Yuchuan_linux_C 编程之八 文件操作相关函数
一、整体大纲

st_mode整体介绍:
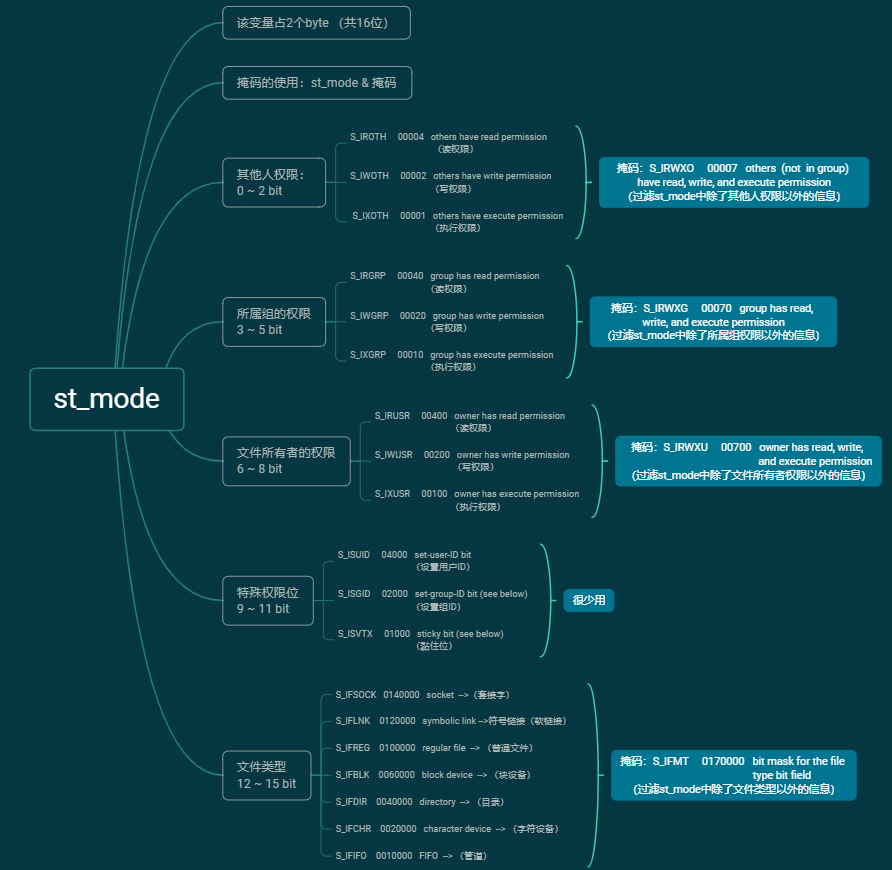
st_mode详细介绍:
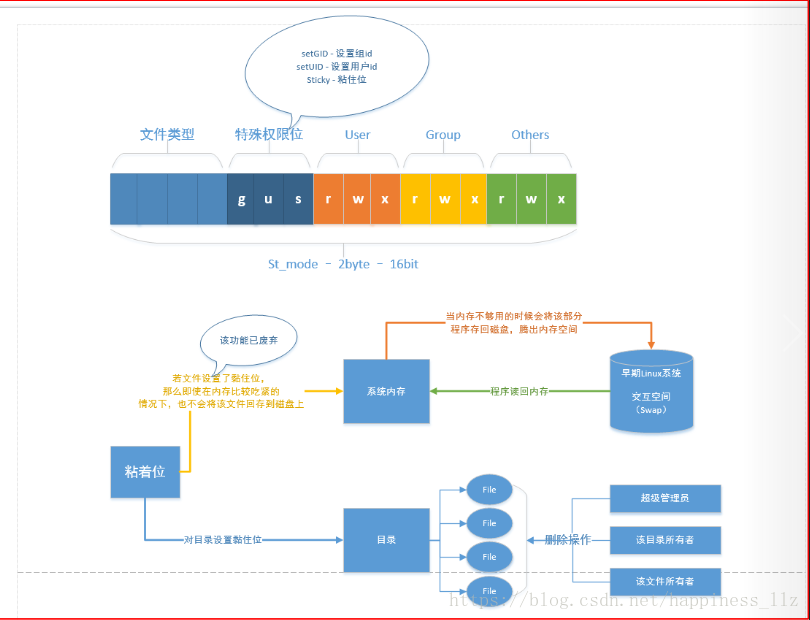
二、 Linux文件操作相关函数
1. stat
- 作用:获得文件信息,也可以获取文件大小。
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
- 参数说明:
path文件名
buf传出参数,定义结构体struct stat sb; &sb
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:返回0
注意: stat碰到链接,会追溯到源文件,穿透!!!lstat并不会穿透。
stat结构体:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};
struct stat
linux命令stat执行结果:
[root@centos linuxC]# stat stat.c
文件:"stat.c"
大小: 块: IO 块: 普通文件
设备:fd00h/64768d Inode: 硬链接:
权限:(/-rw-r--r--) Uid:( / root) Gid:( / root)
环境:unconfined_u:object_r:usr_t:s0
最近访问:-- ::15.149083960 +
最近更改:-- ::15.149083960 +
最近改动:-- ::15.202084912 +
注意三个时间的区别
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ 文件被读,比如cat,open读等
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ 文件内容发生改变
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ 文件属性发生变化,比如大小,权限,硬连接数等
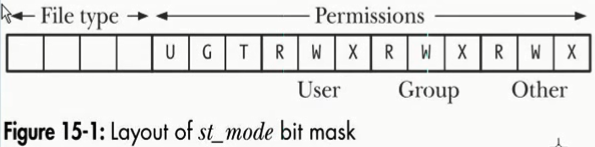
上图的解释:
- 其他用户权限
- 组用户权限
- 用户权限
- 特殊权限位
- 文件类型
示例:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat sb; if (argc != ) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <pathname>\n", argv[]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} if (stat(argv[], &sb) == -) {
perror("stat");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} printf("File type: "); switch (sb.st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO/pipe\n"); break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("symlink\n"); break;
case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break;
case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break;
default: printf("unknown?\n"); break;
}
printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_ino); printf("Mode: %lo (octal)\n",
(unsigned long) sb.st_mode); printf("Link count: %ld\n", (long) sb.st_nlink);
printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",
(long) sb.st_uid, (long) sb.st_gid); printf("Preferred I/O block size: %ld bytes\n",
(long) sb.st_blksize);
printf("File size: %lld bytes\n",
(long long) sb.st_size);
printf("Blocks allocated: %lld\n",
(long long) sb.st_blocks); printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb.st_ctime));
printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb.st_atime));
printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb.st_mtime)); exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} Linux自带示例(打印文件相关信息)
Linux自带示例(打印文件相关信息)
需求:使用stat实现实现 ls -l 的功能?如下所示
[root@centos linuxC]# ll -l xx.log
-rw-r--r--. root root 4月 : xx.log
在实现的过程中需要获取用户名及组名,因此先看两个函数:
1)getpwuid
- 作用:通过用户的uid获取用户名
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <pwd.h>
- 函数原型
struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid);
- 参数说明:
uid用户的uid
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct passwd * 结构体指针
其中:
struct passwd {
char *pw_name; /* username */ 用户名
char *pw_passwd; /* user password */
uid_t pw_uid; /* user ID */
gid_t pw_gid; /* group ID */
char *pw_gecos; /* user information */
char *pw_dir; /* home directory */
char *pw_shell; /* shell program */
};
