09:vuex组件间通信
1.1 vuex简介
官网:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/first-time/p/6815036.html
1、什么是Vuex?
1. 官方说法:Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式。
2. 它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
3. 个人理解:Vuex是用来管理组件之间通信的一个插件
2、vuex作用
1. 我们知道组件之间是独立的,组件之间想要实现通信,我目前知道的就只有props选项,但这也仅限于父组件和子组件之间的通信。
2. 如果兄弟组件之间想要实现通信呢?当做中大型项目时,面对一大堆组件之间的通信,还有一大堆的逻辑代码,会不会很抓狂??
3. 那为何不把组件之间共享的数据给“拎”出来,在一定的规则下管理这些数据呢? 这就是Vuex的基本思想了。
总结:使用vuex作用就是实现组件间数据共享
3、vuex原理
1. vue团队为了简化组件间的通信,将state抽象成一个单例模式,将其放到全局,让各个组件都能共享使用
2. vuex数据传递是单向的:action ---> mutation ---> state ---> component ---> action
vue component指的就是我门定义的组件
action 交互中产生的动作
mutations 动作产生的修改数据的行为
state 共享数据
3. vuex设计的时候相对修改的行为做单测(测试),开发了devtools来做测试,只能检测同步的操作
4. 规范定义:只能在mutations中做同步操作,所以增加了action来异步处理数据
5. 将mutations中的异步操作转移到actions中了,这样就可以测试同步的操作了
4、vuex使用场景
1. 如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择。
2. 如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁琐冗余的。
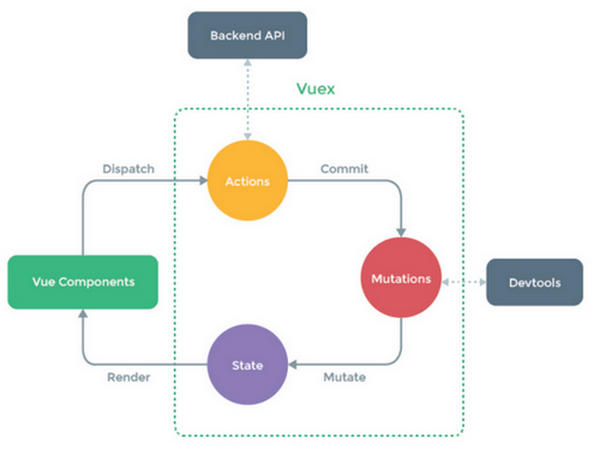
5、vuex流程图
1、vue组件(Vue Components)会 发出(Dispatch)一些动作(Actions)
2、动作会 提交(Commit)一个对数据的改变(Mutations)
3、提交的改变数据存放在 状态(State) 中的
4、最后 State将改变的数据再 渲染(Render)到组件(Vue Components),展示被改变后的数据
1.2 vuex使用(vuex使用分为以下两步)
1、第一步:实例化一个store
注:vuex.store用来创建store,参数对象中,可以定义各个模块
1. state定义状态模块(存储数据的),存放组件之间共享的数据
2. getters定义动态的数据,类似组件中的computed动态数据
3. mutations:定义改动states的动作行为,类似观察者模式中的订阅事件on
4. action:定义这些交互动作(异步),类似观察者模式中的订阅事件方法on(只不过是用来处理异步的)
2、第二步:在vue实例化对象中,注册store
1. 将第一步的实例化对象注册进来,注册路由后,组件实例化对象有了$route属性对象
2. 注册store,组件实例化对象有了$store属性对象,这个store对象有下面这些方法
$.store.commit用来触发mutations订阅的消息
$.store.dispatch用来触发action订阅的消息的
$.store.state使用状态中的数据
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
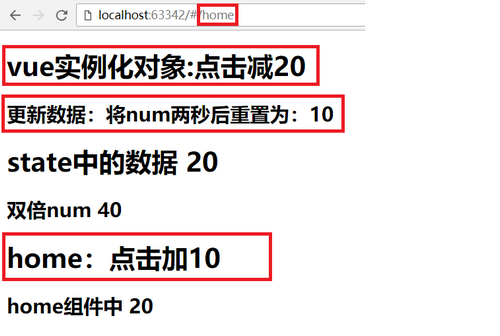
<h1 @click="$store.commit('reduce', 20);">vue实例化对象:点击减20</h1>
<h2 @click="$store.dispatch('dealNum', 10, 20, 30)">更新数据:将num两秒后重置为:10</h2>
<h1>state中的数据 {{$store.state.num}}</h1>
<h2>双倍num {{$store.getters.doubleNum}}</h2>
<router-view></router-view> <!-- 定义渲染的容器 -->
</div>
<template id="home">
<div>
<h1 @click="$store.commit('add', 10, 'hello')">home:点击加10</h1>
<h2>home组件中 {{$store.state.num}}</h2>
<router-view></router-view> <!-- 第一步 定义子路由渲染的容器 -->
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vue-router.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="vuex.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
// 定义组件
var Home = {
template: '#home'
}; // 第一步 定义路由规则
var routes = [
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: Home
}
]; // 定义store第一步 定义store实例化对象
var store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { // 定义状态
num: 0
},
getters: { // 定义动态绑定的数据
doubleNum: function(state) {
return state.num * 2;
}
},
mutations: { // 修改的消息
add: function(state, num) { // 增加num值
state.num += num;
},
reduce: function(state, num) { // 减少num值
state.num -= num;
},
resetNum: function(state, num) {
state.num = num;
}
},
actions: { // 定义actions
dealNum: function(context, num) {
setTimeout(function() { // 我们可以异步提交
context.commit('resetNum', num)
}, 2000)
}
}
}); // 第二步 实例化路由对象
var router = new VueRouter({
routes: routes // 定义路由规则
}); // 第三步 注册路由 和 store对象
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app', // 注册路由
router: router,
store: store // 使用vuex第二步 注册store
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
vuex基本使用
1.3 vuex基本用法
1、初始化环境
vue init webpack-simple vuex-demo
cd vuex-demo
npm install
cnpm install vuex -S # 安装vuex
npm run dev
2、在main.js中导入并配置store.选项(创建 sre/store.js文件,可以是一个空文件)
1. 在main.js中导入 store对象: import store from './store'
2. 配置store选项后,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中,在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue' import store from './store' // 导入store对象 new Vue({
store, // 配置store选项后,指定为store对象,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中
// 在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
});
main.js
3、编辑store.js文件
注1:Vuex的核心是Store(仓库),相当于是一个容器,一个store实例中包含以下属性的方法:
注2:不能直接修改数据,必须显式提交变化,目的是为了追踪到状态的变化
1) state 定义属性(状态、数据)
2) getters 用来获取属性
3) actions 定义方法(动作)
4) commit 提交变化,修改数据的唯一方式就是显式的提交mutations
5) mutations 定义变化
/**
* vuex配置:store.js
**/
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); //1、定义属性(数据)
var state = {
count:6
}; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数
