Linkedlist源码详解
介绍
LinkedList同时实现了List接口和Deque接口,也就是说它既可以看作一个顺序容器,又可以看作一个队列(Queue),同时又可以看作一个栈(Stack)。这样看来,LinkedList简直就是个全能冠军。当你需要使用栈或者队列时,可以考虑使用LinkedList,一方面是因为Java官方已经声明不建议使用Stack类,更遗憾的是,Java里根本没有一个叫做Queue的类(它是个接口名字,无法直接创建)。关于栈或队列,现在的首选是ArrayDeque,它有着比LinkedList(当作栈或队列使用时)有着更好的性能。
对于频繁的插入或删除元素的操作,建议使用LinkedList类,效率较高;底层使用双向链表存储
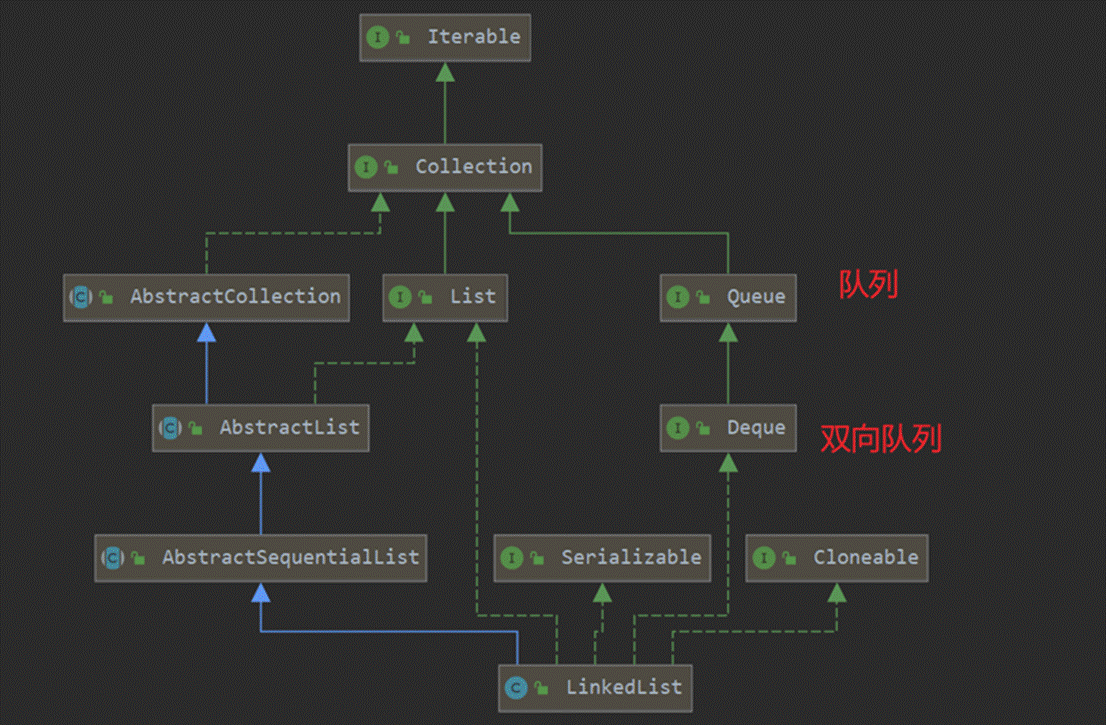
//存储链表的第一个节点
transient Node<E> first;
//存储链表的最后一个节点
transient Node<E> last;
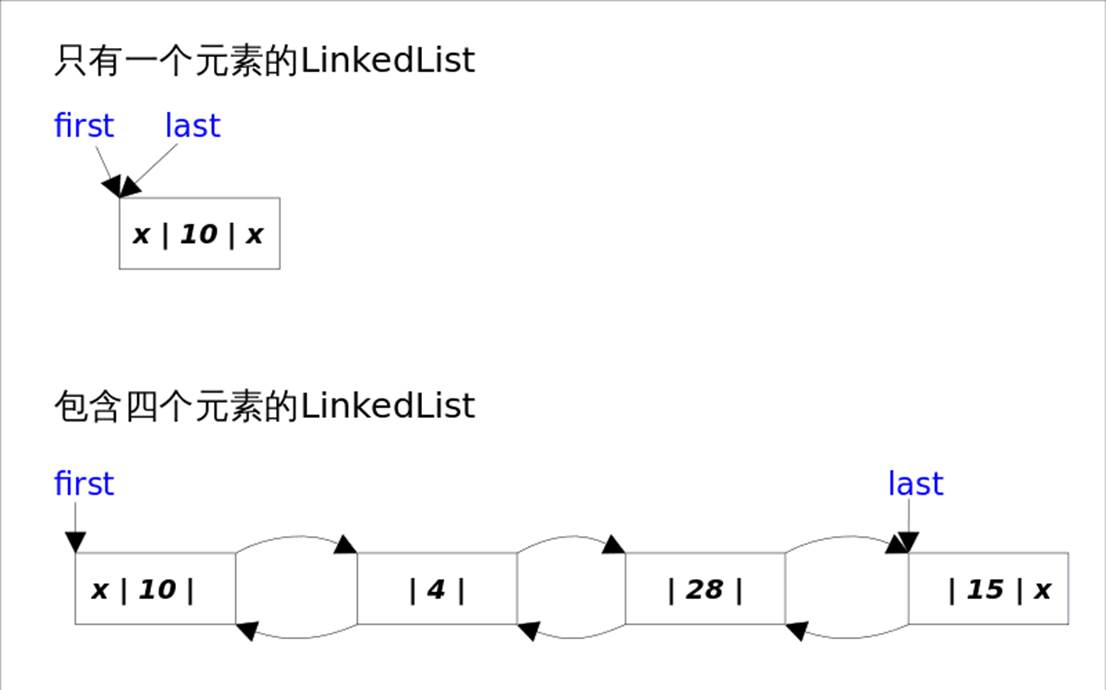
LinkedList的实现方式决定了所有跟下标相关的操作都是线性时间,而在首段或者末尾删除元素只需要常数时间。为追求效率LinkedList没有实现同步(synchronized),如果需要多个线程并发访问,可以先采用Collections.synchronizedList()方法对其进行包装。
底层实现
底层数据结构
LinkedList底层通过双向链表实现。双向链表的每个节点用内部类Node表示。LinkedList通过first和last引用分别指向链表的第一个和最后一个元素。注意这里没有所谓的哑元(也就是没有虚拟变量),当链表为空的时候first和last都指向null。
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node <E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node <E> last;
其中Node是私有的内部类:
private static class Node <E> {
E item;
Node <E> next;
Node <E> prev;
Node(Node <E> prev, E element, Node <E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
构造函数
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection <? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
getFirst(), getLast()
获取第一个元素, 和获取最后一个元素:
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node <E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node <E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
get方法
get方法是根据索引获取元素的
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
//找到具体索引位置的 Node
Node <E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//类似二分法,size >> 1 即元素数量的一半
if (index < (size >> 1)) { //索引小于一半,就从头开始找
Node <E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else { //否则就从尾部开始找
