codeforces_D. Treasure Hunting_[DP+Binary Search]
http://codeforces.com/contest/1201/problem/D
题意:n行m列的矩阵中,有k个targets,从[1, 1]出发,每次只能向上下左右四个方向移动一步,且只有在q个safecolumns上进行向上移动,最少需要多少次移动才能获得所有的targets。(2≤n,m,k,q≤2*10^5,q≤m)。
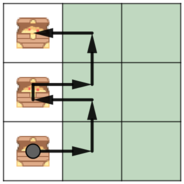


思路:
Make two arrays: left and right. left[i] is the treasure in the leftmost position in row i (0 if there are no treasures in row ii). right[i] is the treasure in the rightmost cell in row ii (0 if there are no treasures in row ii).
We can simply take out rows where there is no treasure (and add 1 to the result if there are treasure above that line, because we have to move up there).
For every row, except the last, we have to leave that row at one of the safe columns. Let's notice that the last treasure we collect in the row will be either left[i] or right[i]. Let's take a look at both possibilities: If we collect the left[i] treasure last, we have to leave the row either going left or going right to the closest safe column, because going further wouldn't worth it (consider moving up earlier and keep doing the same thing at row i+1). The same is true for right[i]. For the first row, we start at the first column, we can calculate the moves required to go up the second row at the for cells. For all the other rows, we have 4 possibilities, and we have to calculate how many moves it takes to reach the row i+1 at the 4 possible columns. For the last row, we don't have to reach a safe column, we just have to collect all the treasures there. We can count the answer for the problem from the calculated results from the previous row. Time complexity: O(16∗n)
1. 对于存在宝藏的行,最后得到的宝藏要么是最左边的要么是最右边的;
2. 假设最后拿到的是最左边的,那么可以通过这个宝藏左右最近的safecolumns离开;最后拿到的是最右边的情况也同理;
3. 对于第一行来说,若有宝藏,则获得最右边的宝藏后离开;所无宝藏,则通过离[1, 1]最近的safecolumn离开;
4. 对于其他行来说,最多可以有四种方式离开此行,最后一行不需要到达safecolumn,获得所有宝藏即可;
宝藏左右最近的safecolumn,可以通过binary search求得。
注意,若最左边的宝藏就在safecolumn上,则其左右最近的safecolumn都是此列。
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std; typedef long long LL; int findSafe(vector<int>& safes, int x){
int l = , r = safes.size()-, ret;
while(l <= r){
int m = (l+r)>>;
if(safes[m] == x)
return m;
if(safes[m] > x)
r = m - ;
else{
ret = m;
l = m + ;
}
}
return ret;
} int dist(int layer, int p1, int p2, vector<int>& leftmost, vector<int>& rightmost, vector<int>& safecol){
if(safecol[p1] > safecol[p2])
swap(p1, p2);
int d = safecol[p2] - safecol[p1];
if(rightmost[layer] > safecol[p2])
d += * (rightmost[layer]-safecol[p2]);
if(leftmost[layer] < safecol[p1])
d += * (safecol[p1]-leftmost[layer]);
return d;
} int main(){
int n, k, m, q;
cin>>n>>m>>k>>q;
vector<int> leftmost(n+, m+), rightmost(n+, ), safecol{};
for(int i=; i<k; i++){
int row, col;
cin>>row>>col;
leftmost[row] = min(leftmost[row], col);
rightmost[row] = max(rightmost[row], col);
}
for(int i=; i<q; i++){
int safe;
cin>>safe;
safecol.push_back(safe);
} sort(safecol.begin(), safecol.end()); while(leftmost[n] == m+) n--; if(n==){
cout<<rightmost[]-<<endl;
return ;
}
vector<LL> now_step{, , ,}, lst_step{, , , };
vector<int> lst_gate{-, -, -, -};
if(rightmost[] == ){
int rsafe = findSafe(safecol, );
if(safecol[rsafe] < )
rsafe++;
lst_gate[] = rsafe;
lst_step[] = safecol[rsafe]-;
}else{
int lsafe = findSafe(safecol, rightmost[]);
//cout<<rightmost[1]<<"*"<<lsafe<<endl;
lst_gate[] = lsafe;
lst_step[] = *rightmost[]-safecol[lsafe]-;
//cout<<"l10:"<<lst_step[0]<<endl;
