 亚洲区上海站 A - An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何)的更多相关文章
- HDU 5572 An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何+对称点模板)
HDU 5572 An Easy Physics Problem (计算几何) 题目链接http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5572 Descripti ...
- hdu 5444 Elven Postman(二叉树)——2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online
Problem Description Elves are very peculiar creatures. As we all know, they can live for a very long ...
- 2016 ACM/ICPC亚洲区青岛站现场赛(部分题解)
摘要 本文主要列举并求解了2016 ACM/ICPC亚洲区青岛站现场赛的部分真题,着重介绍了各个题目的解题思路,结合详细的AC代码,意在熟悉青岛赛区的出题策略,以备战2018青岛站现场赛. HDU 5 ...
- (并查集)Travel -- hdu -- 5441(2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online )
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5441 Travel Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memo ...
- (二叉树)Elven Postman -- HDU -- 54444(2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5444 Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- 2015 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changchun Online HDU 5444 Elven Postman【二叉排序树的建树和遍历查找】
Elven Postman Time Limit: 1500/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- hdu 5572 An Easy Physics Problem 圆+直线
An Easy Physics Problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/ ...
- HDU 5572--An Easy Physics Problem(射线和圆的交点)
An Easy Physics Problem Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/ ...
- 2015 ACM / ICPC 亚洲区域赛总结(长春站&北京站)
队名:Unlimited Code Works(无尽编码) 队员:Wu.Wang.Zhou 先说一下队伍:Wu是大三学长:Wang高中noip省一:我最渣,去年来大学开始学的a+b,参加今年区域赛之 ...
随机推荐
- vue搭建项目步骤(二)
上篇是搭建Vue项目的基本,接下来是继续对做项目的记录.顺序并不一定. 五.对页面入口文件的修改: 众所周知,main.js 程序入口文件,加载各种公共组件,App.Vue为 页面入口文件.但是有时候 ...
- 安装php时,configure: error: xml2-config not found. Please check your libxml2 installation
参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/anljf/article/details/6981247 安装php时的报错configure: error: xml2-config not f ...
- 同步架构OR异步架构
把智能系统比喻成KFC营业厅,处理器是窗口和窗口后面的服务员(把一个窗口当作一个核心),指令集是后面排队的人,窗口是数据吞吐量.当中午就餐人多的时候,一个窗口肯定忙不过来,这时候可以增加窗口,有两种方 ...
- selenium,webdriver模仿浏览器访问百度 基础1
这是一种比较好的反反爬技术 #安装:pip install selenium=2.48.0 #显示:pip show selenium #卸载:pip uninstall selenium #模拟用户 ...
- 逃脱 (简单BFS)
题目传送门 G逃脱 题目描述 这是mengxiang000和Tabris来到幼儿园的第四天,幼儿园老师在值班的时候突然发现幼儿园某处发生火灾,而且火势蔓延极快,老师在第一时间就发出了警报,位于幼儿园 ...
- Visual Studio Code如何编写运行C、C++
Visual Studio Code如何编写运行C.C++ 作者:知乎用户链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/30315894/answer/154979413来源:知 ...
- SHOW - 显示运行时参数的数值
SYNOPSIS SHOW name SHOW ALL DESCRIPTION 描述 SHOW 将显示当前运行时参数的数值. 这些变量可以通过 SET 语句来设置,或者通过编辑 postgresql. ...
- go语言从例子开始之Example20.错误处理
Go 语言使用一个独立的·明确的返回值来传递错误信息的.这与使用异常的 Java 和 Ruby 以及在 C 语言中经常见到的超重的单返回值/错误值相比,Go 语言的处理方式能清楚的知道哪个函数返回了错 ...
- python中二维数组的建立,输入和输出
''' for循环: for i in range(x,y,dir): pass 首先这个区间是左闭右开 其次dir在省略的情况下默认为1,就是每次加一,也可以指定 python的数组: python ...
- spring mvc 整合 druid
环境: ubuntu eclipse maven 一. pom.xml 加入druid 依赖 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibab ...
