poj 3687 Labeling Balls - 贪心 - 拓扑排序
Windy has N balls of distinct weights from 1 unit to N units. Now he tries to label them with 1 to N in such a way that:
- No two balls share the same label.
- The labeling satisfies several constrains like "The ball labeled with a is lighter than the one labeled with b".
Can you help windy to find a solution?
Input
The first line of input is the number of test case. The first line of each test case contains two integers, N (1 ≤ N ≤ 200) and M (0 ≤ M ≤ 40,000). The next M line each contain two integers a and b indicating the ball labeled with a must be lighter than the one labeled with b. (1 ≤ a, b ≤ N) There is a blank line before each test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the balls' weights from label 1 to labelN. If several solutions exist, you should output the one with the smallest weight for label 1, then with the smallest weight for label 2, then with the smallest weight for label 3 and so on... If no solution exists, output -1 instead.
Sample Input
5 4 0 4 1
1 1 4 2
1 2
2 1 4 1
2 1 4 1
3 2
Sample Output
1 2 3 4
-1
-1
2 1 3 4
1 3 2 4
题目大意 找出原图的一个拓扑序,使得1尽量靠前,2尽量靠前....(注意输出的是第i个球的重量是第几小)。无解输出-1.
我学长给出了一个正确性很显然的做法
正向建图,把当前集合中的点中最小点找出来,然后再暴力统计有多少个点指向它,那么这些点一定在它之前,就可以将原DAG分成两部分递归处理。时间复杂度O(n(n + m))
Code
还有个做法是反向建图,然后用大根堆去跑拓扑排序,最后输出的时候reverse一遍。虽然n变成了log2n,但是似乎正确性不是那么的显然。
如果解释的话可以这么想,正向建图,跑小根堆先把小的取走,保证了在大的尽量在后面,但是无法保证小的尽量在前面,比如说下面这个建出来的DAG。
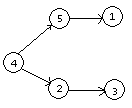 这真是一个优美的反例。
这真是一个优美的反例。
而反向建图跑大根堆,可以保证大的先被取走,自然小的就留在后面,reverse后,小的就跑到前面去了。
下面给出一个并不太严谨的证明(有问题一定要指出来)
假定存在一个更优的答案,那么第一处不相同的地方一定满足这个算法跑出来的值比这个答案大,因为前面的都相同,又因为都是1 ~ n的一个排列,那么意味着一定存在某个位置,这个答案比这个算法跑出来的值大。这意味着答案取出了比拓扑序某个时候,入度为0的点的最大值还大的数,这显然是不可能的。所以不存在更有的答案,所以这个答案就是最优的答案。
Code
/**
* poj
* Problem#3687
* Accepted
* Time:32ms
* Memory:1116k
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cctype>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#ifndef WIN32
#define Auto "%lld"
#else
#define Auto "%I64d"
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean;
const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << ) - );
const double eps = 1e-;
const int binary_limit = ;
#define smin(a, b) a = min(a, b)
#define smax(a, b) a = max(a, b)
#define max3(a, b, c) max(a, max(b, c))
#define min3(a, b, c) min(a, min(b, c))
template<typename T>
inline boolean readInteger(T& u){
char x;
int aFlag = ;
while(!isdigit((x = getchar())) && x != '-' && x != -);
if(x == -) {
ungetc(x, stdin);
return false;
}
if(x == '-'){
x = getchar();
aFlag = -;
}
for(u = x - ''; isdigit((x = getchar())); u = (u << ) + (u << ) + x - '');
ungetc(x, stdin);
u *= aFlag;
return true;
} ///map template starts
typedef class Edge{
public:
int end;
int next;
Edge(const int end = , const int next = -):end(end), next(next){}
}Edge; typedef class MapManager{
public:
int ce;
int *h;
vector<Edge> edge;
MapManager(){}
MapManager(int points):ce(){
h = new int[(const int)(points + )];
memset(h, -, sizeof(int) * (points + ));
}
inline void addEdge(int from, int end){
edge.push_back(Edge(end, h[from]));
h[from] = ce++;
}
inline void addDoubleEdge(int from, int end){
addEdge(from, end);
addEdge(end, from);
}
Edge& operator [] (int pos) {
return edge[pos];
}
inline void clear() {
edge.clear();
delete[] h;
}
}MapManager;
#define m_begin(g, i) (g).h[(i)]
#define m_endpos -1
///map template ends int n, m;
MapManager g;
int* dag;
int* dep; inline boolean init() {
if(!readInteger(n)) return false;
readInteger(m);
g = MapManager(n);
dag = new int[(n + )];
dep = new int[(n + )];
memset(dag, , sizeof(int) * (n + ));
for(int i = , a, b; i <= m; i++) {
readInteger(a);
readInteger(b);
g.addEdge(b, a);
dag[a]++;
}
return true;
} priority_queue<int> que;
inline void topu() {
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
if(!dag[i]) {
que.push(i);
}
int cnt = ;
while(!que.empty()) {
int e = que.top();
dep[e] = cnt++;
que.pop();
for(int i = m_begin(g, e); i != m_endpos; i = g[i].next) {
int& eu = g[i].end;
dag[eu]--;
if(!dag[eu])
que.push(eu);
}
}
} inline void solve() {
topu();
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) {
if(dag[i]) {
puts("-1");
return;
}
}
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d ", n - dep[i]);
putchar('\n');
} inline void clear() {
g.clear();
delete[] dep;
delete[] dag;
} int T;
int main() {
readInteger(T);
while(T--) {
init();
solve();
clear();
}
return ;
}
poj 3687 Labeling Balls - 贪心 - 拓扑排序的更多相关文章
- POJ 3687 Labeling Balls【拓扑排序 优先队列】
题意:给出n个人,m个轻重关系,求满足给出的轻重关系的并且满足编号小的尽量在前面的序列 因为输入的是a比b重,但是我们要找的是更轻的,所以需要逆向建图 逆向建图参看的这一篇http://blog.cs ...