if(safecol[lsafe]<rightmost[] && lsafe+ < safecol.size()){
lst_gate[] = lsafe+;
lst_step[] = safecol[lsafe+]-;
}
} for(int i=; i<n; i++){
if(leftmost[i] == m+){
for(int j=; j<; j++)
lst_step[j]++;
continue;
}else{
vector<int> now_gate{-, -, -, -};
int g1 = findSafe(safecol, leftmost[i]);
int g2 = findSafe(safecol, rightmost[i]);
//cout<<g1<<" "<<g2<<endl;
now_gate[] = g1;
if(safecol[g1] < leftmost[i] && g1+ < safecol.size())
now_gate[] = g1+;
now_gate[] = g2;
if(safecol[g2] < rightmost[i] && g2+ < safecol.size())
now_gate[] = g2+;
for(int j=; j<; j++){
now_step[j] = (*1e5+) * (*1e5);
for(int u=; u<; u++)
if(lst_gate[u]> && now_gate[j]>){
int d = +dist(i,now_gate[j], lst_gate[u], leftmost, rightmost, safecol);
//cout<<now_gate[j]<<" "<<lst_gate[u]<<endl;
//cout<<"d:"<<i<<" "<<d<<endl;
//cout<<"ld:"<<" "<<lst_step[u]<<endl;
now_step[j] = min(now_step[j], lst_step[u]+d);
}
}
lst_step = now_step;
lst_gate = now_gate;
}
}
LL ret = (*1e5+) * (*1e5);
for(int u=; u<; u++)
if(lst_gate[u] > ){
int d = +rightmost[n]-leftmost[n]+min(abs(rightmost[n]-safecol[lst_gate[u]]), abs(leftmost[n]-safecol[lst_gate[u]]));
//cout<<"d:"<<" "<<d<<endl;
//cout<<"lst_step:"<<lst_step[u]<<endl;
ret = min(ret, lst_step[u]+d);
}
printf("%I64d\n", ret);
return ;
}
codeforces_D. Treasure Hunting_[DP+Binary Search]的更多相关文章
- 96. Unique Binary Search Trees (Tree; DP)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees(dp)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees I&II——给定n有多少种BST可能、DP
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees 独一无二的二叉搜索树
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees II 独一无二的二叉搜索树之二
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n. For e ...
- Leetcode 86. Unique Binary Search Trees
本题利用BST的特性来用DP求解.由于BST的性质,所以root左子树的node全部<root.而右子树的node全部>root. 左子树 = [1, j-1], root = j, 右子 ...
- Unique Binary Search Trees
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- LeetCode-96. Unique Binary Search Trees
Description: Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1.. ...
- LeeCode - Unique Binary Search Trees
题目: Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For e ...
随机推荐
- 004-unity3d MonoBehaviour脚本方法简介
一.MonoBehaviour 1.公共方法 CancelInvoke Cancels all Invoke calls on this MonoBehaviour. Invoke Invokes t ...
- LeetCode——141 设计链表
题目: 简单说下思路: 用两个指针,一个跑得快,一个跑得慢(例如一个每次前进两步,一个前进一步),这样只要快指针不会撞上NULL(如果遇到了NULL的情况那么必然不存在环),快指针肯定会和慢指针碰面( ...
- 003/kubernetes基础:开启云原生之门(Mooc)
一.简介:(https://www.imooc.com/learn/978) 在2017年Kubernetes战胜了两个强大的竞争对手Swarm和Mesos,成为容器管理与调度编排领域的首选平台和事实 ...
- 谷歌,火狐浏览器不能禁用自动补齐的bug缺陷
IE浏览器里有autocomplete="off",可以禁止自动补全账号和密码,为了防止信息泄露,需要去除自动补齐. 自动补齐产生的场景是,form里面有密码框,因此只要将该密码框 ...
- windows10安装ipython
Win10中如何装IPython?(其他Windows版本,如win7.win8/8.1也通用)我的这个方法比较简单,配置好环境变量敲几行命令就行了 .安装IPython的前提是已经安装好了Pytho ...
- 使用git版本管理时的免密问题
方式1 使用ssh 方式 方式2 使用命令 git config --global credential.helper store 会把密码存放到当前用户的home目录下的 该文件中 [root@ ...
- 使用sql追踪
在会话层面使用sql追踪 1.查看sql追踪默认文件位置 2.设置trace文件名 alter session set tracefile_identifier='ymtrace001'; trace ...
- SpringMVC Controller单例和多例(转)
首先上测试代码 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import org.springframework.stereotype.C ...
- 洛谷 - P4567 - 文本编辑器 - 无旋Treap
https://www.luogu.org/problem/P4567 事实证明无旋Treap是不是不可能会比Splay快? #include<bits/stdc++.h> using n ...
- C# XML 解析包含特殊字符的内容
xml结构会解析一些特殊字符,特别是& < ,导致XmlDocument 解析错误 解决方法:将内容放在<![CDATA[ ]]>中,例如<![CDATA[2]] ...