struct passwd
2)getgrgid
- 作用:通过用户的gid获取用户组名
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <grp.h>
- 函数原型
struct group *getgrgid(gid_t gid);
- 参数说明:
gid用户组的gid
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct group * 结构体指针
其中:
struct group {
char *gr_name; /* group name */
char *gr_passwd; /* group password */
gid_t gr_gid; /* group ID */
char **gr_mem; /* group members */
};
struct group
3)localtime
- 作用:获取本地时间
- 头文件
#include <time.h>
- 函数原型
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);
- 参数说明:
timep:一个时间相关的结构体
- 返回值
失败:返回NULL
成功:返回 struct tm * 结构体指针
其中:
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* seconds */
int tm_min; /* minutes */
int tm_hour; /* hours */
int tm_mday; /* day of the month */
int tm_mon; /* month */
int tm_year; /* year */
int tm_wday; /* day of the week */
int tm_yday; /* day in the year */
int tm_isdst; /* daylight saving time */
};
struct tm
传入参数 timep 对应stat函数得到的结构体的秒数(time_t类型)。
最终实现:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<time.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <pwd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
}
struct stat sb;
stat(argv[], &sb); char stmode[] = {};
memset(stmode, '-', sizeof(stmode)-); //解析文件属性
if (S_ISREG(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = '-'; //普通文件
if (S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 'd';
if (S_ISCHR(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 'c';
if (S_ISBLK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 'b';
if (S_ISFIFO(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 'p';
if (S_ISLNK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 'l';
if (S_ISSOCK(sb.st_mode)) stmode[] = 's'; //解析权限
//user
if (sb.st_mode & S_IRUSR) stmode[] = 'r';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IWUSR) stmode[] = 'w';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IXUSR) stmode[] = 'x';
//group
if (sb.st_mode & S_IRGRP) stmode[] = 'r';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IWGRP) stmode[] = 'w';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IXGRP) stmode[] = 'x';
//other
if (sb.st_mode & S_IROTH) stmode[] = 'r';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IWOTH) stmode[] = 'w';
if (sb.st_mode & S_IXOTH) stmode[] = 'x'; //分析 用户名,组名可以通过函数获得 getpwuid, getgrgid
//时间获取
struct tm *filetm = localtime(&sb.st_atim.tv_sec);
char timebuf[] = {};
sprintf(timebuf, "%d月 %d %02d:%02d", filetm->tm_mon+, filetm->tm_mday, filetm->tm_hour, filetm->tm_min); printf("%s %ld %s %s %ld %s %s\n", stmode, sb.st_nlink, getpwuid(sb.st_uid)->pw_name,
getgrgid(sb.st_gid)->gr_name, sb.st_size, timebuf, argv[]); return ;
} 使用stat实现一个ls -l命令
使用stat实现一个ls -l命令
2. access
- 作用:测试指定文件是否有某种权限
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);
- 参数说明:
pathname文件名
mode:
R_OK
W_OK
X_OK
F_OK
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:如果有权限或者文件存在,对应返回0
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
}
if (access(argv[], R_OK) == ) printf("%s read ok!\n", argv[]);
if (access(argv[], W_OK) == ) printf("%s write ok!\n", argv[]);
if (access(argv[], X_OK) == ) printf("%s exe ok!\n", argv[]);
