R Tidyverse dplyr包学习笔记2
Tidyverse 学习笔记
1.gapminder 我理解的gapminder应该是一个内置的数据集
加载之后使用
> # Load the gapminder package
> library(gapminder)
> # Load the dplyr package
> library(dplyr)
> # Look at the gapminder dataset
> gapminder
A tibble: 1,704 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.
3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.
4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836.
5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740.
6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786.
7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978.
8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852.
9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649.
10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635.
... with 1,694 more rows
1.1 filter 函数
解释:过滤/筛选,按条件,可以有很多条件
gapminder %>%filter(year==2002,country=="China")
A tibble: 1 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 China Asia 2002 72.0 1280400000 3119.
1.2 排序函数arrange,默认升序,参数desc降序
> # Sort in ascending order of lifeExp
> gapminder %>%
arrange(lifeExp)
A tibble: 1,704 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 Rwanda Africa 1992 23.6 7290203 737.
2 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
3 Gambia Africa 1952 30 284320 485.
4 Angola Africa 1952 30.0 4232095 3521.
5 Sierra Leone Africa 1952 30.3 2143249 880.
6 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.
7 Cambodia Asia 1977 31.2 6978607 525.
8 Mozambique Africa 1952 31.3 6446316 469.
9 Sierra Leone Africa 1957 31.6 2295678 1004.
10 Burkina Faso Africa 1952 32.0 4469979 543.
... with 1,694 more rows
按照lifeExp 降序
> # Sort in descending order of lifeExp
> gapminder %>%
arrange(desc(lifeExp))
A tibble: 1,704 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 Japan Asia 2007 82.6 127467972 31656.
2 Hong Kong, China Asia 2007 82.2 6980412 39725.
3 Japan Asia 2002 82 127065841 28605.
4 Iceland Europe 2007 81.8 301931 36181.
5 Switzerland Europe 2007 81.7 7554661 37506.
6 Hong Kong, China Asia 2002 81.5 6762476 30209.
7 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435.
8 Spain Europe 2007 80.9 40448191 28821.
9 Sweden Europe 2007 80.9 9031088 33860.
10 Israel Asia 2007 80.7 6426679 25523.
... with 1,694 more rows
筛选和排序组合使用:
> library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
>
> # Filter for the year 1957, then arrange in descending order of population
> gapminder%>%filter(year==1957)%>%arrange(desc(pop))
A tibble: 142 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 China Asia 1957 50.5 637408000 576.
2 India Asia 1957 40.2 409000000 590.
3 United States Americas 1957 69.5 171984000 14847.
4 Japan Asia 1957 65.5 91563009 4318.
5 Indonesia Asia 1957 39.9 90124000 859.
6 Germany Europe 1957 69.1 71019069 10188.
7 Brazil Americas 1957 53.3 65551171 2487.
8 United Kingdom Europe 1957 70.4 51430000 11283.
9 Bangladesh Asia 1957 39.3 51365468 662.
10 Italy Europe 1957 67.8 49182000 6249.
... with 132 more rows
2 mutute 函数
2.1 修改变量,并且将新变量增加到数据框或者矩阵的左侧
> # Use mutate to change lifeExp to be in months
> gapminder%>%mutate(lifeExp=12*lifeExp)
A tibble: 1,704 x 6
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 346. 8425333 779.
2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 364. 9240934 821.
3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 384. 10267083 853.
4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 408. 11537966 836.
5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 433. 13079460 740.
6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 461. 14880372 786.
7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 478. 12881816 978.
8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 490. 13867957 852.
9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 500. 16317921 649.
10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 501. 22227415 635.
... with 1,694 more rows
>
2.2 增加新的变量
> Use mutate to create a new column called lifeExpMonths
> gapminder%>%mutate(lifeExpMonths=12*lifeExp)
A tibble: 1,704 x 7
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap lifeExpMonths
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779. 346.
2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821. 364.
3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853. 384.
4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836. 408.
5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740. 433.
6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786. 461.
7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978. 478.
8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852. 490.
9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649. 500.
10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635. 501.
