ML_note1
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, we are given a data set and already know what our correct output should look like, having the idea that there is a relationship between the input and the output.
Supervised learning problems are categorized into "regression" and "classification" problems. In a regression problem, we are trying to predict results within a continuous output, meaning that we are trying to map input variables to some continuous function. In a classification problem, we are instead trying to predict results in a discrete output. In other words, we are trying to map input variables into discrete categories.
Example 1:
Given data about the size of houses on the real estate market, try to predict their price. Price as a function of size is a continuous output, so this is a regression problem.
We could turn this example into a classification problem by instead making our output about whether the house "sells for more or less than the asking price." Here we are classifying the houses based on price into two discrete categories.
Example 2:
(a) Regression - Given a picture of a person, we have to predict their age on the basis of the given picture
(b) Classification - Given a patient with a tumor, we have to predict whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning allows us to approach problems with little or no idea what our results should look like. We can derive structure from data where we don't necessarily know the effect of the variables.
We can derive this structure by clustering the data based on relationships among the variables in the data.
With unsupervised learning there is no feedback based on the prediction results.
Example:
Clustering: Take a collection of 1,000,000 different genes, and find a way to automatically group these genes into groups that are somehow similar or related by different variables, such as lifespan, location, roles, and so on.
Non-clustering: The "Cocktail Party Algorithm", allows you to find structure in a chaotic environment. (i.e. identifying individual voices and music from a mesh of sounds at a cocktail party).
Cost Function
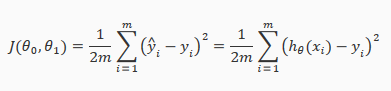
This function is otherwise called the "Squared error function", or "Mean squared error".
ML_note1的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- 帝国cms文章内容tags关键词设置调用方法以及tags静态化
说实话帝国cms用起来真的不好找一些功能,就比如说帝国cms的tag标签调用.需要注意的是帝国CMS文章的关键词和tags标签并非一码事,关键词标签是设置文章的关键词的,是用来给搜索引擎说明本篇文章的 ...
- 修改maven本地仓库路径
修改maven配置文件conf/settings.xml 在setting标签中添加 <localRepository>E:/bhuwifi_java/repo</localRepo ...
- Ubuntu将新增磁盘挂载到home下
home磁盘空间不足,其他闲置硬盘是原来windows的,不能直接使用(磁盘格式及权限等原因),比如编译安卓源码等. 这样的话就需要将新的磁盘格式化成fat32后挂载到/home下的一个目录,这样就可 ...
- 转 android学习—— context 和 getApplicationContext()
在android中常常会遇到与context有关的内容 浅论一下context : 在语句 AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder( ...
- SD卡读写扇区注意事项(转)
源:http://blog.163.com/zhaojun_xf/blog/static/30050580201151410635516/ 在调试SD卡时,大家都喜欢使用扇区进行验证.也就是说,一般都 ...
- 一个有意思的 hta 程序 (html application)
哈哈,刚才同事给我讲了一个hta 程序,他自己说最近在学html5 开发坦克大战,不错,这种好奇心, 好学的精神值得我这个程序员学习,感觉他的视野面比我这个程序员还广,有点小惭愧. 什么是hta 呢? ...
- ptrace
http://zhangwenxin82.blog.163.com/blog/static/114595956201171510512459/
- windows server2012 图形加速,玩游戏不掉帧
研究了很久,其实就是将 电源管理设置成 高级 ....
- 前端开发chrome与fireFox浏览器都使用
chrome查看元素的样式时,显示的很方便和准确,方便开发快速辨别结构. 而fireFox在css3上,我发现好像比chrome支持得更全面.
- java中基本数据类型和C语言中基本数据类型转换
java中 1 short = 2 byte 1 char = 2 byte 1 int = 4 byte 1 long = 8 byte C语言中 typedef unsigned char ...