if (access(argv[], F_OK) == ) printf("%s file exists!\n", argv[]); return ; } 判断文件读写执行及文件是否存在
判断文件读写执行及文件是否存在
3. chmod
#include <sys/stat.h>
int chmod(const char *path, mode_t mode);
4. truncate
- 函数作用:截断文件
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
- 函数原型
int truncate(const char *path, off_t length);
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length);
- 参数说明:
path文件名
length长度,长度如果大于原文件,直接拓展,如果小于原文件,截断为length长度。
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdio.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
}
truncate(argv[], );
return ;
} truncate示例
truncate示例
5. link
- 函数作用:创建硬连接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int link(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
- 参数说明:
oldpath原文件
newpath硬连接文件
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
} char filename[] = {};
sprintf(filename, "%s_hard", argv[]); link(argv[], filename); return ;
} 创建硬连接示例
创建硬连接示例
6. symlink
- 函数作用:创建软连接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int symlink(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
- 参数解释:
oldpath原文件
newpath创建软连接文件
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
} char filename[] = {};
sprintf(filename, "%s_soft", argv[]); symlink(argv[], filename); return ;
} 创建软连接
创建软连接
6. readlink
- 函数作用:读取文件链接信息
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
ssize_t readlink(const char *path, char *buf, size_t bufsiz);
- 参数解释:
path链接名
buf缓冲区
bufsiz缓冲区大小
- 返回值
成功:返回buf填充的大小
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
} char buf[] = {};
readlink(argv[], buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("buf is %s\n", buf); unlink(argv[]); return ;
} readlink示例
readlink示例
7. unlink
- 函数作用:删除软硬链接
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int unlink(const char *pathname);
- 函数参数:
pathname 链接名,文件也可以
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/types.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
} int fd = open(argv[], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, );
//注意只要有进程在使用该文件,则unlink在该文件退出时删除该文件
unlink(argv[]); int ret = write(fd, "hello", );
if (ret > )
{
printf("write ok! %d\n", ret);
}
if (ret < )
{
perror("write err");
} close(fd); return ;
} unlink示例
unlink示例
8. chown
- 函数作用:修改文件属主及属组
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
- 函数原型
int chown(const char *path, uid_t owner, gid_t group);
- 函数参数:
path文件名
owner用户ID,/etc/passwd
owner组ID,/etc/group
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
9. rename
- 函数作用:文件或者目录重命名
- 头文件
#include <stdio.h>
- 函数原型
int rename(const char *oldpath, const char *newpath);
- 参数说明:
oldpath文件名
newpath文件新名
- 返回值
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,设置errno
示例:
#include<stdio.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != )
{
printf("./a.out filename\n");
return -;
} char buf[] = {};
sprintf(buf, "%s_new", argv[]);
rename(argv[], buf); return ;
} rename示例
rename示例
Yuchuan_linux_C 编程之八 文件操作相关函数的更多相关文章
- C语言文件操作相关函数
在实际应用中,我们往往需要对文件进行操作,下面我将介绍C语言的一些关于操作文件的函数. 一.计算机文件 计算机文件是以计算机硬盘为载体存储在计算机上的信息集合,是存储在某种长期储存设备上的一段数据流. ...