... with 1,694 more rows
2.3 combine
> library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
> # Filter, mutate, and arrange the gapminder dataset
> gapminder%>%filter(year==2007)%>%mutate(
lifeExpMonths=12 * lifeExp,
)%>%arrange(desc(lifeExpMonths))
A tibble: 142 x 7
country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap lifeExpMonths
<fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Japan Asia 2007 82.6 127467972 31656. 991.
2 Hong Kong, China Asia 2007 82.2 6980412 39725. 986.
3 Iceland Europe 2007 81.8 301931 36181. 981.
4 Switzerland Europe 2007 81.7 7554661 37506. 980.
5 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435. 975.
6 Spain Europe 2007 80.9 40448191 28821. 971.
7 Sweden Europe 2007 80.9 9031088 33860. 971.
8 Israel Asia 2007 80.7 6426679 25523. 969.
9 France Europe 2007 80.7 61083916 30470. 968.
10 Canada Americas 2007 80.7 33390141 36319. 968.
... with 132 more rows
3 浅谈:ggplot2 绘图
基本的制图,不添加任何图形元素是可以看下面的小demo,但是用到其他的元素了,就可以
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ggplot2/ggplot2.pdf这个说明文当还是挺全面的
library(gapminder)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
Change to put pop on the x-axis and gdpPercap on the y-axis
ggplot(gapminder_1952, aes(x = pop, y = gdpPercap)) +
geom_point()

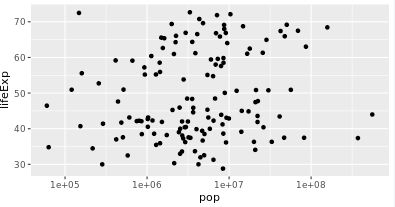
3.1 x坐标取对数
zheyang
> library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
> library(ggplot2)
>
> gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
>
> # Change this plot to put the x-axis on a log scale
> ggplot(gapminder_1952, aes(x = pop, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point()+
scale_x_log10()
> library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
> library(ggplot2)
>
> gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
>
> # Change this plot to put the x-axis on a log scale
> ggplot(gapminder_1952, aes(x = pop, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point()+
scale_x_log10()+
scale_y_log10()
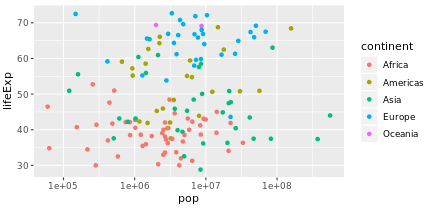
3.2 设置color和size
设置国家的颜色是不一样的
gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
>
> # Scatter plot comparing pop and lifeExp, with color representing continent
> ggplot(gapminder_1952,aes(x=pop,y=lifeExp,colour= continent))+geom_point()+
scale_x_log10()
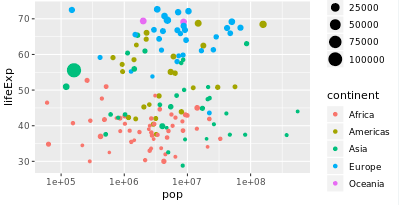
3.3 设置size
> gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
>
> # Add the size aesthetic to represent a country's gdpPercap
> ggplot(gapminder_1952, aes(x = pop, y = lifeExp, color = continent,size=gdpPercap)) +
geom_point() +
scale_x_log10()
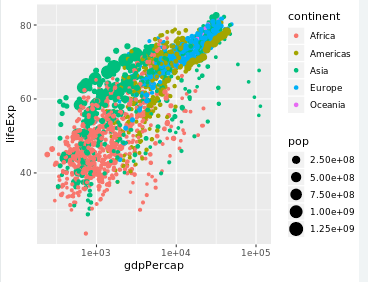
3.4 Faceting
Faceting is a powerful way to understand subsets of your data separately
可以按照条件分类显示数据
facet_wrap(~condi):按照condi来显示数据分类
and size representing population, faceted by year
> ggplot(gapminder,aes(x=gdpPercap,y=lifeExp,colour=continent,size=pop))+
geom_point()+
scale_x_log10()
> facet_wrap(~year)
<ggproto object: Class FacetWrap, Facet, gg>
compute_layout: function
draw_back: function
draw_front: function
draw_labels: function
draw_panels: function
finish_data: function
init_scales: function
map_data: function
params: list
setup_data: function
setup_params: function
shrink: TRUE
train_scales: function
vars: function
super: <ggproto object: Class FacetWrap, Facet, gg>
4.summarize
类似与summary的函数,可以描述性输出。
但是里面的内置函数只有:sum,mean,median,min,max。
Filter for 1957 then summarize the median life expectancy and the maximum GDP per capita
gapminder%>%filter(year==1957)%>%summarize(
medianLifeExp=median(lifeExp),
maxGdpPercap=max(gdpPercap)
)
5 group_by
分组求解
> # Find median life expectancy and maximum GDP per capita in each continent in 1957
> gapminder%>%filter(year==1957)%>%group_by(continent)%>%summarize(
medianLifeExp=median(lifeExp),
maxGdpPercap=max(gdpPercap)
)
A tibble: 5 x 3
continent medianLifeExp maxGdpPercap
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Africa 40.6 5487.
