hadoop机架感知与网络拓扑分析:NetworkTopology和DNSToSwitchMapping
hadoop网络拓扑结构在整个系统中具有很重要的作用,它会影响DataNode的启动(注册)、MapTask的分配等等。了解网络拓扑对了解整个hadoop的运行会有很大帮助。
首先通过下面两个图来了解与网络拓扑有关的类。
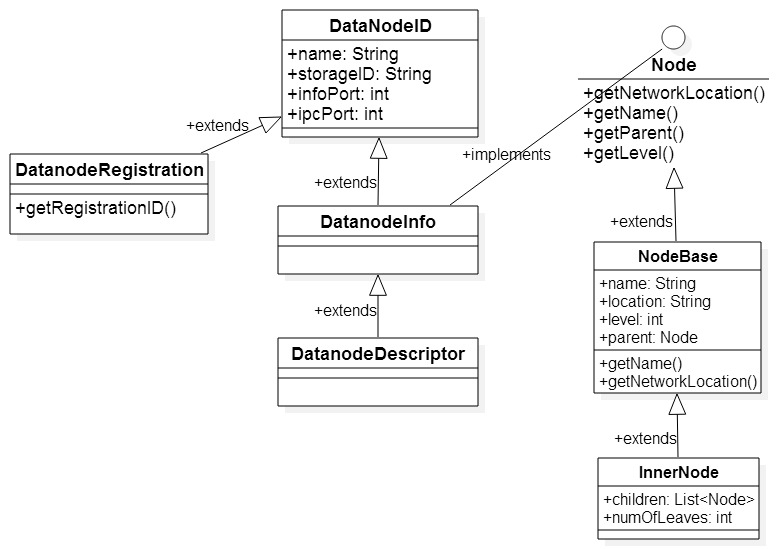
NetworkTopology用来表示hadoop集群的网络拓扑结构。hadoop将整个网络拓扑组织成树的结构(可以参考这篇文章https://issues.apache.org/jira/secure/attachment/12345251/Rack_aware_HDFS_proposal.pdf),其中Node接口代表树中的结点,既可以是树的内部结点(如data center,rack),也可以是叶子结点(就是host);而NodeBase实现了Node;NetworkTopology.InnerNode则代表树的内部结点。
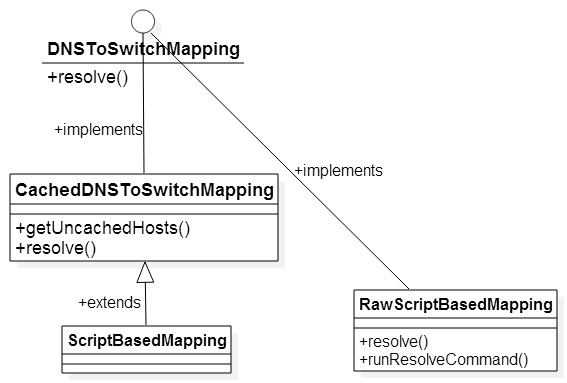
DNSToSwitchMapping用来把集群中的node转换成对应的网络位置,比如将域名/IP地址转换成集群中对应的网络位置。CachedDNSToSwitchMapping则用来缓存已经被解析出来的映射。ScriptBasedMapping主要是解析用户配置的映射脚本,并根据脚本中的转换规则进行映射;这个脚本的位置由配置文件“core-site.xml”中的参数“topology.script.file.name”来指定。RawScriptBasedMapping是ScriptBasedMapping的内部类,脚本的执行由这个类中的resolve()方法完成。
下面以DataNode启动时向NameNode注册自己的结点为例,来说明映射过程。当DataNode启动的时候以DatanodeRegistration的形式,通过RPC调用NameNode的register()方法,向NameNode来注册本结点的信息,使得NameNode通过网络拓扑确定该DataNode在网络拓扑中的位置。其具体实现过程在FSNamesystem中的registerDatanode()方法中,具体代码如下:
/**
* Register Datanode.
