MATLAB神经网络(2)之R练习
1. AMORE
1.1 newff
newff(n.neurons, learning.rate.global, momentum.global, error.criterium, Stao, hidden.layer, output.layer, method)
- n.neurons:包含每层神经元的数值向量。第一个元素是输入神经元的数量,最后一个元素是输出神经元的数量,剩余的是隐含层神经元的数量;
- learning.rate.global:每个神经元训练时的学习效率;
- momentum.global:每个神经元的动量,仅几个训练算法需要该参数;
- error.criterium:用于度量神经网络预测目标值接近程度的标准,可以使用以下几项:
"LMS":Least Mean Squares
"LMLS":Least Mean Logarithm Squared
"TAO":TAO Error
- Stao:当上一项为TAO时的Stao参数,对于其他的误差标准无用
- hidden.layer:隐含层神经元的激活函数,可用:"purelin"、"tansig"、"sigmoid"、"hardlim"、"custom",其中"custom"表示需要用户自定义神经元的f0和f1元素;
- output.layer:输出层神经元的激活函数;
- method:优先选择的训练方法,包括:
"ADAPTgd": Adaptative gradient descend.(自适应的梯度下降方法)
"ADAPTgdwm": Adaptative gradient descend with momentum.(基于动量因子的自适应梯度下降方法)
"BATCHgd": BATCH gradient descend.(批量梯度下降方法)
"BATCHgdwm": BATCH gradient descend with momentum.(基于动量因子的批量梯度下降方法)
1.2 train
train(net, P, T, Pval=NULL, Tval=NULL, error.criterium="LMS", report=TRUE, n.shows, show.step, Stao=NA, prob=NULL, n.threads=0L)
- net:要训练的神经网络;
- P:训练集输入值;
- T:训练集输出值;
- Pval:验证集输入值;
- Tval:验证集输出值;
- error.criterium:度量拟合优劣程度的标准;
- Stao:用于TAO算法的参数初始值;
- report:逻辑值,是否打印训练过程信息;
- n.shows:当上一项为TRUE时,打印的总次数;
- show.step:训练过程一直进行到函数允许打印报告信息时经历的迭代次数;
- prob:每一个样本应用到再抽样训练时的概率向量;
- n.threads:用于BATCH*训练方法的线程数量,如果小于1,它将产生NumberProcessors-1个线程,其中NumberProcessors为处理器的个数,如果没有找到OpenMP库,该参数将被忽略。
1.3 example
library(AMORE)
# P is the input vector
P <- matrix(sample(seq(-1,1,length=1000), 1000, replace=FALSE), ncol=1)
# The network will try to approximate the target P^2
target <- P^2
# We create a feedforward network, with two hidden layers.
# The first hidden layer has three neurons and the second has two neurons.
# The hidden layers have got Tansig activation functions and the output layer is Purelin.
net <- newff(n.neurons=c(1,3,2,1), learning.rate.global=1e-2, momentum.global=0.5,
error.criterium="LMS", Stao=NA, hidden.layer="tansig",
output.layer="purelin", method="ADAPTgdwm")
result <- train(net, P, target, error.criterium="LMS", report=TRUE, show.step=100, n.shows=5 )
P_test <- matrix(sample(seq(-1,1,length=1000), 100, replace=FALSE), ncol=1)
target_test <- P_test^2
y_test <- sim(result$net, P_test)
plot(P_test,y_test-target_test)
index.show: 1 LMS 0.0893172434474773
index.show: 2 LMS 0.0892277761187557
index.show: 3 LMS 0.000380711026069436
index.show: 4 LMS 0.000155618390342181
index.show: 5 LMS 9.53881309223154e-05

1.4 exercise
P <- matrix(rnorm(2000),ncol=2)
target <- apply(P^2,1,mean)
net <- newff(n.neurons=c(2,20,1),
learning.rate.global=1e-2,
momentum.global=0.5,
error.criterium="LMS",
Stao=NA,
hidden.layer="tansig",
output.layer="purelin",
method="ADAPTgdwm")
result <- train(net, P, target,
error.criterium="LMS",
report=TRUE,
show.step=100,
n.shows=10)
P_test <- matrix(rnorm(200),ncol=2)
target_test <- apply(P_test^2,1,mean)
y_test <- sim(result$net, P_test)
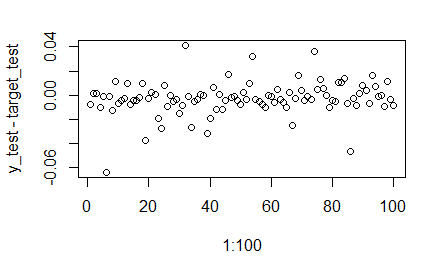
plot(1:100,y_test-target_test)
(mean(abs(y_test-target_test)/target_test))
