吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:图形初阶(续一)



















# ----------------------------------------------------#
# R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 3 #
# Getting started with graphs #
# requires that the Hmisc and RColorBrewer packages #
# have been installed #
# install.packages(c("Hmisc", "RColorBrewer")) #
#-----------------------------------------------------# par(ask=TRUE)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # make a copy of current settings attach(mtcars) # be sure to execute this line plot(wt, mpg)
abline(lm(mpg~wt))
title("Regression of MPG on Weight")
# Input data for drug example
dose <- c(20, 30, 40, 45, 60)
drugA <- c(16, 20, 27, 40, 60)
drugB <- c(15, 18, 25, 31, 40) plot(dose, drugA, type="b") opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE) # make a copy of current settings
par(lty=2, pch=17) # change line type and symbol
plot(dose, drugA, type="b") # generate a plot
par(opar) # restore the original settings plot(dose, drugA, type="b", lty=3, lwd=3, pch=15, cex=2) # choosing colors
library(RColorBrewer)
n <- 7
mycolors <- brewer.pal(n, "Set1")
barplot(rep(1,n), col=mycolors) n <- 10
mycolors <- rainbow(n)
pie(rep(1, n), labels=mycolors, col=mycolors)
mygrays <- gray(0:n/n)
pie(rep(1, n), labels=mygrays, col=mygrays) # Listing 3.1 - Using graphical parameters to control graph appearance
dose <- c(20, 30, 40, 45, 60)
drugA <- c(16, 20, 27, 40, 60)
drugB <- c(15, 18, 25, 31, 40)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(pin=c(2, 3))
par(lwd=2, cex=1.5)
par(cex.axis=.75, font.axis=3)
plot(dose, drugA, type="b", pch=19, lty=2, col="red")
plot(dose, drugB, type="b", pch=23, lty=6, col="blue", bg="green")
par(opar) # Adding text, lines, and symbols
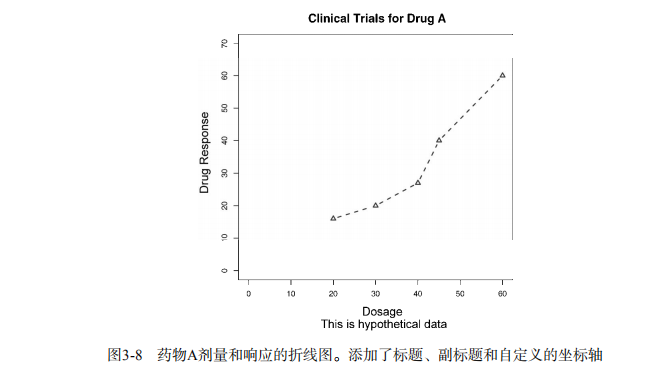
plot(dose, drugA, type="b",
col="red", lty=2, pch=2, lwd=2,
main="Clinical Trials for Drug A",
sub="This is hypothetical data",
xlab="Dosage", ylab="Drug Response",
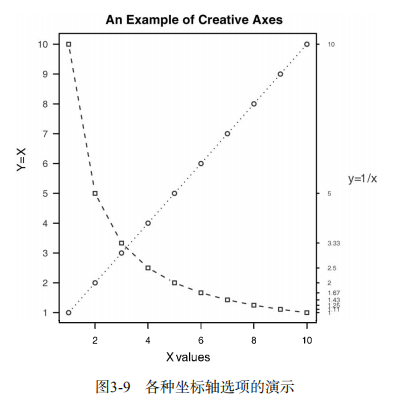
xlim=c(0, 60), ylim=c(0, 70)) # Listing 3.2 - An Example of Custom Axes
x <- c(1:10)
y <- x
z <- 10/x
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mar=c(5, 4, 4, 8) + 0.1)
plot(x, y, type="b",
pch=21, col="red",
yaxt="n", lty=3, ann=FALSE)
lines(x, z, type="b", pch=22, col="blue", lty=2)
axis(2, at=x, labels=x, col.axis="red", las=2)
axis(4, at=z, labels=round(z, digits=2),
col.axis="blue", las=2, cex.axis=0.7, tck=-.01)
mtext("y=1/x", side=4, line=3, cex.lab=1, las=2, col="blue")
title("An Example of Creative Axes",
xlab="X values",
ylab="Y=X")
par(opar) # Listing 3.3 - Comparing Drug A and Drug B response by dose
dose <- c(20, 30, 40, 45, 60)
drugA <- c(16, 20, 27, 40, 60)
drugB <- c(15, 18, 25, 31, 40)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(lwd=2, cex=1.5, font.lab=2)
plot(dose, drugA, type="b",
pch=15, lty=1, col="red", ylim=c(0, 60),
main="Drug A vs. Drug B",
xlab="Drug Dosage", ylab="Drug Response")
lines(dose, drugB, type="b",
pch=17, lty=2, col="blue")
abline(h=c(30), lwd=1.5, lty=2, col="gray")
library(Hmisc)
minor.tick(nx=3, ny=3, tick.ratio=0.5)
legend("topleft", inset=.05, title="Drug Type", c("A","B"),
lty=c(1, 2), pch=c(15, 17), col=c("red", "blue"))
par(opar) # Example of labeling points
attach(mtcars)
plot(wt, mpg,
main="Mileage vs. Car Weight",
xlab="Weight", ylab="Mileage",
pch=18, col="blue")
text(wt, mpg,
row.names(mtcars),
cex=0.6, pos=4, col="red")
detach(mtcars) # View font families
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(cex=1.5)
