机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Python(numpy)实现
题目太长了!下载地址【传送门】
第1题
简述:识别图片上的数字。
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.optimize as op #显示图片数据
def displayData(X):
m = np.size(X, 0) #X的行数,即样本数量
n = np.size(X, 1) #X的列数,即单个样本大小
example_width = int(np.round(np.sqrt(n))) #单张图片宽度
example_height = int(np.floor(n / example_width)) #单张图片高度
display_rows = int(np.floor(np.sqrt(m))) #显示图中,一行多少张图
display_cols = int(np.ceil(m / display_rows)) #显示图中,一列多少张图片
pad = 1 #图片间的间隔
display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad),
pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad))) #初始化图片矩阵
curr_ex = 0 #当前的图片计数
#将每张小图插入图片数组中
for j in range(0, display_rows):
for i in range(0, display_cols):
if curr_ex >= m:
break
max_val = np.max(abs(X[curr_ex, :]))
jstart = pad + j * (example_height + pad)
istart = pad + i * (example_width + pad)
display_array[jstart: (jstart + example_height), istart: (istart + example_width)] = \
np.array(X[curr_ex, :]).reshape(example_height, example_width) / max_val
curr_ex = curr_ex + 1
if curr_ex >= m:
break
display_array = display_array.T
plt.imshow(display_array,cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show() #计算hθ(z)
def sigmoid(z):
g = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
return g #计算cost
def lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lamb):
theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1))
m = np.size(y)
h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))
J = 1 / m * (-np.dot(y.T, np.log(h)) - np.dot((1 - y.T), np.log(1 - h)))
theta2 = theta[1:, 0]
Jadd = lamb / (2 * m) * np.sum(theta2 ** 2)
J = J + Jadd
return J.flatten() #计算梯度
def gradient(theta, X, y, lamb):
theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1))
m = np.size(y)
h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta))
grad = 1/m*np.dot(X.T, h - y)
theta[0,0] = 0
gradadd = lamb/m*theta
grad = grad + gradadd
return grad.flatten() #θ计算
def oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lamb):
m = np.size(X, 0)
n = np.size(X, 1)
all_theta = np.zeros((num_labels, n+1))
one = np.ones(m)
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1)
for c in range(0, num_labels):
initial_theta = np.zeros(n+1)
y_t = (y==c)
result = op.minimize(fun=lrCostFunction, x0=initial_theta, args=(X, y_t, lamb), method='TNC', jac=gradient)
all_theta[c, :] = result.x
return all_theta #计算准确率
def predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X):
m = np.size(X, 0)
num_labels = np.size(all_theta, 0)
p = np.zeros((m, 1)) #用来保存每行的最大值
g = np.zeros((np.size(X, 0), num_labels)) #用来保存每次分类后的结果(一共分类了10次,每次保存到一列上)
one = np.ones(m)
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1)
for c in range(0, num_labels):
theta = all_theta[c, :]
g[:, c] = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta.T))
p = g.argmax(axis=1)
# print(p)
return p.flatten() #加载数据文件
data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
y = y%10 #因为数据集是考虑了matlab从1开始,把0的结果保存为了10,这里进行取余,将10变回0
m = np.size(X, 0)
rand_indices = np.random.randint(0,m,100)
sel = X[rand_indices, :]
