第34-2题:LeetCode113. Path Sum II
题目
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和sum = 22,5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1
返回:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
考点
1.前序遍历
2.stack
3.递归
思路
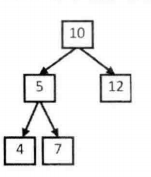
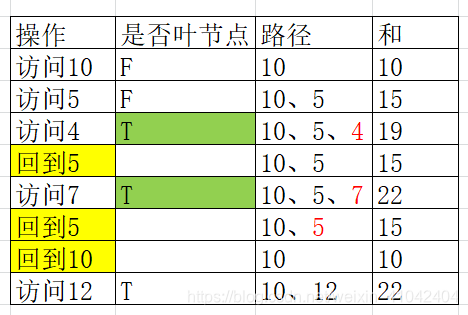
代码
/*
struct TreeNode {
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) :
val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {
}
};*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> FindPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
// 变量
std::vector<int> path;
std::vector<vector<int>> ret;
int cur = 0;
// 入口
if(!root)
return ret;
// 出口
return FindPath(root,sum,path,cur,ret);
}
vector<vector<int>> FindPath(TreeNode* root,int sum,vector<int> &path,int cur,vector<vector<int>> &ret)
{
// 1.更新cur 和 path
cur+=root->val;
path.push_back(root->val);
// 标记叶子节点bool
bool isLeaf = !root->left && !root->right;
// 2.如果是叶子节点且路径之和等于目标值,保存path到ret中,清空path
if(isLeaf && cur == sum )
{
ret.push_back(path);
path.pop_back();
return ret;
}
// 3.如果不是叶子节点,访问其左右子树
if(root->left)
{
ret = FindPath(root->left,sum,path,cur,ret);
}
if(root->right)
{
ret = FindPath(root->right,sum,path,cur,ret);
}
// 4.递归结束之前,还原到父节点操作
cur-=root->val;
path.pop_back();
// 5.出口
return ret;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
static const void* ___ = []() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
return nullptr;
}();
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
list<int> cur;
pathSum(result, cur, root, sum);
return result;
}
private:
void pathSum(vector<vector<int>> &result, list<int> &cur, TreeNode *root, int sum) {
if (!root) return;
if (!root->left && !root->right)
{
if (sum == root->val)
{
result.emplace_back(cur.begin(), cur.end());
result.back().push_back(sum);
}
} else
{
cur.push_back(root->val);
pathSum(result, cur, root->left, sum - root->val);
pathSum(result, cur, root->right, sum - root->val);
cur.pop_back();
}
}
};问题
1.执行用时快的原因
解析 static auto x = []() { std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);std::cin.tie(nullptr);return 0;}()
第34-2题:LeetCode113. Path Sum II的更多相关文章
- LeetCode113 Path Sum II
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals the given su ...
- Leetcode113. Path Sum II路径总和2
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径. 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点. 示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22, 5 / \ 4 8 ...
- LeetCode之“树”:Path Sum && Path Sum II
Path Sum 题目链接 题目要求: Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path suc ...
- 【LeetCode】113. Path Sum II
Path Sum II Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals ...
- 【LeetCode】113. Path Sum II 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]113. Path Sum II 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): LeetCode 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fu ...
- Leetcode 笔记 113 - Path Sum II
题目链接:Path Sum II | LeetCode OJ Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each ...
- Path Sum II
Path Sum II Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals ...
- [leetcode]Path Sum II
Path Sum II Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals ...
- 【leetcode】Path Sum II
Path Sum II Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals ...
随机推荐
- [转]创建一个JavaScript弹出DIV窗口层的效果
本文转自:http://www.soso.io/article/23698.html <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> &l ...
- 在rails 中返回 zip 文件
在平日的开发当中我们一般只返回html,json 等等,但是偶尔情况下也会使用到其他文件的返回,比如 pdf ,csv 文件 今天在开发中使用的是将大量的文字返回给用户. ## 知识点 `Tempfi ...
- Spark Streaming简介
离线计算和实时计算对比 1)数据来源 离线:HDFS历史数据 数据量比较大 实时:消息队列(Kafka),实时新增/修改记录过来的某一笔数据 2)处理过程 离线:MapReduce: map+redu ...
- Cloudera Kudu是什么?
不多说,直接上干货! Cloudera Kudu是什么? kudu是cloudera在2012开始秘密研发的一款介于hdfs和hbase之间的高速分布式列式存储数据库.兼具了hbase的实时性.hdf ...
- 分布式任务框架elastic-job 学习笔记
官方资料:https://github.com/dangdangdotcom/elastic-job ------------------------------------------------- ...
- Java反射机制分析指南
一.JAVA是动态语言吗? 一般而言,说到动态言,都是指在程序运行时允许改变程序结构或者变量类型,从这个观点看,JAVA和C++一样,都不是动态语言. 但JAVA它却有着一个非常突出的动态相关机制:反 ...
- WebGL 踩坑系列-3
WebGL 踩坑系列-3 绘制球体 在 WebGL 中绘制物体时需要的顶点是以直角坐标表示的, 当然了,gl_Position 是一个四维的向量,一般将顶点赋值给 gl_Position 时,最后一维 ...
- c# 小数点格式化
1.只要求保留N位不四舍5入 float f = 0.55555f; int i =(int)(f * 100); f = (float)(i*1.0)/100 ...
- wamp的安装
1.下载wamp. 2.如果安装了apache,先卸载. 进入到你的apache的bin目录,输入指令 httpd.exe -k stop停止服务,再输入httpd.exe -k uninstall. ...
- window下隐藏apache版本和PHP脚本等敏感信息
隐藏Apache信息 1.1 主配置中启用httpd-default.conf 文件: conf/httpd.Conf 找到httpd-default.conf,删除前面的注释“#”,改成如下 Inc ...