2 Americas 56.1 14847.
3 Asia 48.3 113523.
4 Europe 67.6 17909.
5 Oceania 70.3 12247.
可以有多个条件进行分组
> # Find median life expectancy and maximum GDP per capita in each continent/year combination
> gapminder%>%group_by(continent,year)%>%summarize(
medianLifeExp=median(lifeExp),
maxGdpPercap=max(gdpPercap)
)
A tibble: 60 x 4
# Groups: continent [5]
continent year medianLifeExp maxGdpPercap
<fct> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Africa 1952 38.8 4725.
2 Africa 1957 40.6 5487.
3 Africa 1962 42.6 6757.
4 Africa 1967 44.7 18773.
5 Africa 1972 47.0 21011.
6 Africa 1977 49.3 21951.
7 Africa 1982 50.8 17364.
8 Africa 1987 51.6 11864.
9 Africa 1992 52.4 13522.
10 Africa 1997 52.8 14723.
# ... with 50 more rows
6.expand_limits(y=0)
让y轴从0开始
ibrary(gapminder)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
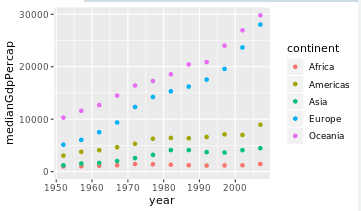
# Summarize medianGdpPercap within each continent within each year: by_year_continent
by_year_continent<-gapminder%>%group_by(continent,year)%>%summarize(
medianGdpPercap=median(gdpPercap))
# Plot the change in medianGdpPercap in each continent over time
ggplot(by_year_continent,aes(x=year,y=medianGdpPercap,colour=continent))+geom_point()+
expand_limits(y = 0)
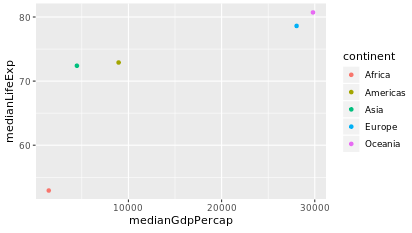
> # Use a scatter plot to compare the median GDP and median life expectancy
> ggplot(by_continent_2007,aes(x=medianLifeExp,y=medianGdpPercap,colour=continent))+geom_point()
> library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
> library(ggplot2)
>
> # Summarize the median GDP and median life expectancy per continent in 2007
> by_continent_2007 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 2007) %>%
group_by(continent) %>%
summarize(medianGdpPercap = median(gdpPercap),
medianLifeExp = median(lifeExp))
>
> # Use a scatter plot to compare the median GDP and median life expectancy
> ggplot(by_continent_2007, aes(x = medianGdpPercap, y = medianLifeExp, color = continent)) +
geom_point()
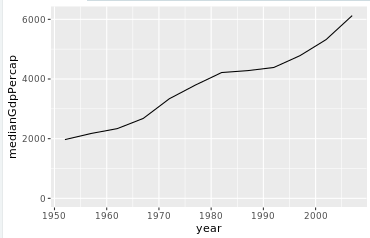
line plot
线图
上面画的都是散点图
library(gapminder)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
# Summarize the median gdpPercap by year, then save it as by_year
by_year<-gapminder%>%group_by(year)%>%summarize(medianGdpPercap=median(gdpPercap))
