Linux驱动技术(一) _内存申请
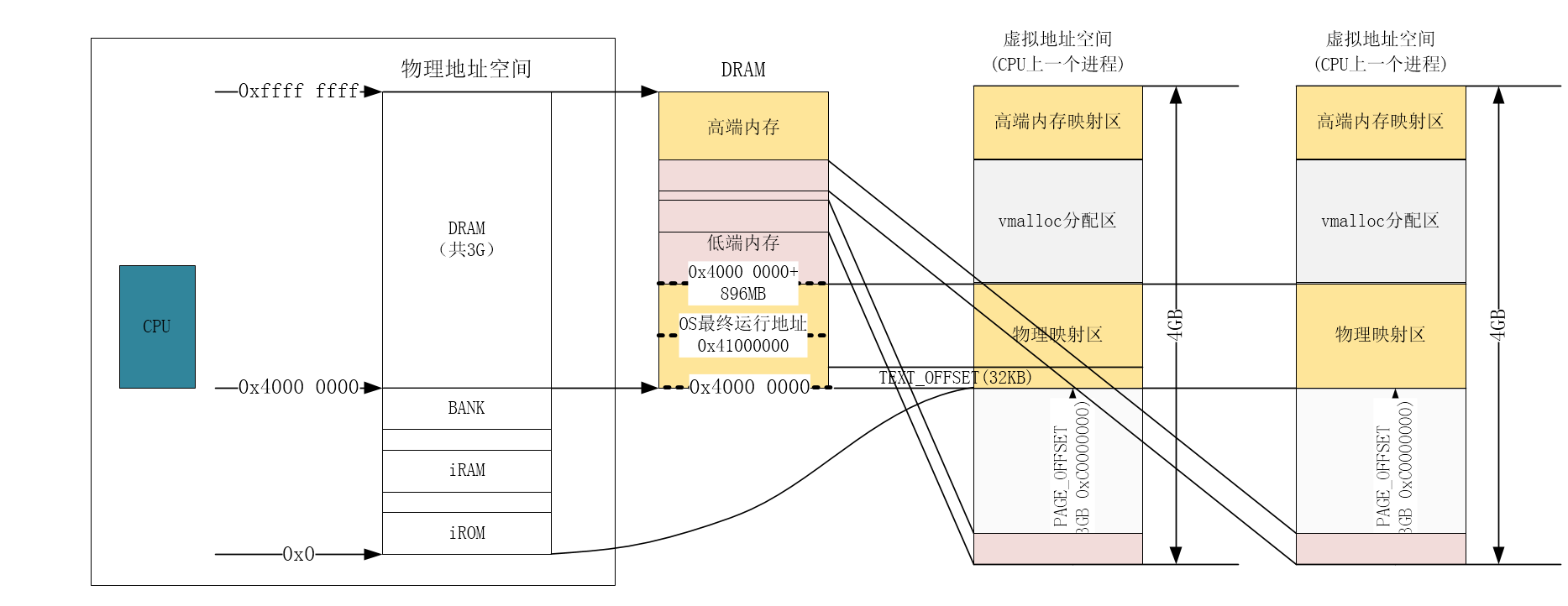
先上基础,下图是Linux的内存映射模型
- 每一个进程都有自己的进程空间,进程空间的0-3G是用户空间,3G-4G是内核空间
- 每个进程的用户空间不在同一个物理内存页,但是所有的进程的内核空间对应同样的物理地址
- vmalloc分配的地址可以高端内存,也可以是低端内存
- 0-896MB的物理地址是线性映射到物理映射区的。
- 内核参数和系统页表都在TEXT_OFFSET保存,除了进程除了访问自身的用户空间对应的DRAM内存页外,都要经过内核空间,也就是都要切换到内核态
内存动态申请
和应用层一样,内核程序也需要动态的分配内存,不同的是,内核进程可以控制分配的内存是在用户空间还是内核空间,前者可以用于给用户空间的堆区分配内存,eg,用户进程的用户空间的malloc最终就会通过系统调用回调内核空间的内存分配函数,此时该内存分配函数就属于该用户进程,可以给在该用户进程的堆区分配空间并返回,最终使得一个用会进程在自己的用户空间获得内存分配;后者只在内核空间分配,所以用户进程不能直接访问该空间,所以多用在满足内核程序自身的内存需求,下面是Linux内核空间申请内存常用API:
kmalloc - kfree
kmalloc申请的内存在物理内存上是连续的,他们与真实的物理地址只有一个固定的偏移,因此存在简单的转换关系。这个API 多用来申请不到一个page大小的内存。kmalloc的底层需要调用__get_free_pages,参数中表示内存类型的gtp_t flags正是这个函数的缩写,常用的内存类型有GFP_USER,GFP_KERNEL,GFP_ATOMIC几种。
GFP_USER表示为用户空间页分配内存,可以阻塞;
GFP_KERNEL是最常用的flag,注意,使用这个flag来申请内存时,如果暂时不能满足,会引起进程阻塞,So,一定不要在中断处理函数,tasklet和内核定时器等非进程上下文中使用GFP_KERNEL!!!
