函数wait和waitpid
函数wait
一个进程在终止时会关闭所有文件描述符,释放在用户空间释放的内存,但它的PCB还保留着,内核在其中保存一些信息:如果是正常终止时则保存着退出状态,如果是异常终止则保存着导致该进程终止的信号是哪个,这个进程的父进程可以调用wait或waitpid获取这些信息,然后彻底清除这个进程,我们知道一个进程的退出状态可以在shell用特殊变量$?查看,因为shell是它的父进程,当它终止时shell调用wait或waitpid得到它的退出状态同时彻底清除这个进程。
1. 函数wait:一次只能回收一个子进程
pid_t wait(int *status); status传出参数
进程终止时,操作系统隐式回收机制会:1. 关闭所有的文件描述符 2. 释放用户空间分配的内存。内核PCB仍存在,其中保存该进程的退出状态。(正常终止--------退出值;异常终止-------终止信号)
可使用wait函数传出参数status来保存进程的退出状态,借助宏函数来进一步判断进程终止的具体原因,宏函数可分为三组:
- WIFEXITED(status):为非0,进程正常结束;WEXITSTATUS(status) :如上宏为真,使用此宏 获取进程退出状态(exit的参数)
- WIFSIGNALED(status):为非0,进程异常终止;WTERMSIG(status):如上宏为真,使用此宏 获取进程终止的那个信号编号
- WIFSTOPPED(status) :为非0,进程处于暂停状;WSTOPSIG(status):如上宏为真,使用此宏 获取进程暂停的那个信号编号
1. 测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/wait.h> int main(void)
{
pid_t pid, wpid;
pid = fork(); if(pid == )
{
printf("---child, my parent = %d, going to sleep 10s\n", getpid());
sleep();
printf("---------child die --------------\n");
}
else if(pid > )
{
wpid = wait(NULL);
if(wpid == -)
{
perror("wait error: ");
exit();
}
while()
{
printf("I am parent, pid = %d, my son = %d\n", getpid(), pid);
sleep();
}
}
else
{
perror("fork");
return ;
}
return ;
}
输出结果
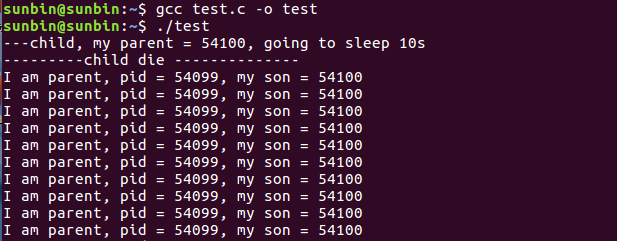
1. 测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h> int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid > ) // 父进程
{
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
int status;
pid_t wpid = wait(&status); if (WIFEXITED(status))
printf("exit value: %d", WEXITSTATUS(status));
if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
printf("exit by signal: %d\n", WTERMSIG(status)); //是否被信号杀死 printf(" die child pid = %d\n", wpid);
}
else if(pid == )
{
sleep();
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}
for (int i = ; i<; ++i)
printf(" i = %d\n", i);
return ;
}
输出结果:
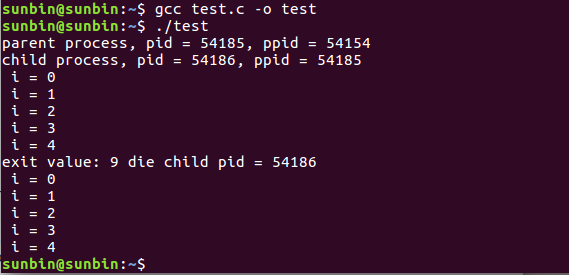
3. 测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include<sys/wait.h> int main(int argc, const char* argv[])
{
pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid > ) //父进程
{
printf("parent process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
int status;
pid_t wpid = wait(&status); if (WIFEXITED(status))
printf("exit value: %d", WEXITSTATUS(status));
if (WIFSIGNALED(status))
printf("exit by signal: %d\n", WTERMSIG(status)); //是否被信号杀 printf(" die child pid = %d\n", wpid);
}
else if (pid == )
{
while()
{
sleep();
printf("child process, pid = %d, ppid = %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
}
}
for (int i = ; i<; ++i)
printf(" i = %d\n", i);
return ;
}
采取操作:
pts/ S+ : ./test
pts/ S+ : ./test
pts/ R+ : ps ajx
sunbin@sunbin:~$ kill -
输出结果:
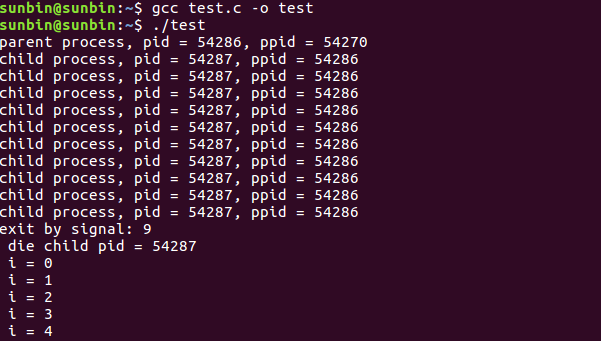
函数waitpid
函数waitpid原型:作用同wait,但可指定pid进程清理,可以不阻塞( 一次只能回收一个子进程)
pid_t wait(pid_t pid, int *staloc, int options);
1. 参数pid:
- pid == -1:回收任一子进程
- pid > 0 :回收指定pid的进程
- pid == 0 :回收与父进程同一个进程组的任一个子进程
- pid < -1 :回收指定进程组内的任意子进程
2. 参数options:
- 设置为WNOHANG:函数不阻塞;
- 设置为0:函数阻塞。
函数wait和waitpid的更多相关文章
- 阻塞进程函数 wait()和waitpid()
1. wait()和waitpid()函数说明 wait() 进程一旦调用了wait(), 就立即阻塞自己,由wait自动分析是否有当前进程的某个子进程已经退出,如果让它找到了一个已经变成僵尸的子进 ...