* <p>
* The purpose of registration is to identify whether the new datanode
* serves a new data storage, and will report new data block copies,
* which the namenode was not aware of; or the datanode is a replacement
* node for the data storage that was previously served by a different
* or the same (in terms of host:port) datanode.
* The data storages are distinguished by their storageIDs. When a new
* data storage is reported the namenode issues a new unique storageID.
* <p>
* Finally, the namenode returns its namespaceID as the registrationID
* for the datanodes.
* namespaceID is a persistent attribute of the name space.
* The registrationID is checked every time the datanode is communicating
* with the namenode.
* Datanodes with inappropriate registrationID are rejected.
* If the namenode stops, and then restarts it can restore its
* namespaceID and will continue serving the datanodes that has previously
* registered with the namenode without restarting the whole cluster.
*
* @see org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.datanode.DataNode#register()
*/
public synchronized void registerDatanode(DatanodeRegistration nodeReg
) throws IOException {
String dnAddress = Server.getRemoteAddress();
if (dnAddress == null) {
// Mostly called inside an RPC.
// But if not, use address passed by the data-node.
dnAddress = nodeReg.getHost();
} // check if the datanode is allowed to be connect to the namenode
if (!verifyNodeRegistration(nodeReg, dnAddress)) {
throw new DisallowedDatanodeException(nodeReg);
} String hostName = nodeReg.getHost(); // update the datanode's name with ip:port
DatanodeID dnReg = new DatanodeID(dnAddress + ":" + nodeReg.getPort(),
nodeReg.getStorageID(),
nodeReg.getInfoPort(),
nodeReg.getIpcPort());
nodeReg.updateRegInfo(dnReg);
nodeReg.exportedKeys = getBlockKeys(); NameNode.stateChangeLog.info(
"BLOCK* registerDatanode: "
+ "node registration from " + nodeReg.getName()
+ " storage " + nodeReg.getStorageID()); //在datanodeMap与host2DataNodeMap查找该DataNode
//但如果该DataNode是第一次注册的话(而不是重启后的注册),nodeS与nodeN都为null
DatanodeDescriptor nodeS = datanodeMap.get(nodeReg.getStorageID());
DatanodeDescriptor nodeN = host2DataNodeMap.getDatanodeByName(nodeReg.getName()); if (nodeN != null && nodeN != nodeS) {
NameNode.LOG.info("BLOCK* registerDatanode: "
+ "node from name: " + nodeN.getName());
// nodeN previously served a different data storage,
// which is not served by anybody anymore.
removeDatanode(nodeN);
// physically remove node from datanodeMap
wipeDatanode(nodeN);
nodeN = null;
} if (nodeS != null) {
if (nodeN == nodeS) {
// The same datanode has been just restarted to serve the same data
// storage. We do not need to remove old data blocks, the delta will
// be calculated on the next block report from the datanode
NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug("BLOCK* registerDatanode: "
+ "node restarted");
} else {
// nodeS is found
/* The registering datanode is a replacement node for the existing
data storage, which from now on will be served by a new node.