var getters={
count(state){
return state.count;
}
}; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法()
const actions = {
increment({commit,state}){ // context包含属性(函数):commit,dispatch,state
if(state.count<10){ // 当count数值小于10才会提交改变(大于10就不增加了)
commit('increment');
}
// 1、commit提交改变(不能直接修改数据)
// 2、commit中的参数 'increment' 是自定义的,可以认为是类型名
// 3、commit提交的改变会给 mutations
}
}; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变)
const mutations={
increment(state){
state.count++;
}
}; // 创建一个store对象(对象里定义需要导出的变量)
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations,
}); // 导出store对象
export default store;
sre/store.js
4、 编辑App.vue
1. 在子组件中访问store对象的两种方式
方式1:通过this.$store访问
方式2:通过辅助函数:mapState、mapGetters、mapActions 访问,vuex提供了两个方法
mapState 获取state
mapGetters 获取getters(获取属性:数据)
mapActions 获取actions(获取方法:动作)
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="increment">增加</button>
<button>减小</button>
<p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p>
</div>
</template> <script>
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
}, // 方式二:使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据
computed:mapGetters([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的属性
'count', // 这里的count就是 store.js中getters定义的属性
]),
methods:mapActions([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的方法
'increment' // 这里的increment就是 store.js中actions定义的函数
]) // // 方式一:通过this.$store访问vuex组件中的数据
// computed:{
// count(){
// return this.$store.state.count;
// }
// }
}
</script> <style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
} h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
} ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
} li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
} a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>
App.vue
5、效果图

6、异步操作
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue' import store from './store' // 导入store对象 new Vue({
store, // 配置store选项后,指定为store对象,vue就会自动将store对象注入到所有子组件中
// 在子组件中通过this.$store 访问store对象
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
});
main.js
/**
* vuex配置:store.js
**/
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); //1、定义属性(数据)
var state = {
count:6
}; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数
var getters={
count(state){
return state.count;
}
}; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法()
const actions = {
increment({commit,state}){ // context包含属性(函数):commit,dispatch,state
if(state.count<10){ // 当count数值小于10才会提交改变(大于10就不增加了)
commit('increment');
}
// 1、commit提交改变(不能直接修改数据)
// 2、commit中的参数 'increment' 是自定义的,可以认为是类型名
// 3、commit提交的改变会给 mutations
}, /** 定义异步操作 **/
incrementAsyn({commit,state}){
var p=new Promise((resolve,reject) => { // 异步操作
setTimeout(() => {
resolve()
},3000)
});
p.then(() => { // 上面执行完成后才执行 p.then()
commit('increment');
}).catch(() => { // 异常处理
console.log('异步操作失败')
})
}
}; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变)
const mutations={
increment(state){
state.count++;
}
}; // 创建一个store对象(对象里定义需要导出的变量)
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations,
}); // 导出store对象
export default store;
store.js
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="increment">增加</button>
<button @click="incrementAsyn">异步增加</button>
<p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p>
</div>
</template> <script>
import {mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
}, // 方式二:使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据
computed:mapGetters([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的属性
'count', // 这里的count就是 store.js中getters定义的属性
]),
methods:mapActions([ // 这里定义一个数组,数组中指定要从vuex中获取的方法
'increment', // 这里的increment就是 store.js中actions定义的函数
'incrementAsyn' // 异步提交
])
}
</script> <style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
} h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
} ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
} li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
} a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>
App.vue

1.4 分模块组织Vuex
1、初始化环境
vue init webpack-simple vuex-demo2
cd vuex-demo2
npm install
cnpm install vuex -S # 安装vuex
npm run dev
2、Vuex模块化结构
|-src
|-main.js // 项目入口文件
|-App.vue |-store