Node <E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
removeFirst(), removeLast(), remove(e), remove(index)
remove()方法也有两个版本
删除跟指定元素相等的第一个元素remove(Object o)
删除指定下标处的元素remove(int index)
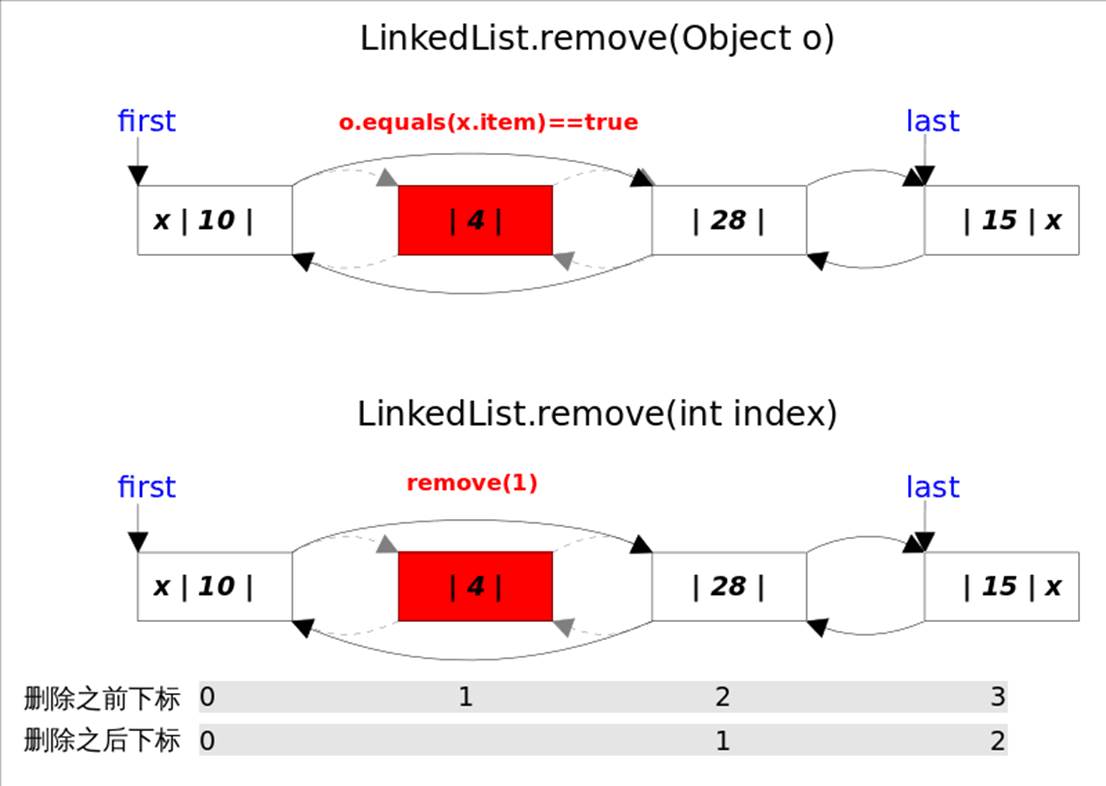
删除元素:指的是删除第一次出现的这个元素, 如果没有这个元素,则返回false;判断的依据是equals方法, 如果equals,则直接unlink这个node;
由于LinkedList可存放null元素,故也可以删除第一次出现null的元素;
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node <E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node <E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node <E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node <E> next = x.next;
final Node <E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) { // 第一个元素
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) { // 最后一个元素
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null; // GC
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
linklist是有序的,可重复存储数据的,并且可以存储null值,但remove方法在找到需要删除的元素时,就return了,因此只能删除找到的第一个元素
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList();
list.add("1");
list.add(null);
list.add(null);
list.add("1");
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(null);
list.remove("1");
System.out.println(list);
//输出:
[1, null, null, 1]
[null, 1]
add方法
add()方法有两个版本:
add(E e),该方法在LinkedList的末尾插入元素,因为有last指向链表末尾,在末尾插入元素的花费是常数时间。只需要简单修改几个相关引用即可;
add(int index, E element),该方法是在指定下表处插入元素,需要先通过线性查找找到具体位置,然后修改相关引用完成插入操作。
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);//默认add方法是在尾部插入元素
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;//旧的尾部元素
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;//尾部元素为 newNode
if (l == null)//说明集合中没有元素
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;//旧的尾部元素 指向 newNode,即添加newNode
size++;
modCount++;
}
//同理。链表头部添加元素