plot(1:7,1:7,type="n")
text(3,3,"Example of default text")
text(4,4,family="mono","Example of mono-spaced text")
text(5,5,family="serif","Example of serif text")
par(opar) # Combining graphs
attach(mtcars)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(2,2))
plot(wt,mpg, main="Scatterplot of wt vs. mpg")
plot(wt,disp, main="Scatterplot of wt vs. disp")
hist(wt, main="Histogram of wt")
boxplot(wt, main="Boxplot of wt")
par(opar)
detach(mtcars) attach(mtcars)
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(mfrow=c(3,1))
hist(wt)
hist(mpg)
hist(disp)
par(opar)
detach(mtcars) attach(mtcars)
layout(matrix(c(1,1,2,3), 2, 2, byrow = TRUE))
hist(wt)
hist(mpg)
hist(disp)
detach(mtcars) attach(mtcars)
layout(matrix(c(1, 1, 2, 3), 2, 2, byrow = TRUE),
widths=c(3, 1), heights=c(1, 2))
hist(wt)
hist(mpg)
hist(disp)
detach(mtcars) # Listing 3.4 - Fine placement of figures in a graph
opar <- par(no.readonly=TRUE)
par(fig=c(0, 0.8, 0, 0.8))
plot(mtcars$mpg, mtcars$wt,
xlab="Miles Per Gallon",
ylab="Car Weight")
par(fig=c(0, 0.8, 0.55, 1), new=TRUE)
boxplot(mtcars$mpg, horizontal=TRUE, axes=FALSE)
par(fig=c(0.65, 1, 0, 0.8), new=TRUE)
boxplot(mtcars$wt, axes=FALSE)
mtext("Enhanced Scatterplot", side=3, outer=TRUE, line=-3)
par(opar)
吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:图形初阶(续一)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:聚类分析(续一)
#-------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 16 # # Clu ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续三)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续二)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:时间序列(续一)
#-----------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 15 # # Time series # # r ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:方差分析(续二)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapte ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:方差分析(续一)
#-------------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapte ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续四)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续三)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续二)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然 R语言开发学习:回归(续一)
#------------------------------------------------------------# # R in Action (2nd ed): Chapter 8 # # ...
随机推荐
- 微信支付的Demo
是在一个子项目完成的, 依赖: <dependencies> <!-- spring-boot--> <dependency> <groupId>org ...
- MBProgressHUD覆盖键盘
发送消息的时候,需要用MBProgressHUD来覆盖窗口等待发送成功,但是无论如何键盘都覆盖不上. 于是各种研究,添加到view,添加到window,都无果..想破了脑子,总觉得加到window都覆 ...
- 寒假day06
今天完善了毕设的数据抽取功能,新增了几点: 1.已经抽取过的表由系统给出相应提示 2.生成数据抽取记录并展示 3.界面优化
- 编程基础-servlet1
1.Servelet是什么 sevlet是Server与Applet 的缩写,即服务端小程序.Sun公司提供的开发动态web资源的技术. servelet本质是java类,但遵循Servlet规范,没 ...
- JKFZ%你赛炸裂祭
Md爆40了身败名裂 上来就刚T1是什么习惯?居然不看T2导致明明能刚出正解却止步40 , T3找到原题看懂题解后却不敢交+难码 , 最近怕不是做毒瘤%你赛多了总以为T1能刚到点分 md最近怕不是炸了 ...
- 一、Cookie和Session介绍
会话跟踪 1. 什么是会话 * 用户拨打10086,从服务台接通后会话开始: * 用户发出话费查询请求,服务台响应.这是该会话中的一个请求: * 用户发出套餐变更请求,服务台响应.这是该会话中的 ...
- 七、Shell脚本高级编程实战第七部
一.写网络服务的系统启动脚本 利用case语句开发类似系统启动rsync服务的脚本 代码: #!/bin/sah. /etc/init.d/functionspidfile="/var/ru ...
- 14 微服务电商【黑马乐优商城】:day04-ES6语法入门
day01-springboot(理论篇) :day01-springboot(实践篇) day02-springcloud(理论篇一) :day02-springcloud(理论篇二) :day ...
- 题解 P3061 【[USACO12DEC]疯狂的栅栏Crazy Fences】
这道题的思想是首先我们找到所有的栅栏围成的空间,然后求每一只奶牛在哪几个栅栏空间之中,最后比较他们在的所有栅栏空间-----如果奶牛a和b同时在空间c,d和e内,那么他们一定在同一群中. 测试围栏的方 ...
- fatal: remote origin already exists.
解决方法: 先删除, 再添加 1. git remote rm origin 2. git remote add origin https://github.com/zjulanjian/eshop. ...