index.show: 1 LMS 0.00334168377394762
index.show: 2 LMS 0.00234274830312042
index.show: 3 LMS 0.00153074744985914
index.show: 4 LMS 0.00107702325684643
index.show: 5 LMS 0.000808644341077497
index.show: 6 LMS 0.000618371026226565
index.show: 7 LMS 0.000464896136767987
index.show: 8 LMS 0.000367196186841271
index.show: 9 LMS 0.00030261519286547
index.show: 10 LMS 0.000256892157194439
[1] 0.02934992
2. RSNNS
2.1 mlp
mlp(x, y, size = c(5), maxit = 100, initFunc = "Randomize_Weights", initFuncParams = c(-0.3, 0.3), learnFunc = "Std_Backpropagation", learnFuncParams = c(0.2, 0), updateFunc = "Topological_Order", updateFuncParams = c(0),
hiddenActFunc = "Act_Logistic", shufflePatterns = TRUE, linOut = FALSE, outputActFunc = if (linOut) "Act_Identity" else "Act_Logistic", inputsTest = NULL, targetsTest = NULL, pruneFunc = NULL, pruneFuncParams = NULL, ...)
- x:一个矩阵,作为训练数据用于神经网络的输入;
- y:对应的目标值;
- size:隐含层单元的数量,默认为c(5),当设置多个值时,表示有多个隐含层;
- maxit:学习过程的最大迭代次数,默认为100;
- initFunc:使用的初始化函数,默认为Randomize_Weights,即随机权重;
- initFuncParams:用于初始化函数的参数,默认参数为c(-0.3,0.3);
- learnFunc:使用的学习函数,默认为Std_Backpropagation;
- learnFuncParams:用于学习函数的参数,默认为c(0.2,0);
- updateFunc:使用的更新函数,默认为Topological_Order;
- undateFuncParams:用于更新函数的参数,默认为c(0);
- hiddenActFunc:所有隐含层神经元的激活函数,默认为Act_Logistic;
- shufflePatterns:是否将模式打乱,默认为TRUE;
- linOut,设置输出神经元的激活函数,linear或者logistic,默认为FALSE;
- inputsTest:一个矩阵,作为测试数据用于神经网络的输入,默认为NULL;
- targetsTest:与测试输入对应的目标值,默认为NULL;
- pruneFunc:使用的修剪函数,默认为NULL;
- pruneFuncParams:用于修剪函数的函数,默认为NULL。
2.2 example
数据准备
library(RSNNS)
data(iris) #shuffle the vector
iris <- iris[sample(1:nrow(iris),nrow(iris)),] irisValues <- iris[,1:4]
irisTargets <- decodeClassLabels(iris[,5])
#irisTargets <- decodeClassLabels(iris[,5], valTrue=0.9, valFalse=0.1)
- decodeClassLabels: This method decodes class labels from a numerical or levels vector to a binary matrix, i.e., it converts the input vector to a binary matrix.
> head(irisTargets)
setosa versicolor virginica
[1,] 1 0 0
[2,] 0 1 0
[3,] 0 0 1
[4,] 1 0 0
[5,] 0 0 1
[6,] 0 0 1
抽样
iris <- splitForTrainingAndTest(irisValues, irisTargets, ratio=0.15)
iris <- normTrainingAndTestSet(iris)
- splitForTrainingAndTest: Split the input and target values to a training and a test set. Test set is taken from the end of the data. If the data is to be shuffled, this should be done before calling this function.
- normTrainingAndTestSet: Normalize training and test set as obtained by splitForTrainingAndTest in the following way: The inputsTrain member is normalized using normalizeData with the parameters given in type. The normalization parameters obtained during this normalization are then used to normalize the inputsTest member. if dontNormTargets is not set, then the targets are normalized in the same way. In classification problems, normalizing the targets normally makes no sense. For regression, normalizing also the targets is usually a good idea. The default is to not normalize targets values.