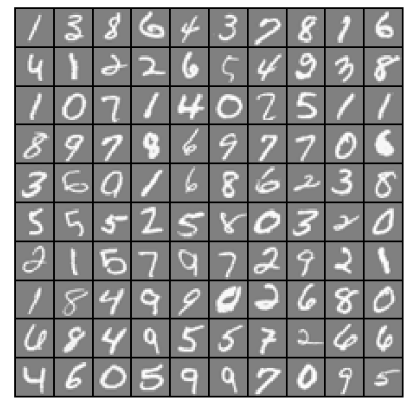
displayData(sel) #计算θ
lamb = 0.1
num_labels = 10
all_theta = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lamb)
# print(all_theta) #计算预测的准确性
pred = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
# np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
#在计算这个上遇到了一个坑:
#pred输出的是[[...]]的形式,需要flatten变成1维向量,y同样用flatten变成1维向量
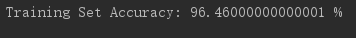
acc = np.mean(pred == y.flatten())*100
print('Training Set Accuracy:',acc,'%')
运行结果:
第2题
简介:使用神经网络实现数字识别(Θ已提供)
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.optimize as op #显示图片数据
def displayData(X):
m = np.size(X, 0) #X的行数,即样本数量
n = np.size(X, 1) #X的列数,即单个样本大小
example_width = int(np.round(np.sqrt(n))) #单张图片宽度
example_height = int(np.floor(n / example_width)) #单张图片高度
display_rows = int(np.floor(np.sqrt(m))) #显示图中,一行多少张图
display_cols = int(np.ceil(m / display_rows)) #显示图中,一列多少张图片
pad = 1 #图片间的间隔
display_array = - np.ones((pad + display_rows * (example_height + pad),
pad + display_cols * (example_width + pad))) #初始化图片矩阵
curr_ex = 0 #当前的图片计数
#将每张小图插入图片数组中
for j in range(0, display_rows):
for i in range(0, display_cols):
if curr_ex >= m:
break
max_val = np.max(abs(X[curr_ex, :]))
jstart = pad + j * (example_height + pad)
istart = pad + i * (example_width + pad)
display_array[jstart: (jstart + example_height), istart: (istart + example_width)] = \
np.array(X[curr_ex, :]).reshape(example_height, example_width) / max_val
curr_ex = curr_ex + 1
if curr_ex >= m:
break
display_array = display_array.T
plt.imshow(display_array,cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show() #计算hθ(z)
def sigmoid(z):
g = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z))
return g #实现神经网络
def predict(theta1, theta2, X):
m = np.size(X,0)
p = np.zeros((np.size(X, 0), 1))
#第二层计算
one = np.ones(m)
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1)
a2 = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta1.T))
#第三层计算
one = np.ones(np.size(a2,0))
a2 = np.insert(a2, 0, values=one, axis=1)
a3 = sigmoid(np.dot(a2, theta2.T))
p = a3.argmax(axis=1) + 1 #y的值为1-10,所以此处0-9要加1
return p.flatten() #读取数据文件
data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
m = np.size(X, 0)
rand_indices = np.random.randint(0,m,100)
sel = X[rand_indices, :]
# displayData(sel) theta = scio.loadmat('ex3weights.mat')
theta1 = theta['Theta1']
theta2 = theta['Theta2'] #预测准确率
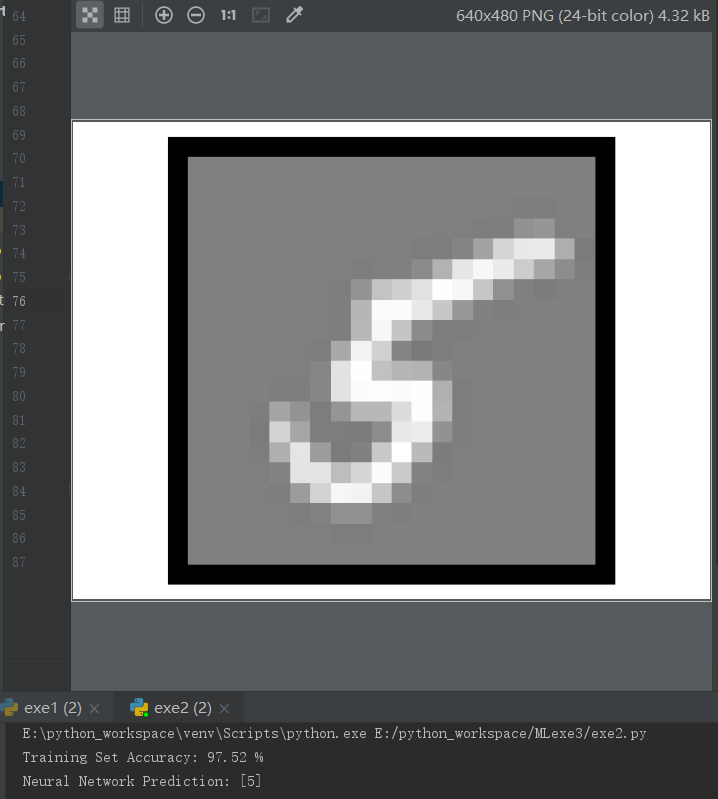
pred = predict(theta1, theta2, X)
acc = np.mean(pred == y.flatten())*100
print('Training Set Accuracy:',acc,'%') #识别单张图片
for i in range(0, m):
it = np.random.randint(0, m, 1)
it = it[0]
displayData(X[it:it+1, :])
pred = predict(theta1, theta2, X[it:it+1, :])
print('Neural Network Prediction:', pred)
print('input q to exit:')
cin = input()
if cin == 'q':
break
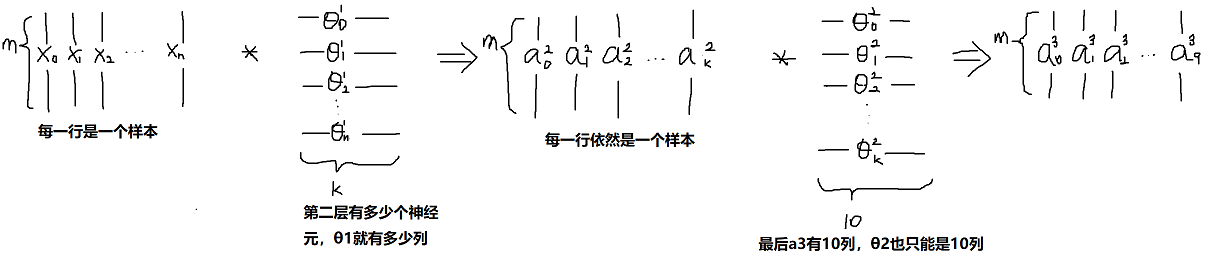
神经网络的矩阵表示分析:
运行结果:
机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Python(numpy)实现的更多相关文章
- 机器学习作业(三)多类别分类与神经网络——Matlab实现
题目太长了!下载地址[传送门] 第1题 简述:识别图片上的数字. 第1步:读取数据文件: %% Setup the parameters you will use for this part of t ...