# Create a line plot showing the change in medianGdpPercap over time
ggplot(by_year, aes(x = year, y = medianGdpPercap)) +
geom_line() +
expand_limits(y = 0)
直线图和散点图的区别就是geom_point()与geom_line()
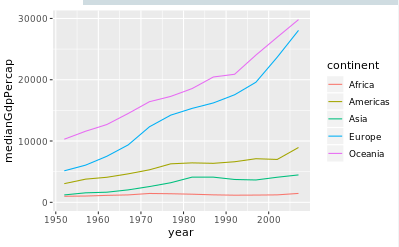
library(ggplot2)
>
> # Summarize the median gdpPercap by year & continent, save as by_year_continent
> by_year_continent<-gapminder%>%group_by(year,continent)%>%summarize(
medianGdpPercap=median(gdpPercap)
)
>
> # Create a line plot showing the change in medianGdpPercap by continent over time
> ggplot(by_year_continent,aes(x = year, y = medianGdpPercap,color=continent))+
geom_line()+
expand_limits(y = 0)
bar plot
library(gapminder)
> library(dplyr)
> library(ggplot2)
>
> # Summarize the median gdpPercap by year and continent in 1952
> by_continent<-gapminder%>%filter(year==1952)%>%group_by(continent)%>%summarize(
medianGdpPercap=median(gdpPercap))
>
> # Create a bar plot showing medianGdp by continent
> ggplot(by_continent,aes(x=continent,y=medianGdpPercap))+geom_col()
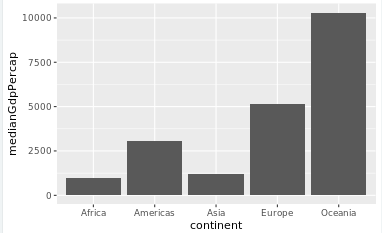
library(ggplot2)
gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952) %>%
mutate(pop_by_mil = pop / 1000000)
# Create a histogram of population (pop_by_mil)
ggplot(gapminder_1952,aes(x=pop_by_mil))+
geom_histogram(bins=50)

boxplot
# Create a boxplot comparing gdpPercap among continents
> ggplot(gapminder_1952,aes(x=continent,y=gdpPercap))+
geom_boxplot()+
scale_y_log10()
> ggplot(gapminder_1952,aes(x=continent,y=gdpPercap))+
geom_boxplot()+
scale_y_log10()
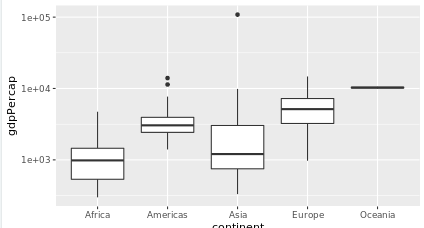
ggtitle
如果给表加上标题就用ggtitle("标题名")
gapminder_1952 <- gapminder %>%
filter(year == 1952)
>
> # Add a title to this graph: "Comparing GDP per capita across continents"
> ggplot(gapminder_1952, aes(x = continent, y = gdpPercap)) +
geom_boxplot() +
scale_y_log10()+
ggtitle("Comparing GDP per capita across continents")
不同的图形按照ggplot来说只是修改geom_*的参数
ggplot2
R Tidyverse dplyr包学习笔记2的更多相关文章
- R语言与机器学习学习笔记
人工神经网络(ANN),简称神经网络,是一种模仿生物神经网络的结构和功能的数学模型或计算模型.神经网络由大量的人工神经元联结进行计算.大多数情况下人工神经网络能在外界信息的基础上改变内部结构,是一种自 ...
- R语言与显著性检验学习笔记
R语言与显著性检验学习笔记 一.何为显著性检验 显著性检验的思想十分的简单,就是认为小概率事件不可能发生.虽然概率论中我们一直强调小概率事件必然发生,但显著性检验还是相信了小概率事件在我做的这一次检验 ...
- R语言函数化学习笔记3
R语言函数化学习笔记3 R语言常用的一些命令函数 1.getwd()查看当前R的工作目录 2.setwd()修改当前工作目录 3.str()可以输出指定对象的结构(类型,位置等),同理还有class( ...
