Hibernate关系映射之many-to-many
1、建表
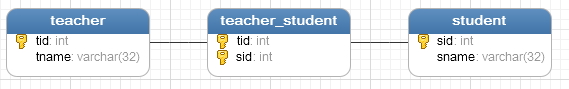
2、创建实体类及映射文件
Student.java类
public class Student implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private Integer sid;
private String sname;
private Set<Teacher> teachers=new HashSet<Teacher>();
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Student() {
}
/** full constructor */
public Student(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
// Property accessors
public Integer getSid() {
return this.sid;
}
public void setSid(Integer sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getSname() {
return this.sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public Set<Teacher> getTeachers() {
return teachers;
}
public void setTeachers(Set<Teacher> teachers) {
this.teachers = teachers;
}
}
使用多对多注解应该是:
@ManyToMany
@JoinTable(name="teacher_student",joinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="sid")},inverseJoinColumns={@JoinColumn(name="tid")})
public Set<Teacher> getTeachers() {
return teachers;
}
Teacher.java类
public class Teacher implements java.io.Serializable {
// Fields
private Integer tid;
private String tname;
private Set<Student> students=new HashSet<Student>();
// Constructors
/** default constructor */
public Teacher() {
}
/** full constructor */
public Teacher(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
// Property accessors
public Integer getTid() {
return this.tid;
}
public void setTid(Integer tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return this.tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
public Set<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(Set<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
}
被控方注解是:
@ManyToMany(mappedBy="teachers")
public Set<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
Student.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.db.Student" table="student" catalog="mydb">
<id name="sid" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="sid" />
<generator class="native" />
</id>
<property name="sname" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="sname" length="32" />
</property>
<!-- 通过table属性告诉hibernate中间表,cascade指明级联操作的类型,inverse属性说明Student实体类是主控方,负责维护关系表 -->
<set name="teachers" table="teacher_student" cascade="save-update,delete" inverse="false">
<!-- 通过key属性告诉hibernate在中间表里面查询sid值相应的student记录 -->
<key>
<column name="sid" not-null="true" />
</key>
<!-- 通过column项告诉hibernate对teacher表中查找tid值相应的teacher记录 -->
<many-to-many class="com.db.Teacher" column="tid"/>
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Teacher.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.db.Teacher" table="teacher" catalog="mydb">
<id name="tid" type="java.lang.Integer">
<column name="tid" />
<generator class="native" />
</id>
<property name="tname" type="java.lang.String">
<column name="tname" length="32" />
</property>
<!-- 通过table属性告诉hibernate中间表,cascade指明级联操作的类型,inverse属性说明Teacher实体类是被控方,不负责维护关系表 ,不能触发对象和数据库的同步更新的。-->
<set name="students" table="teacher_student" inverse="true"
cascade="save-update,delete">
<key>
<column name="tid" not-null="true" />
</key>
<many-to-many class="com.db.Student" column="sid" />
</set>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
hibernate.cfg.xml
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="dialect">
org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect
</property>
<property name="connection.url">
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb
</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">123456</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
</property>
<property name="myeclipse.connection.profile">
MyDBAccount
</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="com/db/Student.hbm.xml" />
<mapping resource="com/db/Teacher.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
3、建立测试用例
测试用例一:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Session session=HibernateSessionFactory.getSession();
Student stu1=new Student();
stu1.setSname("StudentAmy");
Teacher t1=new Teacher();
t1.setTname("TeacherSusan");
Teacher t2=new Teacher();
t2.setTname("TeacherLily");
Teacher t3=new Teacher();
t3.setTname("TeacherMaike");
Set<Teacher> teachers=new HashSet<Teacher>();
teachers.add(t1);
teachers.add(t2);
teachers.add(t3);
stu1.setTeachers(teachers);
session.save(stu1);
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
对应的SQL语句是:
Hibernate: insert into mydb.student (sname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.teacher (tname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.teacher (tname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.teacher (tname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into teacher_student (sid, tid) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into teacher_student (sid, tid) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into teacher_student (sid, tid) values (?, ?)
测试用例二:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Session session=HibernateSessionFactory.getSession();
Student stu1=new Student();
stu1.setSname("StudentJhon1");
Student stu2=new Student();
stu2.setSname("StudentLihua1");
Teacher t1=new Teacher();
t1.setTname("TeacherJay1");
t1.getStudents().add(stu1);
t1.getStudents().add(stu2);
session.beginTransaction();
session.save(t1);
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
}
对应的SQL语句是:
Hibernate: insert into mydb.teacher (tname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.student (sname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.student (sname) values (?)
测试用例三:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Session session=HibernateSessionFactory.getSession();
Student stu1=new Student();
stu1.setSname("StudentJhon1");
Student stu2=new Student();
stu2.setSname("StudentLihua1");
Teacher t1=new Teacher();
t1.setTname("TeacherJay1");
t1.getStudents().add(stu1);
t1.getStudents().add(stu2);
stu2.getTeachers().add(t1);
session.beginTransaction();
session.save(t1);
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
}
对应的SQL语句是:
Hibernate: insert into mydb.teacher (tname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.student (sname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into mydb.student (sname) values (?)