- 机器学习入门16 - 多类别神经网络 (Multi-Class Neural Networks)
原文链接:https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/multi-class-neural-networks/ 多类别分类, ...
- 機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations) 机器学习基石 作业三 课后习题解答
今天和大家分享coursera-NTU-機器學習基石(Machine Learning Foundations)-作业三的习题解答.笔者在做这些题目时遇到非常多困难,当我在网上寻找答案时却找不到,而林 ...
- 机器学习实验报告:利用3层神经网络对CIFAR-10图像数据库进行分类
PS:这是6月份时的一个结课项目,当时的想法就是把之前在Coursera ML课上实现过的对手写数字识别的方法迁移过来,但是最后的效果不太好… 2014年 6 月 一.实验概述 实验采用的是CIFAR ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(四)之神经网络 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7365730.html 前言 ...
- 斯坦福深度学习与nlp第四讲词窗口分类和神经网络
http://www.52nlp.cn/%E6%96%AF%E5%9D%A6%E7%A6%8F%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6%E5%AD%A6%E4%B9%A0%E4%B8%8Enlp%E7%A ...
- 用Python开始机器学习(2:决策树分类算法)
http://blog.csdn.net/lsldd/article/details/41223147 从这一章开始进入正式的算法学习. 首先我们学习经典而有效的分类算法:决策树分类算法. 1.决策树 ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-第三周:浅层神经网络(Shallow neural networks) -课程笔记
第三周:浅层神经网络(Shallow neural networks) 3.1 神经网络概述(Neural Network Overview) 使用符号$ ^{[
- 基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,详解自然语言处理
摘要:这篇文章将详细讲解自然语言处理过程,基于机器学习和TFIDF的情感分类算法,并进行了各种分类算法(SVM.RF.LR.Boosting)对比 本文分享自华为云社区<[Python人工智能] ...
随机推荐
- 图解Java设计模式之设计模式七大原则
图解Java设计模式之设计模式七大原则 2.1 设计模式的目的 2.2 设计模式七大原则 2.3 单一职责原则 2.3.1 基本介绍 2.3.2 应用实例 2.4 接口隔离原则(Interface S ...
- Cesium案例解析(五)——3DTilesPhotogrammetry摄影测量3DTiles数据
目录 1. 概述 2. 案例 3. 结果 1. 概述 3D Tiles是用于传输和渲染大规模3D地理空间数据的格式,例如摄影测量,3D建筑,BIM / CAD,实例化特征和点云等.与常规的模型文件格式 ...
- mysql必知必会--创建计算字段
计算字段 存储在数据库表中的数据一般不是应用程序所需要的格式.下面举 几个例子. * 如果想在一个字段中既显示公司名,又显示公司的地址,但这两 个信息一般包含在不同的表列中. * 城市.州和邮政编码存 ...
- VMware使用与安装
VMware安装 下载完Vmware -> 双击打开安装包 -> 选择下一步(如下图界面) 选择接受协议,点击下一步 选择经典进行安装.这个是默认安装,会把默认插件安装到相对应的路径 选择 ...
- 全面了解Python中的特殊语法:filter、map、reduce、lambda。
这篇文章主要介绍了Python中的特殊语法:filter.map.reduce.lambda介绍,本文分别对这个特殊语法给出了代码实例,需要的朋友可以参考下filter(function, seque ...
- Git操作:一次性强制push所有分支
现在手上有两个分支,master和rotation,想一次性推送所有分支,可以用--all参数来实现: git push --all origin 如果远程仓库有更改,但你需要直接推送,那就可以使用强 ...
- SpringCloud入门学习
我相信,如果小伙伴们能来到这里,肯定对微服务有一定的认识. 我们之前创建web项目的时候,常见的有两种方式: 1).创建一个war包,然后放在servlet容器中运行(比如Tomcat等); 2).使 ...
- C语言编写程序的大小端问题
有时候,用C语言写程序需要知道大端模式还是小端模式,,由于寄存器大于一个字节(8bit),就会存在一个字节安排的问题,例如(16bit)的short型,(32bit)的int型,具体需要看具体的编译器 ...
- 小白的linux笔记7:批量运行复杂的linux命令组合——BASH简单使用法
linux的BASH就相当于windows下的BAT文件,可以批处理命令.比如写好一个python脚本后,需要在运行时候加参数,但这个参数又不想每次输入,就可以用BASH的方式写好整条命令,然后直接运 ...
- centos的安装与配置,Linux下基本命令、权限控制,解压缩文件以及软件的安装与卸载
centos安装与网络配置 关机:shutdown -h now 重启:shutdown -r now 或 reboot linux目录结构与操作命令 使用ls命令查看目录结构 目录查看: ls [- ...