> attr(iris$inputsTrain,"normParams")$type
[1] "norm"
> attr(iris$inputsTest,"normParams")$type
[1] "norm"
训练&测试
model <- mlp(iris$inputsTrain, iris$targetsTrain,
size=5,
learnFuncParams=c(0.1),
maxit=50,
inputsTest=iris$inputsTest,
targetsTest=iris$targetsTest) summary(model)
SNNS network definition file V1.4-3D
generated at Tue Feb 18 16:06:54 2020
network name : RSNNS_untitled
source files :
no. of units : 12(4+5+3=12个神经元)
no. of connections : 35(4×5+5×3=35权重)
no. of unit types : 0
no. of site types : 0
learning function : Std_Backpropagation
update function : Topological_Order
unit default section :
act | bias | st | subnet | layer | act func | out func
---------|----------|----|--------|-------|--------------|-------------
0.00000 | 0.00000 | i | 0 | 1 | Act_Logistic | Out_Identity
---------|----------|----|--------|-------|--------------|-------------
unit definition section :(给出偏置等参数)
no. | typeName | unitName | act | bias | st | position | act func | out func | sites
----|----------|-------------------|----------|----------|----|----------|--------------|----------|-------
1 | | Input_1 | 0.30243 | 0.27615 | i | 1,0,0 | Act_Identity | |
2 | | Input_2 | -0.55103 | 0.28670 | i | 2,0,0 | Act_Identity | |
3 | | Input_3 | 0.51752 | 0.05927 | i | 3,0,0 | Act_Identity | |
4 | | Input_4 | -0.00309 | 0.27664 | i | 4,0,0 | Act_Identity | |
5 | | Hidden_2_1 | 0.76338 | 1.91173 | h | 1,2,0 |||
6 | | Hidden_2_2 | 0.20872 | -2.48788 | h | 2,2,0 |||
7 | | Hidden_2_3 | 0.19751 | -0.35229 | h | 3,2,0 |||
8 | | Hidden_2_4 | 0.03343 | -1.45754 | h | 4,2,0 |||
9 | | Hidden_2_5 | 0.89784 | 0.82294 | h | 5,2,0 |||
10 | | Output_setosa | 0.05013 | -0.63914 | o | 1,4,0 |||
11 | | Output_versicolor | 0.82301 | -0.62233 | o | 2,4,0 |||
12 | | Output_virginica | 0.11542 | -1.02579 | o | 3,4,0 |||
----|----------|-------------------|----------|----------|----|----------|--------------|----------|-------
connection definition section :(给出权重矩阵)
target | site | source:weight
-------|------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
5 | | 4:-2.27555, 3:-1.59991, 2: 0.00019, 1: 0.26665
6 | | 4: 2.54355, 3: 1.83954, 2:-0.49918, 1:-0.21152
7 | | 4:-1.29117, 3:-0.90530, 2: 0.95187, 1:-0.20054
8 | | 4:-1.49130, 3:-1.54012, 2: 1.55497, 1:-0.85142
9 | | 4: 1.35965, 3: 1.07292, 2:-1.20123, 1: 0.45480
10 | | 9:-2.51547, 8: 2.26887, 7: 1.42713, 6:-2.24000, 5: 0.08607
11 | | 9: 1.31081, 8:-3.15358, 7:-1.09917, 6:-3.07740, 5: 2.55070
12 | | 9: 1.16730, 8:-2.03073, 7:-2.15568, 6: 2.90927, 5:-2.84570
-------|------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
> model
Class: mlp->rsnns
Number of inputs: 4
Number of outputs: 3
Maximal iterations: 50
Initialization function: Randomize_Weights
Initialization function parameters: -0.3 0.3
Learning function: Std_Backpropagation
Learning function parameters: 0.1
Update function:Topological_Order
Update function parameters: 0