- R语言dplyr包初探
昨天学了一下R语言dplyr包,处理数据框还是很好用的.记录一下免得我忘记了... 先写一篇入门的,以后有空再写一篇详细的用法. #dplyr learning library(dplyr) #fil ...
- R语言函数化学习笔记6
R语言函数化学习笔记 1.apply函数 可以让list或者vector的元素依次执行一遍调用的函数,输出的结果是list格式 2.sapply函数 原理和list一样,但是输出的结果是一个向量的形式 ...
- R parallel包学习笔记2
这个部分我在datacamp上面学习笔记,可视化的性能很差,使用的函数也很少. 可以参考一下大佬的博客园个人感觉他们讲的真的很详细 https://cosx.org/2016/09/r-and-par ...
- R语言函数话学习笔记5
使用Tidyverse完成函数化编程 (参考了家翔学长的笔记) 1.magrittr包的使用 里面有很多的管道函数,,可以减少代码开发时间,提高代码可读性和维护性 1.1 四种pipeline 1.1 ...
- 【数据分析 R语言实战】学习笔记 第八章 方差分析与R实现
方差分析泛应用于商业.经济.医学.农业等诸多领域的数量分析研究中.例如商业广告宣传方面,广告效果可能会受广告式.地区规模.播放时段.播放频率等多个因素的影响,通过方差分析研究众多因素中,哪些是主要的以 ...
- pandas包学习笔记
目录 zip Importing & exporting data Plotting with pandas Visual exploratory data analysis 折线图 散点图 ...
随机推荐
- nginx location展示及文件共享
nginx 目录展示及文件访问 效果: [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-d5G9wfKK-1570116907804)(E:\Users\FangJunX ...
- .Net Core通过json文件 配置管理后台导航菜单
先来看个最终效果图 以前我们配置后台菜单 一般都是把菜单链接, 图标, 以及层级关系 配置到数据库,Core很容易通过json文件来配置导航菜单 而不用存数据库了 先添加个menuconfig.js ...
- ConcurrentHashMap的size()方法(1.7和1.8)
在1.7和1.8版本中,计算size()方法有写不同.先介绍1.7版本的实现. 1.7版本 在1.7版本中,有一个重要的类Segment,利用它来实现分段锁 static final class Se ...
- opencv —— 读取并播放视频 VideoCapture capture("C:/1.mp4");
VideoCapture 读入视频的方法有两种: ①先实例化再初始化:VideoCapture capture:capture.open("C:/Users/齐明洋/Desktop/1.mp ...
- 数据结构(集合)学习之List
集合 框架关系图: Collection接口下面有三个子接口:List.Set.Queue.此篇是关于List<E>的简单学习总结. 补充:HashTable父类是Dictionary,不 ...
- Nginx-3.控制nginx
原文 nginx 通过信号来控制.对应linux系统就是用kill命令. The command kill sends the specified signal to the specified pr ...
- Docker入门(windows安装)
Docker入门(安装)Docker是一种轻量级容器技术,实际中直接运行在当前操作系统(Linux)上,而不是虚拟机中.PaaS提供了存储,数据库,网络,负载均衡,自动扩展等功能,Docker云平台就 ...
- ng-指令
在 Angular 中最常用的指令分为两种,它们分别是 属性型指令 和 结构型指令. NgClass 作用:添加或移除一组 CSS 类 NgStyle 作用:添加或移除一组 CSS 样式 NgMode ...
- 洛谷P1067 多项式输出 NOIP 2009 普及组 第一题
洛谷P1067 多项式输出 NOIP 2009 普及组 第一题 题目描述 一元n次多项式可用如下的表达式表示: 输入输出格式 输入格式 输入共有 2 行 第一行 1 个整数,n,表示一元多项式的次数. ...
- gulp常用插件之gulp-sourcemaps使用
更多gulp常用插件使用请访问:gulp常用插件汇总 gulp-sourcemaps这是一款用来生成映射文件的一个插件,SourceMap 文件记录了一个存储源代码与编译代码对应位置映射的信息文件.我 ...