|-index.js // 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
|-getters.js // 公共的 getters (用来获取公共属性)
|-actions.js // 根级别的 action (提交公共改变)
|-mutations.js // 根级别的 mutation (处理状态,数据的改变)
|-types.js // 定义类型常量(commit中提交的常量) |-modules //分为多个模块,每个模块都可以拥有自己的state、getters、actions、mutations
|-user.js // 用户模块(这里仅以user模块作为事例)
Vuex模块化结构
3、代码事例
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue' import store from './store/index.js' new Vue({
store,
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
});
main.js
<template>
<div id="app"> <button @click="increment">增加</button>
<button @click="decrement">减小</button>
<button @click="incrementAsync">增加</button>
<p>当前数字为:{{count}}</p>
<p>{{isEvenOrOdd}}</p> </div>
</template> <script>
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapActions} from 'vuex' export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
},
computed:mapGetters([
'count',
'isEvenOrOdd'
]),
methods:mapActions([
'increment',
'decrement',
'incrementAsync'
])
}
</script> <style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
} h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
} ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
} li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
} a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>
App.vue
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); import getters from './getters.js'
import actions from './actions.js'
import user from './modules/user.js' export default new Vuex.Store({
getters,
actions,
modules:{
user
}
});
store/index.js
const getters={
isEvenOrOdd(state){
return state.user.count%2==0?'偶数':'奇数'; // user模块中的count
}
};
export default getters;
store/getters.js
import types from './types.js'
const actions={
incrementAsync({commit,state}){
//异步操作
var p=new Promise((resolve,reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve();
},3000);
});
p.then(() => {
commit(types.INCREMENT);
}).catch(() => {
console.log('异步操作');
});
}
};
export default actions;
store/actions.js
/**
* 定义类型常量
*/ const INCREMENT='INCREMENT';
const DECREMENT='DECREMENT'; export default {
INCREMENT,
DECREMENT
}
store/types.js
/**
* 用户模块
*/ import types from '../types.js' const state={
count:6
}; var getters={
count(state){
return state.count;
}
}; const actions = {
increment({commit,state}){
commit(types.INCREMENT); //提交一个名为increment的变化,名称可自定义,可以认为是类型名
},
decrement({commit,state}){
if(state.count>10){
commit(types.DECREMENT);
}
}
}; const mutations={
[types.INCREMENT](state){ // ES6中中括号里表示 变量
state.count++;
},
[types.DECREMENT](state){
state.count--;
}
}; export default {
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}
store/modules/user.js
4、项目结构

5、简化版
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue' import store from './store/index' new Vue({
store,
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})
main.js
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>app</h1>
<p>数据:{{count}}</p>
<p @click="increment">增加</p>
</div>
</template> <script>
import {mapGetters, mapActions} from 'vuex' export default {
name: 'app',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
},
computed:mapGetters([
'count',
]),
methods:mapActions([
'increment'
])
}
</script> <style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
} h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
} ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
} li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
} a {
color: #42b983;
}
</style>
App.vue
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); // import getters from './getters.js'
// import actions from './actions.js'
import user from './modules/user.js' export default new Vuex.Store({
// getters,
// actions,
modules:{
user
}
});
src\store\index.js
//1、定义属性(数据)
var state = {
count:6
}; //2、定义gettters获取属性:在App.vue中使用 辅助函数 访问 vuex 组件中数据调用此函数
var getters = {
count(state){
return state.count
}
}; //3、定义actions提交变化:其他组件中调用的方法()
var actions = {
increment({commit,state}){
commit('increment')
}
}; //4、定义mutations定义变化,处理状态(数据的改变)
var mutations = {
increment(state){
state.count++
}
}; //5、导出store对象
export default {
state,
getters,
actions,
mutations
}
src\store\modules\user.js
09:vuex组件间通信的更多相关文章
- Vuex状态管理——任意组件间通信
核心概念 在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信. 每一个 Vuex 应用的 ...