Patterns are shuffled internally: TRUE
Compute error in every iteration: TRUE
Architecture Parameters:
$`size`
[1] 5
All members of model:
[1] "nInputs" "maxit"
[3] "initFunc" "initFuncParams"
[5] "learnFunc" "learnFuncParams"
[7] "updateFunc" "updateFuncParams"
[9] "shufflePatterns" "computeIterativeError"
[11] "snnsObject" "archParams"
[13] "IterativeFitError" "IterativeTestError"
[15] "fitted.values" "fittedTestValues"
[17] "nOutputs"
weightMatrix(model)
#extractNetInfo(model)
| Hidden_2_1 | Hidden_2_2 | Hidden_2_3 | Hidden_2_4 | Hidden_2_5 | Output_setosa | Output_versicolor | Output_virginica | |
| Input_1 | 0.2666532695 | -0.2115191 | -0.2005364 | -0.8514175 | 0.4547978 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Input_2 | 0.0001948424 | -0.4991824 | 0.9518659 | 1.5549698 | -1.2012329 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Input_3 | -1.5999110937 | 1.8395387 | -0.9053020 | -1.5401160 | 1.0729166 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Input_4 | -2.2755548954 | 2.5435514 | -1.2911705 | -1.4912956 | 1.3596520 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Hidden_2_1 | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.08606748 | 2.550698 | -2.845704 |
| Hidden_2_2 | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | -2.24000168 | -3.077400 | 2.909271 |
| Hidden_2_3 | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 1.42712903 | -1.099168 | -2.155685 |
| Hidden_2_4 | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 2.26887059 | -3.153584 | -2.030726 |
| Hidden_2_5 | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | -2.51547217 | 1.310814 | 1.167299 |
| Output_setosa | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Output_versicolor | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
| Output_virginica | 0.0000000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.0000000 | 0.00000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 |
结果分析
绘出随迭代次数增加,误差平方和(SSE)的变化情况。
plotIterativeError(model)

散点为真实值和预测值的分布,黑色线为$y=x$,红色线为一次回归线。
predictions <- predict(model,iris$inputsTest) plotRegressionError(predictions[,2], iris$targetsTest[,2])

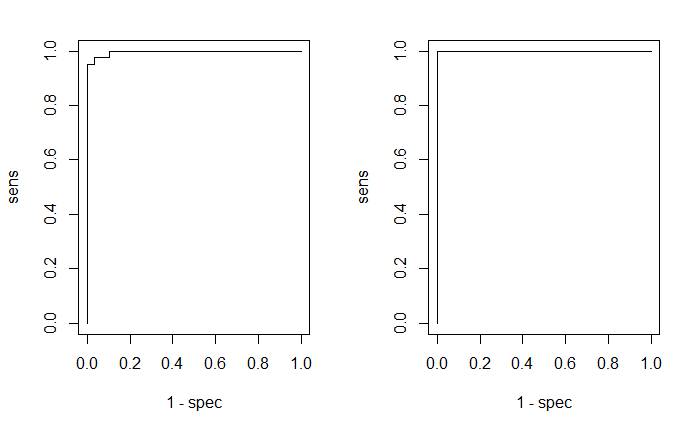
列出混淆矩阵,绘出EOC曲线。
> confusionMatrix(iris$targetsTrain,fitted.values(model))
predictions
targets 1 2 3
1 42 0 0
2 0 38 2
3 0 1 44
> confusionMatrix(iris$targetsTest,predictions)
predictions
targets 1 2 3
1 8 0 0
2 0 9 1
3 0 0 5
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
plotROC(fitted.values(model)[,2], iris$targetsTrain[,2])
plotROC(predictions[,2], iris$targetsTest[,2])
给出更严格的检验,若3项中1项大于0.6,其余两项小于0.4,则将其归为该项,否则标0,视为无法判定。
> confusionMatrix(iris$targetsTrain,
+ encodeClassLabels(fitted.values(model),
+ method="402040", l=0.4, h=0.6))
predictions
targets 0 1 2 3
1 0 42 0 0
2 4 0 36 0
3 3 0 0 42
MATLAB神经网络(2)之R练习的更多相关文章
- MATLAB神经网络(1)之R练习
)之R练习 将在MATLAB神经网络中学到的知识用R进行适当地重构,再写一遍,一方面可以加深理解和记忆,另一方面练习R,比较R和MATLAB的不同.如要在R中使用之前的数据,应首先在MATLAB中用w ...