- wait/waitpid函数与僵尸进程、fork 2 times
一.僵尸进程 当子进程退出的时候,内核会向父进程发送SIGCHLD信号,子进程的退出是个异步事件(子进程可以在父进程运行的任何时刻终止) 子进程退出时,内核将子进程置为僵尸状态,这个进程称为僵尸进程, ...
- 【Linux】僵尸进程,孤儿进程以及wait函数,waitpid函数(有样例,分析很详细)
本文内容: 1.僵尸进程,孤儿进程的定义,区别,产生原因,处理方法 2.wait函数,waitpid函数的分析,以及比较 背景:由于子进程的结束和父进程的运行是一个异步的过程,即父进程永远无法预测子进 ...
- wait函数与waitpid函数(僵尸进程)
当子进程退出时,内核会向父进程发送SIGCHLD信号,子进程的退出是个异步事件(子进程可以在父进程运行的任何时刻终止) 子进程退出时,内核将子进程置为僵尸状态,这个进程称为僵尸进程.它只保留最小的一些 ...
- 父进程等待子进程结束 waitpid wait
我们一直在强调一个概念就是进程是一个程序执行的实例,是内核在虚拟概念下创建的实体,它实例化的体现在用户态就是程序代码和代码使用的变量(存储空间),在内核态就是内核为我们每个进程所保存的数据结构(状态信 ...
- 对于linux下system()函数的深度理解(整理)
原谅: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_8043547601017qk0.html 这几天调程序(嵌入式linux),发现程序有时就莫名其妙的死掉,每次都定位在程序中不同 ...
- 【转】linux中waitpid及wait的用法
原文网址:http://www.2cto.com/os/201203/124851.html wait(等待子进程中断或结束) 表头文件 #include<sys/types.h> ...
- system函数的总结
最近在看APUE第10章中关于system函数的POSIX.1的实现.关于POSIX.1要求system函数忽略SIGINT和SIGQUIT,并且阻塞信号SIGCHLD的论述,理解得不是很透彻,本文就 ...
- linux中waitpid及wait的用法
wait(等待子进程中断或结束) 表头文件 #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/wait.h> 定义函数 pid_t wa ...
随机推荐
- Python3-join()和split()
Python join()方法 Python join()方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串. #例如:列表 -- 字符串 str.join(sequence) 参数: sequ ...
- Linux查看本机IP:curl cip.cc
curl http://members.3322.org/dyndns/getip curl ip.6655.com/ip.aspx curl ifconfig.me curl icanhazip.c ...
- Gitlab 备份迁移恢复报错gtar: .: Cannot mkdir: No such file or directory
1. 版本信息 OS: centos 6.9 Gitlab: gitlab-ce.10.7.4 gitlab-ce.10.8.0 gitlab-ce.10.8.3 gitlab-ce.10.8.4 2 ...
- 用vue+element-ui开发后台笔记
1.前端通过 formData: new FormData(), 构造对象传数值给后台! 当传给后台的参数中有图片的时候,需要把需要传输的数据通过构造对象new FormData()的形式存数据,并且 ...
- C#委托delegate、Action、Func、predicate 对比用法
委托是一个类,它定义了方法的类型,使得可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递.事件是一种特殊的委托. 一.委托的声明 (1) delegate delegate我们常用到的一种声明 Delega ...
- 写markdown博客如何将截图快速上传到图床——记一个工具插件的实现(windows版 开源)
打造一个上传图片到图床利器的插件(Mac版 开源)(2018-06-24 19:44) 更新于2018年2月 做了以下改动: 1.修复了一个bug,把服务器区域做成可配: 七牛有华北,华东,华南以及美 ...
- vue中更换.ico图标报错路径找不到图片
问题描述: vue项目中,想要更换.ico图片,更换完成后刷新页面报错,找不到路径. 解决: 更换完图片,重新启动下vue项目(npm run dev)就可以啦~ 哈哈哈 补充知识: 网页title旁 ...
- $.each() 与 $(selector).each()的区别
$.each( dataArr,function(i,item){}) 可用于遍历任何的集合(无论是数组或对象). 如果是数组,回调函数每次传入数组的索引(也就是i)和对应的值(item)(值亦可以 ...
- QTableWidget
1.QTableWidget继承自QTableView. QSqlTableModel能与QTableView绑定,但不能于QTableWidget绑定. QTableWidget是QTableVi ...
- jqueryui插件slider的简单使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>slider</title> <meta charset=& ...