If this message repeats, both nodes might have same storageID
by (insanely rare) random chance. User needs to restart one of the
nodes with its data cleared (or user can just remove the StorageID
value in "VERSION" file under the data directory of the datanode,
but this is might not work if VERSION file format has changed
*/
NameNode.stateChangeLog.info( "BLOCK* registerDatanode: "
+ "node " + nodeS.getName()
+ " is replaced by " + nodeReg.getName() +
" with the same storageID " +
nodeReg.getStorageID());
}
// update cluster map
clusterMap.remove(nodeS);
nodeS.updateRegInfo(nodeReg);
nodeS.setHostName(hostName); // resolve network location
resolveNetworkLocation(nodeS);
clusterMap.add(nodeS); // also treat the registration message as a heartbeat
synchronized(heartbeats) {
if( !heartbeats.contains(nodeS)) {
heartbeats.add(nodeS);
//update its timestamp
nodeS.updateHeartbeat(0L, 0L, 0L, 0);
nodeS.isAlive = true;
}
}
return;
} // this is a new datanode serving a new data storage
//正常启动的DataNode,其StorageID都不会为“”
if (nodeReg.getStorageID().equals("")) {
// this data storage has never been registered
// it is either empty or was created by pre-storageID version of DFS
nodeReg.storageID = newStorageID();
NameNode.stateChangeLog.debug(
"BLOCK* registerDatanode: "
+ "new storageID " + nodeReg.getStorageID() + " assigned");
}
// register new datanode
//NetworkTopology.DEFAULT_RACK实际上为/default-rack
//系统会将该DataNode的网络位置设置为默认的网络位置:/default-rack
//然后在后续的操作中,如果发现用户配置了映射脚本,则对该网络位置进行修正
DatanodeDescriptor nodeDescr
= new DatanodeDescriptor(nodeReg, NetworkTopology.DEFAULT_RACK, hostName);
//解析该node的网络位置
resolveNetworkLocation(nodeDescr);
unprotectedAddDatanode(nodeDescr);
//clusterMap就是NetworkTopology,将解析出来的node添加到网络拓扑中
clusterMap.add(nodeDescr); // also treat the registration message as a heartbeat
synchronized(heartbeats) {
heartbeats.add(nodeDescr);
nodeDescr.isAlive = true;
// no need to update its timestamp
// because its is done when the descriptor is created
} if (safeMode != null) {
safeMode.checkMode();
}
return;
}
其中,网络位置的解析在resolveNetworkLocation()方法中:
/* Resolve a node's network location */
//这个方法就开始解析某个DataNode的网络位置了
private void resolveNetworkLocation (DatanodeDescriptor node) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<String>(1);
if (dnsToSwitchMapping instanceof CachedDNSToSwitchMapping) {
//通过getClass()方法知道,dnsToSwitchMapping是ScriptBasedMapping的实例
// get the node's IP address
names.add(node.getHost());
} else {
// get the node's host name
String hostName = node.getHostName();
int colon = hostName.indexOf(":");
hostName = (colon==-1)?hostName:hostName.substring(0,colon);
names.add(hostName);
} // resolve its network location
//因为ScriptBasedMapping继承了CachedDNSToSwitchMapping
//所以此处会调用CachedDNSToSwitchMapping的resolve()方法
//返回的是已经被解析出来的网络位置
List<String> rName = dnsToSwitchMapping.resolve(names);
String networkLocation;
if (rName == null) {
LOG.error("The resolve call returned null! Using " +
NetworkTopology.DEFAULT_RACK + " for host " + names);
networkLocation = NetworkTopology.DEFAULT_RACK;
} else {
networkLocation = rName.get(0);
}
//修正该node的网络位置
node.setNetworkLocation(networkLocation);
}
resolveNetworkLocation()方法又会调用CachedDNSToSwitchMapping的resolve()方法来解析网络位置:
public List<String> resolve(List<String> names) {