- 12.Matlab神经网络工具箱
概述: 1 人工神经网络介绍 2 人工神经元 3 MATLAB神经网络工具箱 4 感知器神经网络 5 感知器神经网络 5.1 设计实例分析 clear all; close all; P=[ ; ]; ...
- MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解视频教程
教程内容:<MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解>随书附带源程序.rar9.随机神经网络.rar8.反馈神经网络.rar7.自组织竞争神经网络.rar6.径向基函数网络.rar5.BP神经网 ...
- 《精通Matlab神经网络》例10-16的新写法
<精通Matlab神经网络>书中示例10-16,在创建BP网络时,原来的写法是: net = newff(minmax(alphabet),[S1 S2],{'logsig' 'logsi ...
- Matlab神经网络
1. <MATLAB神经网络原理与实例精解> 2. B站:https://search.bilibili.com/all?keyword=matlab&from_source=na ...
- 使用opencv-python实现MATLAB的fspecial('Gaussian', [r, c], sigma)
reference_opencv实现高斯核 reference_MATLAB_fspecial函数说明 # MATLAB H = fspecial('Gaussian', [r, c], sigma) ...
- Matlab神经网络工具箱学习之一
1.神经网络设计的流程 2.神经网络设计四个层次 3.神经网络模型 4.神经网络结构 5.创建神经网络对象 6.配置神经网络的输入输出 7.理解神经网络工具箱的数据结构 8.神经网络训练 1.神经网络 ...
- matlab神经网络工具箱创建神经网络
为了看懂师兄的文章中使用的方法,研究了一下神经网络 昨天花了一天的时间查怎么写程序,但是费了半天劲,不能运行,百度知道里倒是有一个,可以运行的,先贴着做标本 % 生成训练样本集 clear all; ...
- Matlab神经网络验证码识别
本文,将会简述如何利用Matlab的强大功能,调用神经网络处理验证码的识别问题. 预备知识,Matlab基础编程,神经网络基础. 可以先看下: Matlab基础视频教程 Matlab经典教程--从 ...
随机推荐
- kaggle下载不了比赛数据?
先看这个 kaggle数据集下载 -------------------------------- 有时发现下载不了kaggle数据 关于kaggle没有办法下载数据集dataset问题 安装kagg ...
- Jumpserver 一键部署(支持离线安装)
1.教程介绍1.1::通过本教程起到抛砖引玉效果,希望各位喜爱Jumpserver堡垒机的朋友受益良多. 1.2::以下提供的任何软件仅供学习交流使用. 2.下载链接2.1::centos_1810最 ...
- Golang Middleware Part 1 · To Be A Better Man
如何在Golang中实现中间件-Part 1 当使用net/http包实现服务的时候,一般使用的是如下的两中处理方式: http.HandleFunc http.Handle http.HandleF ...
- 推送至远程仓库使用git push -u的原因
第一次把本地仓库推送至远端时,为了以后方便一定要使用 git push -u origin master [此处是把本地的master分支推送至远程的master分支]
- highcharys去掉x轴,y轴轴线和刻度
x轴 xAxis: { lineWidth :,//去掉x轴线 tickWidth:,//去掉刻度 labels: { enabled: false },//去掉刻度数字 }, y轴 yAxis: { ...
- JavaScript 事件代理
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/silence516/archive/2009/09/03/delegateEvent.html 如果你想给网页添加点JavaScript的交互性, ...
- RDS的tar文件恢复到本地mysql5.7版本数据库
参考博客: 安装qpress软件 https://blog.csdn.net/a18838964650/article/details/82800621 文章介绍补充 https://www.cnbl ...
- Memcached笔记——(三)Memcached使用总结
为了将N个前端数据同步,通过Memcached完成数据打通,但带来了一些新问题: 使用iBatis整合了Memcached,iBatis针对每台server生成了唯一标识,导致同一份数据sql会产生不 ...
- Bar条形图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np n = 12 X = np.arange(n) Y1 = (1 - X / float(n)) * ...
- Html学习笔记(二) 简单标签
标签的重点 标签的用途 标签在浏览器中的默认样式 <body>标签: 在网页上显示的内容 <p>标签: 添加段落 <hx>标签: 添加标题 标签一共有6个,h1.h ...