GFP_ATOMIC就可以用于上述三种情境,这个flag表示如果申请的内存不能用,则立即返回。
/**
* kmalloc - allocate memory
* @size: how many bytes of memory are required.
* @flags: the type of memory to allocate.
* The @flags argument may be one of:
* %GFP_USER - Allocate memory on behalf of user. May sleep.
* %GFP_KERNEL - Allocate normal kernel ram. May sleep.
* %GFP_ATOMIC - Allocation will not sleep. May use emergency pools.
*
* For example, use this inside interrupt handlers.
*/
void *kmalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags);
/**
* kfree - free previously allocated memory
* @objp: pointer returned by kmalloc.
* If @objp is NULL, no operation is performed.
*/
void kfree(const void *objp);
同系列API还有
void *kzalloc(size_t size, gfp_t flags)
__get_free_pages - free_pages
__get_free_pages()与kmalloc()一样是物理连续的内存,这一系列函数是Linux内核中最底层的用于获取空闲内存的方法,因为底层的buddy算法都是以(2^n)×PAGE_SIZE来管理内存的,所以他们总是以页为单位分配内存的
unsigned long __get_free_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
void free_pages(unsigned long addr, unsigned int order)
同系列API还有
unsigned long __get_free_page(gfp_t gfp)
unsigned long get_zeroed_page(gfp_t gfp_mask)
struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
void free_page(unsigned long addr)
vmalloc - vfree
vmalloc在虚拟内存空间给出一块连续的内存区,实质上,这片连续的虚拟内存在物理内存中并不一定连续,所以vmalloc申请的虚拟内存和物理内存之间也就没有简单的换算关系,正因如此,vmalloc()通常用于分配远大于__get_free_pages()的内存空间,它的实现需要建立新的页表,此外还会调用使用GFP_KERN的kmalloc,so,一定不要在中断处理函数,tasklet和内核定时器等非进程上下文中使用vmalloc!
/**
* vmalloc - allocate virtually contiguous memory
* @size: allocation size
* Allocate enough pages to cover @size from the page level allocator and map them into contiguous kernel virtual space.
*/
void *vmalloc(unsigned long size)
/**
* vfree - release memory allocated by vmalloc()
* @addr: memory base address
*/
void vfree(const void *addr)
同系列的API还有
/**
* vmalloc_32 - allocate virtually contiguous memory (32bit addressable)
* @size: allocation size
* Allocate enough 32bit PA addressable pages to cover @size from the page level allocator and map them into contiguous kernel virtual space.
*/
void *vmalloc_32(unsigned long size)
slab缓存
我们知道,页是内存映射的基本单位,但内核中很多频繁创建的对象所需内存都不到一页,此时如果仍然按照页映射的方式,频繁的进行分配和释放就会造成资源的浪费,同时也会降低系统性能。为了解决的这样的问题,内核引入了slab机制,使对象在前后两次被使用时被分配在同一块内存或同一类内存空间,且保留了基本的数据结构,就可以大大提高效率。kmalloc的底层即是使用slab算法管理分配的内存的。注意,slab依然是以页为单位进行映射,只是映射之后分割这些页为相同的更小的单元,从而节省了内存。slab分配的单元不能小于32B或大于128K。
/**
* kmem_cache_create - 创建slab缓存对象
* @name:slab缓存区名字,
* @size:slab分配的缓存区的每一个单元的大小
* @align:缓存区内存的对齐方式,一般给0
* @flags:控制分配的位掩码,
* %SLAB_POISON - Poison the slab with a known test pattern (a5a5a5a5) to catch references to uninitialised memory.