// normalize all input names to be in the form of IP addresses
names = NetUtils.normalizeHostNames(names);
List <String> result = new ArrayList<String>(names.size());
if (names.isEmpty()) {
return result;
}
//确认该IP地址是否已经被缓存
List<String> uncachedHosts = this.getUncachedHosts(names);
// Resolve the uncached hosts
//通过getClass()知道,rawMapping是RawScriptBasedMapping的实例
//如果用户指定了映射脚本,则根据脚本进行转换
//否则返回默认的网络位置:/default-rack
List<String> resolvedHosts = rawMapping.resolve(uncachedHosts);
//将未缓存的IP地址与其对应的网络位置进行缓存
this.cacheResolvedHosts(uncachedHosts, resolvedHosts);
//返回该IP地址对应的网络位置
return this.getCachedHosts(names);
}
而在CachedDNSToSwitchMapping的resolve()方法中,又会调用RawScriptBasedMapping的resolve()方法来完成网络位置解析。该方法主要是两方面功能:如果用户没有指定映射脚本,那么返回默认的网络位置:/default-rack;否则根据指定脚本中国的映射规则来进行转换。
//SCRIPT_FILENAME_KEY的值为"topology.script.file.name"
this.scriptName = conf.get(SCRIPT_FILENAME_KEY); public List<String> resolve(List<String> names) {
List <String> m = new ArrayList<String>(names.size()); if (names.isEmpty()) {
return m;
} //若没有指定脚本
if (scriptName == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < names.size(); i++) {
m.add(NetworkTopology.DEFAULT_RACK);
}
return m;
} //若指定了脚本,则运行脚本进行解析
String output = runResolveCommand(names);
if (output != null) {
StringTokenizer allSwitchInfo = new StringTokenizer(output);
while (allSwitchInfo.hasMoreTokens()) {
String switchInfo = allSwitchInfo.nextToken();
m.add(switchInfo);
} if (m.size() != names.size()) {
// invalid number of entries returned by the script
LOG.warn("Script " + scriptName + " returned "
+ Integer.toString(m.size()) + " values when "
+ Integer.toString(names.size()) + " were expected.");
return null;
}
} else {
// an error occurred. return null to signify this.
// (exn was already logged in runResolveCommand)
return null;
} return m;
}
至此,网络位置的解析工作结束。但有几点需要注意:
1、网络位置是该结点的父目录的位置,也就是说,如果集群中有一个结点node1,其在集群中所处的位置为:/d1/r1/node1,则其网络位置则为:/d1/r1,并不包含自身。
2、如果集群中没有配置映射脚本,那么默认所有的叶子结点都在同一个rack下,这个rack就是“/default-rack”,即所有叶子结点都在“/default-rack”下。
3、关于结点的Level。在Node接口中,定义了getLevel()方法,用来获取该node在网络拓扑树中的层级。其中,树的根的level为0,其孩子(也就是rack)为1,而叶子结点(就是host)为2。
但无论集群是否配置了映射脚本,所有rack的level都是1,所有叶子结点的level都是2。也就是说,在/default-rack/node结构与/d1/r1/node结构中,rack的level都是1,node的level都是2。
在本次学习源代码的过程中,更重要的是掌握了一种能够辅助阅读hadoop源代码的方法,那就是看测试类。根据测试类中的运行原理,来推测实际的运行情况,然后加以验证。事实上,这种方法有很大帮助。
本文基于hadoop1.2.1。如有错误,还请指正
参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/shirdrn/article/details/4610578
http://caibinbupt.iteye.com/blog/298079
http://blog.csdn.net/azhao_dn/article/details/7091258
http://blog.csdn.net/xhh198781/article/details/7162270
http://blog.csdn.net/xhh198781/article/details/7106215
http://www.cnblogs.com/ggjucheng/archive/2013/01/03/2843015.html
https://issues.apache.org/jira/secure/attachment/12345251/Rack_aware_HDFS_proposal.pdf
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/gwgyk/p/4525463.html
附件下载地址: UML图
hadoop机架感知与网络拓扑分析:NetworkTopology和DNSToSwitchMapping的更多相关文章
- 【转载】Hadoop机架感知
转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/ggjucheng/archive/2013/01/03/2843015.html 背景 分布式的集群通常包含非常多的机器,由于受到机架槽位和交换机 ...
- hadoop机架感知
背景 分布式的集群通常包含非常多的机器,由于受到机架槽位和交换机网口的限制,通常大型的分布式集群都会跨好几个机架,由多个机架上的机器共同组成一个分布式集群.机架内的机器之间的网络速度通常都会高于跨机架 ...
- 第十三章 hadoop机架感知
背景 分布式的集群通常包含非常多的机器,由于受到机架槽位和交换机网口的限制,通常大型的分布式集群都会跨好几个机架,由多个机架上的机器共同组成一个分布式集群.机架内的机器之间的网络速度通常都会高于跨机架 ...