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
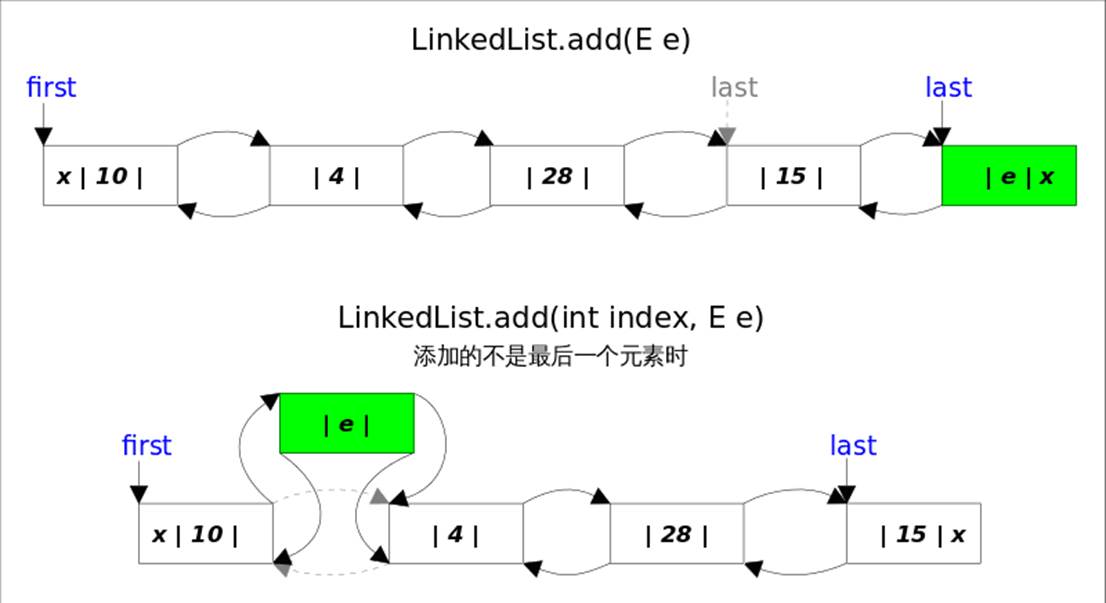
add(int index, E element),当index==size时,等同于add(E e); 如果不是,则分两步:
- 先根据index找到要插入的位置,即node(index)方法;
- 修改引用,完成插入操作。
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
上面代码中的node(int index)函数有一点小小的trick,因为链表双向的,可以从开始往后找,也可以从结尾往前找,具体朝那个方向找取决于条件index < (size >> 1),也即是index是靠近前端还是后端。从这里也可以看出,linkedList通过index查询元素的效率没有arrayList高。
Node <E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node <E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node <E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
addAll()
addAll(index, c) 实现方式并不是直接调用add(index,e)来实现,主要是因为效率的问题,另一个是fail-fast中modCount只会增加1次;
public boolean addAll(Collection <? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection <? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node <E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o: a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node <E> newNode = new Node <> (pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
clear()
这里是将node之间的引用关系都变成null,这样GC可以在年轻代回收元素了
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node <E> x = first; x != null;) {
Node <E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
注意:有些同学可能注意到这里的判定条件是x != null,但是 LinkedList 是可以设置null值的,那是不是当链表中有null的元素,并且爱clear遍历到元素为null时,条件 x != null就为false了,那就不会继续执行,也就是后续的元素都无法置为空了?
实际上不是的,这里的x != null是没有这个元素,而LinkedList 中可以设置null值是指,x.item = null ,也就是有Node,但是Node的item属性为null
Positional Access 方法
通过index获取元素
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
将某个位置的元素重新赋值:
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node <E> x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
将元素插入到指定index位置:
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