- 聊聊Vue.js组件间通信的几种姿势
写在前面 因为对Vue.js很感兴趣,而且平时工作的技术栈也是Vue.js,这几个月花了些时间研究学习了一下Vue.js源码,并做了总结与输出. 文章的原地址:https://github.com/a ...
- python 全栈开发,Day91(Vue实例的生命周期,组件间通信之中央事件总线bus,Vue Router,vue-cli 工具)
昨日内容回顾 0. 组件注意事项!!! data属性必须是一个函数! 1. 注册全局组件 Vue.component('组件名',{ template: `` }) var app = new Vue ...
- Angular : 响应式编程, 组件间通信, 表单
Angular 响应式编程相关 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
- vue组件间通信六种方式(完整版)
本文总结了vue组件间通信的几种方式,如props. $emit/ $on.vuex. $parent / $children. $attrs/ $listeners和provide/inject,以 ...
- Vue组件间通信6种方式
摘要: 总有一款合适的通信方式. 作者:浪里行舟 Fundebug经授权转载,版权归原作者所有. 前言 组件是 vue.js 最强大的功能之一,而组件实例的作用域是相互独立的,这就意味着不同组件之间的 ...
- vue-learning:31 - component - 组件间通信的6种方法
vue组件间通信的6种方法 父子组件通信 prop / $emit 嵌套组件 $attrs / $liteners 后代组件通信 provide / inject 组件实例引用 $root / $pa ...
- Vue中组件间通信的方式
Vue中组件间通信的方式 Vue中组件间通信包括父子组件.兄弟组件.隔代组件之间通信. props $emit 这种组件通信的方式是我们运用的非常多的一种,props以单向数据流的形式可以很好的完成父 ...
- React独立组件间通信联动
React是现在主流的高效的前端框架,其官方文档 http://reactjs.cn/react/docs/getting-started.html 在介绍组件间通信时只给出了父子组件间通信的方法,而 ...
随机推荐
- CentOS6.5配置MYSQL一主多从详解
一.环境 操作系统 :CentOS 6.5 数据库版本:MySQL 主机A:192.168.1.1 (Master) 从机B:192.168.1.2 (Slave) 从机B:192.168.1.3 ( ...
- MySQL数据类型--与MySQL零距离接触2-8查看数据表
SHOW COLUMNS FROM tb_name 写入列之后,需要写入行,也就是记录:INSERT 插入记录:INSERT [INTO] tbl_name [(col_name,...)] V ...
- JAVA编程思想学习笔记3-chap7-9-斗之气3段
1.子类构造器会自动调用基类的默认构造器,如果为有参数构造器,则需要手动调用 ①this(args):调用本类中的其它构造器(只能调用一次) ②super(args):调用基类带参数的构造器 2.组合 ...
- C++二进制字符串转十六进制字符串 十六进制字符串转二进制字符串
============================================== 二进制转十六进制 ============================================ ...
- JSP—简介
BS/CS的区别? CS模式: client:客户端:存放操作界面的图片样式本地数据和缓存等 server:服务端:保存核心数据 请求响应模式:收到请求后,服务器只需要返回核心的数据 优缺点:需要安装 ...
- sitecore系统教程之默认收集数据库MongoDB注意事项
MongoDB是一个高度可扩展的基于文档的NoSQL数据库解决方案,Sitecore体验数据库(xDB)用于收集数据库.在安装MongoDB之前,您应该考虑以下事项: 确定您是需要基于公共云的解决方案 ...
- IO model
上节的问题: 协程:遇到IO操作就切换. 但什么时候切回去呢?怎么确定IO操作完了? 很多程序员可能会考虑使用“线程池”或“连接池”.“线程池”旨在减少创建和销毁线程的频率,其维持一定合理数量的线程, ...
- python之小数据池
代码块 Python 程序 是由代码块构造的.块是一个python程序的文本,它是作为一个执行单元的. 代码块:一个模块,一个函数,一个类,一个文件等都是一个代码块. 而作为交互方式输入的每个命令都是 ...
- redis的数据类型命令
存储sortedset: 存储:zadd key score menber1 score menber2 ... 升序排列:zrange key start end [withscores] 降序排列 ...
- 转:【专题九】实现类似QQ的即时通信程序
引言: 前面专题中介绍了UDP.TCP和P2P编程,并且通过一些小的示例来让大家更好的理解它们的工作原理以及怎样.Net类库去实现它们的.为了让大家更好的理解我们平常中常见的软件QQ的工作原理,所以在 ...