- (安全之路)从头开始学python编程之文件操作
0x00 python学习路径 b站(哔哩哔哩)视频,w3cschool(详情百度),官方文档,各大群内获取资料等等方式 0x01 python的学习要点 open()函数:有两个参数,文件名跟模式, ...
- linux编程之文件操作
在linux下用文件描述符来表示设备文件盒普通文件,文件描述符是一个整型的数据,所有对文件的操作都是通过文件描述符来实现的. 文件描述符是文件系统中连接用户空间和内核空间的枢纽,当我们打开一个或者创建 ...
- Java IO编程——File文件操作类
在Java语言里面提供有对于文件操作系统操作的支持,而这个支持就在java.io.File类中进行了定义,也就是说在整个java.io包里面,File类是唯一 一个与文件本身操作(创建.删除.重命名等 ...
- 文件操作相关函数(POSIX 标准 open,read,write,lseek,close)
POSIX标准 open函数属于Linux中系统IO,用于“打开”文件,代码打开一个文件意味着获得了这个文件的访问句柄. int fd = open(参数1,参数2,参数3): int fd = op ...
- java学习笔记之IO编程—File文件操作类
1. File类说明 在Java语言里面提供有对于文件操作系统操作的支持,而这个支持就在java.io.File类中进行了定义,也就是说在整个java.io包里面,File类是唯一一个与文件本身操作( ...
- POJ C++程序设计 编程题#3 编程作业—文件操作与模板
编程题#3: 整数的输出格式 来源: POJ(Coursera声明:在POJ上完成的习题将不会计入Coursera的最后成绩.) 注意: 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 1000kB 描述 利 ...
- POJ C++程序设计 编程题#2 编程作业—文件操作与模板
编程题#2: 实数的输出格式 来源: POJ (Coursera声明:在POJ上完成的习题将不会计入Coursera的最后成绩.) 注意: 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 1000kB 描述 ...
- POJ C++程序设计 编程题#1 编程作业—文件操作与模板
编程题#1 来源: POJ (Coursera声明:在POJ上完成的习题将不会计入Coursera的最后成绩.) 注意: 总时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 65536kB 描述 实现一个三维数组 ...
随机推荐
- Springmvc多视图
Springmvc多视图 多视图是一个方法可以返回json/xml等格式的数据 第一步:导入xml格式支持的jar包 spring-oxm-3.2.0.RC2.jar 第二步:配置支持多视图 < ...
- Laravel5.4 队列简单配置与使用
概述 什么是队列? 百度百科是这样说的 “队列”是在传输过程中保存数据的容器. 举几个生活中例子: * iphone手机新款发布,三里屯iphone进的新货.大家要排队买,不能说一大堆人一起冲进去,那 ...
- Qt QLabel show 显示图像、填充、缩放
主要成员函数: 1.void setText(QString); //设置label框内的文本. 2.void hide(); //隐藏label框. 3.void setBuddy(QWidget* ...
- EmguCV C# 安装入门教程
EmguCv3的安装. EmguCv3下载网址 http://sourceforge.net/projects/emgucv/files/emgucv/3.0.0/ 推荐下载第一个: 点击direct ...
- 前端-bootstrap-长期维护
############### bootstrap简介 ################ Bootstrap是Twitter开源的基于HTML.CSS.JavaScript的前端框架. ...
- Heartbeat(注意iptables和selinux的问题)
安装 yum –y install heartbeat libnet配置 通过yum安装配置文件目录/etc/ha.d目录下没有配置文件需要从doc目录中复制三个文件.ha.cf.authkeys.h ...
- (警告)不要轻易删除libc.so.6,以及误删恢复
网上有很多帖子介绍升级libc.so.6库的帖子,这里存在巨大的坑: 如: Linux/CentOS 升级C基本运行库CLIBC的注意事项(当想解决GLIBC_2.x找不到的编译问题) 里边都会有这样 ...
- IT男频繁猝死背后的心理探秘
"深圳36岁IT男猝死酒店马桶上"这条新闻再次成为人们眼球的焦点,每每发生这样的事情,难免让人扼腕唏嘘,他们本该是风华正茂的年纪,家有老母贤妻爱子,甚至房子车子票子都不缺,该是一边 ...
- JS数字千分
JS数字千分: 1.例子:1000--->1,000 2.实现如下: salesToFormat: function (num) { var num = (num || 0).toString( ...
- 杂谈php之什么是cgi,fastcgi,fpm,cli,mod
杂谈PHP极少关注的问题 本话题来自于我使用PHP进行网页爬虫的一次经历.对于一个web开发者来说,PHP解释器本身却知之甚小,实在是惭愧呐! 首先这个话题要从几个提问开始. PHP是什么? 外文名: ...