- hadoop之 hadoop 机架感知
1.背景 Hadoop在设计时考虑到数据的安全与高效,数据文件默认在HDFS上存放三份,存储策略为本地一份,同机架内其它某一节点上一份,不同机架的某一节点上一份.这样如果本地数据损坏,节点可以从同一机 ...
- 【Hadoop】Hadoop 机架感知配置、原理
Hadoop机架感知 1.背景 Hadoop在设计时考虑到数据的安全与高效,数据文件默认在HDFS上存放三份,存储策略为本地一份, 同机架内其它某一节点上一份,不同机架的某一节点上一份. 这样如果本地 ...
- 【原创】Hadoop机架感知对性能调优的理解
Hadoop作为大数据处理的典型平台,在海量数据处理过程中,其主要限制因素是节点之间的数据传输速率.因为集群的带宽有限,而有限的带宽资源却承担着大量的刚性带宽需求,例如Shuffle阶段的数据传输不可 ...
- Hadoop hadoop 机架感知配置
机架感知脚本 使用python3编写机架感知脚本,报存到topology.py,给予执行权限 import sys import os DEFAULT_RACK="/default-rack ...
- hadoop配置机架感知
接着上一篇来说.上篇说了hadoop网络拓扑的构成及其相应的网络位置转换方式,本篇主要讲通过两种方式来配置机架感知.一种是通过配置一个脚本来进行映射:另一种是通过实现DNSToSwitchMappin ...
- hadoop(三):hdfs 机架感知
client 向 Active NN 发送写请求时,NN为这些数据分配DN地址,HDFS文件块副本的放置对于系统整体的可靠性和性能有关键性影响.一个简单但非优化的副本放置策略是,把副本分别放在不同机架 ...
随机推荐
- 利用Javascript判断操作系统的类型实现不同操作系统下的兼容性
原文地址 http://www.jb51.net/article/33640.htm 在通过Javascript实现客户端和服务端的交互时,有时候需要对操作系统进行判断,以便实现不同操作系统下的兼容性 ...
- ES6 笔记
1.箭头函数 箭头函数里的this会引用 定义 箭头函数时,外部作用域 的 this .箭头函数只是 引用 外部作用域的 this ,本身不存在 this.同时因为没有 this ,所以 无法用new ...
- 什么是原生的javascript
在www.cocos.com的cocos2d-js的介绍中写道“Cocos2d-JS 是跨全平台的游戏引擎,采用原生JavaScript语言,可发布到包括Web平台,iOS,Android,Windo ...
- JFinal 的初始化
浅析初始化过程 首先要从 web 容器进行初始化 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-ap ...
- android:layout_weight的真实含义(转)
首先声明只有在Linearlayout中,该属性才有效.之所以Android:layout_weight会引起争议,是因为在设置该属性的同时,设置android:layout_width为wrap_c ...
- Makefile中头文件在依赖关系中作用
摘于:http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/120024677 (1)在makefile的依赖关系中用不用体现.h头文件?(2)如果在依赖关系中要体现.h头文件,应该体现到什么层次?= ...
- angularjs的$on、$emit、$broadcast
如何在作用域之间通信呢? 1.创建一个单例服务,然后通过这个服务处理所有子作用域的通信. 2.通过作用域中的事件处理通信.但是这种方法有一些限制:例如,你并不能广泛的将事件传播到所有监控的作用域中.你 ...
- Asp.Net_Mvc_@Html.xxx()的扩展
/// <summary> /// 生成分类下拉-列表框,选中指定的项 /// </summary> /// <param name="html"&g ...
- JDBC与Hibernate中SQL语句参数设置的顺序问题
JDBC中:设置从1开始 例: Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/...", ...
- VB关闭其他进程的输入法
http://files.cnblogs.com/files/liuzhaoyzz/%E5%85%B3%E9%97%AD%E5%85%B6%E4%BB%96%E8%BF%9B%E7%A8%8B%E8% ...