* %SLAB_RED_ZONE - Insert `Red' zones around the allocated memory to check for buffer overruns.
* %SLAB_HWCACHE_ALIGN - Align the objects in this cache to a hardware cacheline. This can be beneficial if you're counting cycles as closely as davem.
* %SLAB_CACHE_DMA - Use GFP_DMA memory
* %SLAB_STORE_USER - Store the last owner for bug hunting
*define SLAB_PANIC - Panic if kmem_cache_create() fails
*/
struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache_create(const char *name, size_t size, size_t align,unsigned long flags, void (*ctor)(void *))
/**
* kmem_cache_alloc - Allocate an object from this cache.
* @cachep: The cache to allocate from.
* @flags: See kmalloc().
* The flags are only relevant if the cache has no available objects.
*/
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags)
/**
* kmem_cache_free - Deallocate an object
* @cachep: The cache the allocation was from.
* @objp: The previously allocated object.
* Free an object which was previously allocated from this cache.
*/
void kmem_cache_free(struct kmem_cache *cachep, void *objp)
void kmem_cache_destroy(struct kmem_cache *s)
范例
//创建slab对象
struct kmem_cache_t *xj_sbcache;
xj_sbcache = kmem_cache_create("xjslab",sizeof(struct xj_unit_t),0,SLAB_CACHE_DMA|SLAB_PANIC,NULL,NULL);
//分配slab缓存
struct xj_unit_t *xj_unit;
xj_unit = kmem_cache_alloc(xj_sbcache,GFP_KERNEL);
/* 使用slab缓存 */
/* 释放slab缓存 */
kmem_cache_free(xj_sbcache, xj_unit);
/* 销毁slab缓存 */
kmem_cache_destroy(xj_sbcache);
内存池
除了slab机制,内核还提供了传统的内存池机制来管理小块内存的分配。内存池主要是用来解决可能出现的内存不足的情况,因为一个内存池在创建的时候就已经分配好了一内存,当我们用mempool_alloc向一个已经创建好的内存池申请申请内存时,该函数首先会尝试回调内存池创建时的分配内存函数,如果已经没有内存可以分配,他就会使用内存池创建时预先分配的内存,这样就可以避免因为无内存分配而陷入休眠,当然,如果预分配的内存也已经使用完毕,还是会陷入休眠。slab机制的目的是提高内存使用率以及内存管理效率,内存池的目的是避免内存的分配失败。下面是内核中提供的关于内存池的API
/**
* mempool_create - create a memory pool
* @min_nr: the minimum number of elements guaranteed to be allocated for this pool.
* @alloc_fn: user-defined element-allocation function.
* @free_fn: user-defined element-freeing function.
* @pool_data: optional private data available to the user-defined functions.
*
* this function creates and allocates a guaranteed size, preallocated memory pool. The pool can be used from the mempool_alloc() and mempool_free() functions.
* This function might sleep. Both the alloc_fn() and the free_fn() functions might sleep - as long as the mempool_alloc() function is not called from IRQ contexts.
*/
mempool_t *mempool_create(int min_nr, mempool_alloc_t *alloc_fn, mempool_free_t *free_fn, void *pool_data)
/**
* mempool_alloc - allocate an element from a specific memory pool
* @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create().
* @gfp_mask: the usual allocation bitmask.
* this function only sleeps if the alloc_fn() function sleeps or returns NULL. Note that due to preallocation, this function never* fails when called from process contexts. (it might fail if called from an IRQ context.)
*/
void * mempool_alloc(mempool_t *pool, gfp_t gfp_mask)
/**
* mempool_free - return an element to the pool.
* @element: pool element pointer.
* @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create().
*
* this function only sleeps if the free_fn() function sleeps.
*/
void mempool_free(void *element, mempool_t *pool)
/**
* mempool_destroy - deallocate a memory pool
* @pool: pointer to the memory pool which was allocated via mempool_create().
*
* Free all reserved elements in @pool and @pool itself. This function only sleeps if the free_fn() function sleeps.