删除指定位置的元素:
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
其它位置的方法:
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: " + index + ", Size: " + size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
查找操作
查找操作的本质是查找元素的下标:
查找第一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node <E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node <E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
查找最后一次出现的index, 如果找不到返回-1;
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node <E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node <E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
LinkedList 存在的性能问题
从速度的角度:ArrayDeque 基于数组实现双端队列,而 LinkedList 基于双向链表实现双端队列,数组采用连续的内存地址空间,通过下标索引访问,链表是非连续的内存地址空间,通过指针访问,所以在寻址方面数组的效率高于链表。
从内存的角度:虽然 LinkedList 没有扩容的问题,但是插入元素的时候,需要创建一个 Node 对象, 换句话说每次都要执行 new 操作,当执行 new 操作的时候,其过程是非常慢的,会经历两个过程:类加载过程 、对象创建过程。
类加载过程
会先判断这个类是否已经初始化,如果没有初始化,会执行类的加载过程
类的加载过程:加载、验证、准备、解析、初始化等等阶段,之后会执行 <cinit> 方法,初始化静态变量,执行静态代码块等等
对象创建过程
如果类已经初始化了,直接执行对象的创建过程
对象的创建过程:在堆内存中开辟一块空间,给开辟空间分配一个地址,之后执行初始化,会执行 <init>方法,初始化普通变量,调用普通代码块
关于作者
来自一线程序员Seven的探索与实践,持续学习迭代中~
本文已收录于我的个人博客:https://www.seven97.top
公众号:seven97,欢迎关注~
Linkedlist源码详解的更多相关文章
- Java集合——LinkedList源码详解
)LinkedList直接继承于AbstractSequentialList,同时实现了List接口,也实现了Deque接口. AbstractSequentialList为顺序访问的数据存储结构提供 ...
- RocketMQ源码详解 | Producer篇 · 其二:消息组成、发送链路
概述 在上一节 RocketMQ源码详解 | Producer篇 · 其一:Start,然后 Send 一条消息 中,我们了解了 Producer 在发送消息的流程.这次我们再来具体下看消息的构成与其 ...
- Spark Streaming揭秘 Day25 StreamingContext和JobScheduler启动源码详解
Spark Streaming揭秘 Day25 StreamingContext和JobScheduler启动源码详解 今天主要理一下StreamingContext的启动过程,其中最为重要的就是Jo ...
- spring事务详解(三)源码详解
系列目录 spring事务详解(一)初探事务 spring事务详解(二)简单样例 spring事务详解(三)源码详解 spring事务详解(四)测试验证 spring事务详解(五)总结提高 一.引子 ...