- POJ 3687 Labeling Balls(拓扑排序)题解
Description Windy has N balls of distinct weights from 1 unit to N units. Now he tries to label them ...
- POJ 3687 Labeling Balls (top 排序)
Labeling Balls Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 15792 Accepted: 4630 D ...
- POJ - 3687 Labeling Balls (拓扑)
(点击此处查看原题) 题意 此处有n盏灯,编号为1~n,每盏灯的亮度都是唯一的,且在1~n范围之间,现已知m对灯之间的关系:a b ,说明灯a的亮度比灯b小,求出每盏灯的亮度,要求字典序最小(编号小的 ...
- [ACM] POJ 3687 Labeling Balls (拓扑排序,反向生成端)
Labeling Balls Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 10161 Accepted: 2810 D ...
- POJ 3687 Labeling Balls(反向拓扑+贪心思想!!!非常棒的一道题)
Labeling Balls Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 16100 Accepted: 4726 D ...
- poj 3687 Labeling Balls(拓扑排序)
题目:http://poj.org/problem?id=3687题意:n个重量为1~n的球,给定一些编号间的重量比较关系,现在给每个球编号,在符合条件的前提下使得编号小的球重量小.(先保证1号球最轻 ...
- poj 3687 Labeling Balls【反向拓扑】
Labeling Balls Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 12246 Accepted: 3508 D ...
- poj 3687 Labeling Balls(拓补排序)
Description Windy has N balls of distinct weights from 1 unit to N units. Now he tries to label them ...
随机推荐
- (已解决)Xcode 换电脑提示 Could not attach to pid:“XXXX”错误
在运行项目时出现了如下错误 (基本上重新启动项目即可) 紧接着再次运行又没有问题了. 稍微查询了一下得知,这个问题并不是由我们的操作引起的,有时就会莫名其妙的出现,但是有一些不同的情况 下面列出如何解 ...
- python知识补足
1.class的init功能,初始化class,给出一些初始值 __init__可以理解成初始化class的变量,取自英文中initial 最初的意思.可以在运行时,给初始值附值, class Cal ...
- 10.用js下载文件(需要后端链接)
用js下载文件 PS:本文说的,并非如何用js创建流.创建文件.实现下载功能. 而是说的:你已知一个下载文件的后端接口,前端如何请求该接口,实现点击按钮.下载文件到本地.(可以是zip啦. ...
- UVALi 3263 That Nice Euler Circuit(几何)
That Nice Euler Circuit [题目链接]That Nice Euler Circuit [题目类型]几何 &题解: 蓝书P260 要用欧拉定理:V+F=E+2 V是顶点数; ...
- JavaScript 深入了解对象中的属性
本篇主要介绍JS中对象的属性,包括:属性的分类.访问方式.检测属性.遍历属性以及属性特性等内容. 目录 1. 介绍:描述属性的命名方式.查找路径以及分类 2. 属性的访问方式:介绍'.'访问方式.'[ ...
- java 中多线程和锁的使用以及获取多线程执行结果
多线程一:原生的写法 关键词 implements 实现 Runnable 类 run() 方法 注意点 : 创建类的实例 InterfaceController inter=new Int ...
- 删除SQL Server大容量日志的方法(转)
删除SQL Server大容量日志的方法 亲自实践的方法 1.分享数据库,如果提示被其他连接占用,不能分离,刚勾上drop connections 2.复制下所有文件,一定要备份好,以防自己操作失误 ...
- 如何让多个dz论坛共用一个用户数据库
用户数据库在论坛中是可以独立备份的,备份方法:论坛后台——站长——数据库,备份所有ucenter数据表,也就是用户数据.其他DZ论坛搭建完成以后,可以上传用户数据库,将备份文件使用上传至网站所使用的主 ...
- pyinstaller将python脚本生成exe
一.下载pyinstaller 二.生成exe 下载pyinstaller 1.在C:\python27\Scripts目录下打开cmd界面,执行命令:pip install PyInstaller ...
- JavaScript(四):运算符&数据类型转换
+:算符的加法:连接字符串 加法会将其它类型的值,自动转为字符串,然后再进行连接运算! var a=1+2; console.log('first: '+a); var a=1+2+'3';//先计算 ...