Hibernate: insert into teacher_student (sid, tid) values (?, ?)
通过测试用例发现,两个实体类都进行了级联操作,但是只有将Teacher实体对象添加到Student的teachers属性集合中时才能更新维护中间表。因为Student中的teachers集合的inverse属性是false,使得Student类成为主控方,负责维护关联关系;而Teacher中的students集合的inverse属性为true,使得Teacher类成为被控方,不会维护关联关系。
Hibernate关系映射之many-to-many的更多相关文章
- Hibernate学习笔记-Hibernate关系映射
1. 初识Hibernate——关系映射 http://blog.csdn.net/laner0515/article/details/12905711 2. Hibernate 笔记8 关系映射1( ...
- 【SSH 基础】浅谈Hibernate关系映射(4)
继上篇博客 多对多关联映射(单向) 多对多对象关系映射,须要增加一张新表完毕基本映射. Hibernate会自己主动生成中间表 Hibernate使用many-to-many标签来表示多对多的关联,多 ...
- web进修之—Hibernate 关系映射(3)
概述 Hibernate的关系映射是Hibernate使用的难点或者是重点(别担心,不考试哦~),按照不同的分类方式可以对这些映射关系做一个分类,如: 按对象对应关系分: 一对一 多对一/一对多 多对 ...
- Hibernate关系映射时出现的问题
在学习Hibernate框架的关系映射时,遇到了一个问题: INFO: HHH000422: Disabling contextual LOB creation as connection was n ...
- hibernate关系映射
多对一:比如多个订单对应同一个用户,需要在订单表中添加一个用户的属性 订单类: private Integer orderId; private Date createTime; private Us ...
- Hibernate关系映射(注解)
1.类级别注解 @Entity 映射实体类 @Table 映射数句库表 @Entity(name="tableName") - 必须,注解将一个类声明为一个实体bea ...
- Hibernate关系映射(三) 多对多
一.使用用户User和Role实现多对多的示例 User.java,实现对Role的引用 package com.lxit.entity; import java.util.HashSet; impo ...
- Hibernate关系映射(三) 多对一和一对多
一.多对一 学生Student和班级Grade实现多对一,多个学生对应一个班级. Student.java实体类,映射了班级的属性. package com.lxit.entity; import j ...
- Hibernate关系映射(二) 基于外键的双向一对一
基于外键的双向一对一关联映射 需要在一端添加<one-to-one>标签,用property-ref来指定反向属性引用. 还是通过刚才用户和地址来演示双向一对一关联. 代码演示 一.实体类 ...
随机推荐
- Mysql数据库防SQL注入原理
每个语言都有自己的数据库框架或库,无论是哪种语言,哪种库,它们在数据库防注入方面使用的技术原理无外乎下面介绍的几种方法. 一.特殊字符转义处理 Mysql特殊字符指在mysql中具有特殊含义的字符,除 ...
- VMware Workstation 12 Pro 之安装林耐斯优麒麟 X64系统
VMware Workstation 12 Pro 之安装林耐斯优麒麟 X64系统... --------------------- 先去官网下载ISO格式的系统安装包:http://www.ubun ...
- java web方面的面试问题,Spring MVC方面的面试问题,摘自java web轻量级开发面试教程
本文摘自java web轻量级开发面试教程: https://baike.baidu.com/item/Java%20Web%E8%BD%BB%E9%87%8F%E7%BA%A7%E5%BC%80%E ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week5(下)
Neural Networks: Learning 内容较多,故分成上下两篇文章. 一.内容概要 Cost Function and Backpropagation Cost Function Bac ...
- Tomcat启动:Container StandardContext[] has not been started
Container StandardContext[] has not been started\root.xml 初始化失败,检查数据源配置
- CentOS7.3虚拟机扩展数据磁盘
操作之前需要重点查看: 由于扩容磁盘的操作非同小可,一旦哪一步出现问题,就会导致分区损坏,数据丢失等一系列严重的问题,因此建议:在进行虚拟机分区扩容之前,一定要备份重要数据文件,并且先在测试机上验证以 ...
- Java 随笔记录
1. java对象转json Message msg = generateMessage();ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();String json ...
- C++中值传递、指针传递、引用传递的总结
C++中值传递.指针传递.引用传递的总结 指针传递和引用传递一般适用于:函数内部修改参数并且希望改动影响调用者.对比值传递,指针/引用传递可以将改变由形参"传给"实参(实际上就 ...
- import和require
es6 的 import 语法跟 require 不同,而且 import 必须放在文件的最开始,且前面不允许有其他逻辑代码,这和其他所有编程语言风格一致. import不同与require,它是编译 ...
- UIImageView动画制作
1.先初始化一个UIImageView的视图窗口 如:anima UIImageView *anima = [UIImageView alloc]initWithFrame(0,0,100,100); ...