- 条件随机场之CRF++源码详解-预测
这篇文章主要讲解CRF++实现预测的过程,预测的算法以及代码实现相对来说比较简单,所以这篇文章理解起来也会比上一篇条件随机场训练的内容要容易. 预测 上一篇条件随机场训练的源码详解中,有一个地方并没有 ...
- [转]Linux内核源码详解--iostat
Linux内核源码详解——命令篇之iostat 转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/york-hust/p/4846497.html 本文主要分析了Linux的iostat命令的源码, ...
- saltstack源码详解一
目录 初识源码流程 入口 1.grains.items 2.pillar.items 2/3: 是否可以用python脚本实现 总结pillar源码分析: @(python之路)[saltstack源 ...
- Shiro 登录认证源码详解
Shiro 登录认证源码详解 Apache Shiro 是一个强大且灵活的 Java 开源安全框架,拥有登录认证.授权管理.企业级会话管理和加密等功能,相比 Spring Security 来说要更加 ...
- udhcp源码详解(五) 之DHCP包--options字段
中间有很长一段时间没有更新udhcp源码详解的博客,主要是源码里的函数太多,不知道要不要一个一个讲下去,要知道讲DHCP的实现理论的话一篇博文也就可以大致的讲完,但实现的源码却要关心很多的问题,比如说 ...
- Activiti架构分析及源码详解
目录 Activiti架构分析及源码详解 引言 一.Activiti设计解析-架构&领域模型 1.1 架构 1.2 领域模型 二.Activiti设计解析-PVM执行树 2.1 核心理念 2. ...
随机推荐
- 4.分布式事务方案-Saga
1. Saga是什么 保证最终一致性的一种分布式事务方案 2. Saga流程 有多个事务参与者,每个参与者都有两块逻辑:正向操作和逆向操作 把事务分成两个阶段 第一阶段每个参与者执行正向操作 第二阶段 ...
- rustdesk自建服务器
前言 rustdesk是一款免费开源的 远程控制软件. 它内置服务器 开箱即用. 不过提供的免费服务器在国外,白嫖起来 有点卡顿 建议自建服务器 . 下边是教程 安装docker和docker com ...
- react发布一个组件库 系列篇(一)
前言 经常使用别人写好的组件库,然后安装引入使用即可.比如: npm install beautiful-table import BeautifulTable from 'beautiful-tab ...
- leetcode 1573
简介 我们自己观察题目发现了什么这是一道数学题,哈哈哈. 个人的思路是分成两类去判断, 第一种: 全是0 使用 \[ (n-1) * (n - 2) / 2 \] 第二种: 有1 然后观察10101 ...
- SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics-V-Statistics:Quantifing Uncertainty+ANOVA(ANalysis Of VAriance)方差分析原理
SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics-V- Statistics:Quantifing Uncertainty ANOVA(ANalysis Of VAr ...
- SciTech-Math-Complex Analysis复分析: Complex复数 + De Moivre's Formula:帝魔服公式 + Euler's Formula:欧拉公式
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/v1nugr08y5 https://mathvault.ca/euler-formula/ https://www.britann ...
- Saga Reader 0.9.9 版本亮点:深入解析核心新功能实现
Saga Reader 在 0.9.9 版本中迎来了一系列激动人心的更新,显著增强了其功能性.灵活性和用户体验.本次更新的核心亮点包括对更多外部大语言模型(LLM)的支持.引入了经典的 RSS 订阅源 ...
- 文人的激情和诗人的写意敲出来的UI 框架-Layui
https://www.ilayuis.com/ 由职业前端倾情打造,面向全层次的前后端开发者,易上手开源免费的 Web UI 组件库 返璞归真 身处在前端社区的繁荣之下,我们都在有意或无意地追逐.而 ...
- NAS和SAN存储基本知识
1 NAS存储是一台网络局域存储服务器,相当于是一台存储服务器,就和web服务器,邮件服务器一样的道理,因为接在了网络上面去了,所以有大量访问NAS的时候,也是很容易造成网络停顿:作为存储,主要目的是 ...
- CAD插件『PDF转CAD格式』安装教程
在工程设计领域,常规流程是将完成的CAD图纸直接转换为PDF格式或输出为纸质蓝图进行分发.由于PDF文件具有跨平台兼容性强.防篡改等特性,在工程交付环节被广泛采用.但当需要对既有图纸进行二次修改时,P ...