*/
void mempool_destroy(mempool_t *pool)
Linux驱动技术(一) _内存申请的更多相关文章
- Linux驱动技术(二) _访问I/O内存
ARM是对内存空间和IO空间统一编址的,所以,通过读写SFR来控制硬件也就变成了通过读写相应的SFR地址来控制硬件.这部分地址也被称为I/O内存.x86中对I/O地址和内存地址是分开编址的,这样的IO ...
- Linux驱动技术(八) _并发控制技术
为了实现对临界资源的有效管理,应用层的程序有原子变量,条件变量,信号量来控制并发,同样的问题也存在与驱动开发中,比如一个驱动同时被多个应用层程序调用,此时驱动中的全局变量会同时属于多个应用层进程的进程 ...
- Linux驱动技术(五) _设备阻塞/非阻塞读写
等待队列是内核中实现进程调度的一个十分重要的数据结构,其任务是维护一个链表,链表中每一个节点都是一个PCB(进程控制块),内核会将PCB挂在等待队列中的所有进程都调度为睡眠状态,直到某个唤醒的条件发生 ...
- Linux驱动技术(七) _内核定时器与延迟工作
内核定时器 软件上的定时器最终要依靠硬件时钟来实现,简单的说,内核会在时钟中断发生后检测各个注册到内核的定时器是否到期,如果到期,就回调相应的注册函数,将其作为中断底半部来执行.实际上,时钟中断处理程 ...
- Linux驱动技术(五) _设备阻塞/非阻塞读写【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiang1025/p/6377925.html 等待队列是内核中实现进程调度的一个十分重要的数据结构,其任务是维护一个链表,链表中每一个节 ...
- Linux驱动技术(四) _异步通知技术
异步通知的全称是"信号驱动的异步IO",通过"信号"的方式,放期望获取的资源可用时,驱动会主动通知指定的应用程序,和应用层的"信号"相对应, ...
- Linux驱动技术(六) _内核中断
在硬件上,中断源可以通过中断控制器向CPU提交中断,进而引发中断处理程序的执行,不过这种硬件中断体系每一种CPU都不一样,而Linux作为操作系统,需要同时支持这些中断体系,如此一来,Linux中就提 ...
- Linux驱动技术(四) _异步通知技术【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiang1025/p/6376561.html 异步通知的全称是"信号驱动的异步IO",通过"信号&quo ...
- Linux驱动技术(三) _DMA编程【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaojiang1025/archive/2017/02/11/6389194.html DMA即Direct Memory Access,是一 ...
随机推荐
- (简单) POJ 1511 Invitation Cards,SPFA。
Description In the age of television, not many people attend theater performances. Antique Comedians ...
- [iOS Animation]-CALayer 定时器动画
定时器的动画 我可以指导你,但是你必须按照我说的做. -- 骇客帝国 在第10章“缓冲”中,我们研究了CAMediaTimingFunction,它是一个通过控制动画缓冲来模拟物理效果例如加速或者减速 ...
- 原来在ARC下还有这么多不同?!
1.ARC空声明变量 使用ARC的另一个优势是所有未初始化的变量默认都是"空值化"的.这意味着像下面这样的声明使用ARC编译后指向的是空值(nil): NSObject myObj ...
- iOS 为label添加删除线
UILabel *testLabel = [[ UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(, , , )]; testLabel.numberOfLines = ...
- Android高斯模糊技术,实现毛玻璃效果(转)
本博客转自郭霖公众号:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA5MzI3NjE2MA==&mid=2650235930&idx=1&sn=e328 ...
- lPC1788的GPIO驱动
#include "led.h" void led_init(void) { //p1.14 p0.16 p1.13 p4.27 LPC_SC->PCONP |= (1< ...
- Javascript 页面刷新
Javascript 页面刷新的实现代码收藏 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 history.go(0) location.reload() location=location location.as ...
- java实现FFT变换(转)
源:java实现FFT变换 /************************************************************************* * Compilati ...
- ui主线程控件的更新就让这个activity的异步任务做完整
项目中使用的SingleMessageView,控件实例化后,点击用户头像,此时跳转到UserInfo里查看这个用户的头像.用户名.签名.标签. 之前,师兄在SingleMessage里写了个头像的点 ...
- Oracle用户管理和角色管理
原博:http://liwx.iteye.com/blog/1182251 一.创建用户的Profile文件 SQL> create profile student limit // stude ...